04/04/2020 449 X-ray
Author: Tatyana
Dental X-ray is a procedure that dentists need to make a diagnosis, understand the amount of work and to avoid unpleasant consequences. This is a simple type of diagnosis that causes virtually no harm to health.
- 2
Indications for use - 3
What does the study show? - 4
Are dental x-rays harmful or not and how often can they be done? - 5
Contraindications and restrictions5.1
Can it be done during pregnancy?
Types of research
- 6.1
Intraoral bite radiography
Extraoral (extraoral) radiography
Tomography
Electroradiography
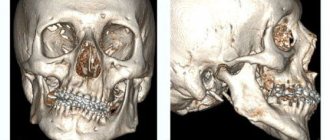
CT scan
Radiography using contrast agents
Preparing for an X-ray
How long does the procedure take and how does it work by type?
- 8.1
Prikusnoy
Sighting
Panoramic
Digital or 3D X-ray
X-ray analysis
Who gives directions for x-rays, where is the best place to do it and how much does it cost?
Photo gallery
Video
Comments and Reviews
Description of the method
The study is based on the passage of X-rays through body tissue. The image is formed depending on the ability of a certain body structure to absorb radiation. During a dental X-ray, the patient applies a light-sensitive film to the desired area, thereby ensuring that this place is visualized in the image.
The specifics of the procedure depend on the disease. To identify different pathologies, different types of x-ray examination are used.
Is it possible to carry out diagnostics during pregnancy?
According to SanPiN, X-ray examinations are allowed in the second half of pregnancy using protective equipment, provided that the radiation dose does not exceed the same 1000 μSv. However, it is recommended to refrain from taking x-rays in the first and last 12 weeks, i.e. in the first and last trimesters.
Do not be afraid of undergoing diagnostic procedures during pregnancy. Even ordinary caries is an infection that, if not properly treated, can spread throughout the body and lead to infection of the fetus. Therefore, it is better to receive a small and completely safe dose of radiation than to carry out complex dental treatment blindly, not knowing how deep the inflammatory process is.
After the baby is born, i.e. During breastfeeding, dental x-rays can be taken, even more than once (within reasonable limits). Radiation doses are minimal, so radiation does not accumulate in breast milk, and there will be absolutely no harm to the baby. There is also no need to pump or skip feedings.
Indications for use
X-rays are necessary to diagnose many diseases, such as:
- periodontitis;
- periodontitis;
- caries (if there are hidden lesions);
- crack or fracture of the tooth root;
- abscess;
- various neoplasms (cysts, granulomas, etc.);
- abnormalities of the temporomandibular joint.
In addition to the above cases, this study must be carried out:
- before implantation;
- in the treatment of dental canals;
- before orthodontic treatment;
- for dental prosthetics.
After tooth extraction and other surgical procedures, the doctor needs an image to assess the condition of the root canals.
In addition, X-rays can provide information about the alignment of teeth and monitor the eruption of wisdom teeth.
Photo of an x-ray of a child's baby teeth
As practice shows, children undergo x-ray examinations more often than adults. This fact can be explained by the fact that their teeth are more intensively exposed to carious lesions, and the areas of localization of the disease are usually located in places that cannot be seen in any other way.
Radiography helps to identify anomalies in the process of growth of distant teeth in a row, pathologies of bone and soft tissues, and to carry out high-quality therapeutic manipulations.
The procedure is also relevant if it is necessary to perform orthopedic correction, if anomalies in the development of the jaw arch are detected.
For children under 2 years of age, X-ray examinations are prescribed only in exceptional situations. For example, if a child falls - to assess the integrity of the dental elements, when receiving a birth injury, to monitor the process of development of the dentofacial apparatus.
To adequately diagnose oral diseases in children and adolescents, the doctor needs to have as much information as possible. An x-ray of a child’s baby teeth can provide this information. More than 50% of the tooth is hidden, and the dentist simply does not see some areas where pathological processes may occur.
