It is not for nothing that there is an expression that blood is life. It circulates through blood vessels literally throughout our body and nourishes every organ and every cell with the necessary nutrients and oxygen, regulates the acid-base balance and internal water-salt balance, stabilizes the required temperature and protects the body with the help of antibodies.
Coagulation function
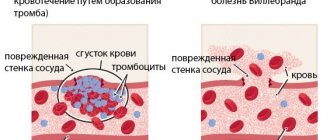
Coagulation is a mechanism for converting liquid blood into a clot with a dense consistency. This mechanism is activated at the slightest damage to the walls of a blood vessel, which provokes the release of a certain type of protein. The group of platelets closest to the affected area changes its normal shape to a spherical one, which has additional processes for adhesion to other cells. The purpose of this transformation and connection of cells is the formation of compacted adhesions. Such clots perform the function of blocking ruptures in the tissue, preventing the loss of valuable blood by the vessel and preventing harmful substances from the outside from entering the open bleeding wound.
This clotting process is called hemostasis.
Characteristic symptoms and signs
Symptoms that a patient has poor blood clotting include:
- frequent nosebleeds that are difficult to stop;
- heavy periods in women;
- the appearance of bruises and hemorrhages on the skin for no apparent reason;
- bleeding gums;
- dizziness, weakness;
- the presence of blood in the stool, which may be a sign of internal bleeding.
If you have these signs, you should consult a doctor. He will conduct diagnostics that will help understand the cause of coagulation disorders and prescribe treatment.
Existing clotting assays
It is worth noting that there is no separate test for platelets or clotting. These indicators are detected during the following diagnostic studies:
- Complete blood count (gives information about the number of platelets in the patient’s blood).
- Lee-White study.
- Blood test for clotting according to Sukharev.
- Coagulogram.
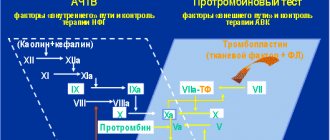
First phase of blood clotting
Plasma blood coagulation factors are a set of inactive enzymes and non-enzymatic compounds that live in the plasma part of the blood and blood platelets. Blood clotting requires, among other things, Ca(IV) ions and vitamin K.
When tissues are damaged, blood vessels rupture, hemolysis of blood cells occurs, and a series of reactions with enzyme activation occurs. The onset of activation is due to the interaction of plasma coagulation factors with destroyed tissues (external type of coagulation activation), parts of the endothelium and formed elements (internal type of coagulation activation).
External mechanism
From the shell of destroyed cells, a specific protein, thromboplastin (factor III), enters the bloodstream. It activates factor VII by attaching a calcium molecule, this newly formed substance affects factor X for subsequent activation. After X factor combines with tissue phospholipids and V factor. The formed complex converts a fraction of prothrombin into thrombin in a couple of seconds.
Internal mechanism
Under the influence of destroyed endothelium or formed elements, factor XII is activated, which, after exposure to plasma kininogen, activates factor XI. XI acts on factor IX, which, after entering the active phase, forms a complex: “coagulation factor (IX) + Antihemophilic factor B (VIII) + platelet phospholipid + Ca (IV) ions.” It activates the Stewart-Prower factor (X). Activated X, together with V and Ca ions, act on the phospholipid membrane of the cell and form a new formation - blood prothrombinase, which ensures the transition of prothrombin to thrombin.
Plasma coagulation factors include non-enzymatic proteins - accelerators (V, VII). They are needed for efficient and rapid blood sedimentation, because they accelerate coagulation thousands of times.
The external blood clotting mechanism lasts approximately 15 seconds, the internal one takes from 2 to 10 minutes. This coagulation phase ends with the formation of thrombin from prothrombin.
Prothrombin is synthesized in the liver; for synthesis to take place, vitamin K is needed, which comes with food and accumulates in the liver tissue. Thus, with liver damage or vitamin K deficiency, the blood coagulation system does not function normally, and uncontrolled blood flow from the vascular bed often occurs.
Analysis according to Sukharev
The Sukharev blood clotting test is a simple method of analyzing blood taken from a capillary. This is done as follows:
- 1 ml of blood taken from a finger is placed in a special test tube (Panchenkov apparatus).
- Time is recorded.
