The bladder is one of the important organs of the excretory system, and the coordinated work of the whole organism depends on the quality of its function. Therefore, at the slightest suspicion of abnormalities in activity, you should visit a urologist and get advice. As a rule, along with tests, examinations based on computer diagnostics are prescribed.
In cases where X-ray or computed tomography methods do not provide reliable results or do not provide enough information to make a final diagnosis, an MRI of the bladder is prescribed for clarification. Using its capabilities, it is easy for a doctor to differentiate many pathologies and prescribe appropriate therapy.
Diseases that are detected using tomography
MRI diagnoses pathologies of the genitourinary system of an inflammatory, destructive nature, developmental anomalies leading to dysfunction of organs.
Used to identify changes resulting from trauma and tumor processes. List of bladder diseases:
- benign neoplasms (papilloma, polyp, endometriosis);
- malignant neoplasia (transitional cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma);
- invasion of the bladder neck by tumor cells in men with prostate cancer;
- organ duplication, diverticulum, cervical contracture;
- traumatic rupture;
- urolithiasis disease;
- cystitis.
Muscle-invasive bladder tumor
Other indications for bladder examination
The operating principle of MRI is based on the operation of a magnetic field and receiving a response from body tissues, so after the procedure, high-quality images of soft tissues and hollow organs will be obtained. This diagnostic method will provide information about the condition of both the bladder itself and structures close to it.
In addition to suspicion of cancer, a tomography of the bladder is often performed in a woman complaining of signs of chronic cystitis, if there is no objective picture from ultrasound. It is recommended to perform the procedure for the following symptoms:
- Difficulty urinating
- Painful urination
- Change in color, smell, volume of urine
- Pain in the lower abdomen with exertion, at rest
Since such a clinic has a number of pathologies, tomography will help differentiate these diseases and make an accurate diagnosis. For example, diseases of the prostate and urethra in men also give a similar symptom complex, so an MRI will help refute or confirm the doctor’s fears.
When to choose MRI as an examination method
If, in the presence of complaints and clinical symptoms of diseases of the genitourinary organs, laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods have not yielded results to establish a diagnosis, an MRI is prescribed.
Tomography is indicated for enlarged and painful inguinal lymph nodes, suspicion of a tumor process, as a dynamic monitoring of inoperable formations and for deciding on treatment methods (conservative or surgical).
Indications for referral
Considering the information content of the study, it can be prescribed as a main or clarifying diagnosis. If there are problems with the urinary system, a woman may experience inflammation in the tract if the patient complains of symptoms of cystitis, and other studies have not given an accurate result.
Urinary diagnostics are also mandatory for men. The procedure is especially important for older people, when the body’s work rate drops, it is more difficult to remove sand that enters the body with water, and it is more difficult for the immune system to cope with inflammation.
The genitourinary system of a man and a woman, when infected, can prevent pregnancy. You can undergo the procedure during the planning stage along with an abdominal examination.
Symptoms for prescribing the procedure:
- frequency or suspicious infrequency of urination (profusely or sparingly);
- cramps, pain, burning in the urinary canal;
- internal pain, especially during exercise.
Such manifestations may indicate a number of diseases. And what the diagnostics shows allows us to determine the true source of the disease.
Indications for the use of contrast agents
MRI of the bladder using contrast based on gadolinium chelates helps to obtain images where contrast differences between normal and pathologically altered structures and tissues are clearly visible.
The standard dose of paramagnetic for an adult is 14-20 ml. Administration of the drug is indicated:
- if a tumor disease of malignant origin is suspected;
- for differential diagnosis with benign processes;
- to detect metastases and tumor growth from the bladder into surrounding tissues.
What pathologies are diagnosed?
This method is prescribed quite often, because MRI of the bladder shows many pathologies with different symptoms and stages that affect the normal functioning of the organ. The procedure reveals:
MRI of the pelvic organs with contrast
- benign and malignant processes in the bladder;
- congenital abnormalities in the development of the genitourinary system;
- various tissue pathologies;
- diseases of the lymphatic system (when studying the inguinal lymph nodes);
- the presence of concretions (stones), their location and size;
- hernias, diverticula, cervical sclerosis (Morion's disease).