In these cases, x-rays come to the aid of the doctor. An image of a child’s baby teeth will show whether there is caries between the teeth, whether the roots of the teeth are changed, and how the rudiments of permanent teeth are located. This way, the dentist can predict the timing of the loss of baby teeth and identify the presence of impacted, or crooked, rudiments.
The Ministry of Health has developed the timing of the examination, as well as safety rules under which neither the patient nor the clinic staff will be exposed to unnecessary radiation. According to his recommendations, children should have an X-ray of their children's teeth once every two years, and after the eruption of permanent teeth - once every 1.5 - 3 years.
Are dental x-rays harmful or not and how often can they be done?
Due to the short exposure time and protective measures, the harm from this procedure is minimized. The radiation dose received by a person during research is about 2 μSv (microsievert) when using a digital radiovisiograph and about 10 μSv using film. SanPiN 2.6.1.1192-03 establishes the permissible level of radiation during medical procedures not exceeding 1000 μSv per year.
That is, up to 500 digital photographs or 100 film photographs can be taken per year. The severity of the treatment determines how many times x-rays need to be taken.
Are x-rays dangerous in dentistry?
X-ray radiation does not accumulate in the environment, but, like light waves, passes through objects, lingering a little longer in a dense environment, a little less in a more rarefied environment. So, all those who are concerned about the question of whether a nursing mother can have a dental x-ray done should answer: “Yes, you can!”
Irradiation will not “spoil” milk. It can only linger in the mammary glands themselves. In dentistry in particular and in medicine in general, microdoses of radiation are used, several tens of times less than those recognized as dangerous and causing immediate dire consequences, so dental x-rays during breastfeeding, if there are indications and high-quality devices, are quite safe. For your own peace of mind after the procedure, you can skip one feeding - this will be enough.
When conducting an X-ray examination, the body's exposure to radiation should not exceed 1000 microsieverts (µSv) in one year1. In this case, we are talking about a procedure that is carried out specifically for the purpose of prevention, while for therapeutic purposes this figure is many times higher. Acceptable standards in quantitative terms are presented below:
- 500 x-rays,
- 80 OPTG images,
- 20 CT scans.
The following are the radiation doses that the patient receives when performing appropriate diagnostics in modern dentistry. For comparison, radiation doses hazardous to health are also presented.
- targeted image (1-3 µSv) – at 750 thousand µSv certain changes in blood composition are observed,
- panoramic image (13-17 µSv) – at 1 million µSv mild radiation sickness develops,
- CT scan (50-60 µSv) – the lethal dose starts from 7 million µSv.
It is obvious that it is impossible to cause serious harm to the body in a dental X-ray room. Therefore, even 20 CT images or 80 panoramic images do not pose any danger to your health.
Contraindications and restrictions
Despite the safety of the study, there are categories of people who should treat it with caution. The question of refusing x-rays usually arises when this diagnostic procedure is prescribed to pregnant women and children.
Contraindications include:
- bleeding;
- reduced immunity;
- severe condition of the body.
This is due to the negative effect of X-ray radiation on blood cells (especially lymphocytes).
Can it be done during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, you can take an x-ray; this is not prohibited by the recommendations of SanPiN dated 2.6.1.1192-03. However, even taking into account the low dose of radiation and the short duration of exposure, a pregnant woman should take into account that the effect on the fetus may be unpredictable.
In the early stages (especially in the first trimester), X-ray examinations should not be performed, since at this time the child is most susceptible to the negative effects of rays. In a later period, X-rays are only possible if absolutely necessary.
BabyLenta channel - about the features of dental x-rays in pregnant women.
