Survey
When your baby turns 1 month old, it’s time for you to check the baby’s health. The initial and main study is the diagnosis of the hip joint to identify dysplasia or congenital dislocation. Neurosonography (ultrasound of the brain) and ultrasound of the heart and internal organs (usually the abdominal organs) are also performed. Referrals for these procedures will be given to you by your pediatrician at the children's clinic.
Recently, to be on the safe side, many doctors send children for an ECG (study of cardiac biopatentials).
In addition to the ultrasound examination, the baby must also be shown to a neurologist, pediatric surgeon and orthopedic traumatologist. Other doctors are seen only as needed, which is considered on a case-by-case basis. But most often the child is also examined per month by an ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist and cardiologist.
During the examination, it is advisable to approach specialized specialists with the results, so that each of them acquaints you with the norms of ultrasound of a newborn at 1 month.
Features of preparing and carrying out the procedure in a child
No special preparation is required for the examination. You need to pay attention to the following points:
- A cardiac echo is performed in a calm state, with a normal heart rate, since when they increase, the parameters of cardiac activity also change, which will complicate the diagnosis. Therefore, it is advisable that the child does not undergo physical activity before the study, and also does not cry and lies quietly during it.
- It is advisable to come to the examination with a fresh (done more than a month before) electrocardiogram. This will help the doctor to suggest possible problem areas in the organ and pay close attention to them during the procedure.
- If the hospital does not have disposable supplies (sheets, napkins), then you need to take a towel with you to lay it on the couch, and then wipe off the remaining gel applied to the skin.
- For children under three years of age, ultrasound is performed with special children's sensors. Therefore, before performing the procedure, it is necessary to find out their presence from the doctor.
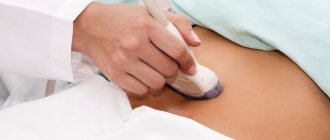
During echocardiography, the child lies on the couch.
Immediately before the examination, a special gel is applied to the skin of the chest in the area where the heart is projected. Its functions are to reduce the layer of air between the sensor and the surface of the chest and ensure free movement of the scanner over the skin. Different parts of the heart are better visualized in different body positions. Therefore, during the examination, the doctor may ask you to lie on your left side, on your stomach, and hold your breath while inhaling or exhaling. Ultrasound diagnostics is absolutely safe and painless; the only thing the child will feel is a slight tickle. The duration of the examination ranges from 10 minutes to half an hour.
Importance of the procedure
The first year of a child’s life is the most crucial in all development. It is at this time that all the baby’s organs and systems develop and improve. And if this development goes wrong from the very beginning, then it will be much more difficult to correct it, and in some cases even impossible. The sooner a violation is identified and correction is started, the greater the chances of quickly getting rid of the defect or disease without unpleasant consequences.
Therefore, it is in the first year of a baby’s life that all vital organs need to be examined and unpleasant diagnoses excluded. For this purpose, an ultrasound examination (ultrasound) is performed. It is usually carried out in conjunction with other tests.
Ultrasound of a newborn at 1 month allows you to show how the child has adapted to the external conditions of existence and identify hidden diseases. After all, some anomalies can arise even before the birth of a child, and some during labor.
The prevalence of ultrasound of a child aged 1 month is explained by the fact that this procedure is the safest for such a small person.
Echo CG of a child’s heart – what is it?
Echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart) is a study of the functioning of an organ in real time, allowing one to determine both the static characteristics of the heart (size, wall thickness, condition of the myocardium and valves) and dynamic (the volume of blood ejected during contraction, the direction of blood flow, valve function) . Knowledge of these parameters allows you to assess the state of the child’s cardiovascular system with minimal time and effort.
During the Echo CG process, the scanner receives information from the organ in three different modes:
- Standard two-dimensional B-mode. This makes it possible to assess the size of the parts of the heart, the thickness of their walls, the functioning of the valves, and myocardial contractility.
