Endometriosis is the most common disease that occurs in women 25–45 years old. A feature of this pathology is considered to be asymptomatic at the initial stage of manifestation. However, treatment for endometriosis must be started as soon as possible, since it can lead to undesirable developments, the most striking of which is infertility. In the modern world there are many effective techniques that help in the fight against this disease, the leading place in which is given to laparoscopy.
Causes of endometriosis
There is currently no single version of the causes of endometriosis.
1 theory “Retrograde menstruation or implantation theory”
Some women have a tendency to experience retrograde menstruation (when the muscle layer of the uterus contracts in the opposite direction from the cervix). During menstruation (regulus), blood with elements of the endometrium, due to the peristaltic movements of the smooth muscle muscles of the uterus, is carried into the abdominal cavity and fallopian tubes, where the endometrium is implanted into the tissues of various organs. During the normal menstrual cycle, the inner layer of the uterus (endometrium) is separated and removed from the uterine cavity, while microhemorrhages and aseptic inflammation occur in other organs affected by endometriotic lesions. The likelihood of endometriosis may increase due to such reasons as: structural features of the uterine appendages, immune pathological processes, abortion, uterine surgery, cesarean section, surgical treatment of cervical diseases, hereditary predisposition.
The role of heredity in the pathology under consideration is especially high and suggests a very high possibility of the disease occurring in the daughter if her mother previously suffered such a disease. Knowing about the predisposition to this pathology, a woman, following preventive measures, can prevent the occurrence of the disease. For example, after surgical interventions on the organs of the reproductive system, a woman needs systematic monitoring of her health to prevent possible complications.
2 theory “Gene mutations”
3 theory “Deviations in the function of cellular enzymes and reactions of hormone receptors”
However, the last two theories have not received widespread popularization due to the small evidence base. The classification of endometriosis is divided by location.
Recovery period
Treatment of endometriosis does not end after laparoscopy.
The recovery period is considered very important for the further normal well-being of a woman. Its duration is determined by the doctor and depends on some features of the treatment.
After surgery, the medical professional recommends that the woman follow these rules:
- Do not visit the sauna or take a hot bath for a month;
- Try to take a shower every day, if possible - twice a day;
- Monitor your body temperature. If there is a deviation from the norm, contact a medical facility;
- Limit yourself from using tampons;
- Try not to douche;
- Eliminate salty, fried and pickled foods from your diet;
- Avoid intense physical activity;
- Walk outdoors more often.
Classification of endometriosis
- Genital.
From the name itself it follows that during the course of the disease in this form, endometriotic foci are located in the tissues of the patient’s reproductive organs.
- Peritoneal (peritoneal) endometriosis
- affects the ovaries, pelvic peritoneum, fallopian tubes.
- Extraperitoneal (extraperitoneal)
endometriosis occurs in organs not covered by peritoneum: in the lower parts of the genital organs, the vulva, in the cervix of the uterus (its vaginal segment), the retrovaginal septum, etc. In the muscular layer of the uterus, internal endometriosis (adenomyosis) can form, and the uterus takes on a spherical shape and reaches sizes up to 5-6 weeks of pregnancy.
- Extragenital endometriosis.
In this form, endometriosis lesions are located outside the reproductive system (digestive tract, respiratory system, urinary system, postoperative scars).
- In serious, complicated cases of the disease, endometriosis can be mixed.
Depending on the depth and distribution of endometriosis foci, there are 4 degrees:
- I degree - superficial and single lesions;
- II degree - the lesions are deeper and more numerous;
- III degree - deep multiple endometriotic foci, as well as endometrioid ovarian cysts, individual peritoneal adhesions;
- IV degree - multiple and deep foci, large endometrioid cysts of both ovaries, extensive adhesions. The endometrium can grow into the walls of the vulva and rectum. As a rule, this degree of endometriosis is difficult to treat and is characterized by the scale and degree of invasion of the process.
Adenomyosis of the uterus is classified separately - according to the depth of invasion of the pathological process into the muscular layer of the uterus (myometrium):
- Stage I: initial growth of the myometrium;
- Stage II, foci of endometriosis grow to half the depth of the myometrium;
- Stage III: the myometrium completely grows to the serosa of the uterus;
- Stage IV: germination of the walls of the uterus with the spread of foci to the serous membrane (peritoneum).
Endometriotic lesions are also characterized by other parameters. For example, they can take on different shapes: from round to neoplasms that do not have clear contours, and vary in size - from several millimeters to several centimeters. As a rule, neoplasms are separated from adjacent structures by adhesions or a cicatricial process and have a brown color.