When X-rays, OPTG and CT may be required
An x-ray is a targeted photograph of one or more teeth. OPTG or orthopantomogram is a panoramic image that captures both jaws. CT is a computer tomogram. It allows you to obtain three-dimensional or volumetric images of the entire human jaw system. Each of these types of diagnostics is used for certain indications:
- X-rays are performed when treating a specific tooth: in the presence of caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, suspected cyst or granuloma. Allows you to determine the extent of tooth damage, as well as the condition of the tissues around the root,
- An orthopantomogram is indispensable in the presence of inflammatory processes in periodontal tissues and jaw bone. It is carried out both during multiple dental treatment and in preparation for orthopedic, orthodontic treatment or dental implantation. Allows you to assess the condition and volume of bone tissue, clarify the position of the maxillary (nasal) sinuses of the upper jaw, nerves and other anatomically important elements,
- CT scan is performed for certain indications. Most often in the presence of tumors of the jaw system (to determine their volume in all dimensions), as well as before dental implantation, especially in complex cases.
Today in dentistry (and in medicine in general) digital devices are used instead of film ones. They have a much lighter load, and they also use shorter shutter speeds to create a photo. For comparison: a modern digital visiograph takes up to 0.3 seconds to take an image, a film X-ray machine requires up to 1.5 seconds.
The Smile-at-Once clinic uses the latest generation CT-Scan tomograph. It allows you to get both a targeted or panoramic, and a three-dimensional digital image. Thanks to minimal radiation exposure, the equipment is completely safe and allows repeated diagnostics without harm to the human body.
Types of research
In dentistry, there are several methods that help the doctor make a diagnosis and, based on it, prescribe treatment:
- intraoral bite radiography;
- extraoral (extraoral) radiography;
- tomography;
- electroradiography;
- CT scan;
- radiography using contrast agents.
Intraoral bite radiography
With this type of examination of the oral cavity, the patient must squeeze a film measuring 5x6 or 6x8 cm with his teeth. Bite X-rays are needed to analyze the condition of all parts of the upper and lateral and anterior sections of the lower jaw, as well as the anterior and all maxillary teeth.
Extraoral (extraoral) radiography
If the intraoral image is uninformative or there are difficulties in taking it (for example, due to an increased gag reflex, lockjaw), extraoral radiography is performed. Extraoral radiographs show less structural tissue in the mouth.
Tomography
Tomography involves a layer-by-layer examination of organs. Using this method, you can obtain an image of a certain layer of the area under study, which is formed when the X-ray tube and film move in opposite directions. The use of a tomograph helps in diagnosing pathology of the temporomandibular joint and lower jaw.
Electroradiography
An X-ray image in this method is created by removing an electrostatic charge from the surface of a selenium plate, further spraying colored powder and transferring the image onto paper. The procedure is carried out using an electroradiographic apparatus.
CT scan
This type of research is quite sensitive and informative. Passing through tissue, X-rays are captured by a detector, the signals from which are transmitted to a computer. It reconstructs body structures based on knowledge of their ability to absorb radiation. CT is of great help in diagnosing inflammatory processes, injuries and tumors of the upper jaw.
Radiography using contrast agents
Diseases of the salivary glands (inflammation, salivary stones) are diagnosed by radiography with filling of their ducts with an iodine-containing preparation.
How to take a panoramic photograph of the jaw -
Devices for obtaining panoramic images are called orthopantomographs. Technically, the procedure is as follows: the patient is placed in the center of the device and allowed to bite a special plate between the teeth to achieve immobility of the jaws. Next, the moving part of the orthopantomograph moves around the patient’s head, which consists of an x-ray source on one side, and x-ray film or a digital sensor on the other.
The entire procedure lasts from 8 to 20 seconds, which depends on the equipment, and the shorter the irradiation time, the better. Depending on what the image is recorded on (film or digital media), orthopantomographs are divided into film and digital. Let's say right away that film orthopantomographs provide a fuzzy, blurry image - especially in the area of the central teeth of the upper and lower jaw, and therefore are frankly outdated.
Digital orthopantomographs are of great value for diagnostics due to the fact that a special computer program for such devices improves the quality of the image, which can then be viewed in detail on a computer screen. In addition, if necessary, a digital image can also be printed later on film or photo paper (if necessary), but it is still best to have a digital medium.