- Color Doppler mode. It allows you to evaluate cardiac hemodynamic parameters and blood flow in the heart without invasive intervention.
- One-dimensional M-mode. The method displays organ contractions and valve function in the form of a graphic curve on the device monitor. Used as an auxiliary study to assess ventricular contractile function and valve movement.
Ultrasound of the brain
At 1 month, girls and boys are recommended to undergo a brain examination. It is called neurosonography. It is carried out through the fontanelles - areas of the skull between the bones, covered with connective tissue. They are the ones capable of transmitting ultrasonic waves. Most often, the large fontanelle, which is located on the top of the child’s head, is involved. Even parents can see it with the naked eye.
All brain structures must be symmetrical, excluding the appearance of neoplasms and changes in structure. The specialist pays special attention to the cerebral hemispheres and ventricles.
The ventricles are cavities in the brain that communicate with each other and the spinal cord. They contain cerebrospinal fluid, which nourishes the brain and protects it from damage.
Thanks to ultrasound, the development of the following diseases can be detected in the early stages:
- cysts (areas with fluid);
- hydrocephalus (dropsy of the brain, increased amount of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles of the brain);
- intracranial hemorrhages;
- ischemic lesions (consequences of hypoxia);
- congenital developmental anomalies.
Three trips to the ultrasound
The foundations of a child’s health are laid at a very early age. Therefore, infants need special attention from parents and regular medical supervision. The most effective diagnostic procedures include ultrasound examination.
Today it is impossible to imagine qualified medical monitoring of a baby’s development without the use of ultrasound examination. Ultrasound methods make it possible to assess the anatomical structure and condition of the brain, kidneys, liver, spleen, pancreas, heart and hip joints of small children, and allow the identification of congenital malformations.
I would like to emphasize that ultrasound examinations are additional methods in medical examination and should be prescribed by the doctor monitoring the child. But among the many ultrasound techniques, there are several studies that it is advisable for all infants to undergo. Thus, in the first 3 months of life, it is advisable for all infants to undergo an ultrasound scan of the brain, kidneys and hip joints.
The fact is that structural changes in the brain, kidneys, and hip joints do not always have clear clinical manifestations, that is, symptoms that parents and doctors can notice, and ultrasound diagnostics helps to identify pathology in the early stages and begin timely treatment. Other ultrasound examinations should be carried out strictly as prescribed by the attending physician to exclude or confirm the suspected diagnosis. As for voluntary health insurance, different contract systems include different numbers of ultrasound scans.
Neurosonography
The method of ultrasound examination of the brain in young children is called neurosonography.
This study allows you to evaluate the anatomical structure of the brain, the state of the brain matter and the spaces containing cerebrospinal fluid. Neurosonography can reveal malformations of the brain, brain lesions resulting from complicated pregnancy and childbirth, inflammatory changes. The method makes it possible to assume the presence of hydrocephalus.
Hydrocephalus (dropsy of the brain) is characterized by an increase in the amount of cerebrospinal fluid in the intracranial space, which in different children can increase, decrease or remain unchanged over time. Excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid most often occurs as a complication after inflammatory, traumatic, ischemic (as a result of insufficient blood supply) brain lesions and hemorrhages and can lead to increased intracranial pressure with subsequent changes in the brain substance.
It is especially unfavorable if the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in a child increases. Pediatric neurosonography is recommended for all young children, but it is especially important for premature babies and children born after difficult births. Neurosonography performed at an early age makes it possible to assess the impact of complications during pregnancy and childbirth on the condition of the child’s brain, and to select appropriate treatment. With timely treatment, it is possible to completely restore the structure and function of the central nervous system, but if treatment is started late, the likelihood of developing various complications increases.
