What will an MRI of the eye orbits show?
Magnetic resonance imaging of the orbits is a study that produces highly accurate results.
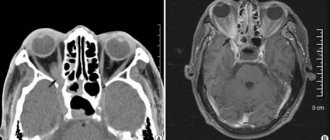
It has been successfully used to study and visualize in photographs the components and tissues of human eye sockets.
These components include:
- eyeball (consists of the lens and vitreous body, has several membranes);
- blood vessels (these are retinal veins and the central artery);
- optic nerve;
- adipose tissue of the orbit;
- lacrimal glands.
Scanning makes it possible to determine pathological changes occurring in the eyes and their motor systems. This is facilitated by the capabilities of the tomograph, which help to obtain images of the examined area in several projections at once. The range of diseases detected using this method varies from simple inflammatory processes to the penetration of foreign objects into the retrobulbar space (the space between the apple of the eye and the bone of the orbit).
In medicine, tomographic scanning is used after the usual methods of identifying diseases of the visual apparatus have failed. The MR method, due to its accuracy, will determine such ophthalmological problems as changes in the tissues of the eye apparatus, injury, blockage of blood vessels by a blood clot, tumors and the degree of their progression. It will help to identify the cause of decreased visual acuity, increased intraocular pressure, and impaired mobility of the apple.
Our center will help you undergo MRI of the orbits. By calling us you can sign up for the procedure at a time that suits you. In addition, we also perform MRI of the orbits with contrast. In terms of price, it will be slightly more expensive. Our operators will advise you on the cost of the examination and its progress.
What the pictures show
MRI of the orbits makes it possible to obtain a clear three-dimensional image of this organ. With its help, you can examine ocular structures such as nerves, blood vessels, and fatty tissue. The results of the examination reveal:
- at what stage is the inflammatory process and what area does it occupy;
- size, location and nature of the tumor, as well as the location of metastases;
- areas with hemorrhage or poor circulation;
- places of thrombus formation;
- which components were damaged when the organ was injured;
- integrity and homogeneity of structures or their violation;
- the state of the optic nerve, on which the transmission of information to the brain depends;
- various pathologies of the eyeball, including infectious diseases;
- optic nerve atrophy;
- what stage the disease is at.
If the information obtained is sufficient to make a diagnosis, then additional diagnostics are not required. The doctor analyzes the received images and prescribes treatment.
Using MRI, it is possible to detect diseases of any nature - traumatic, bacterial, autoimmune. This method also makes it possible to identify pathologies that are not associated with abnormalities in the organ of vision, but affect their functioning.
Why do an MRI of the eye orbits?
Although diagnostics in ophthalmology is used less often than other ways to find out the root cause of the disease, it has direct indications for use:
- suspected neoplasms in the eyeball (benign or malignant; if an oncological tumor is suspected, then scanning will determine the presence of metastasis to nearby organs and structures);
- strong intensity of pain in the eyes (both in a calm state and when trying to look around, can be accompanied by headaches);
- loss or impairment of visual functions without a known cause (when the pathology that caused them was not detected by other diagnostic methods);
- to confirm alleged violations.
Rare cases of prescribing MRI of the eye orbits:
- when other ophthalmological examination methods are prohibited for the patient or it is not possible to carry them out in the near future;
- intraocular bleeding (due to injury or aneurysm, can be in the vitreous body, the anterior chamber of the eye, or in the parabalbar tissue);
- complex injuries;
- penetration of foreign bodies into the cavity of the eyeball;
- loss of vision due to atrophic damage to the optic nerve;
- problems with blood vessels (thrombosis, destruction of the artery wall).
Causes of eye diseases
A decrease in visual acuity may be associated with age-related changes or pathogenic effects on the body. There are diseases that disrupt the functions of the eyeball and the protective mechanism, the optic nerve, and the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual images.
Depending on the etiology, pathological processes are classified as follows:
- congenital developmental anomalies (ptosis, astigmatism, aphakia, etc.);
- inflammatory infectious diseases (conjunctivitis, blepharitis, cyclitis, etc.);
- autoimmune processes that cause visual impairment (lupus, Behcet's disease);
- allergic inflammatory phenomena;
- oncological processes;
- pathologies caused by metabolic disorders (cataractogenic effect in diabetes mellitus, etc.);
- degenerative processes caused by age-related changes;
- traumatic injuries (chemical, thermal, mechanical, etc.)
The development of ophthalmological diseases is influenced by a number of negative factors:
- long-term load when working at a computer;
- brain tumors;
- hypertonic disease;
- diseases of the circulatory system of the eye;
- head injuries;
- general intoxication;
- dry eye syndrome;
- endocrine disorders;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules.
