Normal indicators
Acceptable limits of values, defined as the MCV norm in a blood test, change throughout a person’s life.
In addition, several factors may affect the examination materials, for example, a large breakfast, laboratory inaccuracies, drinking drinks containing alcohol, taking antidepressants or hormonal medications. In children under one year of age, 71–112 fl are considered normal values, with newborns having the highest values for childhood. However, as a child grows and develops, the MCV level gradually decreases to levels accepted as normal in an adult. Then, as the body matures, the standard values increase again. It is noted that the MCV rate in women is slightly higher than in men.
MCV standards - children and adolescents
What blood tests are done on cats and why?
For preventive purposes, it is recommended to conduct blood tests every year even in healthy cats. Thanks to a hemogram - a detailed table containing indicators of the hematopoietic system, it is possible to prevent the development of asymptomatic pathological processes.
If a cat has been seriously ill with a bacterial or viral infection, it is recommended to undergo a repeat blood test six months later - often the disease causes hidden complications in internal organs. They are not easy to detect until they reach a critical point.
Even if the treating veterinarian did not advise you to repeat the test 6-8 months after recovery, it is better to do it yourself. This way you will protect the animal from irreversible consequences.
General (clinical) analysis
Gives a general picture of the condition of a mustachioed patient. Helps detect some parasitic infestations and confirm the presence of allergies, as well as inflammation in almost any part of the body.
Biochemistry
Takes into account deviations in basic indicators that affect the state of the hematopoietic system. Helps identify a disease with vague symptoms. Identifies the location of the problem and the extent of damage to internal organs.
Exceeding the norm
There are a number of painful conditions in which the average volume of red blood cells increases:
- types of anemia (decrease in the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin) with an increase in the volume of red blood cells;
- a condition associated with a deficiency of B vitamins or folic acid in the body;
- some liver diseases;
- hereditary characteristics of the hematopoietic system.
The head of the Clinical Center for Preventive Medicine, Morozov, believes that “any significant changes in blood test parameters should be carefully analyzed to exclude serious pathology.”
An increase in the average volume of red blood cells in itself does not confirm any of the above pathologies. To make a final diagnosis, analysis of other blood parameters is required. In addition, a thorough examination of the patient and the appointment of instrumental studies are necessary.
A relatively common cause of increased MCV is stomach disease. This is due to the fact that the stomach produces a special substance necessary for the absorption of B vitamins. If the absorption processes of these vitamins are disrupted, hematopoietic processes in the bone marrow are blocked and improper maturation of red blood cells occurs. This is manifested in the impossibility of their division to a normal size and their average volume increases.
Deviations of indicators
Description of the analysis
The mcv value is calculated based on data obtained from a general blood test. This is one of the most widespread and frequently prescribed laboratory tests. It allows you to comprehensively assess the condition of the entire hematopoietic system.
Erythrocyte indices, which are part of a general blood test, allow one to diagnose and classify various anemias with fairly high accuracy. Thanks to this, the doctor will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment regimen.
Since the analysis is simple, inexpensive and publicly available, it is used as a screening technique for identifying disorders in the hematopoietic system. Another advantage of the technique is the possibility of dynamic monitoring of the effectiveness of the treatment and timely adjustment of the dosages of drugs prescribed to the patient.
The result of the study may be affected by the presence of severe leukocytosis, a large number of reticulocytes, and a significant excess of normal glucose levels. All these conditions lead to an increase in the average size of the red blood cell.
It should also be taken into account that a simultaneous increase in macrocytic (large) and microcytic (small) red blood cells can create the appearance of normality. This is due to the fact that mcv is a calculated indicator that does not always reflect the objective state of blood cells. To identify abnormalities in such cases, direct microscopy of a blood smear taken from the subject is required.
MCV blood test norms and possible causes of deviations
An indicator such as MCV in a blood test was not always available to the practicing physician. Its study became possible with the widespread introduction of hardware testing methods, and it is automatically issued when a certain amount of blood is loaded into a biochemical analyzer.
Previously, throughout almost the entire 20th century, the MCV indicator was not taken into account in blood tests, since such methods did not exist. It was only possible to estimate the size of red blood cells under a microscope, which was labor-intensive and subjective. Of course, when deciphering the blood test, doctors necessarily took into account the size of the blood cells, but it was impossible to estimate this indicator - the average volume of red blood cells - for each blood cell.
MCV in a blood test, or mean red blood cell volume, is an average that more or less likely reflects the volume of a red blood cell. It does not have high information content and cannot accurately indicate what pathological processes are occurring in the body. Translated from English, MCV in a blood test, or Mean Cell Volume, means the average volume of a red blood cell.
This indicator belongs to the so-called erythrocyte indices; these indices allow you to determine the main characteristics of red blood cells. These indices also include such well-known studies as the determination of the average hemoglobin content in a cell, which has now replaced the routine determination of the color index.
Of course, if we take each individual blood transport cell, we will see that its volume is within the range quite close to this value, since the average volume of red blood cells is the median value. There are necessary conditions under which the results of this analysis can be accepted as true, namely: with normal, mature red cells with approximately the same volume.
In the event that a general blood test is represented by red blood cells of different shapes or sizes, that is, in the presence of anisocytosis, then an indicator such as the mcv analysis will have very low value, since the average volume of red blood cells cannot be calculated reliably. This analysis in laboratory practice can be used for the differential diagnosis of various anemias, and will help identify the causes of deviations.
It should be said that cellular red indices can only speak about red blood: the iron content in the patient’s body and the presence or absence of hypoxia of organs and tissues. The average volume of erythrocytes - MCV, does not tell us anything about leukocytes, blood coagulation, platelets, and it is not even possible to evaluate some simple indicators, for example, the ESR value, using this index.
Reference or normal values
If we talk about age-related changes, then the largest cell sizes, and, consequently, their volume, exist in newborns and in children in the first month of life. At this time, red blood cells are finally freed from fetal hemoglobin and switch to new hemoglobin.
Normal adult hemoglobin works more efficiently during air gas exchange in the lungs, and a red blood cell with a smaller volume is able to perform the same full function. Also in old age, and even starting from the age of 45, our oxygen carriers have a large volume. Therefore, it is possible to construct a certain curve, where the norm of the average volume of red blood cells in adults is slightly lower than at extreme age limits.
