How harmful is it to undergo an X-ray of the spine?
Everyone has long known that, in addition to the many advantages of radiography, there is one significant and usually frightening disadvantage for many patients - this is the receipt of radiation exposure during the procedure. In fear of exposure, patients try to persuade the doctor to prescribe MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), which does not emit a radiation field and is not a very expensive method.
But as a rule, the attending physician tries to convince the patient by explaining how an MRI differs from an x-ray and what an x-ray of the spine shows. And the differences, in addition to the presence of radioactive radiation, also lie in the inability to visualize bone tissue when using MRI, and this method is aimed at a detailed study of soft organs. Therefore, for the study of bone structures, fluoroscopy is always a priority - examination using x-rays.
Then the next question arises: if the described study can cause some harm, how often can an X-ray of the spine be taken? When undergoing an X-ray of the spine, a person receives a dose of 1.5 mSv (milisievert), corresponding to the natural radiation to which he is exposed for six months. And if compared with the benefits of diagnosing and curing a disease, then its value leaves no doubt.
A new generation X-ray machine used for diagnostics.
The creation of modern equipment used for the procedure makes it possible to take X-rays of the spine with much lower radiation doses. Therefore, when prescribing it, it is worth looking for a clinic with devices made according to new developments, where the diagnosis will be much safer. In cases where it is necessary to undergo regular X-ray examinations, doctors must record the number of procedures completed, monitoring the patient's radiation doses received.
Also, the patient should take care of minimizing radiation in his body. This can be done by including natural grape juice, milk, green tea in your diet, and immediately after the study you can drink a glass of red wine, which will help quickly rid the body of radiation exposure.
X-ray
Fluoroscopy makes it possible to evaluate how organs function. For example:
- the contractions of the heart and the movements of the lungs during breathing are clearly visible on the screen;
- it is possible to determine the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract due to the speed of contrast spread and detect pathologies;
- vascular catheterization and angiography are monitored;
- The image can be obtained in any position - horizontal, vertical.
If an urgent examination is necessary, precious seconds are not wasted to give the patient’s body the desired position.
The main difference between fluoroscopy and radiography is the ability to assess the condition of organs when they are in motion.
Despite the fact that the radiation dose is higher, modern devices are equipped with protection, so that the rays do not cause significant harm to the body.
The advantages of the technique, and what are the negative effects of x-rays on the body
X-rays obtained as a result of X-ray scanning provide an accurate understanding of the condition of the organ being examined and allow doctors to make an accurate diagnosis. The minimum duration of such an examination and modern equipment significantly reduce the possibility of receiving a dose of ionizing radiation dangerous to human health. A couple of minutes is enough for detailed visualization of the organ. During this time, in the absence of contraindications for the patient, it is impossible to cause irreparable harm to the body.
How to minimize the effects of radiation
All forms of disease diagnosis using X-rays are carried out only for medical reasons. Fluorography is considered the safest, which is recommended to be performed annually for the purpose of early detection and prevention of tuberculosis and lung cancer. All other procedures are prescribed taking into account the intensity of X-ray radiation, and information about the dose received is entered into the patient’s chart. The specialist always takes this indicator into account when selecting diagnostic techniques, which allows not to exceed the norm.
To reduce the effects of radiation, it is recommended to eat foods containing selenium, potassium, pectin and fiber, methionine, milk and dairy products, and honey.
Is it possible to do x-rays for children?
In accordance with international and domestic standards, any research based on the effects of ionizing radiation is permitted to be carried out by persons over 14 years of age. As an exception, a doctor may prescribe an x-ray to a child only if he suspects he has dangerous lung diseases with the consent of the parents. Such an examination is necessary in acute situations that require quick and accurate diagnosis. Before this, the specialist always weighs the risks of the procedure and the threat to the child’s life if it is not carried out.
Is it possible to have an x-ray during pregnancy?
Such an examination is usually not prescribed during pregnancy, especially in the first trimester. If it is so necessary that the lack of timely diagnosis threatens the health and life of the expectant mother, then during it a lead apron is used to protect internal organs from X-rays. Compared to other similar methods, x-rays are the safest, but in most cases doctors prefer not to use them during pregnancy, protecting the fetus from harmful ionizing effects.
Alternative to X-ray
The 120-year practice of using x-rays and similar techniques (fluorography, computer, multispiral, positron emission tomography and others) has shown that today there is no more accurate way to diagnose a number of pathologies. Using X-ray examination, you can quickly identify lung diseases, bone injuries, identify diverticula in older patients, perform high-quality retrograde urethrography, timely detect oncology at the initial stage of development, and much more.