- The temperature inside the apparatus must be maintained at exactly 37 degrees so that the biological material being analyzed is at the same temperature.
- At 30-second intervals, the capillary is tilted to the sides so that non-coagulated blood can spread along the walls.
- As soon as the blood stopped spreading, it completely clotted. The stopwatch stops and the clotting time is determined.
The blood clotting test according to Sukharev is performed immediately from the moment the biological material is submitted. Accordingly, if the laboratory is located remotely, the analysis results may not be particularly reliable. It is for this reason that this method is not performed in every hospital.
The time of the entire procedure (from blood sampling to recording the results) is no more than fifteen minutes.
How dangerous is this?
Low blood clotting has dangerous consequences for human life. Any damage to blood vessels causes bleeding, which is often impossible to stop on your own.
Damage to large arteries and veins is the most dangerous. In this case, emergency assistance will be required, otherwise severe blood loss can lead to death.
Pregnant women and patients during surgery require special attention.
Under normal conditions, blood is constantly in a liquid state. If a vessel is damaged, tissue particles enter the bloodstream and the blood clotting process begins. In this case, a blood clot forms, which clogs the damaged area.
Poor blood clotting may occur under certain circumstances. This is fraught with severe bleeding and health problems. Therefore, it is important to promptly find out the reasons for this phenomenon and take action.
Indications for prescribing analysis according to Sukharev
An analysis is prescribed by the attending physician in the following cases:
- The test for blood clotting according to Sukharev in a child and an adult is necessarily checked in the preparation process before surgery. This estimates the future risk of probable life-threatening blood loss.
- During pregnancy, it is necessary to take clotting tests several times. If blood clotting is normal according to Sukharev in women during pregnancy, permission is given for childbirth (natural or cesarean section).
- In case of internal or external bleeding resulting from injuries.
- During a routine medical examination.
- With a predisposition to the formation of blood clots, thrombosis, varicose veins, thromboembolism.
- After a heart attack or stroke.
- In pre-infarction condition.
- For coronary heart disease.
- In the presence of regular arrhythmia.
- When pathologies are detected in the circulatory system.
- In cases of liver dysfunction.
- When taking anticoagulant drugs.
- For hemorrhagic pathological processes in the body.
- When diagnosing chronic anemia.
- With constant unpredictable nosebleeds.
- With heavy and long menstrual flow.
- If there is blood in the urine or stool.
- With sudden onset blindness.
- With a long course of taking anabolic steroids, glucocorticosteroids, oral contraceptives.
What to do if blood doesn't clot well
If you have the symptoms listed above, you should definitely consult a doctor and undergo an examination. At the moment of bleeding itself, first aid should be provided in accordance with general recommendations, based on the location and type of injury. If necessary, call an ambulance.
Diagnostics
To diagnose blood clotting, the doctor first reviews the patient's medical history. To do this, he will ask questions about your health problems and medications you are taking. You need to answer something like this list of questions:
- What are the accompanying symptoms?
- How often does bleeding occur?
- How long does the bleeding last?
- What were you doing before the bleeding started (for example, were you sick, took medications)?
Basic tests to check blood clotting :
- A complete blood count to check the blood loss at the time the test was taken and the number of red and white blood cells.
- Platelet aggregation test, which shows the extent to which platelets are able to adhere to each other.
- Measuring bleeding time to see how quickly blood vessels clog after pricking a finger with a feather.
Treatment options for poor blood clotting
Treatment for a bleeding disorder is based on the causes that cause it. If possible, the diseases that caused the disorder, such as cancer or liver disease, are immediately treated. Additional treatments include:
- Taking vitamin K by injection;
- Drugs aimed at improving clotting function;
- Transfusion of frozen donor blood plasma or donor platelets;
- Other drugs, including hydroxyurea (Droxia, Hydrea), and oprelvequin (Neumega) to treat platelet-related disorders.
Treatment of consequences caused by blood loss
Iron supplements
If there is significant blood loss, the doctor may prescribe medications containing iron to replenish its amount in the body. Low iron levels can lead to iron deficiency anemia, which is accompanied by feelings of weakness, shortness of breath and dizziness. One of the most common and accessible drugs in this case is Hematogen. In addition to treatment with iron supplements, blood transfusions may be required.