An ultrasound of the brain is performed through the large fontanel, an area of the child’s skull consisting of cartilaginous tissue. Cartilage protects the brain from mechanical impact, but does not interfere with the passage of ultrasound waves, which allows for detailed images of intracranial structures. As a rule, by the age of 1 year the large fontanel closes, as the cartilage tissue is replaced by bone. After the fontanel is closed, neurosonography becomes impossible, and neurologists prescribe other diagnostic tests to assess the condition of intracranial structures.
Neurosonography does not require special preparation of the child and can be performed both during sleep and while awake in the presence of parents. It is advisable that the first study be carried out at the age of 1-3 months. If no pathology was detected during the first neurosonography, then this study does not need to be repeated without the appointment of a neurologist. If any deviations from the norm were detected, then a repeat study is recommended after 1-2 months.
If necessary, standard neurosonography can be supplemented with Doppler ultrasound, which allows one to assess the state of cerebral blood flow in a child. Doppler ultrasound is a complex modern technique that must be performed at rest. Crying, anxiety and motor activity of a child significantly change the state of cerebral circulation and distort the data obtained. Since young children cannot lie still for a long time, the use of this painstaking method must be strictly justified by a neurologist.
Is ultrasound harmful?
Parents often ask: is ultrasound harmful, how often can ultrasound be performed, is it possible to perform several ultrasound examinations on a child in one day? Most likely, parents' anxiety is caused by information about the side effects that can be caused by excessive radiation exposure during frequent X-ray and radioisotope examinations. Therefore, it is important to emphasize that ultrasound diagnostics is based on the physical properties of the ultrasound wave, and not on penetrating radiation. The ultrasound wave does not have any negative effects on the child’s body, therefore ultrasound examinations can be used from the first hours of the child’s life and, if necessary, are carried out for children already in the maternity hospital. Ultrasound diagnostics is widely used in hospital settings and is used to monitor children in clinics. Ultrasound can be repeated as often as the condition of a given child requires, and the number of studies performed in one day is not limited.
Ultrasound of the hip joints
Ultrasound examination of the hip joints is recommended for all infants aged 1-3 months. This test allows you to diagnose underdevelopment of the hip joints, which is called dysplasia. Structural changes in underdevelopment of the hip joints can be expressed to varying degrees; the most severe form of dysplasia is congenital hip dislocation.
Treatment for different degrees of hip dysplasia differs, but in any case, the sooner a disorder in the development of the joint is identified and treatment is started, the better the results. Even such a severe disorder of joint development as congenital dislocation, detected at an early age, can be successfully treated conservatively.
With late diagnosis of dislocation and subluxation of the hip joint, surgical treatment may be required, and untreated dysplasia can further lead to lameness and poor posture in the child. Therefore, you should not postpone ultrasound examination of the hip joints until the second half of the child’s life, especially since by 10-12 months this examination generally becomes uninformative, since it is difficult to place children at this age in the standard position required for examination, and the subcutaneous the fatty layer makes it difficult to examine the joint structures in detail.
Ultrasound of the hip joints also does not require special preparation for the child. If joint pathology is not detected, then the study does not need to be repeated. In case of dysplastic changes in the hip joints, repeated studies are carried out after 1-1.5 months.
Kidney ultrasound
Ultrasound examination of the kidneys is carried out to identify various malformations of the urinary system, which account for approximately 35-40% of all malformations in children. Various developmental anomalies of the urinary system have different clinical and prognostic significance and can be asymptomatic for a long time. Timely detection of kidney malformations and regular monitoring of the child allows you to choose the right treatment tactics and avoid complications such as secondary infection and decreased kidney function. In addition, an ultrasound examination is carried out if inflammatory kidney damage is suspected, which often occurs in children in the first years of life. But here it is important to consider that inflammatory kidney diseases (pyelonephritis and pyelitis) may not have a clear, specific ultrasound picture. In clinical practice, there are cases of discrepancy between clinical symptoms and ultrasound signs.
An ultrasound examination of the kidneys is performed without prior preparation of the child. When detecting renal malformations, Doppler ultrasound examination of renal blood flow can provide important additional information.