An alternative to such diagnostics in the form of ultrasound can be prescribed only to pregnant women or patients with contraindications to X-rays.
What can an ordinary person see in the photo?
Of course, only a specialist can read an X-ray correctly, but anyone can recognize some deviations from the norm. The image shows a black and white image of the organ under study with areas of differing color intensity. The lightest and most pronounced are the bone structures, but the soft tissues are practically invisible - the rays do not linger in them and are not fixed, passing through them.
A fracture can be easily seen in the image – it looks like a crack or displacement of sections of the bone. Scoliosis is defined as a deviation of the spine to the side. Rounded darkening with clear visualization of boundaries often indicates the presence of neoplasms. Cartilage, as a rule, is not determined by x-rays, but a decrease in their thickness can be determined by the distance between the vertebrae, which is characteristic of osteochondrosis.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
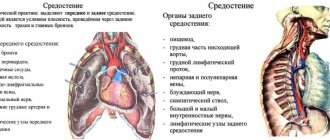
Radiography is widely used in the fields of traumatology and pulmonology. It helps to assess the condition of those organs that can be seen on x-rays, for example:
- lungs and bronchi;
- hearts;
- lymph nodes in the chest area;
- ribs
X-rays are effective for diagnosing pulmonary diseases such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, benign and malignant neoplasms. In addition, it shows inflammatory processes of the pleura (pleurisy, pleural empyema), parasitic diseases of the chest (echinococcosis), mechanical ruptures of the lung tissue (pneumothorax). If there is a suspicion of a violation of the integrity of the skeleton (ribs, spine), an x-ray is also prescribed.
The advantages of radiography are its high efficiency and the ability to establish the location, size and severity of the onset of the disease. These properties of the method are ensured by the way chest photographs are taken. Doctors often prescribe x-rays in two projections. What is a chest x-ray in two projections? This is a photograph of the chest from the front (or back) and sides. This method establishes the exact size and shape of the deviation.
The difference lies in the following factors:
- With fluorography, a higher radiation dose is used (0.5 mSv per procedure with conventional fluorography versus 0.3 mSv with radiography, 0.05 mSv with a digital analogue versus 0.03 mSv with digital radiography). To clarify, the annual radiation dose limit for an adult is 2-3 mSv, for a child – 1 mSv. For this reason, it is not recommended to perform fluorography more than once a year, while x-rays can be prescribed several times.
- The price of fluorography is lower than that of x-rays, so hospitals and clinics often prefer the first procedure.
- X-rays provide a more accurate picture of the development of the disease and are more informative when conducting a targeted study of a specific area.
X-ray of the chest organs
Chest X-ray (CH) is one of the most used studies; today it is one of the routine diagnostic methods. Previously, fluoroscopy was widely used, which allows assessing the condition of organs in real time. Currently, it continues to be used for some diseases.
The disadvantages of X-rays include the negative impact of ionizing radiation on the body. However, the radiation exposure of modern devices is not so great as to refuse this examination. The benefit of making a diagnosis is much greater than the potential harm.
But there are certain groups of people for whom it is undesirable to undergo chest x-rays. First of all, these are pregnant women. Radiation can negatively affect the fetus and cause developmental defects.
It is also not recommended to use this method frequently in children. Radiation causes the greatest harm to the developing organism. However, if there are indications - for example, if pneumonia is suspected - a chest x-ray can be performed on everyone without exception, subject to special protective measures.
The most common indications for referral for radiographic examination are diseases of the respiratory system, which are manifested by the following symptoms:
- cough;
- shortness of breath;
- fever;
- chest pain;
- hemoptysis;
- pronounced loss of body weight.
What can be seen in the picture with such manifestations?
Diseases diagnosed by chest X-ray
It is necessary to find out what a chest x-ray shows if there is a suspicion of lung disease. A large number of diseases occur without any symptoms at all, so a routine examination and questioning of the patient does not provide the necessary amount of information. Using an X-ray, it will be possible to examine all the structures of the lungs and identify the cause of the pathology, after which the doctor will be able to prescribe treatment.
It is an inflammatory disease characterized by significant disturbances in the breathing process. The disease requires quick diagnosis and timely treatment. If you do not know how often an adult can have an x-ray of the lungs in such a situation, it is worth finding out that no more than once a year.
Congestive heart failure
Failure is a complex failure in hemodynamics. Its cause is a dysfunction of the heart, which is provoked by overwork of the cardiomyocyte, as well as defects that are present from birth or acquired with age. A violation of this plan can be detected using a chest x-ray.