Normal values for children are shown in the following table:
General blood analysis
The diagnostic value of tests in veterinary medicine is very great. The animal cannot tell what exactly is hurting it, so tests are important for the doctor to form a complete picture of the disease.
First of all, you need to pass general clinical and biochemical blood tests . These studies will show the general condition of the animal’s body and organs.
The body is always exposed to various environmental factors and gives a specific response to stimuli. Each blood cell performs its functions to protect the body. When the number of certain cells increases or decreases, we can talk about a possible cause of the disease.
A general clinical blood test can show the degree of development of the inflammatory process, whether there is anemia, dehydration, and whether there are neoplasms in the blood system or not. Also, one should not forget about hidden (chronic) infectious, invasive or any other non-infectious processes in the body, which can also be detected by blood testing as one of the diagnostic methods.
A general blood test does not require any special preparation, however, in rare cases, the doctor may ask you to take the test on an empty stomach. The sample itself is taken from peripheral veins.
In our veterinary clinic, a general blood test is performed using an Exigo EOS (VET) automatic analyzer.
It only takes 10 minutes from blood sampling to the results being ready!
Reasons for deviations from the norm in the RDW indicator in a blood test
An elevated RDW level means that there is heterogeneity, i.e., dissimilarity in the volume of the red blood cell population, and may also mean the presence of several populations of red blood cells in the blood (for example, after a blood transfusion).
If in a blood test RDW-CV is increased by 15% or more, this indicates the presence of red blood cells of different volumes in the blood; the higher this index, the greater the difference in the volume of red blood cells. A falsely elevated RDW-CV result may be due to the presence of cold agglutinins in the patient's blood sample - antibodies that cause aggregation, i.e. sticking together of red blood cells when exposed to low temperatures.
An increase in RDW is observed in the following pathologies:
- microcytic anemia;
- hemoglobinopathies;
- lack of iron, vitamin B12 and/or folic acid in the body;
- increased number of leukocytes in the blood (above 50×109/l);
- red blood cell agglutination;
- hemolytic crisis;
- malignant neoplasms (especially with metastases to the bone marrow);
- myelodysplastic syndrome;
- myelofibrosis;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- alcoholism;
- lead poisoning.
Elevated RDW blood test values may also be obtained immediately after surgery or blood transfusion.
The index remains within normal limits or is slightly reduced in acute blood loss, chronic diseases, hemolytic anemia outside of crisis, heterozygous beta thalassemia. If the RDW index is low, this often means the need to retake a general blood test.
When deciphering a general blood test in general and the RDW indicator in particular, the values of the erythrocyte MCV index are taken into account:
- normal RDW value + reduced MCV – after blood transfusion, post-traumatic splenectomy, chemotherapy, with hemorrhages, thalassemia, oncological diseases;
- decreased MCV + increased RDW in blood test – iron deficiency, red blood cell fragmentation, beta thalassemia;
- increased MCV + normal RDW – in liver diseases;
- increased MCV + increased RDW – with hemolytic anemia, vitamin B12 deficiency, the presence of cold agglutinins in the blood sample, as well as during chemotherapy.
If an RDW result is obtained that is outside the reference values, additional research is required.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
Blood chemistry
Glucose is an informative indicator indicating the functioning of a complex enzymatic system in the body, including individual organs (liver, pancreas, kidneys). Glucose metabolism in the body involves 8 different hormones and 4 complex enzymatic processes. A disorder is considered to be either high or low blood sugar levels in a cat.
Total protein in the blood reflects the correctness of amino acid metabolism in the body. Shows the total amount of all protein fractions - globulins and albumins. Proteins in an animal’s body take part in almost all life processes of the body. For specialists, both their increased and decreased amounts are important.
Albumin is the most basic blood protein produced by the liver. Albumin in a cat’s body performs a large number of functions (transporting nutrients, maintaining reserve reserves of amino acids for the body, maintaining osmotic blood pressure, etc.).
Cholesterol is a structural component that ensures the strength of cellular structures and takes part in the synthesis of many vital hormones. Veterinary experts judge lipid metabolism in a cat’s body based on cholesterol levels.
Bilirubin is a bile pigment found in the body in two forms - direct and indirect. Indirect bilirubin is formed in the blood as a result of the breakdown of red blood cells, and bound (direct) bilirubin is converted from indirect bilirubin in the liver. Bilirubin shows the functioning of the hepabiliary system (biliary and hepatic). Refers to “color” indicators i.e. when its content in the body is increased, the tissues turn yellow (jaundice).
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT, ALaT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST, ACaT) are enzymes produced by liver cells, heart cells, red blood cells and skeletal muscles. It is an indicator of the functions of these organs or departments.
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) is an enzyme involved in the final step in the breakdown of glucose. Veterinary LDH specialists monitor the functioning of the cardiac and hepatic systems, and also judge the risks of tumor formation.
ɤ-glutamyltransferase (Gamma-GT) – in combination with other liver enzymes, provides insight into the functioning of the hepabilary system, pancreas and thyroid glands.
Alkaline phosphatase is determined to monitor liver function.
ɑ-Amylase – produced by the pancreas and parotid salivary gland. Their work is judged by its level, but always in conjunction with other indicators.
Urea is the result of protein processing, which is excreted by the kidneys. Some remains circulating in the blood. Using this indicator, you can check your kidney function.
Creatinine is a muscle byproduct excreted from the body by the renal system. The level fluctuates depending on the condition of the urinary excretory system.
Potassium, calcium, phosphorus and magnesium are always assessed in complex and in relation to each other.
Calcium is involved in the conduction of nerve impulses, especially through the heart muscle. By its level, you can determine problems in the functioning of the heart, muscle contractility and blood clotting.
Creatine phosphokinase is an enzyme that is found in large quantities in the skeletal muscle group. By its presence in the blood, one can judge the work of the heart muscle, as well as internal muscle injuries.
Triglycerides in the blood characterize the functioning of the cardiovascular system, as well as energy metabolism. Usually analyzed in conjunction with cholesterol levels.