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs
Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs in children is performed to evaluate the size and structure of the liver, spleen, pancreas, as well as the shape and lumen of the gallbladder.
To correctly assess the condition of the pancreas and gallbladder, an ultrasound of the abdominal organs should be performed on an empty stomach, that is, at least 3-3.5 hours should pass between the examination and the child’s last feeding, provided that the child received milk or formula. This requirement is due to the fact that, according to modern concepts, breast milk is digested in the stomach for 3 hours, and formula milk for 3.5 hours. Until the digestion process in the stomach is completed, the functional state of the organs changes: the gallbladder contracts and cannot be assessed, and increased blood flow to the pancreas can lead to an increase in its size. In addition, the food contained in the stomach makes it difficult to obtain an image of the pancreas and evaluate its true size and structure.
Porridges, vegetable and fruit purees take longer to digest in the stomach than dairy products, so they should not be given to children before the test. If it is difficult for a child to maintain the required interval, you can give him plain drinking water. Sweetened water and various teas in this situation are equivalent to feeding and should not be given.
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs often reveals changes in the size and structure of the pancreas in infants, that is, signs of reactive pancreatitis. Reactive pancreatitis is called nonspecific changes in the pancreas, which can occur in many pathological conditions, for example, against the background of dysbiosis (disturbance of the intestinal bacterial flora), allergies, or after an infectious disease.
Reactive pancreatitis is a reversible condition. With timely treatment of the conditions that caused it, the structure of the pancreas is completely restored, but if the cause of reactive pancreatitis cannot be eliminated in time, it can become chronic. The decision on the need for an ultrasound of the abdominal organs and the timing of its implementation is made by the doctor monitoring the child.
Other studies
Modern ultrasound examination of the heart is performed for children in the first year of life only if a congenital heart defect is suspected.
The study includes echocardiography and Dopplercardiography. It allows you to determine the size of the heart chambers, the integrity of the interatrial and interventricular septa and evaluate the work of the heart muscle. Crying and restlessness of young children significantly complicate this study and reduce its diagnostic value.
Ultrasound examination of the thymus gland is prescribed for suspected enlargement of the thymus gland - thymomegaly, as well as for various disorders of the immune system and for frequently ill children to determine the volume and structural changes of the gland.
Ultrasound examination of the inguinal-scrotal area in children of the first year of life is carried out if an inguinal hernia, cryptorchidism and hydrocele of the testicular membranes are suspected. These conditions occur when the process of movement of the testicles in the fetus is disrupted during its intrauterine development. The fact is that in the early stages of development, the testicles form next to the kidneys. As the fetus grows and develops, the testicles move from the lumbar region through the inguinal canal into the scrotal cavity, carrying with them the underlying peritoneum and forming a process of the peritoneum, which should then stick together (obliterate). If the process of the peritoneum remains open and communicates with the abdominal cavity, then sections of the intestine or greater omentum can penetrate into its lumen, forming an inguinal hernia.
Incomplete obliteration of the peritoneal process leads to the formation of hydrocele of the testicular membranes (accumulation of serous fluid under the testicular membranes). Hydrocele of the testicular membranes in children in the first months of life is a physiological phenomenon. As a rule, it disappears on its own by 1 year. The exception is acute cases of intense dropsy, requiring surgical intervention.
Violation of the mechanisms of testicular movement can lead to its incorrect position - cryptorchidism . Most often, the testicle is retained in the inguinal canal (inguinal form of cryptorchidism), less often in the retroperitoneal space (abdominal form of cryptorchidism). False cryptorchidism is identified as a borderline state between normality and pathology if the testicle is easily removed from the inguinal canal into the scrotum. False cryptorchidism does not require treatment. In cryptorchidism, ultrasound allows one to determine the form of the disease and the condition of the testicular parenchyma, which is very important for choosing treatment tactics.
