After the birth of a child, every mother is concerned about the state of his health. Various external pathologies can be noticed immediately, but most genetic diseases may not manifest themselves in any way in the first year of life. Therefore, a newborn screening test has been introduced in maternity hospitals, which can detect some congenital diseases in the first days of life. This will allow you to start therapeutic measures in time to fully recover, or at least slightly improve the child’s quality of life in the future. Let's take a closer look at what screening is, how it is carried out and what hereditary diseases it detects.
What it is
Screening (sifting) is a blood test that allows you to diagnose a certain congenital disease in a newborn. At the moment, this study is considered the most accurate. Such early diagnosis helps prevent the development of serious complications and disability.
Newborn screening has a popular name - the “heel test”, since blood is taken from the heel. This is the only way to obtain a sufficient volume of blood for testing.
A positive test does not indicate that the child has an identified genetic disease. He will be referred to a doctor for a more detailed examination.
How to prepare your baby for research
Preparation should not be neglected. The reliability of the analysis results depends on it. Newborn screening is usually done no earlier than 3 days after birth. It is recommended not to feed your baby breast milk or formula 2-3 hours before the heel test. This rule is not always followed. Therefore, there is no clear answer to the question of whether a child can eat before neonatal screening.
Rules for preparing for the first screening:
- do not feed;
- wash the leg with soap;
- The laboratory technician wipes the sampling site with a sterile alcohol swab and wipes it dry.
Is it possible to refuse analysis?
The mother may refuse to have her newborn screened. To do this, just write an application. This will not cause any trouble.
By refusing genetic research, the mother takes full responsibility for the health of her child. But before making such a decision, it is worth thinking several times and assessing the potential harm and benefits that such a refusal could bring.
Conducting genetic screening for a child is especially necessary if cases of congenital diseases have been diagnosed in the family, even in distant relatives. It often happens that healthy parents are carriers of defective genes that they can pass on to their children.
What does the study include?
Newborn screening is carried out in the first 4 weeks of the child’s life. It is a mass examination of children for the presence of congenital and hereditary pathologies, which have a severe course and seriously affect health. If treatment is not started on time, these diseases can lead to disability and even death of the child.
Screening research in the neonatal period is mandatory. The examination is carried out for all children without exception. Parents have the right to refuse to conduct it, but must be warned about the consequences of such a decision. In this case, they take responsibility only on themselves. A written refusal to carry out screening is issued.
Newborn examinations are carried out in the United States of America, Europe, and Russia. What is included varies slightly from country to country, but generally follows common patterns.
Newborn screening includes:
- audiological screening of newborns;
- detection of genetic diseases;
- conducting ultrasound examination;
- examination by narrow specialists.
When is the analysis performed?
Screening is done for a newborn in the first week after birth, depending on the circumstances. In full-term infants, blood is drawn onto a filter blank in the maternity hospital on the 3rd day of life, in premature infants - on the 7th day. It is not worth carrying out the test before this time, as there is a risk of obtaining a false negative or false positive result.
If the child was not born in a maternity hospital, but, for example, at home, or screening was not carried out for some reason, then you can donate blood at a clinic at your place of residence.
The need to adhere to early research in newborns is that some serious hereditary pathologies appear in the first month of life and require treatment.
Also, infants can undergo extended genetic screening using the TMS method, which includes the diagnosis of most pathologies. It is done after the age of 3 months. Blood is taken from a finger.
Why is it carried out?
Ultrasound screening of newborns is performed in the first month after birth. It includes an ultrasound examination of the newborn's brain and hip joints. Ultrasound of the brain can reveal congenital malformations of the nervous system or lesions during childbirth. Early treatment significantly improves the prognosis for the baby. A risk group for nervous system pathology are newborns who have experienced hypoxia or asphyxia during childbirth.
Ultrasound examination of the hip joints helps in diagnosing hip dislocation and hip dysplasia. The earlier treatment is started, the easier and shorter it can be. Early treatment of these diseases can avoid surgery, lameness and disability.
What hereditary diseases does it detect?
Mandatory newborn screening includes the following list of the most common pathologies:
- Cystic fibrosis (cystic fibrosis) is a systemic genetic disease that causes the formation of viscous mucus in the body, resulting in disruption of the respiratory system, liver, gastrointestinal tract, and exocrine glands. With early detection of cystic fibrosis, the risk of complications, disability and increased life expectancy can be significantly reduced. Occurs in 1 in 7,000 children.