Blood transfusion
During this procedure, as most people know, blood loss is compensated with the help of donor blood. Donated blood must match your blood type to prevent complications. This procedure can only be performed in a hospital.
If the indicators are above the established norm
If the blood clotting time according to Sukharev is more than five minutes, then this is the result:
- Serious deficiency of plasma factors that are part of the prothrombin complex (ninth, eighth, seventh, first factors).
- Hereditary coagulopathy.
- Impaired fibrinogen conversion.
- Liver diseases.
- A course of treatment with heparin.
How is the treatment carried out?
Treatment for poor blood clotting is aimed at eliminating the cause that causes it.
The following drugs are used in therapy:
- Antienzyme agents are inhibitors of proteolytic enzymes, inhibit fibrinolysis and dissolution of blood clots. These include aminocaproic acid, aminomethylbenzoic acid (Amben), drugs with the active ingredient aprotinin (Ingiprol, Ingitril, Kontrikal, Gordox), protamine sulfate.
- Indirect coagulants - vitamins of group K and their derivatives: Vicasol, desmopressin (synthetic analogue of vasopressin).
- Direct acting coagulants are components and preparations of hemostatic action.
Interesting Facts
Such a rare and life-threatening genetic disease as hemophilia (a blood clotting disorder) causes serious harm only to the male half of the population. A woman can only be a carrier of this gene with pathology, but the disease itself does not affect her health in any way.
There are several names of diseases associated with disturbances in the number of platelets in the blood and their activity:
- Absolutely any deviations in these indicators are called thrombocytopathy.
- If the level of platelets in the blood is low, then this pathology is called thrombocytopenia.
- If the level of such a main component of blood as platelets is higher than normal, then this is the disease thrombocytosis.
- When impaired functional activity is detected, the disease is called thrombasthenia.
At Harvard University, a group of scientists and students discovered an interesting relationship between the amount of fibrinogen (a protein that is produced in the liver and converted into fibrin, the basis for clot formation during the activation of the blood clotting process) and the number of human contacts in society. Based on the research results, it was concluded that the narrower the circle of contacts with people, the higher the level of fibrinogen. And this, in turn, causes irreparable harm to health, especially detrimental to the cardiovascular system. Therefore, communicating with other people is beneficial not only for mental health, but also for physical health!
Some private laboratories provide the service of taking biological material for blood clotting testing directly at home, i.e., you do not need to go to the laboratory yourself. This is very convenient for disabled people, elderly people and small children.
What is this and what does it affect?
It is very important to know how thin or thick a person’s blood is.
Attention! Clotting is an important indicator of health. This is primarily a protective function of the body. This way there is no blood loss and its volume is maintained.
The mechanism of coagulation depends on the physicochemical actions in the molecular system of the plasma:
- The main place in this is occupied by a protein called fibrinogen.
- During the reactions that take place, it is converted into fibrin (which is not able to dissolve), which falls out in the form of the thinnest threads.
- These threads can form into a dense network with small cells that trap the formed elements.
- These changes lead to the formation of a blood clot. As it exists, its base becomes compacted, the edges of the wound are tightened and healing occurs.
- As the clot tightens, it forms a yellowish liquid called serum.
Platelets, which are part of the plasma, influence the compaction of the blood clot.
To use a primitive comparison, the process of blood clotting is reminiscent of the process of turning milk into cottage cheese, when casein (milk protein) coagulates and whey is released. Over time, the wound resolves and the fibrin clot dissolves.
The plasma coagulation test is used when the presence of the following diseases is suspected:
- pathology of the liver organ,
- disorders of the immune system,
- varicose veins.
Specialists also send patients for hemostasis testing before surgery, during pregnancy, and in case of possible large blood losses.
The video explains how the blood clotting system works:
Second phase of blood coagulation
Blood coagulation is associated with the transition of factor I into an insoluble substance - fibrin. Fibrinogen is a glycoprotein that, when exposed to thrombin, breaks down into a low molecular weight substance - fibrin monomers.
The next step is the formation of a loose mass - fibrin gel, from which a fibrin network (white thrombus), an unstable substance, is formed. To stabilize it, fibrin-stabilizing factor (XIII) is turned on and the blood clot is fixed in the damaged area. The formed fibrin network traps blood cells - the clot turns red.