Depending on the cyclicity of the regulation, endometriosis lesions mostly appear on the eve of menstruation. The lesions have very different localizations and are found not only on the surface of organs, but also tend to deeply invade tissue. When the ovaries are involved in the process of endometriosis, the cysts are grouped and filled with bloody contents. Based on the size and depth of endometriotic lesions, as well as the localization of formations, the degree of endometriosis is determined using a scoring system.
Several recipes for dietary dishes
| Name of the dish | Ingredients: | Preparation: |
| Delicate fish soufflé | 200 g hake, 1 carrot, 1 egg, 3 tbsp. tablespoons sour cream, salt to taste | Together with carrots, the fish is boiled and ground in a blender. Add sour cream and egg yolk to the cooled mixture. The remaining protein is separately whipped into foam with the addition of salt, then combined with the fish mass. The finished composition is laid out in a greased form and baked in the oven at t = 180℃ for approximately 20 minutes. |
| Honey-apple marshmallow | 2 apples, 4 egg whites, 2 tbsp. spoons of honey, 10 g gelatin | Peeled and pre-separated slices of seedless apples are baked in the oven until softened. They make puree. The separated egg whites and honey are whipped into foam. Gelatin dissolves. All components of the marshmallow are mixed, the mass is poured into molds and sent to harden in the refrigerator. |
Symptoms of endometriosis
- Pelvic pain.
Occurs in 16-24% of patients. It can have both point and diffuse localization, arises and intensifies in correlation with the menstrual cycle, and can be constant. It is often caused by inflammation and adhesions that develop when affected by endometriosis.
- Dysmenorrhea -
pain during menstruation. The most common complaint, which causes the most suffering and discomfort, occurs in 40-60% of women. The maximum manifestations are expressed in the first few days of regulation. Endometriosis lesions often bleed into the cavity of the ovarian cyst, increasing their pressure, irritating the peritoneum, causing contraction of the smooth muscles of the uterine blood vessels.
- Painful intercourse.
Pain when emptying the bladder or rectum. It is observed in 2-16% of patients. When endometriosis lesions are localized in the pelvic organs in the vulva, utero-rectal space, in the area of the uterosacral ligaments, in the wall of the rectovaginal septum, it can cause discomfort and even pain during sexual intercourse or when emptying the rectum and bladder. These symptoms can also accompany adenomyosis and many other diseases: uterine fibroids, polycystic ovary syndrome, etc.
- Posthemorrhagic anemia.
In 25-40% of patients, due to significant chronic blood loss during menstruation, a state of anemia may occur. Weakness, pallor or yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes, dizziness, fatigue, drowsiness, irritability and mental excitability gradually increase.
- Infertility.
Scientists and doctors today are unable to accurately assess how and why infertility occurs when affected by endometriosis. This is associated with processes in the uterine appendages with endometriosis, with interruptions in the functioning of the general and local immune status of the body as a whole, and as a result, disruptions in ovulatory processes. With endometriosis, the possibility of not getting pregnant is not absolute, but quite high. Endometriosis and its accompanying processes can provoke spontaneous abortions, which in turn radically and significantly reduce the chances not only of pregnancy, but also of its normal course. Therefore, pregnant women with a history of endometriosis should be constantly monitored by a doctor. 15-56% of patients treated for endometriosis become pregnant within 6-12 months.
Reviews
Below are reviews from those women who underwent laparoscopy for endometriosis and successfully became pregnant after the intervention.
Natalya from Ivanovo: I had stage 4 endometriosis, I had a laparoscopy, after which I took medications for 4 months. At the end of the therapeutic course, conception occurred in the first cycle.
Svetlana from Moscow: Stage 1 endometriosis, pregnancy occurred 1 year after laparoscopy. During this time, I took medications prescribed by the doctor.
Ekaterina from Zaporozhye: We performed hysteroscopy and laparoscopy simultaneously. Then she took medications for 4 months. Conception occurred immediately after the restoration of menstruation. She gave birth to a healthy baby on time.
Laparoscopy for endomeriosis is highly effective, cures the disease, relieves unpleasant symptoms, and gives a chance for a long-awaited pregnancy.
Diagnosis of endometriosis
With the introduction of minimally invasive diagnostic and treatment methods (hysteroscopy and laparoscopy), the detection of endometriosis has increased significantly.
