What is WBC indicator
WBC in a blood test is a value that provides a real opportunity to detect an inflammatory process, infectious disease or allergic reaction in time; sometimes it helps to notice neoplasms at the very beginning of their development.
This is one of the main values in a general blood test. Often, together with it, the amount of other blood cells and specific indicators is determined. General analysis is also called clinical analysis.
When conducting this study, the following is determined:
- The number of red blood cells (erythrocytes), abbreviated RBC.
- Hemoglobin concentration in a specified blood volume (HGB or Hb).
- Mean erythrocyte cell volume (MCV).
- The number of platelets, called platelets (PLT).
- White blood cell (WBC) count.
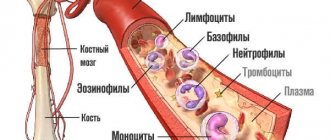
The figure describes the functions of WBC and their norm in a blood test.
Leukocytes are divided into 5 groups, and each of them is responsible for a specific job of neutralizing foreign bodies that have entered the blood. During the research, the quantity of each species is determined. In a cubic millimeter of blood under normal conditions there are from 6 to 8 thousand white blood cells.
Blood test for WBC: interpretation, norm in women, men and children
The main function of WBC cells, that is, leukocytes, is to protect the body from pathogenic microorganisms (viruses, bacteria, fungi), as well as foreign agents - cells and proteins. Therefore, WBC in a blood test is an indicator of inflammatory, infectious, allergic, and sometimes tumor processes. Main indications for its use:
- diseases of infectious and inflammatory nature;
- persistent increase in body temperature;
- frequent headache;
- persistent pain in bones and joints;
- suspicion of malignant diseases of the hematopoietic system;
- dysfunction of the immune system;
- monitoring the effectiveness of therapy.
WBC in the blood can be lowered against the background of long-term depressive states and fasting.
In most cases, a biochemical blood test is also prescribed at the same time as the general blood test.
Determining the amount of WBC in the blood has an important diagnostic value and allows a correct diagnosis to be made in a timely manner. Normally, in adults, both men and women, 1 liter of blood contains 4–8.8 x 10 9 white blood cells. In children, the number of white blood cells in the blood is higher, which is explained by the immaturity of their immune system. The leukocyte norm for children of different ages is presented in the table:
Leukocyte count, x109/l
Children of the first month of life
How and under what conditions are leukocytes produced?
Blood cells that recognize and eliminate foreign elements are called leukocytes. These are special elements of the immune system that are responsible for protecting against pathogenic bacteria and viruses, foreign bodies, any objects that can cause harm, and cleanse it of dead or damaged own cells.
The term “leukocytes” is formed from a combination of two words from the ancient Greek language: “leukos” (white) and “cytos” (receptacle, body).
There are several types of such cells:
- Neutrophils make up 55% of the total. Protection against bacterial and fungal infections depends on them.
- Basophils (0.5%) are scout cells; they find even single foreign elements. Their job is to increase blood flow, mobilize other cells to the site of inflammation, and fight allergens.
- Eosinophils (2.5%) are part of the innate immune system that protects against allergens, parasites, and helminths.
- Monocytes (5%) are responsible for the absorption of dangerous particles and dead cells.
- Lymphocytes (35%) support general immunity, store hereditary information, and regulate the functioning of other types of immune system elements.
White blood cells are produced by red (blood-forming) bone marrow. This organ is located in the internal cavities of the pelvic bones, sternum, and in the end sections of the tubular bones. It is also found inside the vertebrae, but in smaller quantities.
Hematopoietic bone marrow is the only source of cells called stem cells. Their main advantage is that they are close in structure to embryonic ones. The lifespan of leukocyte cells ranges from several hours to several years, depending on the type of leukocyte.
Some leukocytes capture and digest any foreign microorganisms and dead own cells, some produce antibodies that destroy all kinds of pathogens (disease-causing microorganisms) or accelerate blood flow to the necessary places. White blood cells are capable of accumulating hereditary memory, that is, “children” retain information about the threats that their “parents” had to face.
UAC - transcript: normal in adults
A general or complete blood count is a simple and common test. This is part of a routine health check. Depending on the requirements, a result outside the norm requires a more detailed analysis, and the patient needs to visit a hematologist.
Why is a general analysis prescribed:
- assess the general (basic) condition;
- diagnose obvious and subtle problems (for example, weakness, fever, redness, swelling, bleeding);
- monitor current medical conditions and evaluate treatment based on this test.