Pneumothorax
Such a deviation can be traumatic and spontaneous, as well as artificial. If the artificial type of disease is a consequence of treatment, then the traumatic and spontaneous type must be treated urgently. Plain radiography of the lungs allows you to diagnose the disease and assess its severity.
Pleural effusion
It is the accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity. The cause of the effusion allows us to determine its type - exudate or transudate. As a rule, it is not an independent disease, but a complication. It can appear due to pneumonia, congestive heart failure, tuberculosis, pulmonary embolism, as well as HIV infection and oncology. X-ray of the lungs is performed in a vertical position in frontal and lateral projections.
Cardiomegaly
X-ray of the chest organs
may be prescribed due to an increase in heart size. The following indicators are normal:
- 10-11 centimeters in length;
- 8-11 centimeters wide;
- 6-8.5 centimeters in thickness.
The disease can otherwise be called “bull heart” and is characterized by an increase in the size and weight of the organ due to an increase in the width of the muscle wall, as well as expansion of the chambers. This phenomenon is not always a sign of illness. For example, in people who are professionally involved in sports, it is natural and understandable, indicating the general endurance of the body. However, this can also be a manifestation of diseases, so a chest x-ray will be needed to identify the cause.
Pneumoperitoneum
This pathology means filling the abdominal cavity with gas. Finding out what an x-ray of the lungs shows is necessary in order to identify the cause of the disease and prescribe treatment that is adequate to the patient’s current condition. The disease is extremely serious; untimely treatment can become life-threatening and lead to various complications.
Emphysema
It is characterized by a chronic course and a disorder of normal gas exchange in the lungs. Occurs due to overstretching of the alveoli and their excessive filling with air. Emphysema is caused by chronic bronchitis, but it can also be caused by other lung diseases or heredity. To understand what caused the disease, you need to take a chest x-ray.
Types of diagnostics
In medical practice, X-rays have found application in the following diagnostic methods:
- Fluoroscopy is an examination method in which, in the past, the organs being examined were projected onto a screen coated with a fluorescent compound. In the process, it was possible to study the organ from different angles in dynamics. And thanks to modern digital processing, the finished video image is immediately obtained on the monitor or displayed on paper.
- Radiography is the main type of research. The patient is given a film with a fixed image of the examined organ or part of the body.
- X-ray and fluoroscopy with contrast. This type of diagnosis is indispensable when examining hollow organs and soft tissues.
- Fluorography is an examination with small-format X-ray images, which allow it to be used en masse during preventive examinations of the lungs.
- Computed tomography (CT) is a diagnostic method that allows a detailed study of the human body through a combination of X-rays and digital processing. Computer reconstruction of layer-by-layer X-ray images takes place. Of all the methods of radiation diagnostics, this is the most informative.
X-rays are used not only for diagnosis, but also for therapy. Radiation therapy is widely used in the treatment of cancer patients.
In case of emergency care, the patient is initially given a plain radiography.
The following types of X-ray examination are distinguished:
- spine and peripheral parts of the skeleton;
- chest;
- abdominal cavity;
- a detailed image of all teeth with jaws, adjacent parts of the facial skeleton;
- checking the patency of the fallopian tubes using x-rays;
- X-ray examination of the breast with a low dose of radiation;
- X-ray contrast examination of the stomach and duodenum;
- diagnosis of the gallbladder and ducts using contrast;
- examination of the colon with retrograde injection of a radiocontrast agent into it.
Abdominal x-rays are divided into plain x-rays and procedures performed with contrast. Fluoroscopy has been widely used to determine pathologies in the lung. X-ray examination of the spine, joints and other parts of the skeleton is a very popular diagnostic method.
Neurologists, traumatologists and orthopedists cannot give their patients an accurate diagnosis without using this type of examination. X-ray shows spinal hernia, scoliosis, various microtraumas, disorders of the osseous-ligamentous apparatus (pathologies of a healthy foot), fractures (of the wrist joint) and much more.
X-ray of the foot
The x-ray depends on the damaged area, but in any case the procedure will be quick and painless.
If it is necessary to take a picture of the foot, the patient will need to expose the foot and place it on a special stand.
To see foot abnormalities, it is necessary to take a weight-bearing X-ray, so the healthy leg must be bent at the knee - thus, the body weight is completely transferred to the other leg, at which time the doctor can take an image.
When taking a picture of the foot, the X-ray cassette should be positioned along the leg and clamped with a weight.
During the examination, the rest of the patient's body is covered with a special apron that protects from x-rays.
A photograph of the foot is always taken in several projections: first, the doctor removes its anterior-posterior part, then the dorsal-plantar, oblique (taken at different angles) and lateral.