Electrolytes are responsible for membrane electrical properties. Thanks to the electrical potential difference, cells pick up and execute commands from the brain. In pathologies, cells are literally “thrown out” from the nerve impulse conduction system.
Decrease in the values of the average erythrocyte volume parameter
The presence of small and underdeveloped blood cells with an impaired color index in the body can cause hypochromic anemia, in which the MCV index is significantly reduced. Patients who have an increased, decreased average volume of red blood cells experience fatigue, increased absent-mindedness and irritability, general weakness, problems with remembering even the simplest things and with concentrating. These manifestations are a signal of disturbances occurring in the body and require immediate medical attention.
A decrease in the volume of red blood cells in the blood can occur for several reasons:
- Disturbances of metabolic processes, especially disturbances of water-salt metabolism. The balance of ions in the blood cells changes, so the fluid contained in the cells leaks out, causing the MCV to decrease;
- Massive burns;
- Disturbances in the formation of hemoglobin molecules or their rapid destruction. In medical institutions, a diagnosis of hemoglobinopathy is made; this disease is transmitted at the genetic level;
- Violation of the synthesis of blood cells, as a result of which their quality component changes. Red blood cells are smaller and subject to deformation, which gives a reduced MCV parameter in the analysis results;
- Severe dehydration;
- Damage to the human body by lead ions;
- Malignant tumors;
- Taking medications that disrupt polypeptide bonds.
Both in the case of an increased parameter of the average volume of erythrocytes, and in cases of a decrease, in no case should this deviation from the norm be left without attention. It is necessary to identify the causes of pathologies and prescribe effective treatment with specialists, monitoring after a certain time whether it has had a positive effect.
In what cases is analysis prescribed?
The list of indications for a blood test for MVC is as follows:
- Acute infections. In this case, analysis is necessary because the normal water-salt balance is disrupted. Accordingly, following this, the average volume of red blood cells gradually increases (you need to more actively transport oxygen).
And this is against the background of a decrease in the amount of fluid and sodium, potassium, and calcium. Those substances that indirectly help cellular respiration and nutrition.
- Anemia of various types. From classic, iron deficiency to more complex and dangerous forms. For example, megaloblastic or hemolytic. There are several options. In any case, red blood cells are transformed to ensure the normal functioning of the body.
- Violations of local and general immunity. The analysis is carried out without fail, because it is quite possible that the cause of frequent illnesses is a disruption of the hematopoietic system.
Despite the increase in the size of the red blood cell, more oxygen does not reach the tissues. Moreover, the maturation of defective cells takes longer. Hence the decline in the “performance” of the body’s defenses.
- Diabetes. An extremely dangerous disorder that leads to generalized problems. Including in the hematopoietic system. The reason is the negative effect of glucose.
It does not transform and does not decay with the release of energy. On the contrary, it circulates throughout the body unchanged and harms the bone marrow. The study is prescribed among others. You also need to evaluate your sugar level.
- Unstable hormonal levels. Specific substances of the body act as a kind of regulators of all vital processes. If they are produced too little or too much, the body does not work properly. Due to incorrect signals, problems with hematopoiesis begin.
Attention:
Meanwhile, hormonal imbalances can be medicinal. Conditioned by taking medications. The reason needs to be clarified separately. Under the supervision of an endocrinologist.
There are other reasons for ordering analysis. For example, unexplained weight gain. Or metabolic abnormalities. Exercise tolerance disorders and others.
At the discretion of the doctor, he orders the test in many cases. The list is approximate.
How to properly prepare and take a general blood test
A general blood test is a basic study that is carried out for the following indications:
- prevention, with the aim of early detection of probable pathologies;
- diagnosis of diseases;
- control of therapy;
- before surgical interventions;
- monitoring the progress of pregnancy.
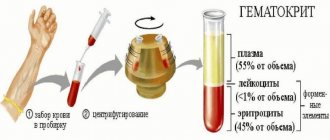
A general blood test includes counting the number of blood cells (erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets), determining hemoglobin concentration, hematocrit level, erythrocyte and platelet indices, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate. A complete blood test includes a leukocyte count.
For preventive purposes, a general blood test should be taken annually. Persons from risk groups (with a family history, chronic diseases, occupational hazards, during pregnancy, etc.) may require this study to be performed more frequently - 2 times a year, 1 time every 3 months, and sometimes more often.
Blood for a detailed general analysis, which includes the determination of erythrocyte indices, including the RDW indicator, is usually taken from a vein. In some cases, capillary blood may be collected from a finger. Blood is donated in the morning on an empty stomach, at least eight hours after the last meal. Before donating blood, you should avoid mental and physical stress and stop smoking. It is advisable not to carry out medical procedures the day before.
The procedure for taking blood for analysis
Blood is taken from the vein of the animal. To do this, the cat is placed on its side, and if the cat resists, it is secured in a special veterinary bag. Blood is taken from the front paw by shaving off a small area of fur. The injection site is treated with a disinfectant solution, a needle from a disposable syringe is inserted into the vein, blood in the amount of 2 ml is drawn into a test tube with heparin or sodium citrate.
What blood tests are performed in veterinary clinics?
In modern veterinary clinics, two laboratory blood tests are performed:
- General or clinical.
- Biochemical.
General blood test for a cat
A general blood test based on the number and condition of formed blood elements shows the health status of the cat’s body. When performing a general blood test, parasites such as dirofilaria (dirofilariasis), hemobartenella can be detected in a cat’s blood.
What indicators does the clinic’s veterinary specialist receive when conducting a general blood test:
- Hematocrit
- Hemoglobin.
- Average content and concentration of hemoglobin in an erythrocyte.
- Color indicator.
- ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate).
- Red blood cells.
- Leukocytes.
- Neutrophils.
- Lymphocytes.
- Eosinophils.
- Monocytes.
- Platelets.
- Basophils.
- Myelocytes.
Biochemical blood test for a cat
Biochemical blood tests allow veterinary specialists to identify subclinical (hidden) cat diseases. A biochemical blood test allows you to determine the functioning of the body’s enzymatic system and provide information about damage to a particular organ in a cat.