Most results are ready in a few hours/days.
WBC indicator table is normal
WBC in a blood test is a kind of description of the immune system in digital terms. Age has the greatest impact on white blood cell levels. In youth, the number of white blood cells in different sexes is almost the same.
Over time, the indicator decreases, as the effect of the immune system gradually deteriorates, and a difference appears in the number of leukocytes in women and men. On average, the leukocyte content is considered to be from 4 to 9.0 x 10 9/l.
| Age | Norm (x 10 9/l) | ||
| Children and teenagers | newborns | 5,5 — 12,5 | |
| up to 1 year | 6,0 — 12,0 | ||
| from 1 to 6 years | 5,0 — 12,0 | ||
| from 6 to 12 years | 4,5 — 10,0 | ||
| from 12 to 15 years | 4,3 – 9,5 | ||
| Adults | women | from 16 to 21 years old | 4,5-11,0 |
| approximately 40 to 60 years | 3,98-10,5 | ||
| over 60 years old | 3,7-9,0 | ||
| men | from 16 to 21 years old | 4,5-11,0 | |
| approximately 40 to 60 years | 4,2-9,0 | ||
| over 60 years old | 3,9-8,5 | ||
Causes of low WBC level in blood test
A decrease in the number of leukocytes in the blood below normal physiological values is called leukopenia. This condition usually indicates a decreased immune response. The reasons for its occurrence:
- immunosuppressive therapy;
- leukemia;
- hypoplastic anemia;
- viral infections (viral hepatitis, rubella, measles, influenza);
- systemic lupus erythematosus and other long-term systemic diseases;
- radiation sickness;
- chronic intoxication.
WBC in the blood can be lowered against the background of long-term depressive states and fasting.
Symptoms of high and low WBC
WBC in a blood test is a number that can be used to fairly accurately assess the functioning of the immune system and overall health. A high value, above the upper limit of normal, is called leukocytosis. This is a signal about inflammatory processes occurring in the body or a decrease in general immunity.
Leukocytosis is not necessarily associated with disease. An increase in the indicator may also depend on heavy physical activity or stress. A small jump also occurs after eating and in women during pregnancy.
Symptoms of leukocytosis:
- causeless fatigue, lethargy;
- temperature increase;
- bruises or hematomas even with minor bruises, and sometimes for no reason;
- pain in the limbs or abdomen;
- decreased appetite and weight loss;
- labored breathing.
A low level of white blood cells is called leukopenia. The danger of this condition is that it does not have pronounced symptoms. Signs of the disease in the initial stage are easily confused with ordinary fatigue.
At a later stage, the following are observed:
- high temperature, chills;
- accelerated pulse;
- causeless anxiety;
- headache;
- exhaustion of the body;
- pneumonia, blood infection.
Swelling of the glands, enlargement of the spleen or tonsils is also possible. If leukopenia develops as a result of taking medications, then the onset of symptoms is explosive.
Reasons for increasing and decreasing the WBC indicator
Leukocytosis is observed when:
- sepsis, purulent processes;
- acute inflammation;
- infections caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi or any other pathogens;
- malignant tumors;
- heart attack;
- various tissue injuries;
- in the last trimester of pregnancy;
- after childbirth, during breastfeeding;
- after vigorous physical activity.
A decrease in the WBC parameter can be caused by taking certain antibiotics, drugs from the sulfonamide group, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, drugs for epilepsy or to relieve spasms, and hormonal medications.
Leukopenia is observed when:
- hereditary pathologies that provoke underdevelopment of tissues or organs (bone marrow hypoplasia) or the absence of an organ or part thereof (aplasia);
- radiation sickness;
- damage to the bone marrow when taking certain medications or other chemical effects on the organ;
- acute intestinal infections (typhoid fever, paratyphoid fever and other types of typhus);
- viral infection;
- anaphylactic shock;
- metastases affecting the bone marrow;
- Addison-Beermer disease (pernicious anemia or malignant anemia);
- collagenosis (connective tissue pathology);
- myelofibrosis (excessive formation of connective tissue in the bone marrow, as a result of which its hematopoietic capacity decreases);
- dysfunction of the spleen, in which blood cells are removed too quickly, and a number of other diseases affecting hematopoiesis.
Leukopenia can only be diagnosed through laboratory tests. A decrease in WBC is a sign of an emerging or existing disease.
Complete blood count: WBC and leukocyte count
Most often, in a general blood test, WBC is determined with a leukocyte formula. There are five types of leukocytes that are examined in a blood test - neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, lymphocytes, monocytes. The leukocyte formula is the percentage of these types of leukocytes.