- Hypothyroidism is a disease in which the thyroid gland produces insufficient thyroid hormones, which greatly impairs the development of all systems and organs of the child. In the absence of therapy, the nervous system begins to suffer first, which negatively affects mental development. The disease also leads to delays in physical development. If diagnosed early, hypothyroidism is highly treatable. Prevalence: 1 case in 5000.
- Phenylketonuria is a disorder of amino acid metabolism caused by insufficient production in the liver of certain enzymes that convert phenylalanine into the amino acid tyrosine. The consequences of the disease are severe - serious impairment of mental development, damage to the central nervous system. But they can be avoided if phenylketonuria is detected at an early stage. Treatment consists of following a special diet. Occurs in 1 baby out of 15,000.
- Adrenogenital syndrome is a violation of the production of the hormone cortisol by the adrenal cortex. The pathology manifests itself in a child as delayed sexual development, impaired growth (after 12 years it stops) and salt metabolism. It is impossible to cure the syndrome, but with the help of hormonal drugs it can be kept under control. Prevalence: 1 case in 10,000.
- Galactosemia is a disorder of carbohydrate metabolism, characterized by the absence of certain enzymes in the child’s body, which causes a failure in the breakdown of galactose (a substance supplied with milk). The disease is incurable, but its course can be alleviated. Early detection will help avoid severe complications (jaundice, organ damage, central nervous system) and even death. The basis of therapy is a specialized diet, which is followed for about 5 years. In severe cases, it will need to be followed for life. Drugs to improve metabolism, vitamins, and calcium are also prescribed. Prevalence: 1 case in 10,000-15,000.
The list includes these particular congenital pathologies, because with early diagnosis they can be cured, or the risk of developing possible severe consequences from them can be significantly reduced. But the number of diseases that this study can identify is much larger, and if desired, parents can conduct advanced screening for their newborn.
Neonatal screening of newborns: why is it needed and how is it carried out?
The main issue that concerns parents of a newborn baby is the health of the child. Many congenital diseases are insidious and do not manifest themselves in the first year of life. It is for this reason that a research method known as newborn screening was developed. This is a simple test that allows you to detect the presence of many congenital diseases in the first days of a child’s life.
What is newborn screening
Newborn screening is a blood test that allows for early diagnosis of at least 50 congenital diseases.
The method is the most accurate method for early diagnosis of genetically determined pathologies to date. According to WHO recommendations, newborn screening is included in the list of mandatory medical tests for babies. Note: In Russia, many mothers call newborn screening a “heel test,” since blood is taken from the baby’s heel.
You should know that a positive result does not always mean that the child actually has a particular disease. To be completely sure, parents will be given a referral for additional examination by an appropriate specialist.
When is neonatal screening performed in newborns?
This test is carried out in the first 10 days of a child's life, but the exact date may vary significantly depending on the circumstances.
Screening of newborns is not recommended in the first 2-3 days of life, since testing carried out so early carries the risk of error - the result may be false negative or false positive.
Usually, blood for analysis from babies born at term is taken in the maternity hospital on the 4th day of life. For premature babies, the test is performed on the 7th day. If the mother and baby have already been discharged from the maternity ward by this time, blood for screening is taken at home or in the clinic.
Such early timing of the analysis is explained by the fact that some genetically determined diseases manifest themselves in the very first weeks of life and it is extremely important to diagnose them in time in order to begin therapy. However, an expanded test that includes the diagnosis of more diseases can be performed later. Starting from the age of three months, blood for analysis is no longer taken from the heel, but from the finger.
What studies are included in the mandatory screening program for hereditary diseases?
Since there are a lot of diseases that can be detected through this study, the list of pathologies for mandatory screening has been reduced to the five most common:
- Hypothyroidism . Pathology of the thyroid gland, which can lead to delays in physical and mental development. Today, timely diagnosed hypothyroidism responds well to hormonal therapy. The prevalence of the disease is 1 case in 5 thousand.
- Androgenital syndrome . Pathology of the adrenal cortex, in which the normal production of the hormone cortisol is disrupted. It can manifest itself in the form of delayed development of the reproductive system, problems with blood vessels and the heart. This syndrome cannot be completely cured, but it can be kept under control with the help of hormonal therapy. The prevalence of the disease is 1 case in 15 thousand.
- Cystic fibrosis . The disease is manifested by a noticeable thickening of secretions in the digestive tract and lungs, which leads to damage to the liver, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory system and other organs. Treatable. The prevalence of the disease is 1 case in 3 thousand.