This method allows you to examine the damaged area of the leg from all sides and make an accurate diagnosis.
Depending on the problem, the doctor will examine the foot in the image for cracks and inflammation, and if flat feet are suspected, he will be able to assess the length and degree of curvature.
X-ray algorithm
For patients preparing for the procedure, there is no need for special preparation, diet, or any other restrictions. The most important point prior to the examination is the study of existing contraindications.
X-rays are performed using special equipment - a wall-mounted box containing a film or matrix for recording the resulting images, and a tube located from the patient at a distance of up to 1.5 m (if the person is immobilized, it is hung directly above him). X-ray films or photographic plates are stored in a box hidden under the laboratory assistant's desk.
Diagnosis of the chest condition is carried out in a separate room, protected from the penetration of radioactive rays. In addition to stationary devices, the procedure is carried out using portable (portable) devices designed for examining patients who have been in a hospital bed for a long time.
Before taking the picture, the patient undresses to the waist and temporarily removes metal objects (jewelry, watches). If you have long hair, you will need to collect it. Next, you need to take a position in front of the shield located in the booth and press your chest against it. After the signal given by the laboratory assistant, you should take a deep breath and hold the air for a short period of time. You will be able to exhale after a few seconds, following the instructions of the healthcare professional.
X-rays of the lungs are performed in one or two projections. Most often it is done in an upright position. Examination in the lateral position is indicated if there are medical indications.
The entire X-ray procedure lasts no more than a minute. During the procedure, the patient does not experience any unpleasant sensations or discomfort. To decipher the results obtained, specialists need varying periods of time - from half an hour to several days.
The resulting x-ray contains information:
- About the condition of the organs of the respiratory system (bronchi, lungs, pleura).
- About the size of the lung fields, the structure of the lung tissue.
- About the features of the location, size of the heart, its parenchyma.
- About the condition of blood vessels and lymph nodes.
If the image has defects or is made in an incorrect projection, it is quite problematic to make a reliable conclusion about the patient’s condition. In this case, the decision to perform a repeat procedure should be made by a specialist.
In the presence of various pathologies, an x-ray will show changes occurring in the affected organ. Thus, in case of pneumonia, it is possible to detect the presence of intensive additional tissues. The presence of venous stagnation is indicated by a special basal shape, which is similar to the wings of a butterfly. With swelling of the lung tissue, the image shows unevenly spaced dark spots in the form of “flakes.”
X-ray of fingers
Unlike foot problems, which are difficult for the patient to ignore, a toe fracture can occur almost unnoticed, especially if there was no displacement or crack during the injury.
In this case, the pain goes away quite quickly, regardless of whether the thumb or any other finger was damaged.
However, lack of treatment can lead to serious complications: improper fusion and deformation of bones, osteomyelitis, or the appearance of a false joint.
Therefore, patients who suspect a finger fracture (see photo) should definitely consult a doctor and get an x-ray.
As in other cases, in case of such violations the whole procedure will take no more than 10 minutes: it will be much easier to examine the toe area than the foot, so a large number of pictures will not be needed.
The examination is carried out in a similar way: the patient will need to expose the leg and place it on a stand, after which the doctor will take an x-ray.
Please note that before the procedure it is necessary to remove all metal objects from the body: jewelry, piercings, etc., as they interfere with the operation of the device.
Unlike some other types of x-rays, no preparation is required to examine foot problems - you just need to show up at the x-ray office at the time specified by your doctor.
How often can you do it
As it turned out, there are no regulations or recommendations regarding the frequency of X-rays of the thoracic region or other parts of the body in the Ministry of Health. Radiation doses should be monitored by a radiologist and recorded in the patient’s outpatient record, but in practice few people do this. Although modern X-ray machines are equipped with built-in dosimeters that allow you to immediately determine the dose of radiation received.
It is believed that a patient receives such a small dose of millisieverts during an X-ray procedure that to develop radiation sickness he would have to undergo a thousand X-rays of the spine or 25,000 digital fluorographs at a time.
There is a MDA (maximum permissible dose) for X-ray room workers who are exposed to radiation when working with each patient - 50 mSv per year. Taking into account the figures stated above, we calculate that exposure to radiation for a second in two projections will “give” your body no more than 0.6 mSv, which is 83 times less than the traffic limit for radiologists. So the frequency of X-ray examination is determined by the doctor, based on the dynamics of the inflammatory process. That is, as many times as the doctor deems possible, it will be possible to “be enlightened.”