Panoramic shot of the jaw: video
An interesting point is that a panoramic photograph of teeth can be obtained not only by using an orthopantomograph. Modern devices for computed tomography (for example, the Sirona Galileos tomograph) allow the patient to simultaneously receive a three-dimensional computed tomography image and a two-dimensional flat panoramic image of the teeth. In some cases, this is very convenient for diagnosis and does not require additional radiation exposure.
Panoramic photo of teeth: disadvantages
Considering that a person’s jaws are curved and not flat, the orthopantomograph has to combine several images (taken in different planes) into one flat two-dimensional image (24stoma.ru). There is a big disadvantage in this process: different people have different jaw shapes and curvatures, but the path of the radiation tube around a person’s head during the procedure is always standard.
This leads to the fact that any panoramic image will always not accurately convey the dimensions of teeth, root canals, and bone tissue dimensions. The distortion from the actual size of these objects from different manufacturers is approximately from 15 to 30%. Therefore, any panoramic photograph of teeth (both film and digital) is always only an approximate diagnostic method, allowing you to see only the general picture of the condition of the teeth and jaws.
Important: since orthopantomographs take an image in only one section on a certain area of the jaw, the root canals of three-rooted teeth in the upper jaw (6-7-8) will always turn out a little blurry (both on digital and film panoramic images). This is because the three roots will always be in different slices/planes and therefore the orthopantomograph will not be able to focus well on each of the roots.
Therefore, only single-rooted, as well as double-rooted teeth of the upper and lower jaws (the two roots are in the same plane) will be clear - and only on digital photographs. But the anterior teeth of both jaws on conventional film orthopantomographs will always be very blurred (Fig. 5) - due to the strong bending of the anterior parts of the jaws, as well as the technical imperfections of the old film equipment.
Comparison of digital and film quality -
Advantages of digital panoramic photographs -
- reducing the time and dose of radiation to the patient,
- higher image clarity,
- the image can be subjected to graphic processing (for example, enlarged on a computer screen to see small details),
- ability to write to a flash drive or disk.
How long does the procedure take and how does it work by type?
Dental X-rays are performed in a special room, the walls of which are covered with paint containing lead. The procedure takes only a few minutes; the actual effect of the radiation lasts no more than a couple of seconds.
When using a computer radiovisiograph, a sensor connected to the device is placed on the area under study.
The type of study depends on which area needs to be imaged for diagnosis:
- bite;
- aiming;
- panoramic;
- digital or 3D x-ray.
Prikusnoy
This type is the most common, allowing you to analyze the condition of several teeth at once. The patient presses the film between his teeth and the doctor takes an x-ray. This way you can identify caries, tartar and the need to correct your bite.
Sighting
A targeted x-ray is needed to diagnose the condition of one tooth.
Conducting a targeted X-ray of the tooth
Using it, you can evaluate the result of treatment that has already been carried out, or study the pathological process in detail:
- pulpitis;
- periodontitis;
- periodontitis;
- caries;
- consequences of injury.
The film is applied to the area of interest, and the picture is taken using a small device that can be located in the dentist's office.
Panoramic
A panoramic x-ray is an x-ray of all teeth. The patient’s movements during the examination will make the picture unclear, so the patient’s head is fixed, and a special device rotates around it so that the tube moves on one side and the film on the other.
This procedure is prescribed for patients with orthodontic pathology or injuries of the lower jaw.
Digital or 3D X-ray
3D dental x-rays provide highly detailed images. You can see affected areas, hidden cavities and root canals that cannot be examined with other types of x-rays. The radiation scans the oral cavity in three planes, and the rays pass through microscopic areas of tissue.
Concept and purpose
This is an X-ray examination showing the actual condition of one or 2-3 adjacent units.
This technique is simple to perform, prompt and accessible in dentistry. Analysis of a targeted image on film or other media allows the dentist to solve several main problems:
- It is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis, which in some situations cannot be done only with the help of a visual examination.
- Select the optimal course of treatment and monitor its progress.
- Monitor the intensity of development of dental pathology.
- Assess the quality of bone tissue restoration and root canal sealing.
- See the actual condition of blood vessels, dentin, bone tissue, root canals.
- Identify hidden pathologies, including fractures, cracks, etc.