Due to the similarity of the course of this disease with other diseases of the genital organs, similar in symptoms, differential diagnosis is very important at all stages of diagnosis.
The doctor carefully collects complaints and anamnesis, information about previous diseases, including the reproductive system, surgical operations, and the presence of gynecological and obstetric history in female relatives.
Further examination includes:
- gynecological examination (vaginal, rectovaginal, speculum) is most informative on the eve of menstruation;
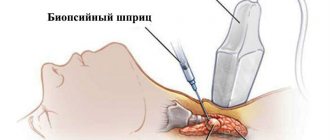
- colposcopy and hysterosalpingoscopy to obtain a biopsy from the affected organs and clarify the location and shape of the lesions;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs and abdominal cavity to clarify the localization and dynamics during the treatment of endometriosis;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging to detail the nature, localization of formations and depth of the lesion.
- laparoscopy, which makes it possible to visualize pathological processes, assess their activity, quantity, and allows one to determine the degree of maturity;
- hysterosalpingography (x-ray examination of the fallopian tubes and uterus with the introduction of contrast into their cavities);
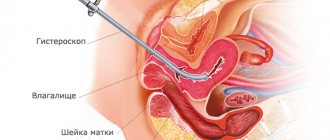
- hysteroscopy (endoscopic visualization of the uterine cavity), which makes it possible to diagnose adenomyosis in 83% of cases;
- Blood tests for the presence of tumor markers during the endometriosis process increase significantly: CA-125, CEA and CA 19-9, PO test.
The complex of all methods makes it possible to identify endometriotic lesions in up to 96% of cases.
A final diagnosis can be made only if a histological examination of a biopsy sample from foci of endometriosis taken during hysteroscopy (laparoscopy) is performed.
Planning pregnancy after laparoscopy
With good rehabilitation, the menstrual cycle is restored after 2-4 weeks. Usually your period comes on time or is delayed by several days. Less commonly, menstruation is delayed by up to 2 months. In this case, you need to do a control ultrasound and make sure there are no complications. If no pathology is detected, you just need to wait for the menstrual cycle to return.
If after laparoscopic surgery there are no periods for a long time, then a control ultrasound should be done.
You can plan a pregnancy 3-6 months after laparoscopy. It is possible to conceive a child naturally or through IVF. The choice of tactics depends on the ovarian reserve, the woman’s age, concomitant pathology and other factors.
Assessment of ovarian reserve after laparoscopy is carried out using a blood test for antimullur hormone. The AMH norm is more than 1 ng/ml. It is an indicator of the functioning of the ovaries. A decrease in AMH indicates that the supply of follicles is depleted. The chances of conceiving a child decrease.
Treatment of endometriosis
It is very important in determining the treatment tactics for endometriosis to take into account the following factors: what age category the patient belongs to, the number of pregnancies, including those ending in childbirth, it is important to know how the birth proceeded and whether there were any complications in the postpartum period. The severity of the pathological process, its location, depth, concomitant pathologies, and the desire to have a child are taken into account.
Therapy can be divided into drug treatment, surgical treatment (surgical removal of endometriosis lesions while preserving organ function - laparoscopically or radical extirpation of the uterus and its appendages), as well as combined.
When treating endometriosis, the doctor’s actions are aimed not just at eliminating the manifestations of the disease in question, but also its consequences (adhesive and cystic formations, psychoneurological manifestations, etc.).
Surgical treatment of endometriosis
In moderate and severe stages of endometriosis, it is recommended to resort to organ-preserving surgical treatment with removal of lesions. Treatment is comprehensively aimed at resection of heterotopias in the affected organ complexes, resection of endometrioid cysts in the ovaries, as well as dissection of adhesions. As a rule, it is used if there is no effect from drug treatment, there are various contraindications, for example, intolerance to drugs or their components, when endometrioid tumors larger than 3-4 centimeters are detected, urinary dysfunction, problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Often, surgical treatment is combined with medication. The intervention is carried out using laparoscopic or laparotomic approaches.
If the patient’s disease is actively progressing after 40 years of age and conservative surgical measures do not give the desired effect, then radical surgical removal of endometriosis is resorted to (extirpation of the uterus and appendages). Such measures are not used often and occur in 12% of patients.
Contraindications
Treatment of endometriosis by laparoscopy is not allowed in all cases. There are a number of absolute and conditional contraindications to this tactic.