Congenital abnormalities of the eye structure can be caused by TORCH infections suffered by the mother during pregnancy or taking teratogenic drugs.
A series of layered photos of the head and orbits
Which is better - MRI or CT of the eye orbits?
Among medical specialists, MRI of the orbits is preferred over CT. This is due to the fact that magnetic resonance scanning is focused on visualizing physical and chemical changes in tissue structures. The photographs show pathologies whose dimensions are minimal, as well as functional changes. What other diagnostics often cannot detect.
Computed tomography of the orbits, compared to MRI, has less “sensitivity” to ocular disorders. Because it shows the structure of bone tissue to a greater extent. The method is suitable for determining fractures in the walls of the orbits and identifying foreign objects. While in case of eye pathology its accuracy will be low.
The need for the study is determined by the doctor, since scanning is considered a last resort diagnostic measure. Typically, ophthalmologists detect eye diseases using other simple methods. Experts advise to undergo tomography in clinics that specialize in it. MRI when examining the eyes requires adherence to a precise procedure. The results obtained during the test should only be interpreted by a professional doctor. In our medical center, these are the specialists who perform scanning.
Alternative research methods
- Ophthalmological research methods - ophthalmoscopy, electrophysiological study, exophthalmometry, etc.
- Ultrasound of the orbits is a simple, painless and safe method of objective examination.
- CT scan of the orbits—diagnosis of bone abnormalities, traumatic, inflammatory or tumor processes.
Contraindications Preparation
the prices for services in the price list or check by calling the phone number listed on the website.
Is the MRI procedure safe?
The study is considered a safe type of diagnosis. If it is not contraindicated for you, then it will not cause any harm to your health and will not complicate existing diseases in the body. You can undergo a magnetic resonance imaging examination a large number of times, which will be determined by your attending physician.
Contraindications for MRI
Like any type of medical examination, MRI contains a number of contraindications. There are a number of important nuances under which scanning will not be allowed:
- The subject's body contains metal objects or installed medical implants with metal components. These can be pacemakers, implanted cochlear devices, an insulin pump, staples and pins, hemostatic clamps on blood vessels, and braces. The tomograph is capable of disrupting the operation of vital devices, heating metal elements and displacing them inside the patient’s body. As a result, life-threatening bleeding or tissue damage may occur. The ban also applies to people with facial tattoos if their ink contains metal.
- The patient is claustrophobic. He may have a seizure in a closed scanner. Sometimes, with such a diagnosis, an examination may be allowed, but with the condition of medicated sleep.
- Mental disorders in which the patient behaves inappropriately. In this case, anesthesia can be applied to him.
- MRI is contraindicated in pregnant women, especially in studies involving the use of a radiocontrast agent. The drug can have a toxic effect on an unborn child. For this reason, contrast is also prohibited for nursing mothers.
- Patients with severe kidney complications or those who are allergic to the dye are also unable to undergo the contrast procedure.
To whom and when is the procedure indicated?
MRI of the orbit of the eye can be prescribed for all types of damage to the eyeball or optic nerve. This type of diagnosis identifies any pathologies and eye diseases. Indications for this procedure are:
- Sudden deterioration of vision.
- Severe injuries to the eyeball.
- The presence of a foreign object in the eye.
- Blood clot formation.
- Suspicions of a tumor, inflammation or infection.
- Impaired blood supply, hemorrhages.
- Unknown causes of eye pain.
- The need to diagnose this organ before or after surgery.
The appropriateness of the procedure is determined by the attending physician, who gives a referral for examination.
Contraindications
MRI of the eye has a minimal set of contraindications. Most of them are associated either with the presence of metal objects in a person or with the introduction of a special substance in cases where contrast enhancement is used. The main contraindications are:
- The presence of a person with non-removable metal objects (prosthesis, implant, pin, etc.).
- Patient use of electronic devices (neuro- and cardiac pacemakers).
- Allergy to contrast agent.
- It is impossible for the patient to remain motionless for a long time.
- Fear of confined spaces.
Children can have an MRI at any age. The main criterion is the child’s ability to lie still during the entire procedure. Pregnant and lactating women should be wary of this examination if it is performed with contrast. It is imperative to consult a doctor. There are also technical difficulties in performing the procedure for people weighing more than 120 kg.
Why contrast is needed
The dye injected through a vein has the ability to stain blood vessels. In addition, it accumulates in the soft tissues of the body. Moreover, healthy cells are weakly capable of accumulating contrast, or do not do this at all. But cells with a malignant process “glow” on the tomograph brighter than others. Therefore, when making an oncological diagnosis, the patient is prescribed an MRI with contrast.