In oncology, MRI is used to select surgical tactics or decide on radiation or chemotherapy. For patients who have already undergone a course of anticancer therapy, magnetic resonance examinations are periodically performed to assess the dynamics of the tumor or to prevent relapse. Due to the absence of radiation exposure in the study, MRI has become the best option for diagnosing cancer patients.
To identify tumors in the bladder, contrast enhancement is used, which can detect this pathology at the initial stages of development.
Preparation and completion of the study
Before examining the genitourinary system, patients undergo preparation to improve visualization of the organs.
To do this, 2 days before the procedure, a diet is prescribed, the purpose of which is to reduce gas formation and intestinal peristaltic activity.
Legumes, cabbage, baked goods, milk, and carbonated drinks are excluded from food products.
It is recommended to perform a cleansing enema the day before. 2 hours before the procedure, the patient drinks 1.5 liters of water and comes to the diagnosis with a full bladder.
Children under 7 years of age are given sedatives after consulting an anesthesiologist.
To undergo an MRI with contrast, the patient provides blood biochemistry results with determination of creatinine levels 3-7 days ago.
Contrast in the diagnosis of the bladder
Often, in order to be able to make final conclusions regarding the diagnosis, especially in cases of suspected oncological processes in the bladder, an MRI with contrast is prescribed. Since the bladder is a hollow organ, the use of a contrast agent will ensure the maximum degree of reliable results.
Of course, the diagnostic process will take a long time - it will take about an hour, the payment will also almost double, but the most accurate data will be obtained. For contrast, preparations made on the basis of gadolinium salts are used, which make it possible to track the difference between affected and healthy tissues of the body.
So, for example, the differences between neoplasms and healthy tissue are that the former have a more developed vascular network, and, therefore, when contrast is administered intravenously, they are stained faster and brighter. This helps to evaluate not only the presence of pathologies, but also their size, as well as clear boundaries. To detect cancer, MRI with contrast is an indispensable diagnostic tool.
How does the procedure work?
In the MRI room, an informed consent form is filled out before the examination. Then the x-ray technician removes metal objects (hearing aids, dentures, earrings) from the patient and helps him change into special disposable clothing.
The patient lies down on a movable table and a surface coil is applied to the area being examined.
An emergency bulb is placed in the hand in case the patient feels unwell and wants to interrupt the procedure.
Headphones are placed on the ears for sound insulation, since the operation of the device is accompanied by noise effects.
The study is consistently carried out in three projections: axial, sagittal, coronal.
If there are indications for the use of a contrast agent, catheters and infusion tubes are installed.
After contrast is administered, a series of scans are performed over 25-30 minutes, then the patient is removed from the table.
The doctor processes the data obtained, documents the images and draws up a conclusion.
Progress of the procedure
After the patient enters the office, he lies down on a mobile table. If the MRI is performed with contrast, a contrast agent is injected into the vein. Then the patient's hands are fixed, and the table is pushed into the MRI machine.
The machine then takes a series of pictures.
During the examination, a person may feel a pleasant warmth in the lower abdomen. There is no need to be afraid of this - this is absolutely normal. If any discomfort arises during the process, you must inform the doctor about this using the feedback system.
During the procedure, the patient will hear noise, which always accompanies the operation of the device. For this reason, he will be given special headphones before the procedure.
During the diagnosis, the patient is alone in the office, and the specialist sits in a nearby office at the computer. However, if the procedure is performed on a child, parents may be present in the office with him.
The duration of an MRI is 15-30 minutes. This depends on the need to administer contrast, as well as the severity of the problem.
After all activities are completed, the patient can go home, to work or for other matters. The diagnosis will not affect his well-being in any way.
In what cases is MRI contraindicated?
Patients whose bodies contain ferrimagnetic metal structures (prostheses, pins, wires, pacemakers, staples) are not allowed for diagnosis.
For women up to 20 weeks of pregnancy, MRI is performed strictly according to indications. Weight restrictions are provided for patients weighing 120-150 kg.
The procedure is not performed on patients in an excited state or under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
Patients suffering from claustrophobia are not allowed to study in closed-type devices.
How is the examination done?
In the absence of contraindications, the attending physician prescribes magnetic tomography with or without contrast. If you weigh more than 130 kg, it is recommended to choose a clinic with a high-field open apparatus. MRI of the pelvis and bladder is carried out in stages:
- Allergy test if a contrast examination is required.