A biochemical blood test for a cat includes enzymatic, electrolyte, fat and substrate indicators.
Basic biochemical parameters:
- Glucose.
- Protein and albumin.
- Cholesterol.
- Bilirubin is direct and total.
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT).
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST).
- Lactate dehydrogenase.
- Gamma glutamyl transferase.
- Alkaline phosphatase.
- a –Amylase.
- Urea.
- Creatinine.
- Calcium.
- Magnesium.
- Creatine phosphokinase.
- Triglycerides.
- Phosphorus, inorganic.
- Electrolytes (potassium, calcium, sodium, iron, chlorine, phosphorus).
Inflated MCV values
Increased values of the average volume of erythrocyte cells indicate the development of macrocytic anemia and other pathological conditions that are characterized by:
- deficiency of vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) due to impaired absorption;
- folate deficiency anemia due to a lack of folic acid;
- megaloblastic anemia caused by impaired synthesis of DNA molecules;
- pernicious anemia;
- hypothyroidism, in which there is a lack of thyroid hormones;
- intestinal diseases;
- liver diseases;
- decreased function of pancreatic cells;
- red bone marrow diseases;
- toxic or drug poisoning;
- alcoholism.
The MCV blood test may be slightly higher than normal when women take hormonal contraceptives. Cigarette smoking can also cause an increase in the average volume of red blood cells.
Reasons for the increase
When the average volume of red blood cells is increased, this means macrocytosis - the predominance of increased red blood cells in the blood. There are no natural causes for the development of the disorder.
Exceeding MCV values is due to a group of factors. It is worth considering them in more detail.
Pancreatic disorders
The classic variant of the pathological process of this localization is pancreatitis. Acute inflammation of the organ. Or a chronic disorder. Accompanied by a sharp deviation in the production of hormones. Including insulin, which can lead to dysfunction of the entire body.
Already in the first hours of the disease, changes in the blood picture begin. Hence the deviations in MCV, the average platelet volume increases to compensate for the oxygen deficiency.
This state persists for some time. Including after an episode of pancreatic dysfunction.
Treatment. In an acute condition, the patient is transported to a surgical hospital and surgery is performed.
If pancreatitis is chronic, a diet is prescribed. The system also shows the use of enzymes. To make the work of an already suffering organ easier.
Intoxication, poisoning
Spicy. For example, salts of heavy metals, vapors of non-metals. Substances such as mercury, lead, antimony, arsenic, and cadmium are especially dangerous. Also some isotopes of these elements.
Acute intoxication is accompanied by severe damage to the bone marrow. If there was contact with radioactive compounds (for example, charged iodine ions and others), the situation will be even worse - the increase in MCV can be tens of times.
Treatment. It is necessary to introduce a specific antidote. Which one depends on the toxic component. The patient is then kept in the hospital for several days. It is necessary to remove the decay products of poisons as quickly as possible. For this purpose, infusion solutions and diuretics are prescribed.
Hyperthyroidism
In other words, an increase in the concentration of thyroid hormones. This small endocrine organ, along with the pituitary gland, acts as the “conductor” of all systems. As soon as the amount of the substance increases, the body begins to work literally for wear and tear.
The pathology is accompanied by a group of symptoms: an increase in pressure, temperature, etc. With hyperthyroidism, the average volume of red blood cells increases, since the bone marrow also intensifies its activity (hormones spur more active work).
This condition early leads to dysfunction of the brain and heart. Emergency disorders are possible - heart attack, stroke or chronic disorders of nutrition and cellular respiration.
Treatment: special diet and iodine preparations. To reduce the intensity of production of the substance.
At the same time, it is necessary to combat the root cause of the disorder. Consequently, they look for the etiology of the process and eliminate the original factor.
Alcoholism
Alcohol consumption has a negative effect in general. As for the increase in MCV, this is an attempt to compensate for the impairment caused by drinking alcohol.
Chronic, especially binge, alcoholics harm their own bodies. Ethanol penetrates the blood and breaks down into toxic components that affect, including the bone marrow. The whole body suffers.
Recovery from a long period of illness will take months, if not years.
Treatment. To reduce the average volume of red blood cells, you need to completely give up alcohol. Coding is available to patients: medication and psychotherapeutic.
Also detoxification techniques. To quickly remove ethanol and its metabolites. Therapy takes place in the clinic.
Anemia
A classic condition in which the average volume of red blood cells increases. The average volume of erythrocytes most often increases in the iron deficiency form of the anemic process.
When there is not enough substance, the maturation of red blood cells is accelerated. Normally, red blood cells carry oxygen with hemoglobin.
If a specific protein is insufficient or defective, the body strives to convert quantity into quality. That is, one red blood cell contains more hemoglobin and oxygen for transport.
This is effective only in the early stages of disorders. Then the disorder enters the decompensation phase.
Treatment. In the case of iron deficiency anemia, it is necessary to take iron supplements. In the first few weeks, the substance is administered by injection. Then, if necessary, ferrocontaining drugs are prescribed for oral use.
For megaloblastic anemia, loading doses of vitamins B9 and B12 are prescribed.
The full course of therapy takes up to several weeks. The patient is then observed.
Bone marrow damage
Of different character. For example, oncological. Or myeloproliferative pathological processes, when the body synthesizes too many red blood cells.
Normally, formed cells are produced by the bone marrow, where they mature.
The tissues of this organ are extremely sensitive to negative factors. Be it toxins, radiation. Deviations occur quickly and are difficult to correct. Especially when you consider that many problems in the functioning of the bone marrow are genetically determined.
Treatment. Treatment depends on the specific condition. In mild cases, drug correction is sufficient. In severe clinical situations, bone marrow transplantation is indicated.
Liver disorders
Several variants. Inflammatory process or hepatitis. Cirrhosis also occurs. Acute tissue death of the largest gland. Or a chronic form, in which the process lasts for months or years.
The liver is responsible for processing substances and purifying the blood. If this biochemical laboratory fails, the entire body suffers. First of all, bone marrow. Because toxic substances are not filtered out and inhibit its functioning.
Treatment depends on the pathology.
- Diet, plus hepatoprotectors like Essentiale, is the gold standard of therapy.
