Diseases of the respiratory system negatively affect the condition of the body, reduce the quality of life and limit performance. If the course of the pathological process is unfavorable, serious complications arise and death is possible.
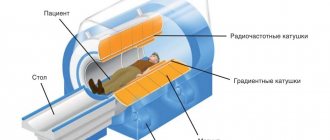
MRI of the lungs and bronchi is used to visualize internal structures. The method is safe for human health and does not require painful manipulations. The study is carried out using a high frequency electromagnetic field. Under the influence of a directed pulse, hydrogen atoms in water molecules resonate, which ensures that a signal is received from the tissues being studied. The intensity of the response directly depends on the volume of liquid in the scanned structures.
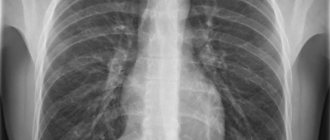
MRI of the chest, frontal projection
To increase the effectiveness of the diagnostic procedure, contrast enhancement is used. In this case, the patient is given an intravenous injection of a drug containing soluble gadolinium salts (chelates). The metal is hypoallergenic, low toxic and completely leaves the body after 24-48 hours.
Contraindications
MSCT without contrast is not performed during pregnancy at any stage, if the patient’s body weight is more than 120 kg, or if the patient has a plaster cast or a non-removable metal structure in the examined area.
MSCT with the introduction of a contrast agent is not performed in similar cases, as well as in severe diabetes mellitus or acute renal failure.
Before performing a procedure with contrast, it is necessary to inform the radiologist in advance about your existing allergy to iodine, as well as the presence of diseases such as asthma, diabetes, thyroid and cardiovascular diseases. An alternative contrast agent or special medications may need to be used to reduce the risk of side effects.
MSCT is not recommended for women planning pregnancy in the second and third decades of the menstrual cycle.
Interpretation of MRI images of the lungs and bronchi
A chest examination includes scanning the pleural cavity, blood vessels, and mediastinal area. In some pathological processes, MRI shows in detail the structure of the lungs and bronchi, which indicates the presence of exudate in the scanned area.
When filling out the study protocol, the doctor describes:
- structural features of the chest organs;
- signs of inflammatory changes (the presence of sputum in the bronchi and alveoli, serous or purulent exudate in the pleural cavity, etc.);
- localization and size of space-occupying formation;
- presence and location of tuberculous infiltrate;
- the nature of the blood supply to the lungs;
- condition of the walls, tone, fullness of blood vessels.
Interpretation of MRI images of the lungs contains information about the extent of the process (number of lesions, presence of cavities, infiltrates). When specifying the location, indicate the affected segment and signs of contamination. Based on the scan results, the doctor makes a preliminary diagnosis and describes the phase of the disease.
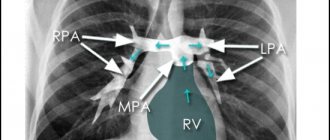
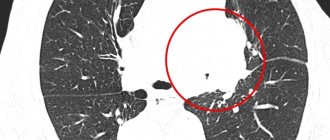
A malignant tumor on an MRI of the lungs, the arrow points to a neoplasm growing into the body of the thoracic vertebra
Inflammatory processes are often detected using native scanning. MR diagnostics of vascular pathologies and neoplasms is carried out using contrast enhancement.
How do they do it?
Before the session, the patient is placed on a special tomograph table on his back, with his arms raised above his head. The presence of metal in the body and on the patient’s body (jewelry, watches, etc.) can create certain defects in the resulting images, therefore all metal objects must be removed before the examination, and the patient himself must be dressed in comfortable clothes that do not restrict movement . However, the presence of metal prostheses or electronic implants in the body is not a contraindication for MSCT.
The patient must remain motionless during the procedure, and this may cause the patient to experience some discomfort. However, due to the short duration of the examination (about 10 minutes), this risk is minimal. When a contrast agent is injected, a burning sensation and heat may occur in the body, but these sensations are usually short-lived.
Preparation for the procedure
Before performing a functional test to diagnose the lungs and bronchi, strict rules and dietary restrictions are not required. Immediately before the session, the patient needs to change clothes that have metal elements, in particular buttons and zippers.