- Filling the bladder: drink fluids (2 liters of still water) and avoid going to the toilet.
- The patient is placed on a sliding table, and the hips are secured with belts to immobilize them.
- The scan lasts 30-60 minutes, during which time the tomograph makes a lot of noise. The radiologist sits in the office, looking at the screen, taking pictures and initial measurements.
While in the control room, you can communicate with a specialist thanks to two-way communication. If you feel nauseous, dizzy, or have a panic attack, the procedure will be stopped. If a malignant tumor is detected in the bladder, additional examination of the pelvic organs is necessary.
Alternative diagnostic methods
If it is impossible to perform MRI, methods that have diagnostic value are used. These include:
- CT scan of the bladder provides a layer-by-layer picture of the walls of the organ and surrounding tissues. Detects formations and foreign bodies (instrumental diagnostics with increased radiation exposure).
- Ultrasound - evaluates the shape, thickness and contour of the walls, the presence of sand in the cavity and the level of residual urine.
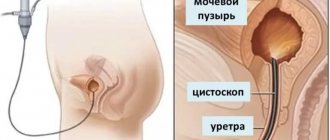
- Cystoscopy - the internal surface and contents of the organ are examined using an endoscopic apparatus. It is performed by introducing a catheter with a camera and a lighting system into the cavity of the bladder through the urethra.
- Cystography is the production of images on X-rays using contrast agents injected into the circulatory system or directly into an organ. Diagnoses stones, wall damage due to tuberculosis, and tumor process.
CT
What does a bladder tomography show?
The procedure performed can solve a number of problems, but the main thing is that it provides accurate information in real time. MRI of the kidneys and bladder shows:
- nephrological abnormalities present in the body from birth;
- bladder damage;
- benign or malignant tumors;
- cysts and other neoplasms of various nature;
- enlarged lymph nodes in the area below the abdomen;
- anomalies of the internal organs of the small pelvis;
- areas of bladder infection;
- inflammatory processes of the urinary tract;
- neoplasms in the genitourinary system.
Due to such an extensive list, not only a urologist, but also a nephrologist, oncologist, infectious disease specialist and even a venereologist can refer you for an MRI of the bladder. The only effective way is to carry out diagnostics in a specialized medical institution, with the direction of a doctor. An independent decision about the need for MRI can lead to negative consequences.
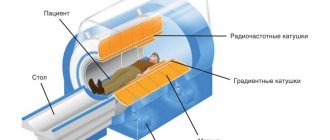
The principle of operation of the tomograph
Magnetic resonance imaging is a unique diagnostic method that provides maximum information in three-dimensional images, without causing any damage to the patient, without causing pain, and is also carried out without the use of radiation.
An MRI is performed using a special machine – a tomograph. But it is thanks to magnetic scanners that it is possible to obtain measurements in 3D format. Under the influence of radiation waves that are sent to the body of the subject by these devices, the smallest particles of hydrogen begin to move. With each new round of electromagnetic influence they vibrate again. This is recorded by the tomograph and reflected as a projection on the monitor of the diagnostic computer.
With the help of MRI images, it is easy to understand the condition of the soft tissues of the bladder, its circulatory system and neighboring organs, to see the extent of damage to the disease and its development.
How much does an MRI cost?
The price for MRI diagnostics of the bladder depends on the power of the machine used for the study, the qualifications of doctors and the use of contrast agent. The cost of the procedure is 4000-6000 rubles.
The contrast agent is paid separately, on average 2000 rubles for 1 bottle (10 ml).
The reliability of MRI in diagnosing bladder diseases is 85%, which shows its advantage compared to other types of research. The disadvantage of the technique is the duration of the procedure and high cost.
Survey area
In women, MRI allows you to examine the bladder, vagina, cervix and body of the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, blood vessels, lymph nodes, soft tissue of the pelvis, lower parts of the colon, part of the lumbar spine, sacrum and coccyx.
MRI of the genitourinary system helps to visualize almost all pelvic organs, and not just the system itself
When examining the pelvis in men, the following are visualized: the bladder, urethra, distal ureters, seminal vesicles and vas deferens, prostate gland, blood vessels (arteries and veins), lymph nodes, soft tissues, fiber, distal intestines and the lower segment of the spine ( part of the lumbar, sacral and coccygeal regions).