- In advanced cases, the only salvation for the patient is an organ transplant.
Caution:
Transplantation is contraindicated in the final stages of cirrhosis. Because lethal bleeding cannot be avoided.
What standards exist?
The MCV index is a factor that changes over the years; it is different for boys and girls. The maximum norm in children is noted in the initial days of life (from 90 to 140 fl).
By the end of the baby’s first year of development, the values range from 71 to 84 fl. At 5-10 years old, this index in a child fluctuates between 75-87 fl.
In adolescence (15-18 years), the norm in women rises: 78-98 µm3. In the period from adulthood to 45 years, the average volume of their red cells reaches 81-100 µm3.
In adolescence and youth, the norm for men is 79-95 µm3. From 18 years old – 80-99 µm3.
In an adult in mature years (45-65 years), regardless of gender, the values are 81-101 µm3.
How is blood drawn?
Some owners are afraid that their pets will be seriously hurt. If you know all the nuances about how a cat’s blood is taken for analysis, then the reasons for concern will evaporate by themselves.
The mustachioed patient is fixed on the examination table or in a special bag. Having selected one of the paws, the doctor shaved off a small area of fur on it and found a vein. Particularly sensitive and fearful individuals are given local anesthesia. The whole procedure takes no more than 5 minutes. Bleeding under the bandage stops by the end of the appointment. For two studies, 3 ml of biomaterial is taken.
Diagnostic role of MCV
Knowing the average volume of red blood cells is necessary to classify anemia into normo-, macro- and microcytic, which, in turn, helps to determine the cause that led to anemia. Without such a diagnosis, it is impossible to prescribe the correct treatment. It is the decoding of the MCV indicator that largely contributes to the fact that doctors do not have to treat red blood diseases at random.
Microcytic anemias include iron deficiency, sideroblastic and thalassemia. The most common reason that the mean red blood cell volume is low is iron deficiency. It is he who is first suspected by a doctor who sees such an analysis result. To confirm or refute this assumption, additional biochemical studies are being carried out in the future.
The main causes of iron deficiency anemia are a decrease in the content of this microelement in the diet, an increase in the need for it (for example, during pregnancy in women), impaired absorption in the gastrointestinal tract, chronic blood loss (including in women with heavy periods). The doctor’s task is to identify one of these factors and eliminate its negative impact.
Normocytic anemias are most often associated with chronic diseases or acute blood loss. This group also includes anemia caused by increased destruction of red blood cells (this happens in case of poisoning with hemolytic poisons, malaria, etc.) and disruption of their formation due to the fact that the level of erythropoietin is reduced (in chronic renal failure) or there is a malignant bone marrow disease .
Of course, the average volume of red blood cells is not the only value that is necessary for diagnosing anemia. A huge role is played by the color indicator, the average hemoglobin content in one red blood cell and in the entire red blood cell mass. Only a comprehensive assessment of the research results when deciphering the analysis can give the doctor the opportunity to understand what caused the anemia and how to deal with it now. And the MCV indicator itself is just numbers that mean nothing in isolation from other laboratory data and the clinical picture. It is not enough to simply compare the obtained value with the norm, as is sometimes the case with other analyses, you must think systematically.
Determination of the average volume of red blood cells is included in the necessary list of studies for a general blood test
This indicator is paid attention mainly when there are deviations in the results indicating anemia. In this case, in order to determine what caused this disease in men, women and children, when deciphering the analysis, it is simply necessary to use all the values related to the red blood system, take into account which of them are low or high
And among them, first of all, they pay attention to MCV and color indicator.
Of course, calculating the average volume of red blood cells in most cases plays an auxiliary role, but it would be stupid to exclude this indicator from a clinical blood test. If anemia was detected, it would still have to be determined, moreover, no special resources are spent to determine it - it’s enough to just count.
Interpretation of a general blood test
Based on the general analysis, the main blood parameters are determined, which are deciphered by the doctor. In your personal account (on our website), the result of the analysis will be published in the form of a schematic table containing the values of blood parameters and the reference range.
Let's look at these indicators and their normal values. It should be borne in mind that deviations from the norm do not necessarily indicate pathology - many of them can be explained by various factors.
Red blood cells (RBCs) are “red blood cells” that contain hemoglobin. The main function is to deliver oxygen from the lungs to the tissues of the body and carbon dioxide from the tissues to the respiratory organs.
Increased (erythrocytosis) - blood diseases (primary erythrocytosis, polycythemia), hypoxia in lung diseases and congenital heart defects, dehydration (vomiting, diarrhea), insufficiency of adrenal cortex function.
Decreased (anemia) - blood loss, hemolysis, deficiency of iron, vitamin B12, folic acid.
Normal value, ×10 12 cells/l:
Hemoglobin (HGB) is a red iron-containing blood pigment that performs the function of transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide and regulating the acid-base state.
Increased : congenital heart defects, pulmonary fibrosis, intestinal obstruction, cancer. It is also typical for “working” dog breeds: with constant intense physical activity, the need for oxygen increases and, accordingly, the level of hemoglobin increases.
Decreased - blood loss, infectious and autoimmune diseases, helminthic infestations, pregnancy and lactation, impaired absorption of iron and vitamin B12, malignant blood diseases, chemotherapy.
Hematocrit (HCT) is the volume fraction of red blood cells in whole blood (the ratio of the volumes of red blood cells and plasma).
Increased - hypoxia, kidney neoplasms with increased erythropotin, polycystic and hydronephrosis of the kidneys, decrease in circulating blood volume (burn disease, peritonitis, etc.), leukemia.
Decreased - anemia, pregnancy, overhydration.
Erythrocyte indices:
Mean erythrocyte volume (MCV) is an indicator characterizing the type of anemia.
Mean erythrocyte hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) is an indicator that determines the saturation of erythrocytes with hemoglobin.
The mean erythrocyte hemoglobin content (MCH) is one of the indicators for determining the type of anemia.
Red blood cell distribution width (RDW) is a measure of how much red blood cells vary in size.
Platelets (PLT) are the formed elements of blood involved in the process of blood clotting.
Increased - exacerbation of chronic diseases, viral or bacterial infections, blood or hematopoietic diseases, conditions after surgical procedures, malignant tumors, consequences of the use of certain groups of drugs.