Currently, ultrasound diagnostics is widely used in pediatrics; it helps to start treatment at an early stage and avoid many complications. Dear parents, take care of the health of your children, and we, in turn, will do everything to help you with this!
Ultrasound of the heart
An ultrasound of a newborn at 1 month also includes a heart examination. While the baby is in the womb, his heart works slightly differently than that of an adult. Since the fetus's lungs are inoperative, it receives oxygen from the mother's blood. This affects the structure and function of the child’s heart.
In the structure of the fetal heart there is an additional hole, which is called the oval window. A few days after the baby is born, this hole should close up. An ultrasound shows whether this process has occurred. If this does not happen, then this is an indication for registering the child with a cardiologist.
In addition, ultrasound will help identify other developmental defects that cannot be detected by other methods.
An ultrasound scan at 1 month in boys and girls can already reveal some differences in the functioning of the heart. It is known that girls have a faster and more intense heartbeat than boys.
Ultrasound of the hip joints
This examination is carried out to exclude hip dysplasia. In this case, the bones that participate in the formation of the joint are formed abnormally, thereby forming a subluxation or dislocation of the joint.
Most often, this pathology occurs in girls (approximately 1-3% of newborns). Your pediatrician can point out the first signs of the disease. A child's legs may vary in length or the folds on the legs may be asymmetrical.
It is in this situation that early diagnosis is crucial. After all, late detection of the disease complicates its treatment and minimizes the chances of a successful recovery.
Various orthopedic devices, gymnastics, physiotherapy and massage are prescribed as treatment for dysplasia.
Kidney ultrasound
Not included in the number of mandatory examinations in 1 month. When visiting doctors at the clinic at one month of age, the pediatrician prescribes a urine test. If no impurities or pathologies are found, then a kidney examination is not necessary.
However, despite this, kidney disease in newborns is quite common. Approximately 5% of children are at risk. The most common disease is pyeloectasia - dilation of the renal pelvis.
If your child has any changes in kidney function, do not be upset ahead of time. Very often everything returns to normal on its own, you just need increased attention to the baby’s genitourinary system.
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs
The list of ultrasound examinations of a newborn at 1 month also includes an examination of the abdominal cavity organs. The liver, pancreas, gall and bladder, kidneys, and spleen are examined. All these organs play an important role in a child’s life, so their diagnosis is also necessary.
Your pediatrician will tell you where to do an ultrasound of a newborn at 1 month. Some even cooperate with private clinics, and therefore can give you a referral to a specific institution. However, the choice of where to undergo the examination is still yours, because it is your child.
It is recommended to carry out the BBP examination 1.5-3 hours after feeding the baby. Otherwise, the specialist will be disturbed by gases in the intestines.
Features of the study of the urinary tract
Preventive ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder is performed in the first month of a child’s life. But if doctors suspect any disease, they prescribe additional research.
Indications for ultrasound of the kidneys are congenital abnormalities of organs, as well as acquired disorders - problems with urination, poor test results, swelling, pain in the lumbar region, genetic predisposition, consequences of injuries.
Using ultrasound, you can draw conclusions about the functionality of the child’s urinary system, its structure and location of organs.
Preparation for the study involves accumulating a strategic supply of fluid in the bladder.
It is not always possible to control the moment of urination in babies, so mothers need to have a bottle of water with them to give their baby something to drink if necessary.
In some cases, a child may drink juice or a sweet drink, with the exception of soda.
Timely detected developmental anomalies and diseases are much easier not only to diagnose, but also to correct with medication, even if it is not possible to eliminate them completely. For a sick child, this is the best way to improve the quality of life.
Ultrasound examination allows you to assess the condition of internal organs and structures and draw conclusions about their functioning. This diagnostic method is used quite often for adults
Sometimes doctors prescribe this type of examination for children. Then parents have a question whether ultrasound is harmful for the child.