As a rule, most diagnostic centers provide spacious clothing for the procedure. The patient should also remove all jewelry and makeup, as cosmetics often contain metal particles, which can cause burns during the examination.
Before carrying out diagnostics, you should make sure that there are no phones, coins, or bank cards in your clothing pockets.
When using contrast, the last meal is taken 3-4 hours before the procedure.
Research result
MSCT of the lungs makes it possible to identify tumors and the extent of their spread, lesions of the lymph nodes inside the chest, pathological processes in lung tissue, and determine the condition of the pulmonary arteries. The results of the examination are given to the patient in the form of images, and the results are often recorded on a CD (this service is usually paid for separately). Based on the results of the examination, the doctor also issues a conclusion to the patient (usually the conclusion is issued the next day). After the procedure, an additional consultation with a specialized specialist is scheduled, which is also paid separately.
Diseases of the lungs and bronchi
Pathological changes in the airways lead to disruptions in the functioning of the respiratory system. The lungs and bronchi perform the following functions in the human body:
- saturate the blood with oxygen and remove carbon dioxide;
- provide thermoregulation;
- protect against pathogens;
- participate in metabolic processes;
- serve as shock-absorbing protection for the heart.
Pathological changes can affect the bronchi, lung parenchyma and pleural cavity. Clinical symptoms depend on the location and severity of the disease. The most characteristic signs of pathologies of the respiratory system are:
- cough (dry or wet, depending on the presence of sputum);
- shortness of breath (in severe cases, asphyxia is possible);
- presence of blood in sputum;
- pain in the chest cavity (more often observed when inhaling/exhaling).
Features of the manifestation of these symptoms suggest the nature of the disease. Instrumental examination (X-ray, CT, MRI of the lungs and bronchi) allows you to clarify the diagnosis and location of the pathological focus.
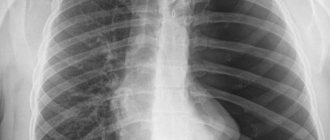
MRI image of the lungs, frontal projection
Diseases of the respiratory system are classified depending on the etiology, location and nature of negative changes. There are the following types of damage to the organs of the thoracic cavity:
- inflammatory processes - acute and chronic bronchitis, pneumonia;
- infectious diseases - tuberculosis;
- granulomatous processes – sarcoidosis;
- malignant tumors – adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, etc.;
- parasitic lung infections - ascariasis, pneumocystis, etc.;
- benign neoplasms – papillomas, adenomas;
- congenital pathologies - aplasia of pulmonary tissue, bronchial stenosis, accessory lobe, sequestration, etc.;
- necrotizing processes - abscess and gangrene of the lung, purulent pleurisy;
- allergic diseases - bronchial asthma;
- vascular diseases – pulmonary hypertension, embolism;
- damage to the pleural cavity - pneumo- and hemothorax, pleurisy.
The causes of respiratory diseases are most often chest injuries, infectious, fungal, viral lesions, and the development of neoplasms. The diagnosis largely depends on what the MRI of the lungs and bronchi shows. The final decision is made by the attending physician based on all examination results.
Advantages of the method
MSCT of the lungs as a diagnostic technique has a number of advantages. For example, MSCT makes it possible to identify most common causes of chest pain, shortness of breath and cough. This allows you to start treatment in a timely manner, avoiding possible complications. In addition, MSCT eliminates the need for painful and less accurate examinations.
MSCT can be used as an emergency diagnostic method if there is a threat to life - in case of rupture of the lungs or bleeding from a large vessel in the chest area. The result obtained in the shortest possible time can often save the patient’s life.
For inflammation and infections that cause more serious pathology, MSCT allows you to establish an accurate diagnosis, significantly reducing the risk of complications.
MSCT, performed on a modern tomograph, is not a very long procedure, and the dose of radiation received by the patient is significantly reduced. This gives the technique a huge advantage, especially when examining children and patients with severe pain who cannot remain motionless for a long time.
Comparison of examination costs
MRI of the lungs is not a cheap procedure. Its cost is much higher than CT, radiography, and fluorography. In Moscow, the average price for lung diagnostics using a magnetic resonance imaging scanner is 6,000 rubles. The cost of the procedure is influenced by many factors (the rating of the clinic where the diagnosis is carried out, the equipment used, the qualifications of the specialist, the scope of the task, the use of a contrast agent).