Neutrophils
The most numerous type of leukocytes, which plays a major role in providing immunity to the body. Normally, the content of neutrophils in the blood is 60–75% of all leukocytes in adults, and 30–65% in children aged 6 to 12 years. An increase in the level of neutrophils (neutrophilia) is observed in infectious diseases (pneumonia, bronchitis, intestinal infection, sinusitis, tonsillitis), arthritis, thyroiditis, peritonitis, pancreatitis, osteomyelitis, gangrene, phlegmon, abscess, cancerous tumors, uremia, diabetes, heart attacks.
A reduced level of neutrophils (neutropenia) may indicate certain infections (rubella, viral hepatitis, chickenpox, influenza, typhoid fever), acute leukemia, aplastic anemia, thyrotoxicosis.
Eosinophils
They take part in protecting the body from parasites and allergic reactions. The norm in the WBC blood test for eosinophils is 1–5% of the number of all types of leukocytes. The reasons for the increased content of this type of leukocytes in the blood are allergic reactions, parasitic infections (enterobiasis, ascariasis, giardiasis, echinococcosis, opisthorchiasis), malignant neoplasms, diseases of the hematopoietic system, scleroderma, periarteritis nodosa, rheumatoid arthritis.
A decrease in eosinophils is observed during sepsis, purulent processes, intoxication with heavy metals, and at the beginning of the development of inflammatory processes.
Lymphocytes
A special type of leukocyte, which is responsible for the formation of the body’s specific immunity. Interestingly, this type of leukocyte predominates in the blood of children under 4–6 years of age. And only after this age does a gradual predominance of neutrophils over lymphocytes occur. The normal content of lymphocytes in the blood of adults is 20–35%.
An increase in the level of lymphocytes in the blood may indicate the development of viral infections (influenza, parainfluenza, adenovirus), tuberculosis, thyrotoxicosis, bronchial asthma, childhood infections (scarlet fever, whooping cough, rubella, measles). A significant increase in lymphocytes occurs with lymphocytic leukemia, a tumor lesion of the bone marrow.
A decrease in the volume of leukocytes can be a symptom of bacterial diseases (pneumonia, sepsis), myocardial infarction, lymphoma, systemic lupus erythematosus, HIV infection.
Monocytes
Immature blood cells that turn into macrophages when they enter body tissues. Macrophages absorb pathogens, foreign microorganisms, and dead body cells. The interpretation of the WBC blood test indicates the normal level of monocytes - 4-10%. Monocytosis, or an increase in the content of monocytes, can occur with lymphogranulomatosis, lymphoma, some types of leukemia, subacute endocarditis, tuberculosis, sepsis, brucellosis, malaria, syphilis, mononucleosis, toxoplasmosis.
A reduced concentration of monocytes occurs with dysfunction or damage to the bone marrow, radiation sickness.
Basophils (mast cells)
A type of white blood cell that is responsible for the release of histamine (a hormone that provokes an allergic reaction in the body). Normally, the basophil content is 0–1%.
An increase in basophils in the blood may indicate allergic diseases, megakaryoblastic leukemia, chronic myeloid leukemia, systemic mastocytosis, some infections (influenza, chickenpox, tuberculosis), Hodgkin's disease.
A decrease in basophil levels is often a symptom of acute infection, hyperthyroidism, anaphylactic shock, and bronchial asthma.
Indications for WBC testing
WBC in a blood test is a value that is used to evaluate existing or potential health threats.
A blood test for leukocytes is prescribed in the following cases:
- suspected infection or inflammatory process;
- a prolonged increase in body temperature that does not subside;
- constant headaches, frequent discomfort in joints or bones;
- suspicion of impaired hematopoietic function;
- to monitor the treatment.
The appointment for the analysis is given by the attending physician. The first specialist to whom the patient turns should be a therapist. If necessary, this doctor prescribes laboratory tests or gives referrals to specialists. If the patient has a chronic disease, then you can immediately contact a specialized specialist.
Increased WBC in a blood test - what does it mean?
The condition when a patient has an increased level of leukocytes in the blood is called leukocytosis. Its detection does not always indicate the presence of any disease. In some cases, leukocytosis can be physiological in nature and occur during pregnancy, physical exertion, psycho-emotional stress, heavy food, overheating or hypothermia. That is why it is recommended to take a blood test for WBC in the morning, after a full night's rest and on an empty stomach.