Features of hemostasis
The hemostasis system regulates blood loss in the body through two mechanisms:
- Vascular-platelet hemostasis;
- Coagulation hemostasis.
We also recommend studying this topic:
What should be the normal hemoglobin level during pregnancy?
The first of them prevents clotting, and the second is responsible for direct blood clotting. Working independently of each other, but at the same time, these two mechanisms make it possible to ensure a proper balance of blood coagulation, that is, to protect the body from decreased or increased coagulation.
The consistency of the blood should be stable. For good circulation through the vessels, it must be sufficiently fluid. But in order not to leak through the walls of blood vessels under pressure, the blood must be thick enough.
Important! If a vessel is damaged, the body forms a blood clot in this place, preventing blood from flowing out. In a healthy body, a local course of this process is observed, that is, a blood clot forms specifically at the site of damage to the vessel wall. If the blood has poor clotting properties, the blood clot forms slowly. With an increased coagulation rate, on the contrary, the process occurs quickly.
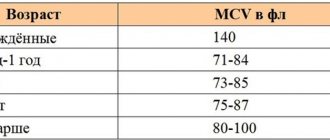
| Analysis name | Indicator norm | What kind of blood is used |
| Platelet level test | In men and women 150-400 g/l | Capillary (finger sampling) |
| In children 150-350 g/l | ||
| Clotting time | Norm according to Sukharev: beginning - 30-120 seconds; end - between 3 and 5 minutes; | Capillary |
| Norm according to Lee-White 5-10 minutes | From Vienna | |
| Duration of bleeding according to Duke | Should not exceed 4 minutes | From the finger |
| Thrombin time (TV) | 12-20 seconds | From Vienna |
| Prothrombin index (PTI) | Capillary blood 93-107% | Finger analysis |
| Venous blood 90-105% | Analysis from a vein | |
| Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) | For all age groups, regardless of gender 35-50 seconds | Venous |
| Fibrinogen | Adults 2-4 g/l; in a child’s first days of life 1.25-3.0 g/l | From Vienna |
The following factors may affect blood clotting time:
- The state in which the vascular walls exist . Increased clotting can occur if the structure of the artery walls is seriously damaged.
- Plasma factor concentrations . For the most part, they are synthesized by the liver. These factors that influence coagulation can be of reduced or increased levels, which directly affects blood clotting.
- Anticoagulation system and concentration of plasma factors . The more of these factors, the thinner the blood will be.
- The number of platelets, as well as the usefulness of their functioning . It is platelets that “monitor” the integrity of blood vessels and provoke the process of blood clotting.
There are three stages of clotting, and if any of them occurs incorrectly, then the entire clotting function can be disrupted.
Blood clotting process
Research methods
Blood clotting can only be determined in laboratory conditions. Such studies are carried out by qualified medical professionals. There are many types of such analyses, among the common ones it is necessary to highlight:
- According to Sukharev's method. Capillary plasma is used, it is taken from a finger in a volume of 30 mm. Afterwards, the specialist shakes the container and records the time when the sample begins to thicken;
- According to Morawitz. Capillary blood is used, it is placed on a special glass, and a stopwatch is turned on to determine clotting. Every half minute, the sample is checked using a glass tube, and the time of appearance of the fibrin thread will be the result of the analysis;
- According to the Duque method. The patient's skin is pierced on the earlobe. This is done with a special needle (Frank). The puncture site is soaked with special paper, which is done every 15 seconds. The result of the study will be the time when blood stains will no longer remain on the paper.
It is necessary to carefully prepare for the diagnosis. To do this, it is enough to adhere to the following established rules:
- Do not eat food 8 hours before the test;
- Do not drink alcohol for a day;
- Do not smoke 3 hours before the test;
- A couple of hours before blood sampling, do not overload the body with physical activity;
If the above recommendations are not followed, the analysis will give incorrect results.
Blood clotting in newborns
During the first week, the blood clotting of a newborn occurs very slowly, but during the second week, the indicators of coagulation factors and prothrombin levels are observed to approach the normal level of an adult.
Already two weeks after birth, the fibrinogen content increases significantly and reaches the levels of an adult.
The content of other coagulation factors approaches the levels normal for an adult by the end of the first year of life.
They reach normal standards by the age of 12 years.