- Phenylketonuria . A disease characterized by impaired production of certain enzymes. The consequences are quite severe. First of all, these include lesions of the central nervous system. However, they can be avoided with a special diet. The prevalence of the disease is 1 case in 15 thousand.
- Galactosemia . This is the name given to the deficiency of the enzyme that breaks down galactose, one of the sugars found in lactose and other substances. The consequences of a lack of this enzyme appear after a few weeks of life. The child begins to develop jaundice, vomiting, and loss of appetite. Over time, severe liver pathologies develop, mental and physical development slows down, and vision deteriorates. This congenital pathology is dangerous and quite rare. Prevalence: 1 case in 30 thousand.
These diseases were also chosen because with early diagnosis they can be cured or at least significantly alleviate the consequences. However, the list of pathologies that can be determined by screening is much wider, and parents can conduct additional tests if desired. In some countries, newborn screening includes the diagnosis of more diseases, for example, in the USA - 40, and in Germany - 14.
How to prepare your baby for research
For the results to be as accurate as possible, blood should be donated on an empty stomach, 3 hours after the last feeding. The test is usually carried out at least 4 days after the start of breastfeeding. Preparing for newborn screening is very simple. Before taking blood, the child’s leg is washed with soap, wiped with alcohol and wiped dry with a sterile napkin - this is where the preparatory measures are limited.
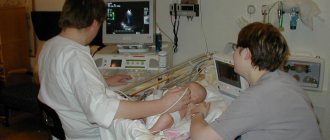
How is blood drawn?
This procedure is a fairly simple set of actions. A small puncture is made on the child's heel. The first drop of blood is removed with a sterile wipe. Then the nurse lightly squeezes the baby's heel and applies the resulting blood to a special paper test form so that the blood soaks through the porous paper. It contains all the information about the newborn, as well as about the institution where the blood was drawn. The form is dried at room temperature for 2–4 hours, placed in an envelope and sent to a laboratory or medical genetic center.
Interpretation of analysis results
It takes 10–14 days to process the samples, after which the parents receive a genetic examination report. The results can only be interpreted by a specialist. Remember that newborn screening results are not a diagnosis. An opinion can only be given by a doctor of the appropriate profile based on additional research.
Although newborn screening is quite accurate, it sometimes produces false-positive or false-negative results (most often due to improper blood sampling technique). If the test result is positive for any disease, parents are offered a repeat test. In case of a repeated positive result, the baby is sent for a detailed examination.
Useful information Most often, a false-positive result when screening newborns is given by a test for cystic fibrosis.
What is advanced neonatal genetic screening using TMS?
Despite the fact that the mandatory newborn screening program includes only five diseases, there are many more genetically determined diseases - about 500. Fortunately, most congenital pathologies are very rare. However, many conscious parents want to receive as complete information as possible about the child’s health and undergo extensive neonatal screening. It allows you to identify congenital metabolic disorders in the first weeks of a baby’s life.
This screening is carried out using tandem mass spectrometry (TMS) and makes it possible to test a child for 37 genetic diseases, including leucinosis, methylmalonic acidemia, biotinidase deficiency, argininemia and many other diseases. From the mandatory list, only phenylketonuria is included in such a study.
The technique for collecting blood for advanced screening is no different from the procedure for a routine study. Test results can be obtained in 2–3 weeks.
Expanded neonatal screening reveals changes in the concentration of metabolites in one direction or another, that is, increased or decreased levels of these substances may indicate the presence of a genetic disease. For example, in phenylketonuria, phenylalanine is increased.
As with mandatory screening, in case of serious deviations from the norm, the doctor refers the baby to specialists to conduct additional research and develop a treatment regimen if the diagnosis is confirmed.
Genetic screening of newborns is especially necessary if there have been cases of hereditary diseases in the family, albeit in the distant past. Quite often, healthy parents are still carriers of defective genes and can pass them on to their offspring. But even if no one in your family suffered from genetic diseases, such expanded screening of newborns is still worth doing, since the child still has a risk of having these pathologies.
How is blood drawn?
The nurse treats the baby's heel with cotton wool soaked in an alcohol solution. Then makes a puncture 1-2 mm deep. With light pressure movements, the blood begins to be squeezed out and applied to a special paper form. Moreover, she must thoroughly soak all 5 circles, each of which is responsible for a specific disease. On the form, the nurse indicates information about the child (height, weight, date of birth), mother (contact phone number, residential address) and maternity hospital (name, number). Then he goes to the laboratory.