Decreased - idiopathic hypoplasia of hematopoiesis, tumor lesions (acute blood leukemia, cancer metastases, sarcoma, osteomyelosclerosis, myelofibrosis), intoxication, viral infections (hepatitis, adenoviruses), autoimmune diseases.
Normal value, ×10 9 cells/l:
The analyzer can also calculate mean platelet volume ( MPV ).
Leukocytes (WBC) are “white blood cells” that have a nucleus. The main function is to protect the body from various pathological agents, as well as from internal typical pathological processes accompanied by severe inflammation.
They are divided into two fractions: granulocytes, or cells with granularity in the nucleus (neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils), and agranulocytes with a monochrome, non-granular nucleus (lymphocytes and monocytes).
Normal value, ×10 9 cells/l:
Leukocyte formula (leukoformula) is the percentage of different types of leukocytes, determined by counting them in a stained blood smear under a microscope.
Granulocytes (GRAN) is the total number of indicators such as band and segmented neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils.
Band neutrophils (NEUT) are a type of neutrophil that have an S-shaped nucleus. They are young forms of neutrophils; over time, band neutrophils mature and transform into segmented neutrophils.
Increased - infections, postoperative period, ischemic tissue necrosis, mercury or lead intoxication, cancer, some inflammatory processes, reaction to certain drugs.
Segmented neutrophils (NEUT) - perform a protective function against various bacterial and fungal infections, and also maintain a normal immune system.
Increased - pneumonia, purulent inflammation, acute ischemia or tissue necrosis, extensive burn, diseases of the circulatory system, acute blood loss.
Decreased - viral infections, autoimmune diseases, chemotherapy or radiation therapy, aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis.
Eosinophils (EOS) are granulocytic leukocytes capable of absorbing various inflammatory mediators, thereby participating in allergic reactions.
Increased (eosinophilia) - parasitic diseases, allergic reactions, lung diseases (eosinophilic pneumonia, asthma, allergic aspergillosis, pulmonary infiltrate), blood diseases, autoimmune diseases, diseases of the stomach and intestines, rheumatic diseases, taking certain medications.
Decreased - B12 deficiency anemia, trauma. Often has no clinical significance.
Basophils (BAS) are a fraction of leukocytes responsible for delayed and immediate allergic reactions (anaphylactic shock reactions).
Increased - blood diseases, chronic inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, allergic reactions (food or iatrogenic nature), hypofunction of the thyroid gland, treatment with estrogens.
Lymphocytes (LYM) are cells of the immune system, a type of leukocytes of the agranulocyte fraction. There are T- and B-lymphocytes. T lymphocytes are responsible for cellular immunity (contact interaction with victim cells), B lymphocytes provide humoral immunity (antibody production), and lymphocytes regulate the activity of other types of cells.
Increased - viral infections, hyperthyroidism, oncological diseases of the blood and bone marrow.
Decreased - bacterial infection, sepsis, treatment with corticosteroids, immunosuppressive therapy, some types of lymphomas, radiation therapy.
Normal value, ×10 9 cells/l:
Monocytes (MONO) are agranulocytic leukocytes with the ability to phagocytose foreign agents.
Increased (monocytosis) - infections of various etiologies, as well as the period after acute infections, blood diseases, phosphorus poisoning.
Decreased - damage to the bone marrow with a decrease in its function (aplastic anemia, B12-deficiency anemia), radiation sickness.
Normal value, ×10 9 cells/l:
Leukocyte shifts
Shift of the leukocyte formula to the left - acute infectious diseases, physical overexertion, acidosis and coma.
Shift of the leukocyte formula to the right - megaloblastic anemia, kidney and liver diseases, conditions after blood transfusion.
Do not forget: only a veterinarian can take into account all the nuances of clinical blood test data. The values of indicators that are considered to be the “norm” are averaged. Depending on many characteristics of the animal: age, gender, size and even its diet, medications taken and past diseases - normal values can differ significantly.
If you have any additional questions, the veterinarians at the Averia Clinic are happy to help you 24 hours a day!
source
High RDW
The coefficient is considered increased when the indicator is more than 15%. This means that red blood cells vary greatly in size.
There are many possible causes for this condition. To determine the most likely diagnosis, RDW is compared with MCV.
High MCV
If we consider that MCV is the average volume of space that each blood cell occupies, then an increased level of both indicators may indicate several possible deviations in the condition of the body.
Liver diseases
The liver is the largest internal organ in the human body, which produces substances necessary for the body, filters blood, and removes harmful chemicals. Liver health worsens with alcoholism, as may be indicated by elevated RDW levels.
Hemolytic anemia
A disease in which red blood cells die or are destroyed earlier than their healthy life cycle would suggest.
Megaloblastic anemia
Large oval red blood cells with an underdeveloped nucleus and a short life cycle appear in the blood. This condition usually occurs due to a lack of folic acid or vitamin B12 in a person's diet or due to impaired absorption of these substances.
Vitamin A deficiency
A minimum amount of vitamin A must be present in the body for cell synthesis in interaction with vitamin B12.
Low MCV
In other cases, the average volume of red blood cells is reduced, while the width of the distribution is still higher than normal. This may be a sign of some less common anemias or iron deficiency conditions.
Decreased hemoglobin level
Hemoglobin is present in red blood cells. It helps deliver oxygen to the cells of the body. Iron is necessary for the synthesis of hemoglobin, so a deficiency of this trace element leads to a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood.
Iron deficiency anemia is usually caused by insufficient iron in the diet or poor absorption of iron from food or dietary supplements.
Thalassemia intermedia
Thalassemia intermedia is a blood disease in which the synthesis of one or more components of hemoglobin is impaired. As a result, the blood cells are fragmented (broken into smaller particles).
If the red blood cell fragments are noticeably different in size but do not take up more space, this may appear in the analysis as a low MCV with a high RDW.
- the initial stage of iron deficiency anemia, leading to a decrease in hemoglobin;
- a decrease in the level of vitamin B12 or folic acid in the body, which is a prerequisite for macrocytosis anemia.