A significant increase in WBC in the blood may indicate a number of diseases, most often caused by bacterial microflora:
- respiratory tract infections;
- otitis;
- sinusitis;
- tonsillitis;
- acute or chronic in the acute stage pancreatitis, cholecystitis;
- abscess, phlegmon;
- appendicitis;
- peritonitis;
- diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract (pyelonephritis, cystitis);
- gynecological infectious and inflammatory diseases (endometritis, adnexitis, pelvioperitonitis);
- purulent arthritis;
- osteomyelitis;
- sepsis.
In severe cases of the pathological process, immature forms of leukocytes begin to appear in the peripheral blood.
In most cases, an increase in WBC levels is combined with the appearance of symptoms of general intoxication, which include:
- general weakness;
- decreased appetite;
- headache;
- pain in muscles and joints;
- increase in body temperature.
Another cause of leukocytosis is malignant neoplasms. In the initial stages of cancer development, the patient's immune system tries to destroy it, which leads to an increase in the number of white blood cells in the blood. However, in the future, the body’s reserves are depleted, cancer intoxication increases, and metastases occur in the bone marrow. At this stage, the number of white blood cells in the blood decreases, and leukopenia occurs, a condition opposite to leukocytosis.
How is WBC determined?
The WBC indicator is calculated by examining venous or capillary blood during a clinical analysis. The essence of the study is to count white blood cells in a certain volume of biological fluid, taking into account their types. The ratio of all types of leukocytes, expressed as a percentage, is called the leukocyte formula.
In modern conditions, blood samples are most often processed using automatic equipment (hematology analyzers), but it is possible to carry out this study using a microscope. Automation is able to test samples simultaneously according to several parameters (from 5 to 24), and build histograms (graphical presentation of information) for red blood cells, platelets, and leukocytes.
Reasons for the decline
Among the factors of the fall are the following points.
Chemotherapy
Cytostatics are able to slow down the division of so-called fast cells. This includes both cancerous structures and standard cytological elements of immunity - leukocytes.
Once the correction is completed, everything will return to normal without outside help.
Genetic disorders
Congenital hematological abnormalities that the patient inherits. They occur quite often and are not subject to total treatment. It is possible to relieve only the symptoms.
Digestive tract diseases
For example. Stomach ulcers, gastritis and others. Those that are accompanied by bleeding. The body has to constantly synthesize additional shaped cells. This requires increased readiness of the body.
Anemia
Any type of pathological process. Accompanied by a decrease in the number of red blood cells, and then other formed cells.
The work of the bone marrow itself, which is responsible for the synthesis and maturation of leukocytes, is disrupted.
Long-term use of certain medications
Anti-inflammatory, non-steroidal drugs, hormones, also cytostatics, which were mentioned earlier. This also includes antibiotics.
The only way for total correction is to stop the medication.
Radiation sickness
As a result of damage to the body by radiation. A deviation occurs as a result of suppression of the bone marrow. Recovery is carried out strictly in a hospital. For a long time. You can wait many months for your condition to normalize.
The list is also far from complete. There are dozens of pathological processes involved. A condition in which white blood cells are lower than normal is called leukocytopenia.
This is an equally dangerous disorder that occurs frequently.
Preparing and conducting WBC analysis
The number of leukocytes is not a constant value; it depends on age, nutrition, time of day and state of health. To obtain the most accurate data, it is necessary to exclude the influence of food and drink, stress and medications on the blood composition. And even in this case, a blood test for WBC does not always provide enough information; this may require additional checks.
On the eve of blood sampling, it is necessary to refrain from fluoroscopy and physiological procedures. High mental load can also affect the result. If the patient is already receiving drug treatment, it is necessary to discuss with the doctor the temporary withdrawal of drugs or injections. When this is not possible, you should warn about the medications you are taking.
Rules for preparing for blood collection:
- limiting any load on the day before taking the test;
- sufficient night rest;
- refusal of alcohol both the day before and on the day of collection;
- stopping smoking before coming to the medical facility (it is advisable not to smoke from the very moment you wake up);
- fasting for 10-12 hours before taking the test;
- postpone breakfast or a morning cup of coffee until after donating blood, you can drink weak tea without sugar;
- Before entering the office, take a short rest (10 minutes) in order to calm down and even out your breathing.
Decoding the results of the analysis of the WBC indicator
Independent interpretation of research results by a non-specialist can only give a superficial idea of the state of health. This is enough for preliminary conclusions, but choosing medications and treatment regimens on your own is dangerous. The result of incorrectly deciphering the WBC indicator is the risk of erroneous self-medication, which can lead to very disastrous consequences.