The cost of CT is much lower. In Moscow, computer diagnostics of the lungs can be done for 3,500 rubles and more. The cost of the procedure depends on the above factors, as well as the need for recording to disk and building a three-dimensional model.
Possible risks
Despite all the advantages, MSCT is a technique that uses X-ray radiation, which cannot but affect the health of the subject. The lungs are a fairly vulnerable and radiation-sensitive organ, and the risk of developing cancer (especially with frequent examinations) remains. In modern tomographs, however, the radiation dose is gradually reduced, and accordingly, the risk of cancer is reduced. The diagnostic capabilities of the method, therefore, significantly exceed the possible risks.
When performing MSCT with contrast, it is also possible to develop complications associated with the appearance of an allergic reaction to iodine, which is contained in the contrast agent. Despite the low likelihood of such reactions, this risk remains and must be taken into account.
Progress of the procedure
To perform an MRI, the patient is placed inside the tomograph; when contrast agents are used, gadolinium is injected intravenously before being placed on the machine’s retractable couch. Inside the tomograph there is bright lighting and two-way communication, which allows you to communicate with the diagnostician, who moves into the next room to the computer monitor. During scanning, quite a lot of noise appears inside the device, which is normal. Some patients are offered to wear headphones to muffle it.
The duration of the study is at least half an hour, during which a scan is carried out and the lungs are visualized on the monitor in three projections - sagittal, frontal and horizontal images, allowing to identify foci of inflammation and other changes in the organ.
Alternatives
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is a safe method that does not use x-rays. However, when it comes to diagnosing the lungs, computed tomography is preferred over MRI. This is due to the fact that MRI visualizes hollow organs, such as the lungs, much worse. In this regard, MRI is significantly inferior to even conventional radiographic examination. CT and, in particular, MSCT are often used as a method to clarify data obtained by MRI. In addition, MRI is not the best technique for imaging objects that are in motion, this is true for the lungs. MRI images are often not very reliable when examining the lungs; MSCT is much more reliable in this regard. MSCT makes it possible to effectively and accurately diagnose neoplasms, clarify their nature, and detect tuberculosis and sarcoidosis.
- Lung ultrasound is a quick examination method that helps identify various lung pathologies at an early stage. However, ultrasound cannot boast of such information content as MRI and MSCT.
- Computed tomography is a painless and highly accurate examination, however, it is inferior in information content to multislice tomography. MSCT makes it possible to reduce procedure time, reduce radiation exposure to the patient’s body, and ultimately obtain much more accurate images.
To summarize, we can conclude that the most accurate and informative method for diagnosing lung diseases is MSCT.
What MSCT allows you to find out
MSCT or multislice computed tomography is one of the most modern methods of examining the body. This method is gradually replacing standard non-invasive studies, combining many diagnostic techniques and techniques. It is based on dosed and controlled x-ray radiation, which passes unhindered through the patient's body.
The latest generation tomograph has several dozen high-frequency sensors that detect any vibrations and signals. The information is converted into images of the organ without defects or projection distortions.
When choosing between MSCT and MRI, it is necessary to take into account the many advantages of the first method: speed of scanning;
- high accuracy of the results obtained;
- possibility of use for emergency cases (diagnosis of lung injuries after an accident, chest wounds);
- reduced x-ray dose;
- the ability to quickly obtain a transcript;
- formation of a three-dimensional image model of the lungs and bronchial tree for virtual reconstruction before surgery or transplantation.
The human lungs are a hollow organ that is filled with air. Therefore, X-rays are able to easily penetrate the cavity and detect any changes and pathologies. By using
MSCT of the lungs can diagnose:
- pathological changes in the structure of tissue, pulmonary pattern, mucous membranes;
- blood clots and bottlenecks in blood vessels;
- complications after injuries or blows;
- anomalies of the development of veins, aorta and small pulmonary vessels;
- severe forms of pulmonary tuberculosis;
- advanced consequences of pneumonia with ascites;
- punctures or rupture of the lobe;
- pneumothorax.
But in most cases, MSCT is prescribed when it is necessary to identify neoplasms of a different nature: oncology, cysts, fibroids. Metastases in the lungs appear at stages 2–3 of many types of cancer, impairing respiratory function and blood circulation.