Analysis processing takes place within two weeks. Parents are notified only if the result is positive. But this does not mean that a diagnosis has already been made. An opinion can only be given by a doctor after additional examination. Sometimes newborn screening shows a false positive result. This often happens due to a violation of the blood collection technique. Therefore, if the analysis reveals a genetic disease in a child, the pediatrician issues a referral to take the test again. If the result is again positive, then he is referred to an appointment with a geneticist or endocrinologist for a more detailed examination.
More often, a false-positive screening result comes for cystic fibrosis. But usually when the test is repeated, it is refuted.
How and when to receive test results
After blood collection, the neonatal screening form is sent to the medical genetic center. The test results will be ready in ten days. As a rule, they are sent to a pediatrician at the child’s place of residence, indicated when the test was taken.
A negative result means the absence of genetic pathologies. In this case, parents are not informed. If the standards for certain substances deviate significantly from the norm, parents are immediately notified. The possibility of the baby’s recovery depends on the delay. A questionable (or false positive) result often occurs for cystic fibrosis. Then repeated tests are done.
Only a specialist of the appropriate profile can decipher the screening results. When making a diagnosis, they are based not only on the findings, but also take into account other factors and the results of additional tests.
Are there false indicators in neonatal screening?
The reliability of the test results is high if the material was collected on time on an empty stomach. Failure to comply with these factors may cause errors – false positives.
If the result is positive, repeat testing will likely be ordered. Then a consultation with a geneticist will be required. He will give parents directions for additional examinations - DNA diagnostics, coprogram, blood test, sweat test.
False negative results are rare. Their danger is that the disease will be detected only after the first symptoms appear.
Enhanced Neonatal Screening
A conventional analysis can detect only 5 genetic pathologies, but there are many more of them, and, fortunately, they are rare. Some parents do paid advanced screening for their baby using tandem mass spectrometry (TMS) to get complete information about his health. The test can identify or exclude a genetic disease from among 37 possible ones.
Blood sampling for advanced analysis occurs in the same order as for normal analysis. The result will be known in 2-3 weeks. If at least one indicator deviates from the norm, the doctor will refer the baby for additional examination.
What to do if the result is positive?
Such complex diagnoses are not made based on screening alone. If the study shows the presence of a negative process in the body, the doctor will suggest you undergo a set of clarifying diagnostic measures, which will allow you to accurately determine the disease.
This can be either additional tests (CBC, dry blood spot analysis, coprogram, sweat test) or ultrasound. And a consultation with a geneticist is a must.
Any screening diagnosis is made only on the basis of at least two studies confirming its presence. And then the treatment begins - the more intense it is, the faster the positive dynamics will come.
Audiological screening
The examination is carried out in the maternity hospital for all newborns. It allows you to detect hearing aid dysfunction in the early stages in order to begin therapeutic measures in a timely manner. The procedure is painless and does not last long.
Audiological screening of a child is carried out on the 3rd day after birth and preferably during sleep. A highly sensitive microphone (acoustic probe) connected to a special device is inserted into the ear. The principle of its operation is the transmission of signals to the ear and registration of the reaction of hair cells to them. After a few minutes, the device screen will show whether the test passed or failed. A negative result does not constitute a diagnosis; additional examination will also be necessary.
Thanks to neonatal diagnostics, it is possible to detect a specific genetic disease in a newborn in the initial stages and begin treatment in a timely manner so that he can continue to grow, develop and live fully. Therefore, you should not refuse screening, because even healthy parents can be carriers of defective genes and can easily pass them on to their children.
Views:
5857.
Types of newborn screening
Newborn screening is a mass study that affects all children. At the request of parents, they can conduct additional tests for a fee.
Neonatal
Acne in newborns - what is it?
Neonatal screening allows early detection of congenital diseases, often leading to disability. To avoid dire consequences, treatment should be started as early as possible. The complete list of genetic abnormalities contains more than 500 items. The diseases selected for screening are the most common in the modern world and can significantly impair the quality of life. Diagnostic methods are simple and safe for the child. There will be no threat to his life and health after the blood collection procedure.
In addition, diagnosed diseases are treated, or there are medications that help maintain health so that the child will feel comfortable and develop fully.
Audiological
Thanks to audiological screening, you can:
- Determine hearing impairment and the presence of hearing loss;
- Use hearing aids. If a child is diagnosed with hearing loss, electrode hearing aids are prescribed;
- Carry out therapeutic measures for noticed deviations;
- Start working with an audiologist, which is recommended from the first years of life, in order to improve the child’s adaptation. Classes are necessary not only for the baby, but also for the parents.