Advantages of the methods
When performing an X-ray, not only the patient, but also the people nearby receive a dose of radiation. During radiography, doctors are in an isolated room; equipment is installed in another room. This eliminates exposure of medical staff. Surveillance is carried out through special protective glass from another room.
The advantages of radiography include:
- the ability to visualize small details;
- long-term storage of images;
- minimum level of radiation;
If necessary, x-rays can be taken more than once. Sometimes this is required to monitor the condition after operations, to monitor lung diseases, the dynamics of the development of pathologies, etc.
Types of mammography
Mammography is not always done alone; there are several types that are radically different from each other:
- Traditional diagnostics. This diagnostic option is the oldest, and it is based on a film mammograph. Despite the fact that this option has already become traditional and classic, now it is better to give preference to alternative types of procedures, because with such an examination the radiation dose will be the highest, and the images have a relatively large percentage of error when compared with the same digital diagnostics.
- Digital mammography. This option is much more modern and has many advantages, for example, relatively small doses of training, as well as good quality, and therefore more informative images. Such images are very easy to analyze, so the risk of errors, especially if an experienced doctor is involved in decoding, is minimized. We also note that traditional diagnostics often require repeated examinations, but with digital diagnostics this can often be avoided.
- Electrical impedance mammography. Such diagnostics were developed more recently to study the structures of the mammary gland. The essence of this method is that healthy and altered tissues conduct current differently, so the same breast sarcoma will be clearly visible on the finished image. Such mammography is quite rare, and, as is clear from the description, it does not use ionizing radiation, that is, the previously described contraindications do not apply to it.
- Magnetic resonance examination. Probably everyone knows about the effectiveness of magnetic resonance imaging. Yes, such a procedure is extremely expensive, but it is completely safe and also does not involve the use of X-rays. Such diagnostics are as informative and accurate as possible.
Radiography and fluoroscopy - what are the differences?
X-ray diagnostics has long been an informative and simple method of examination. It is done for pathologies of internal organs and helps in making the correct diagnosis.
At first, only radiography was used. Then the technique was improved. This is how a new diagnostic method appeared - fluoroscopy.
X-ray results
Did you take an X-ray of your lungs? Let's look at what the transcript shows below:
- Diaphragm defects.
- The presence of fluid in the pleural cavity. A tumor or pleurisy is excluded.
- A cavity in the lung indicates necrosis of the lung tissue. Diagnose tuberculosis, cancer or abscess.
- Small focal darkening is a sign of pneumonia and tuberculosis. Large - tumor of the bronchi, metastases to the lungs.
- Small lesions that are very common are sarcoidosis or tuberculosis.
- A large, round shadow indicates advanced tuberculosis or a malignant neoplasm.
In addition to the above, other changes in the lung tissue and lungs are also detected, which help to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment. Unfortunately, there are cases of false results, or in cases where the study is carried out in the early stages of the disease, it may not be seen. For an accurate conclusion, in addition to the results obtained, other diagnostic methods are used in addition to X-rays, and the necessary laboratory tests are also carried out.
Causes of mediastinal expansion
On an x-ray, pathological changes in the mediastinum are detected in the form of darkening or the formation of a shadow of various shapes and localization. The expansion of the mediastinal shadow occurs against the background of the presence of provocative factors that trigger such pathological changes. These factors are quite diverse and are a consequence of many pathologies of internal organs located in the mediastinum.
Aortic aneurysm
This pathology is one of the most serious conditions. The diffuse form of aortic aneurysm is diagnosed without any particular difficulties. However, when it protrudes, resembling a bag in shape, certain difficulties arise in differentiating it from a tumor neoplasm.
Its main difference from a tumor is its characteristic pulsation, but this sign is not specific, since the pulsation in some cases is transmitted to the tumor.
A specific sign of a limited aortic aneurysm of the syphilitic type is the dilation of the vessel, traced along its entire length (Thoma-Kienbeck rule). As for syphilitic mesaortitis, there is no principle of accurately determining the cause of enlargement, due to the inability to obtain a reliable result using the Wasserman reaction.
The assumption about the risk of developing an aneurysm arises when aortic insufficiency is detected, which is a consequence of various types of syphilitic aneurysm.
The Oliver-Cardarelli method, used when there is pronounced dilatation in the area of the aortic arch or when it is detected in the area of the bronchial tree, reveals the descent of the trachea during pulse beats.
To obtain a more accurate diagnostic picture, in addition to the anterior one, a lateral radiograph is taken, which eliminates the possibility of error in making a diagnosis. Aortic aneurysm is determined with exceptional accuracy in the late stages of the pathological process. In this case, it cannot be confused with other disorders due to the appearance of characteristic outlines that appear on an x-ray in the region of the ribs and vertebrae, observed with the expansion of the mediastinal shadow.