The dose of contrast injection depends on the body weight of the subject. Modern drugs are safe for the patient and do not cause side effects. Within 24 hours, the drug will be excreted from the body through the kidneys.
Contraindications
MRI of the brain and orbits in most cases has absolutely no consequences for the body, except for a few situations. An absolute contraindication is the presence of non-removable metal objects that are attracted by a magnet. Due to the action of a constant magnetic field, such ferromagnetic materials can significantly heat up and move. If you have implants, bolts, wires, braces, retainers, stimulators not made of titanium (a metal neutral to magnetism), then tomography cannot be performed.
Pregnancy imposes great limitations on diagnosis. In the first trimester, MRI of the orbit of the eyes is not performed, either with contrast or without it. The procedure is not recommended for patients with hyperkinesis due to the inability to maintain long-term immobility. As for children, a child can undergo examination starting from 4 years old. This is also due to the need to stay in one position for a long time.
Other contraindications include:
- Cardiac pacemakers.
- Artificial valves in the heart.
- Insulin pumps.
- Hemostatic clips.
- Metal-containing inner ear prostheses.
- Severe and very serious human condition.
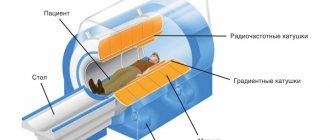
How is the MRI procedure performed?
- The clinic will ask you to fill out a questionnaire containing questions about your health status. This is necessary to control possible contraindications.
- Before the examination you need to change clothes. For this purpose, clinics have special rooms or changing rooms. You must remove all metal jewelry, mobile phones, watches and other electronics from your body. On the day of tomography, you should not apply cosmetics containing iron particles to your face. You may get burned.
- You will be given headphones or earplugs as the operating scanner is noisy.
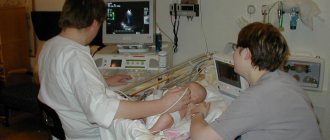
- During the diagnostic process, you will have to lie on a pull-out couch or table. The body, in order to avoid unnecessary movements, will be secured with several belts or bolsters. When the doctor turns on the device, the couch will smoothly move inside the tomograph.
- You will have to lie down without moving for about 20 minutes. If contrast is introduced, the scanning process will take an hour.
- You can contact the doctor conducting the examination via two-way voice communication. The specialist will monitor the progress of the inspection from the next room.
- If you feel more comfortable with someone close to you, tell your doctor.
What equipment and are there any restrictions?
When deciding where to get an MRI of the eye orbits in St. Petersburg, you can contact our call center.
We use the latest scanners with high accuracy of the results obtained. There are both open-type devices (considered the most comfortable for patients) and closed-circuit devices. They are different in power.
Closed-type tomographs with an intensity of 1.5 Tesla:
- Brivo MR355, GE (USA)
- Optima MR360 Advance, GE (USA)
- General Electric Signa Echospeed, GE (USA)
- Siemens Espree, Siemens (Germany)
- Toshiba Excelart, Toshiba (Japan)
With a voltage of 3 Tesla:
- General Electric Signa HDx 3.0 T, GE (USA) - closed circuit, voltage 3 Tesla;
- Siemens Magneton Verio, Siemens (Germany)
The devices have restrictions on patient weight: up to 200 kilograms.
How to prepare for an MRI of the eye orbits, what to take with you
If you plan to have an MRI without contrast, then there are no preparatory manipulations for it. Contrast enhancement is performed on an empty stomach. Therefore, the last meal should be taken 5 hours before the tomography.
You will need to bring with you:
- referral from the treating doctor;
- a short extract from the medical record;
- results of previously completed examinations (all that are available).
What will I get after an MRI, where to go with the results
Within about an hour and a half (if you need it urgently, then sooner) you will receive the photographs and a conclusion to them. If you do not want to wait for the diagnostic results at the center, leave your email address at the reception. As soon as the photos are ready, they will be sent to you.
If a doctor has sent you for a tomography, then bring the results to him. He will study them and decide how to treat you further.
If the procedure was your own initiative, then make an appointment with an ophthalmologist.
a specialist can correctly interpret the images.
Is it possible to do MRI for children?
In clinics, MRIs are performed on children from the age of 7 years. If a younger child needs diagnosis, he should be taken to an institution that specializes in pediatric scanning.
Parents of babies are allowed to be present with them during the scanning period. Since they are unable to maintain a quiet body position for a long period, they are examined under anesthesia or light sedation.