Minimally invasive surgery is strictly prohibited in the presence of the following pathologies:
- diseases of the cardiovascular system and respiratory organs. This is due to the fact that during the procedure gas is injected into the peritoneal cavity, which can provoke a spasm;
- conditions in which the blood clotting process slows down, and hemophilia;
- neoplasms of various nature;
- violations of the structure of the diaphragm.
Relative contraindications include the following:
- recent abdominal surgery;
- malignant formations;
- liver failure in acute form;
- severe inflammation in the ovaries;
- infectious diseases;
- overweight.
Basic principles of surgical treatment of endometriosis from the perspective of evidence-based medicine
Regardless of how far and deep the pathological process has spread, laparoscopy is the preferred surgical approach (the “gold standard”) for the treatment of endometriosis. It promotes better visualization of lesions due to their optical magnification, minimal tissue trauma and faster rehabilitation of patients than after laparotomy. Therapeutic and diagnostic laparoscopy with removal of endometriotic tumors provides a significant reduction in the intensity of pain associated with endometriosis.
Ovarian endometriomas in women with pelvic pain should be surgically removed by laparoscopy.
It is fundamentally important for women of childbearing age to be cured of ovarian endometriosis without the risk of recurrence with maximum preservation of unaffected oocyte tissue. To do this, they perform puncture, drainage of the cyst, alcoholization and destruction of the capsule by exposure to various types of energy. However, all these methods do not completely remove the cyst capsule, which can lead to relapse of the disease.
In women who are not interested in pregnancy, endometriotic lesions can be removed by laparoscopic or combined laparoscopic-vaginal access, if necessary in combination with simultaneous resection of the affected area of the rectal wall or in a single block with the uterus.
Only removal of the uterus (hysterectomy) can be considered a radical method of treating adenomyosis. This operation is usually performed laparoscopically. When performing a hysterectomy, it is very important to remove all visible endometriotic lesions, and bilateral ovarian removal may provide more effective pain relief and reduce the likelihood of disease recurrence.
The issue of removing the ovaries should be discussed with each patient individually.
Conservative treatment is used if endometriosis has a latent course, the patient is under 45 years of age, during premenopause, and there is a need to preserve reproductive function.
Anesthesia during surgery
Laparoscopy is performed under general anesthesia, and each patient undergoes training before it is performed. The anesthesiologist selects the drug and its dose individually for each patient. There are several methods of administering anesthesia before laparoscopic surgery:
- Local epidural anesthesia.
- Regional epidural anesthesia.
- General anesthesia.
During general anesthesia, tracheal intubation is performed to ensure the patient can breathe freely and prevent vomit from entering the respiratory tract.
At the Yusupov Hospital, they carefully select substances for anesthesia, using minimally morphine derivatives. The anesthetic drug should have minimal side effects and not affect muscle relaxation - this can complicate the operation. Anesthesia has a large number of side effects and can cause an allergic reaction in the patient, so every patient undergoes preparation before the operation. The quality of anesthesia depends on the experience and qualifications of the doctor. Reviews of anesthesia vary, depending on how well the patient was prepared and the anesthesia was selected. Epidural local and regional anesthesia is used for short-term surgical interventions.
Hormone therapy in the treatment of endometriosis
Combination therapy with estrogens and progestogens
According to the recommendations, combined oral contraceptives - COCs (hormonal contraceptive pills) are most preferable for eliminating pelvic pain in women who are not planning a pregnancy and have no contraindications to their use. The main advantages of COCs are their relatively low cost, low risk of side effects and acceptable duration of therapy. The use of COCs significantly reduces the intensity of pain associated with endometriosis. Continuous use of COCs has priority in the treatment of endometriosis compared to the cyclic regimen. The drugs help reduce pain intensity after 6 months. by 58%, and after 2 years - by 75% in patients with severe dysmenorrhea.
Progestogens (visanne, norcolut, MPA, duphaston, levonorgestrel).
This group of drugs can be recommended for therapy at various stages of the disease. Patients are prescribed a continuous course of 6 to 8 months. Side effects may occur: spotting during the intermenstrual period, psychological depression, increased sensitivity of the mammary glands.
Antigonadotropic drugs (danazol, danogen, danol, etc.)
Suppress the production of gonadotropins in the hypothalamic-pituitary system. They are taken continuously, usually for at least six months. Contraindication is hyperandrogenism (excess of androgenic hormones). Side effects may appear: sweating, feeling hot, weight fluctuations, decreased tone of voice, increased greasiness of the skin, intense hair growth.
Gonadotropic releasing hormone agonists (triptorelin, goserelin, etc.)