What to do if the indicator deviates from the norm
If the results of a general blood test show a deviation from the norm in the average size of erythrocyte units in the direction of increasing or decreasing their size, the following steps must be taken:
- together with your doctor, try to establish the causative factor influencing the change in red blood cells;
- streamline the daily routine, balance the diet, saturating it with foods containing a sufficient amount of iron, iodine, vitamin B6, B12 (veal, nutria meat, rabbit, turkey, legumes, nuts, ocean fish, seaweed, shellfish, crustaceans);
- take medications that will be prescribed by your doctor;
- completely stop using alcoholic beverages, tobacco products and drugs;
- Avoid a sedentary lifestyle, engage in cycling, athletics, and swimming.
MCV as part of a blood test is an indicator that tends to change under the influence of environmental factors. Therefore, in order for the average cell volume to reach optimal levels, an integrated approach is required using drug therapy, compliance with the instructions of the attending physician and dietary standards.
Article design: Mila Friedan
Differential diagnosis of anemia
To a large extent, the diagnosis of anemia is facilitated by the correct interpretation of morphological changes in red blood cells:
| Index | Type of anemia | |||
| Iron-deficiency anemia | hemolytic anemia | hypoplastic anemia | B12 deficiency anemia | |
| Hemoglobin | reduced | significantly reduced | significantly reduced | sharply reduced |
| Red blood cells | reduced | reduced | reduced | sharply reduced |
| reduced | norm | norm | reduced | |
| Red blood cell diameter | reduced | reduced | elevated | significantly increased |
| norm | elevated | elevated | sharply increased | |
| reduced | elevated | elevated | sharply increased | |
| reduced | norm | reduced | reduced | |
| Reticulocytes | norm | sharply increased | sharply markedly reduced | reduced |
| Clinical Analysis Example | Clinical Analysis Example | Clinical Analysis Example | Clinical Analysis Example |
Normal average erythrocyte volumes depending on age
| Age | Women MCV, fl | Men MCV, fl |
| Umbilical cord blood 1-3 days 1 week 2 weeks 1 month 2 months 3-6 months 6-24 months 3-6 years 7-12 years 13-19 years 20-29 years 30-39 years 40-49 years 50-59 60-65 years old over 65 years old | 95-118 95-121 88-126 86-124 85-123 77-115 77-108 72-89 76-90 76-91 80-96 82-96 81-98 80-100 82-99 80-99 80-100 | 98-118 95-121 88-126 86-124 85-123 77-115 77-108 70-99 76-89 76-81 79-92 81-93 80-93 81-94 82-94 81-100 78-103 |
The average hemoglobin content in a red blood cell is normal depending on age
| Age | Women MCH, pg | Men MCH, pg |
| 1-3 days 1 week 2 weeks 1 month 2 months 3-6 months 6-24 months 3-12 years 13-19 years 20-29 years 30-39 years 40-49 years 50-59 years 60-65 years over 65 years | 31-37 28-40 28-40 28-40 26-34 25-35 24,0-31,0 25,5-33,0 27,0-32,0 27,5-33,0 27,0-34,0 27,0-34,0 27,0-34,5 26,5-33,5 26,0-34,0 | 31-37 28-40 28-40 28-40 26-34 25-35 24,5-29,0 26,0-31,0 26,5-32,0 27,5-33,0 27,5-33,5 27,5-34,0 27,5-34,0 27,0-34,5 26,0-35,0 |
The average hemoglobin concentration in a red blood cell is normal depending on age
| Age | Women MCHC, g/dl | Men MCHC, g/dl |
| 1-3 days 1 week 2 weeks 1 month 2 months 3-6 months 6-24 months 3-6 years 7-12 years 13-19 years 20-29 years 30-39 years 40-49 years 50-59 years 60- 65 years over 65 years | 29,0-37,0 28,0-38,0 28,0-38,0 28,0-38,0 29,0-37,0 30,0-36,0 33,0-33,6 32,4-36,8 32,2-36,8 32,4-36,8 32,6-35,6 32,6-35,8 32,4-35,8 32,2-35,8 32,2-35,8 31,8-36,8 | 29,0-37,0 28,0-38,0 28,0-38,0 28,0-38,0 29,0-37,0 30,0-36,0 32,2-36,6 32,2-36,2 32,0-37,0 32,2-36,4 32,8-36,2 32,6-36,2 32,6-36,4 32,6-36,2 32,2-36,9 32,0-36,4 |
ATTENTION! The information presented on the website DIABET-GIPERTONIA.RU is for reference only. The site administration is not responsible for possible negative consequences if you take any medications or procedures without a doctor’s prescription!
Norms of blood tests in cats
| The name of indicators | Units | Norm |
| Ø hematocrit | % (l/l) | 26-48 (0,26-0,48) |
| Ø hemoglobin | g/l | 80-150 |
| Ø average hemoglobin concentration in an erythrocyte | % | 31-36 |
| Ø average amount of hemoglobin in a red blood cell | pg | 14-19 |
| Ø color indicator; | 0,65-0,9 | |
| Ø ESR | mm/hour | 0-13 |
| Ø red blood cells | million/µl | 5-10 |
| Ø leukocytes | thousand/µl | 5,5-18,5 |
| Ø segmented neutrophils | % | 35-75 |
| Ø band neutrophils | % | 0-3 |
| Ø lymphocytes | % | 25-55 |
| Ø monocytes | % | 1-4 |
| Ø eosinophils | % | 0-4 |
| Ø platelets | million/l | 300-630 |
| Ø basophils | % | — |
| Ø myelocytes | % | — |
Norms of blood tests in cats
General (clinical) blood test
Blood chemistry
| The name of indicators | Units | Norm |
| Ø glucose | mmol/l | 3,2-6,4 |
| Ø protein | g/l | 54-77 |
| Ø albumin | g/l | 23-37 |
| Ø cholesterol | mmol/l | 1,3-3,7 |
| Ø direct bilirubin | µmol/l | 0-5,5 |
| Ø total bilirubin | µmol/l | 3-12 |
| Ø alanine aminotransferase (ALT) | U/l | 17 (19) -79 |
| Ø aspartate aminotransferase (AST) | U/l | 9-29 |
| Ø lactate dehydrogenase | U/l | 55-155 |
| Ø ɤ-glutamyltransferase | U/l | 5-50 |
| Ø alkaline phosphatase | U/l | 39-55 |
| Ø ɑ-Amylase | U/l | 780-1720 |
| Ø urea | mmol/l | 2-8 |
| Ø creatinine | mmol/l | 70-165 |
| Ø calcium | mmol/l | 2-2,7 |
| Ø magnesium | mmol/l | 0,72-1,2 |
| Ø creatine phosphokinase | U/l | 150-798 |
| Ø triglycerides | mmol/l | 0,38-1,1 |
| Ø inorganic phosphorus | mmol/l | 0,7-1,8 |
| Ø Electrolytes | ||
| Ø potassium (K + ) | mmol/l | 3,8-5,4 |
| Ø calcium | mmol/l | 2-2,7 |
| Ø sodium (Na + ) | mmol/l | 143-165 |
| Ø iron | mmol/l | 20-30 |
| Ø chlorine | mmol/l | 107-123 |
| Ø phosphorus | mmol/l | 1,1-2,3 |
MCV is higher than normal
If the results are above normal, this indicates the development of macrocytic anemia. It can be directly related to diseases such as:
- drug intoxication;
- food poisoning;
- problems with the thyroid gland;
- lack of iodine or iron in the body;
- liver dysfunction;
- oncological process of red bone marrow;
- long-term alcoholism;
- disruption of the pancreas.