Intrathoracic struma
A possible reason for the widening of the mediastinum may be the formation of an intrathoracic struma. This is a formation that appears above the collarbone. It pushes back and narrows the trachea. Displacement of the shadow is rarely detected by radiography, so other diagnostic techniques are often used to differentiate the struma.
Specialists obtain a more accurate representation of the intrathoracic struma when performing diagnostic procedures during swallowing. In this case, an expansion of the upper mediastinum is observed - the darkening moves upward.
Symptomatic manifestations specific to the intrathoracic struma rarely help to detect the development of a tumor of this type. Characteristic shortness of breath may be a sign of other pathological conditions. Therefore, to establish an accurate diagnosis, in addition to X-rays, they resort to using other methods.
Tumors
The cause of a mediastinal tumor is often lymphosarcoma. The pathology is accompanied by extremely expressive symptoms, leaving no doubt about the development of the tumor process. This:
- sharp acceleration of ROE;
- anemia developing at an early stage of the disease;
- stagnation in the blood circulation caused by varicose veins.
Even with such characteristic manifestations, a biopsy examination of the supraclavicular lymph node is required to establish an accurate diagnosis. Therefore, the biopsy method is used in all insufficiently clear diagnostic situations.
It is not possible to distinguish lymphosarcoma from lymphogranulomatosis using fluorography, radiography and fluoroscopy. The main difference in this case is the blood test indicators, which are characterized by typical changes specific to each disease. In addition, the general condition of the patient is characterized by a complicated course of clinical manifestations in lymphosarcoma. However, with the development of acute paraleukoblastic leukemia, diagnosing the disease presents certain difficulties.
Thyroid gland
Special manifestations of the shadow with characteristic sharp contours appear with hyperplasia of the thyroid gland. These expansions in the mediastinum are significantly smaller compared to changes in outline in a malignant tumor. Diagnosis of this pathological condition is facilitated by the paralytic manifestations characteristic of this disease. They are easily eliminated after taking prostigmine.
The thymus gland is a possible cause of mediastinal widening
Swelling abscess, phlegmon
The cause of mediastinal expansion is often a developing abscess or mediastinal phlegmon. The presence of mediastinal phlegmon is easily determined by the expressive clinical signs of the disease. This is a significant increase in the blood of leukocytes and pathologically altered neutrophils.
It is much more difficult to differentiate an abscess from a cancerous tumor. The diagnostic picture allows us to establish tuberculous spondylitis. Features of abscess tuberculosis are the occurrence of abscesses against the background of tuberculosis infection of the hilar lymph nodes. The clinical course of the pathological process can be either delayed or acute, with a high risk of spreading to nearby tissues. Their occurrence in young patients is often mistakenly classified as lymphogranulomatosis.
When performing a test biopsy of biomaterial from a lymph node using the Daniels method, an accurate diagnosis is established. In this case, the fact that lymphogranulomatosis is often observed in combination with tuberculosis is taken into account. However, such a complication of lymphogranulomatosis is characteristic only of an advanced form of the disease.
In rare cases, x-rays of the mediastinum show extensive bilateral opacities that simulate megaoesophagus. The condition is often accompanied by difficulty swallowing. But for diagnosing mediastinal darkening, the method of X-ray examination of the esophagus becomes decisive. It determines with 100% accuracy the cause of changes in the mediastinum.
Normal lung x-ray showing roots, ribs, heart
X-ray of the lungs is a summation display of the entire thickness of the anatomical objects of the chest. Before deciphering an x-ray, the radiologist evaluates its physical indicators:
- The correct positioning of the patient is based on the symmetrical arrangement of objects on both sides;
- Hardness or softness - normally, 3-4 upper thoracic vertebrae should be visible on a lung x-ray;
- Coverage of the chest cavity - a normal X-ray includes the apexes and diaphragm;
- Location of the heart.
For readers, the structures described above are of informational interest only, so we will focus on those structures that are mentioned in the description of the x-ray image.
The ribs are of interest to doctors from the point of view of assessing respiratory mobility. If a large amount of air accumulates in the lungs, the intercostal spaces are enlarged.
X-ray film shows the image in negative, so dark spots are represented in white and highlights are represented in black.
A normal photograph of the lungs necessarily contains all the structures described above.
What do lungs look like on an X-ray when infected with coronavirus?
The new virus has devastating effects on the lungs. The picture shows the respiratory system of a 44-year-old man who died from COVID-19. It is clearly visible how the disease progresses.