A positive aspect when using drugs in this group is the possibility of taking them once a month and the absence of severe side effects. Releasing hormone agonists cause inhibition of ovulation and a decrease in estrogen in the body, which leads to the suppression of the spread of endometriotic tumors.
In addition to hormonal drugs, immunostimulating drugs are used in the treatment of this pathology, as well as symptomatic therapy: antispasmodics, painkillers. For severe pain, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, indomethacin, voltaren), antidepressants, and psychotherapy are used.
Complete convalescence in endometriosis occurs only with its early detection and high-quality subsequent therapy.
Estimated indicators of recovery from endometriosis are: good health, no complaints of pelvic pain, no relapses within 5 years after therapy, restoration or preservation of reproductive function.
With the current level of development of surgical gynecology with the extensive use of organ-preserving treatment methods, all of the above can be achieved in 60% of women aged 20 to 36 years. If the patient was treated with radical surgery, the disease does not recur.
How is the operation performed and its duration?
Before the operation, the woman undergoes preparation, the doctor talks about the stages of the operation.
The patient is consulted by a resuscitator who checks that there are no contraindications to anesthesia. The patient is positioned on the operating table, which is tilted in the head area 30 degrees below the legs. In this position, access to the ovaries is easier, as the intestines descend towards the diaphragm. The operation begins with treatment of the anterior abdominal wall, then the surgeon makes three punctures in the anterior abdominal wall, carbon dioxide is injected into the puncture in the navel area, which lifts the anterior abdominal wall in the form of a dome, which greatly facilitates access to the surgical field. Then the laparoscope is inserted, and surgical instruments are inserted into the holes located below to perform the operation. The video camera transmits an image of the surgical field to the monitor screen, and the surgeon watches his actions on the screen during the operation. The duration of the operation depends on the complexity of the disease and the extent of the surgical intervention. On average, a laparoscopic operation lasts from forty minutes to an hour, taking into account preparation it takes about two hours. After the operation is completed, gas, instruments, and a laparoscope are removed from the abdominal cavity, sutures are applied to small holes and covered with a sterile bandage.
Complications of endometriosis
- 1. Endometriotic ovarian cysts (“chocolate” cysts), filled with old menstrual blood.
- 2. Hemorrhages and scar changes.
These two complications are highly likely to lead to infertility. Extensive and widespread endometriotic lesions put pressure on nerve trunks and endings, which leads to a variety of neurological disorders. Malignancy of degenerated foci of endometriosis is rare. According to scientists, women with endometriosis have a 50% higher risk of developing cancer than the statistical average.
Prevention of endometriosis
The sooner a woman consults a gynecologist when the first symptoms of endometriosis appear, the higher the chance of completely eliminating the need for surgical treatment. Attempts at self-therapy or delaying seeking help are completely unjustified: with the next menstrual cycle, new endometriosis lesions appear, cysts appear, cicatricial and adhesive processes intensify, and the condition of the fallopian tubes worsens.
To prevent endometriosis, it is necessary: examination of teenage girls and women with complaints of pain during menstruation; supervision of patients after abortions and other other manipulations on the uterus to eliminate possible consequences; timely and complete elimination of acute and chronic pathologies of the genitals; taking oral hormonal contraceptives.
The risk of endometriosis is higher in women who smoke after 30-35 years of age with a short menstrual cycle, suffering from metabolic disorders, obesity, and overweight; having intrauterine contraceptives; with increased levels of estrogen; those suffering from immunosuppression; having a hereditary predisposition and having undergone uterine surgery.
Additional recommendations
Nutrition after removal of appendicitis and gall bladder surgery requires special attention, since these organs are directly related to the digestive system. Daily diet after laparoscopy:
- first day. After recovery from anesthesia, only table water without gas is allowed in small portions. In the absence of a gag reflex and a feeling of nausea, after 6 hours you can drink weak chicken broth;
- second day. It is optimal to start your meal with low-fat yogurt (you can drink it). You can add vermicelli or noodles to the broth;
- the next 2–3 days involve the introduction of liquid mashed potatoes without oil, boiled fish, chopped boiled chicken in broth, porridge in water, soft cottage cheese, fruit puree;
- on days 4-5, the diet should be enriched with steamed or stewed vegetables. A little marshmallow and baked apples are allowed.
At the end of the week, the operated patient can switch to a full diet of foods from the recommended list of acceptable ones. To normalize the bowel movement process, boiled beets with prunes chopped in a blender are recommended for daily consumption. This salad should be topped with natural yogurt.