Note! If a newborn has hearing problems, then action must be taken immediately. It has been proven that treatment carried out in the first six months of a baby’s life is most effective.
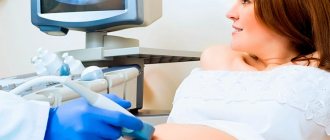
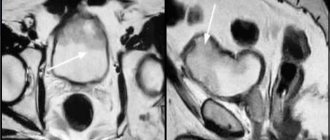
Ultrasound
Ultrasound of newborns includes several studies. During the procedure, the specialist examines:
- Brain. The procedure can be done until the fontanel is overgrown. Ultrasound waves will then be unable to be used for diagnosis. The condition of the brain, its parts, ventricles, their size and functioning is assessed. The procedure also allows you to determine the presence of hematomas, cysts and other formations, and study the functioning of blood vessels;
- Hip joints. The study is necessary for the early diagnosis of dysplasia. The disease causes dislocation of the hip or hip joint. The sooner the deviation is treated, the fewer consequences it will bring. In addition, the lack of rehabilitation procedures at an early age can lead to complications in adult life;
- Heart. As a result of the examination, the structural features of the organ, blood flow speed, and pressure are assessed. The procedure is especially necessary for children with a diagnosed defect in order to monitor changes in dynamics, and for children who had a heart murmur at a pediatrician’s appointment;
- Abdomen and kidneys. The doctor examines the liver, spleen, pancreas, and gall bladder. The size of organs and the condition of the mucous membrane are assessed.
Ultrasound is a painless procedure that does not take much time.
Ultrasound
The first days of a newborn
Every mother wants to know if her child is healthy. After birth, the baby is assessed by neonatologists and given an Apgar score.
Important! The scale includes 5 vital indicators of the baby’s condition. 8-10 points characterize a healthy baby. If the mark is below 8, then there are problems, perhaps gestosis in the mother caused fetal hypoxia. If the score is below 5, severe asphyxia is present.
The Apgar score includes assessment of:
- skin colors;
- presence of muscle reflexes;
- what kind of breathing does the child have;
- does the baby cry, and what kind of cry does it have?
- how the heart contracts.
There are 15 types of congenital reflexes in a newborn. The most basic ones that are monitored after birth are grasping and sucking, since they are responsible for the life and adaptation of the baby in the outside world. The grasping reflex speaks for itself - the baby tries to grab the adult’s fingers and tries to pull them.
Manifestation of the sucking reflex
As soon as the baby is born, it should be attached to the breast. The baby begins to stretch out his lips and look for his mother’s breast - this is the sucking reflex.
Tests in the maternity hospital for a newborn are carried out according to a specific protocol. If the baby is healthy, then he undergoes a major analysis to identify pathology. Other examinations, as a rule, are not done, since there are no indications for them.
Additional Information. The baby may have a blood type test to determine if hemolytic disease of the baby is present. If a suspicion of this disease is detected, blood is taken from the child's heel when newborns are screened to determine the amount of bilirubin. This test will tell you whether the mother can breastfeed her baby.
Many mothers ask why they take blood from the head of newborns. Such an examination will help identify the presence of genetic diseases.
Note! You can refuse tests. It is genetic disorders that manifest themselves not immediately after birth, but in the first or second year of life. At this point, complications may occur and the condition may be difficult to stabilize.
If a woman in labor has HIV, a blood test is also taken from the baby to detect this disease.
Mandatory tests
What vaccinations are given to newborns in the maternity hospital?
What mandatory tests are taken from a child at birth in the maternity hospital:
- Immediately after birth, blood is taken from the umbilical vein to detect HIV infection, syphilis, and hepatitis.
- If jaundice is detected, a liver transaminase test is performed.
- On days 2-3, anemia, insufficient thyroid function and phenylketonuria are detected.
- Blood samples are also taken to identify genetic pathologies, antibodies to cytomegalovirus, herpes, toxo- and mycoplasma, and chlamydia.
- Children who are at risk are subject to additional examinations: urine collection and additional blood testing.
It is important to carry out tests on the newborn to identify the presence of serious diseases in the infant.
Additionally, examinations are carried out:
- Check your hearing;
- Ultrasound examinations;
- Albucid is instilled into the eyes;
- Girls' genitals are also treated with Albucid.
Ultrasound of the heart of a baby
Vaccinations carried out in the maternity hospital include:
- BCG vaccination;
- vaccination against hepatitis C.
Personally, the doctor may prescribe a diet with glucose and an injection of vitamin K.