Along the periphery, an increase in the number of subpleural compactions of the “frosted glass” type can be seen; the lung tissue is filled with fluid more and more, ceasing to perform its functions.
Below is a photo of the lungs of a 54-year-old woman who contracted a coronavirus infection, which led to severe pneumonia. The patient required connection to an artificial lung ventilation device (ALV), and she could not breathe on her own.
The picture shows a similar picture:
- bilateral lung damage;
- increasing damage closer to the chest;
- pronounced “ground glass” syndrome;
- accumulation of a large amount of fluid that interferes with breathing.
X-rays of persons suspected of being infected with the COVID-19 coronavirus allow the disease to be identified more quickly and treatment to begin on time. This approach significantly increases the chances of recovery.
What kind of method is radiography?
X-ray examination is a fairly common diagnostic method based on the passage of X-rays emitted by special equipment through the body. A study using radiation makes it possible to obtain a black-and-white image in which the elements of the examined area will be clearly visible. Depending on the type of tissue and its density, darker or lighter elements will be visible in the X-ray image. Bone tissue appears white in the image, while softer muscle and ligament tissue appears dark, grayish or black.
On a note! X-rays were discovered by physicist V.K. X-ray and were named after him.
By studying the image, the doctor can see certain tissue changes, if any. Sometimes even minor disorders can be detected, which makes it possible to diagnose any disease at an early stage of development. The doctor will also see where the changes are localized and, in accordance with this, prescribe the appropriate treatment tactics.
Advantages of X-ray examination:
- simplicity and low cost of implementation - radiographic equipment is available in any clinic. In a municipal medical institution, you can take a photo free of charge according to your policy;
- high speed of obtaining results - the image can be collected in a few minutes;
- modern equipment makes it possible to obtain an image in digital format instead of a photograph on film;
- Most studies do not require any prior preparation.
Disadvantages of this diagnostic method:
- the negative impact of radiation on the body, so X-rays are often not allowed;
- the presence of a number of contraindications;
- inability to assess the condition of soft tissues;
- insufficient information content compared to a number of other methods.
Only the doctor interprets the images. He is the one who is able to notice even minor manifestations of the disease. But in some cases, an ordinary person can see the problem in the picture and understand what is wrong with his body. In the case of an X-ray of the spine, even the patient himself is able to discern scoliosis and fractures.
Is special preparation required for radiography?
Preliminary preparation is needed before examining the lumbosacral spine. It is aimed at reducing the amount of gases in the intestines and cleansing it of feces. Otherwise, gases may be visible on the images, and a full bowel will cause additional shadows to appear in the image, which overall will distort the result.
When answering the question of how to prepare for an x-ray of the spine, it should be noted that the patient must adhere to a slag-free diet for 3-4 days before the examination. The following should be excluded from the diet:
- sweets;
- bakery products;
- fatty meat and fish;
- cabbage and potatoes in any form;
- milk and fermented milk products with a high percentage of fat;
- legumes;
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- spices;
- tea and coffee;
- carbonated drinks;
- alcohol.
You can eat boiled chicken, beef, steamed fish, low-fat fermented milk products, dietary broths, boiled eggs, biscuits. Recommended drinks include herbal teas, freshly squeezed juices, dried fruit compotes, and water. Before the procedure you should not have dinner, and in the morning you should not have breakfast. Before meals you need to take enzyme medications, and after - activated carbon.
The second part of the preparatory process is an enema before an x-ray of the lumbosacral spine. It is worth doing it twice the day before the procedure - in the evening and in the morning. An alternative option is to take a laxative (for example, Duphalac, Flit or Fortrans).
Another requirement is to quit smoking a few days before diagnosis.
If the patient is in a state of nervous stress, you can drink valerian infusion (10 drops 3 times a day) for 3-4 days before the X-ray examination. Before an x-ray of the spine is taken, the patient is asked to remove all clothing and radiopaque objects (for example, a belt, neck jewelry) from the part of the body being examined.
How is an X-ray examination performed?
The patient, depending on the symptoms with which he came to the medical institution, is prescribed an examination of the entire spine or one of its parts.
X-ray of the cervical spine in 2 projections is indicated for headaches, ripples in the eyes, dizziness, pain when turning the head, neck injuries, and suspected infectious diseases of the bone tissue. To obtain images in frontal and lateral projections, the patient is asked to lie on the table, then stand up. Pictures of the first, second and third vertebrae are taken through an open mouth (transoral radiograph).