An increase in mcv can be caused by:
- long-term use of birth control pills that affect hormonal levels;
- addiction to cigarettes and tobacco products;
- prolonged contact with toxic substances (work in hazardous industries);
- taking medications that increase the level of mcv in the blood.
If left untreated, macrocytic anemia can lead to frequent fainting, poor health, and low hemoglobin levels in the blood. Particularly at risk are:
- people who eat poorly, lead a sedentary lifestyle and ignore exercise;
- patients with chronic liver failure;
- people with a genetic predisposition to the disease;
- men over fifty-five years of age who abuse alcohol.
Experts identify some signs by which one can understand that a person’s red blood cell volume is too high:
- unhealthy pale lips;
- abdominal pain for no particular reason, which appears very often;
- the presence of tachycardia (heartbeat too fast), even when the person is at rest;
- skin with a yellowish tint.
If you notice similar symptoms or detect an increased level of mcv in the blood, you must immediately consult a general practitioner for appropriate treatment.
How is the MCV blood test performed?
To determine the MCV level, you need to visit a laboratory that specializes in determining quality blood parameters, or take tests at a local clinic.
To obtain the most accurate diagnostic results with minimal risk of data errors, you will need to follow the rules for preparing for the donation of biological material, undergo the blood sampling procedure and wait for the test results.
Preparation
Includes the implementation of the following recommendations, which allow you to maintain the cellular composition of the blood at an optimal level without provoking its sudden changes.
The patient who will be tested will need to follow the following rules:
- 3 days before blood sampling, do not drink alcohol;
- take the test in the morning (preferably before 10-00);
- 2 days before diagnosis, exclude physical activity, do not engage in strength sports, do not lift heavy objects;
- have breakfast only after blood sampling, so that the stomach is empty (the best option would be to eat wheat, rice, pearl barley, barley porridge with vegetable salad).
It is recommended not to smoke 8 hours before donating blood. In the evening the day before the test, you should not overeat. All food consumed before laboratory testing should be light and not burden the digestive system.
Blood collection
A mandatory condition for submitting biological material for testing for MCV levels is taking blood on an empty stomach.
This procedure is performed using two methods, namely:
- ring finger bundle - pierced with an automatic pen with needles or a metal scarifier (about 1-2 ml of blood is taken by a laboratory assistant);
- ulnar vein - biological material is collected with a disposable syringe, which is filled with 5-10 ml of blood.
In order to obtain the most accurate research results, it is advisable to perform simultaneous collection of capillary and venous blood. This will allow for a comparative analysis of the selected samples, eliminating the possible occurrence of inaccuracies and errors in the operation of medical equipment.
How long to wait for answers
Modern medical equipment allows you to obtain laboratory test results for the MCV level within 15-20 minutes.
after delivery of biological material. In most cases, determining the average size of red blood cell units is only 1 of more than 20 parameters of the cellular composition of the blood that laboratory specialists need to determine.
If the staff of the clinic where the collected blood is tested uses automatic analyzers, the diagnostic process is significantly accelerated.
In laboratories that are not equipped with modern medical equipment and use microscopic research techniques, you will need to wait from 1 to 2 hours. In this case, the laboratory assistant performs an independent blood test, establishing the average volume of red blood cells using a microscope.
It is believed that the microscopic diagnostic method carries a greater number of errors, because there is a human factor involved. In order to save personal time and obtain the most accurate diagnostic results, it is recommended to donate blood in laboratories that are equipped with automatic analyzers.
Increased values
A marked increase in MCV indicates the development of macrocytosis (macrocytic anemia). In this case, the size and volume of red blood cells increases, and a drop in hemoglobin levels is observed. If the hemoglobin concentration is not lower than the permissible value, this indicates alcohol abuse.
Other reasons for the increase in the indicator:
- deficiency of B vitamins (folic acid and cyanocobalamin) or impaired absorption;
- hemolysis;
- suppression of bone marrow functions;
- some autoimmune diseases;
- myelodysplastic syndrome;
- drug intoxication;
- hormonal imbalances due to disruption of the thyroid gland;
- liver damage, hepatitis, malignant neoplasms;
- imbalance of intestinal microflora;
- infectious and inflammatory process.
Symptoms of macrocytic anemia include abdominal pain, pale skin, severe fatigue, palpitations, migraines, hypotension, and frequent colds.
Important information: What do elevated platelets in an adult indicate (causes and consequences)
A slight excess of standard values can be observed in the absence of systemic pathologies, for example, due to nicotine addiction, hormonal contraception, taking certain medications, bleeding, regular contact with toxic compounds, etc.
A false overestimated result can be obtained with sickle cell anemia, diabetic ketoacidosis, and red blood cell agglutination.