When processing WBC values, the patient’s gender, age, as well as previous or existing diseases and medications taken should be taken into account. Understanding the overall picture of a person’s health can only be achieved with appropriate knowledge and experience. And even under such conditions, doctors often prescribe additional tests to clarify or clarify certain aspects of the patient’s condition.
At what WBC indicator should you consult a doctor?
The number of leukocytes under normal conditions fluctuates over a fairly wide range. It can increase during the day, after eating, with overheating or hypothermia, or physical activity. This is the so-called physiological leukocytosis, this condition does not require seeing a doctor.
In women, the normal limits are slightly expanded, since the WBC value is also influenced by hormonal levels.
However, if the indicator is above or below the limit established for the patient’s gender and age, then contacting a specialist is necessary. The first thing you should do is visit a therapist.
An increase in WBC is not a disease in the literal sense of the word, but only a signal of problems that have arisen. More information will be needed to make an accurate diagnosis. A careful survey and examination of the patient is necessary; additional studies are not excluded.
How to get your WBC back to normal
You can reduce the WBC level, if its increase is caused by an illness, with the help of medications. If the increase in the indicator is caused by physiological reasons, then over time the value will return to normal. The increase in the number of leukocytes occurs mainly due to diet. In this case, medications act only as an auxiliary tool.
It is impossible to raise the WBC value with medications alone. The diet should be prescribed and monitored by the attending physician. In general, it is recommended to increase the proportion of protein foods and foods rich in vitamins, especially ascorbic and folic acid. Meals with a high content of lysine and choline are also needed.
Medications
Medicines to reduce WBC are prescribed depending on the disease that caused leukocytosis:
- for inflammation, anti-inflammatory drugs;
- bacterial infections are treated with antibiotics;
- viruses respond to antiviral drugs;
- helminthiasis is treated with antiparasitic drugs;
- allergic reactions are stopped with antihistamines.
All medications have their contraindications and side effects, so only a doctor has the right to select medications and calculate a treatment regimen, based on the patient’s medical history.
Traditional methods
To increase the WBC level, the following compounds are used:
- Pollen. Mix two parts pollen with one part honey and leave for three days. Take a teaspoon with milk.
- Sweet clover infusion (cold). Add cold boiled water (2 cups) to two teaspoons of dried crushed herb, leave for four hours, strain. Drink a third of a glass 20-40 minutes before meals three times a day.
- Oat decoction. Pour unpeeled oats (2 tablespoons) with hot water (400 ml), boil for 15 minutes, strain. Drink half a glass three times a day for a month.
You can reduce your WBC using the following means:
- Infusion of linden inflorescences. Pour a tablespoon of flowers with hot water (200 ml), boil for five minutes over low heat. The daily dose is two to three glasses.
- Blackthorn berries. Pour a kilogram of berries with water (400 ml), mash. Leave for a day, sweeten to taste, and boil over low heat. Wait until the infusion cools, then strain. Take 50 g. before meals three times a day.
Other methods
The following will help you increase your WBC:
- fresh vegetables and berries, fruits, buckwheat, herbs, oats;
- seafood, red caviar, chicken eggs, nuts, dry red wine in small doses;
- increasing the proportion of fruits and vegetables that are red in color, pomegranate is especially recommended;
- Beetroot juice increases the level of leukocytes, perfect for the prevention of malignant tumors;
- the proportion of meat, liver and animal fats should be reduced.
Elevated WBC levels associated with obesity are corrected with a competent diet developed by specialists. Regular fasting is not considered a diet. Uncontrolled refusal of food can cause great harm to health.
Possible complications
Leukocytosis is not dangerous in itself, it is a kind of emergency signal from the body. However, an increase in leukocytes that is not associated with physiological reasons cannot be ignored, since the time to start treatment will be missed. This will significantly increase the risk of complications from the underlying disease.
A decrease in WBC level means a weakened immune system. The body becomes defenseless against any infections. And the lower the value, the more dangerous the disease becomes. Even ordinary hypothermia can give rise to a serious illness, provoke serious complications, and in critical conditions, death is not excluded.
Elevated or decreased WBC levels are not a disease. This is a signal indicating that a person has health problems. The WBC indicator in a blood test provides information about the state of immunity, the presence of inflammation or other diseases. To bring the blood composition back to normal, it is necessary to identify and treat the underlying disease.