Preparing for the examination
Having learned that the child is undergoing a routine examination, parents may be interested in how to prepare for an ultrasound of the newborn at 1 month. Preparing for the examination depends on what kind of ultrasound you are doing.
For example, ultrasound of the fontanelle, which is included in neurosonography (ultrasound of the brain), is performed without preparation. In addition, there are also no contraindications for this, whatever the child’s condition.
No preparation is required to perform an ultrasound of the hip joints. The result is not affected by the time of feeding, the amount of food, or its components.
But an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is performed only after preliminary preparation. To do this, you need to feed the baby and wait 3 hours. That is, it turns out that the examination is carried out on an empty stomach.
If the child is breastfed, then on the day of the examination the mother must exclude from her diet those foods that can increase gas formation in the baby (soda, cabbage, legumes).
There is no need to cleanse the intestines artificially (that is, give the child an enema). This is only permissible when diagnosing children over 3 years of age.
The effect of ultrasound on the body?
Ultrasound is a type of diagnosis that is performed using special ultrasound equipment. Ultrasound is a high frequency sound wave - 260-600 kHz. It spreads in solid materials, gaseous and liquid media.
It is not perceived by the hearing aid and does not cause any discomfort. It should be noted that the biological effect of ultrasound on the body has not yet been fully studied.
It is believed that it is based on local pressures that are formed in tissues, on a local thermal effect caused by the absorption of energy that occurs when vibrations are suppressed.
It has been revealed that ultrasound stimulates blood circulation, reflex nervous activity, and metabolic processes. With prolonged and intense exposure, cell destruction is possible. But when performing an ultrasound, the exposure to ultrasound is short and safe.
The harm of ultrasound diagnostics has been studied by many doctors. Ultrasound waves pass through tissue during the examination and are then reflected back. This allows you to safely assess the condition of the organ. To carry out such a diagnosis, no special preparation is required.
Harm of ultrasound for a baby
Ultrasound of a newborn at 1 month is certainly a very important and necessary procedure. However, the question arises: “Will the research harm the child?” Parents' concerns are understandable. After all, everyone has heard about the consequences of radiation exposure on the body, so I want to reassure caring parents.
Ultrasound examination is based on the properties of the ultrasonic wave. There is no penetrating influence of radiation in this procedure. Consequently, there is no harm to the baby’s health. That is why this type of diagnosis is used to examine young children from the first minutes of life.
Our grandparents, mothers and fathers argue that frequent examinations during pregnancy can harm the child. We can confidently assure parents, and in particular expectant mothers, that ultrasound during pregnancy can be done without fear for the condition of the fetus. The frequency of ultrasounds does not affect the health of your unborn baby.
Already in the maternity hospital, your child can be examined using ultrasound diagnostics. Since we have found that ultrasound does not cause harm, an unlimited number of examinations can be performed on a child in one day. On the contrary, it will be less painful and unpleasant for a small person if all the necessary ultrasounds are performed at one time, without stretching it out over several appointments.
What's the benefit?
Ultrasound is a unique diagnostic tool; it brings invaluable benefits for monitoring the fetus during pregnancy, and also allows you to monitor its intrauterine development.
Using ultrasound, you can determine the condition and vital functions of the fetus, as well as diagnose its possible death in the early stages. Using an ultrasound, you can find out the sex of the unborn child, determine the number of fetuses and the approximate gestational age, and this, in turn, allows the mother to more carefully prepare for the process of childbirth and the birth of the baby, because even the exact date of birth of the baby can be established. Ultrasound also helps in assessing amniotic fluid and the condition of the placenta.
Naturally, the emotional component cannot be ignored, because the benefit of ultrasound also lies in the fact that future parents have a real opportunity to look at their baby even before his birth, as well as hear the beating of his little heart.
When a baby is born, ultrasound also brings great benefits in the diagnosis of many pathologies and diseases, which makes it possible to prescribe effective, timely treatment.