An X-ray of the thoracic spine in two projections (lateral and direct) is prescribed if this area has been injured or the patient complains of discomfort in the chest, pain when turning the body and bending over. Occasionally, an oblique view may be taken if the front and side views do not show any abnormalities and do not allow the doctor to make a diagnosis. To obtain an oblique image, the x-ray technician himself determines the optimal position and helps the patient take it.
When answering the question of how an X-ray of the lumbar spine is taken, it should also be noted that most often two projections are sufficient to make a diagnosis - direct and lateral. In some cases, the patient is asked to bend his legs while lying on his side to obtain the required images. The procedure is prescribed for curvature of the spine, suspicion of the patient having bone tumors, pain in the back and lower back, and periodic numbness of the lower extremities.
X-rays of the sacroiliac joint are performed for injuries, pain in the lower back and coccyx, oncological and inflammatory processes, and pathologies of the intervertebral discs. Sacroiliitis is very important in the diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and rheumatological pathology. The basic projections of images are frontal and lateral. Sometimes, to make a diagnosis, it becomes necessary to obtain images in the flexed and extended positions of the patient.
On average, an X-ray examination of different parts of the spine takes from 15 to 20 minutes.
Indications for the study
X-ray examination is divided into 2 types: preventive and diagnostic. The first is prescribed to all women who have reached the age of 35, and if there is a genetic predisposition to cancer, the threshold is reduced to 30 years. It is better to have a mammogram of the mammary glands from this age for the reason that when a girl or woman is still young, her breasts are more dense. The results of the study may be unreliable.
Absolute readings
In some situations, x-ray examination is mandatory. Otherwise, there is a high risk of missing malignant tumors that are beginning to develop, including cancer.
Seals in the thickness of the mammary gland
The doctor usually determines this deviation from the norm during a palpation examination. The woman herself can detect it by doing a breast self-examination. Since lumps may indicate the development of a tumor, even in the absence of other frightening symptoms, you should immediately undergo an examination.
Various discharge from the nipple, its deformation
Preparation for mammography of the mammary glands will also be required in the case of nipple discharge. The liquid may be clear, yellowish or pinkish. Bloody and purulent discharge should be especially alarming - they often indicate a malignant neoplasm.
Breast pain, swelling, increase or decrease in size
Painful sensations are associated with purulent inflammation, benign and malignant tumors, and sometimes with neurological and cardiovascular diseases. To confirm the diagnosis, a mammogram of the mammary glands is done before giving a final answer.
Swelling or retraction of any part of the breast
The reason for the change in breast shape, if it is not age-related deformations or the period after pregnancy and lactation, may be in the diseases already identified earlier. In this and all of the above cases, mammograms should be done as often as your doctor requires.
Relative readings
Having understood what mammography is, how this study is done and when it is necessary, it would be correct to move on to the list of diagnoses for which X-ray diagnostics are not necessary, but desirable. The decision in this case is made jointly by the doctor and the patient.
Mastopathy
The study allows you to: make sure that the cyst is benign, determine the volume of the tumor, and the likelihood of surgical intervention.
Obesity
This condition provokes not only diseases of the heart and blood vessels, as well as the musculoskeletal system, but can become a prerequisite for breast cancer.
Inflammatory diseases (mastitis)
X-ray diagnostics is done if the doctor cannot palpate the cause of pain and enlargement of the mammary gland or suspects mastitis, but needs to confirm the diagnosis.
Infertility
X-ray of the mammary glands in this case is of a preventive nature, since women suffering from infertility are more susceptible to cancer.
Contraindications to X-rays
X-ray is a safe procedure, so it is done even for children, but there are a number of contraindications for which it is undesirable to perform this procedure.
Pregnancy is a complete contraindication to x-rays, since radiation, although safe for the mother, can nevertheless harm the development of the fetus, especially in the first trimester.
The patient's serious condition and immobility also complicate certain types of x-rays, for example, of the foot, which must be done under stress in order to detect a number of pathologies.
The presence of open wounds or bleeding on the leg can also complicate the examination, since in this case the image will not be able to show some pathologies.
X-rays are not recommended for young children and people with severe mental disabilities, but for serious indications the procedure can still be performed.
In some cases, for example, if it is necessary to obtain an image of the knee joint, X-rays can be replaced with MRI, which is considered safer and can be prescribed even to pregnant women.
However, in most cases, an x-ray will be more rational, because this procedure is faster, simpler and cheaper than an MRI.
No one doubts the effectiveness of using x-rays today; it makes it possible to establish the presence of almost any pathology of the legs, in particular fractures and cracks in the bones, problems in the functioning of the joints, neoplasms, arthritis, arthrosis and many other problems, therefore, in case of any negative symptoms, it is advisable to contact see a doctor and undergo this examination.