- Determine the size of the carious lesion, the localization of the purulent mass and the source of inflammation.
To perform a targeted image, a digital device is usually used - a radiovisiograph, which gives a very low radiation dosage.
The radiation flux emerging from the equipment is not scattered and irradiates only the required part of the dental element being examined. These two features make the examination absolutely safe.
X-ray analysis
After a photograph of the teeth has been taken, the dentist must correctly interpret the resulting radiograph. Image analysis is based on knowledge of which tissues transmit X-rays better. Fillings and crowns will appear as white spots on the x-ray, areas of inflammation and cavities will appear dark, and the natural tissues of the teeth and gums will appear gray. For comparison, you need an x-ray of a healthy tooth that has a natural cavity containing a nerve.
When deciphering, the doctor receives information about:
- localization of caries;
- shape and location of roots;
- condition of dentin, enamel and periodontium.
Varieties
To obtain one image, two types of equipment are used - an outdated model of an X-ray machine or a digital radiovisiograph (its modern analogue).
In the first case, photographs are taken on film. The procedure is not comfortable for the patient; printing the image takes some time. The image turns out flat and loses quality, fading after one and a half to two years.
The second model of the device allows you to obtain photographs in electronic form of high quality and resolution. If necessary, the image can be expanded several times and a specific area can be studied in detail.
Images do not lose quality during long-term storage (for several years). In addition, the electronic device has 3 times less radiation exposure compared to the outdated model.
With modern equipment you can take two types of pictures:
- Interproximal - the condition of the coronal part is assessed. It is used for filling carious cavities with endomaterial, and for monitoring the correctness of prosthetics.
- Intraoral (done intraorally) - it is possible to determine the caries of adjacent units and the degree of adherence of the filling to the walls of the cavity after treatment.
This image is considered the most informative and effective way to diagnose dental caries and periodontal disease.
Who gives directions for x-rays, where is the best place to do it and how much does it cost?
A referral form for a dental x-ray is given to the patient by the dentist. The patient applies with this document to the radiologist, who makes an appointment for the laboratory assistant performing the procedure.
X-rays are done in private and public dental clinics.
| Name | Price, rub |
| 1. Targeted X-ray | 150-650 |
| 2. Panoramic X-ray | 800-1500 |
| 3. 3D X-ray | 2000-5000 |
| Prices are relevant for three regions: Moscow, Chelyabinsk, Krasnodar. | |
When choosing a facility to perform x-rays, it is important to consider whether all necessary regulations are followed. The presence of a separate office, a specialist radiologist and concern for patient safety are important conditions that allow a person to entrust his health to the clinic staff.
Advantages and disadvantages
A targeted photograph taken on modern digital equipment has the following advantages:
- Safe examination method.
- The photo is clear and of high quality.
- You can zoom in on a specific area of the image and extract more additional information.
- Convenient to store a series of sequential images.
- Images can be printed.
- Conditions for analyzing the clinical picture are better provided.
- No need to wait for the film to develop.
The main advantage, according to dentists, is the information content and fairly high accuracy of the technique, which makes it possible to identify hidden pathologies and diseases in the initial stages.
The disadvantages of the described method are:
- small coverage of the survey area;
- obtaining images from one angle (in one plane);
- a small viewing area, i.e. it is impossible to see the real picture of the condition of 4 or more units;
- it is impossible to detect cracks in the roots and identify perforation.
We suggest you read: The child’s permanent teeth are growing incorrectly
Photo gallery
The photo shows the results of a dental x-ray.
Panoramic photo of teeth
Carious lesions in the picture
Periodontitis
Video
The Planet of Beautiful Teeth channel will tell you more about dental x-rays.
Do you have any questions? Specialists and readers of the HROMOSOMA website will help you ask a question
Was this article helpful?
Thank you for your opinion!
The article was useful. Please share the information with your friends.
Yes
No
X
Please write what is wrong and leave recommendations on the article
Cancel reply
Rate the benefit of the article: Rate the author
Discuss the article: