Leukocytes, or white blood cells, are the most striking marker of the health of the human body. Not a single comprehensive examination is complete without a general blood test (CBC), the results of which are of interest to the doctor almost in the first place.
This action is completely justified, since if leukocytes in the blood are elevated, then in the vast majority of cases a disease of an inflammatory, infectious, allergic or oncological nature develops.
Features and role of leukocytes
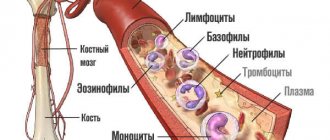
These cells occupy one of the important places in the blood composition and are a heterogeneous group. Leukocytes are distinguished by their irregular round shape, have a nucleus and size 6–20 microns. The very name of these cells can be said to be conditional, since upon closer examination they are not white, but a light pink-violet hue. The main place of production of leukocytes is the bone marrow, which coordinates their sufficient and timely formation.
Reference! The main function of white blood cells is to provide immunity, that is, to protect the body from pathogens and toxic substances. Thanks to their abilities, a person manages to avoid many diseases and various pathological processes.
When pathogens enter the body, the number of white cells rapidly increases to provide resistance and destroy them. Therefore, elevated leukocytes in the blood are a good reason to consult a specialist to find out the reason for such an increase.
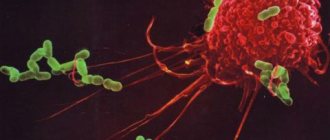
The protective mechanism is as follows: when a foreign object enters the body, it attracts many leukocytes that are able to penetrate through the capillary walls and perform their function. When they encounter a pathogen, they surround it and gradually consume it.
The inflammatory process caused by the actions of white cells can be of varying intensity, which directly depends on the activity and size of the ingested agent. At the same time, all the characteristic signs of inflammation occur: fever, swelling, redness of the skin near the injection site, etc.
In the process of eliminating the threat, white blood cells die in large numbers and come out in the form of pus, which is essentially a collection of dead white cells. This mechanism is called phagocytosis. It can be observed most clearly when a splinter gets under the skin.
Redness appears first, followed by suppuration. If the sliver is small, then the white cells will quickly deal with it themselves, gradually destroying it and bringing it out along with the pus. When the foreign object is larger, you will have to resort to the help of a surgeon, who will remove the splinter and clean the wound from purulent accumulations.
Allergy
This is the main cause of eosinophilic leukocytosis.
Entry of an allergen into the body causes IgE-mediated degranulation of mast cells with the release of mediators of allergic inflammation - leukotrienes, histamine, etc.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UuyyEn-WN40
One of the main functions of eosinophils is to suppress the production of inflammatory mediators, so any allergic reaction is accompanied by an increase in the level of eosinophils.
The maximum level of eosinophilia is achieved at the time of exacerbation of the allergic reaction, then it gradually decreases as symptoms regress and returns to normal levels during the remission stage.
In most allergic diseases (bronchial asthma, rhinoconjunctivitis), moderate leukocytosis is observed.
Only with the development of systemic reactions (Stevens-Jones syndrome, DRESS syndrome) can high leukocytosis occur.
Types and functions of cells
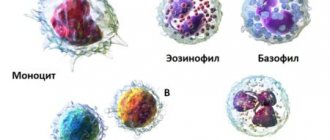
An increase in the content of leukocytes is noted both in general and by their individual types. The leukocyte formula includes several types of white blood cells: neutrophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes, basophils and monocytes, which differ in structure and number, as well as in the functions they perform.
Their specifics are as follows:
- neutrophils - eliminate bacterial infection that has entered the blood;
- lymphocytes – provide immune memory and a defense mechanism in general;
- monocytes - absorb particles of foreign objects in the blood;
- eosinophils - destroy allergenic agents;
- basophils - help other leukocytes find harmful objects.
All leukocytes are very dynamic and mobile, which allows them to carry out their duties. They quickly detect foreign objects, absorb them and, as mentioned earlier, die.
To replace spent leukocytes, new ones are constantly produced in larger quantities, which leads to an increase in their indicator in a blood test. A condition characterized by a high content of white cells is called leukocytosis, and it indicates a fairly wide range of pathologies.
Leukocyte percentage
Diagnostics
Leukocytosis is detected during a clinical blood test. Since there are many reasons for an increase in white blood cell levels, you should first consult a general practitioner.
The doctor collects a detailed medical history, conducts a physical examination of the patient, including measuring body temperature, examining the skin and mucous membranes, etc.
Based on the data obtained, in order to confirm the disease that caused leukocytosis, the following studies are prescribed:
- Blood tests. Markers of inflammation are determined in the blood - high ESR and CRP, autoantibodies (rheumatoid factor, ACCP, antibodies to the cytoplasm of neutrophils). The leukocyte formula (percentage of leukocyte forms) must be calculated. A blood smear is examined for the presence of toxic granularity of neutrophils, atypical mononuclear cells, and Botkin-Gumprecht shadows. If a septic condition is suspected, presepsin is measured.
- Pathogen detection. To identify the infectious pathogen as the cause of leukocytosis, bacterial culture of blood, sputum, and urine is performed. The enzyme immunoassay method detects antibodies (class G and M immunoglobulins) to bacteria, viruses, helminths, and their DNA is detected using the polymerase chain reaction.
- Allergy diagnostics. In order to confirm the allergic nature of the disease, the level of immunoglobulin E (IgE) is measured using the ELISA method. To identify the causative allergen, basophil tests and various allergological tests are performed - skin (scarification, patch, prick tests), provocative (nasal, inhalation, conjunctival).
- Radiography. In case of pneumonia, chest x-rays show infiltrates in the lungs, foci of darkening; x-rays of joints in patients with arthritis show narrowing of the joint space, osteoporosis, and bone erosion. With osteomyelitis, x-rays of bones reveal thickening of the periosteum and sequestration foci (areas of bone necrosis).
- Ultrasound. With pyelonephritis, an ultrasound examination of the kidney reveals an increase in the size of the kidneys, expansion and thickening of the pyelocaliceal system. Infectious mononucleosis is characterized by hepatosplenomegaly. Echocardiography may show vegetations on the valves and effusion into the pericardial cavity.
- Histological studies. If leukemia is suspected, a trephine biopsy or sternal puncture is performed, the material of which reveals hyperplasia of the granulocytic lineage and a large number of blast cells. To diagnose lymphomas, an aspiration biopsy of an enlarged lymph node is performed; the biopsy specimen reveals lymphocytic hypercellularity, collagen proliferation, and Berezovsky-Sternberg giant cells.
Signs of leukocytosis
A condition in which there is an increased number of leukocytes does not have specific, that is, symptoms inherent only to it, since it is not an independent disease. That is why its manifestations are based on the symptoms of the pathology that caused the increase in white cells. Such signs may include:
- feeling of constant fatigue;
- causeless general weakness;
- excessive sweating (especially at night);
- slight increase in body temperature;
- presyncope (fear of losing consciousness);
- dizziness and fainting (most often short-term);
- the appearance of bruises and bruises in the absence of injuries;
- pain in the abdominal cavity and limbs;
- loss of appetite and body weight, problems with respiratory function;
- noticeable visual disturbances.
Reference! Exceeding the white blood cell count is a dangerous condition that should never be left without due attention. This means that you need to visit a doctor as soon as possible and find out from him what to do in such a situation.
In all likelihood, after the consultation, the patient will be given a full examination, the results of which will reveal the reasons for the increase in the coefficient.
Why is the rate increasing?
An elevated white blood cell count does not always necessarily indicate the presence of a disease. Their number can increase in an absolutely healthy person after:
- intense physical activity (data from many studies confirm the fact that playing sports increases the content of leukocytes);
- excessive consumption of spicy and fatty foods;
- strong psycho-emotional experiences;
- prolonged exposure to the sun, in a sauna or in rooms with high temperatures (for example, a hot shop);
- smoking and long-term therapy with certain medications.
This increase in white cell levels is physiological. Its difference lies in the fact that the components of the leukocyte formula are slightly increased (in adults, approximately 11–12 * 109/l) and grow simultaneously in the same proportions. If the level rises to 15–17 * 109/l or more, then this most likely means the development of the disease, and such leukocytosis is called pathological.
It comes in two types: reactive (benign) and leukocytosis in leukemia, a rapid malignant disease that develops in the organs of the hematopoietic system. Reactive leukocytosis occurs due to certain pathologies, which include:
- Inflammatory processes of the respiratory system - pneumonia, bronchitis, usually accompanied by cough and fever.
- Allergies are very common causes of leukocytosis in the blood. Many irritants can lead to them, and the likelihood of developing this pathology is directly related to the quality of immunity.
- Autoimmune diseases caused by failures in the implementation of the protective function. With them, the immune system perceives the body's own cells as foreign and destroys them.
- Burns and frostbite of large areas, which leads to loss of skin barrier function.
- Abdominal operations and injuries with extensive tissue damage.
- Purulent infections - peritonitis, abscess, sepsis.
- Diabetes mellitus and diabetic coma.
- Pathologies of the digestive system.
- Infestation with parasites.
- Heart attack.
Causes of physiological leukocytosis
An increase in the level of benign white cells or reactive leukocytosis is most often short-lived and eliminated after treatment of the underlying disease. Whereas an increase in values in leukemia is extremely dangerous, and in most cases there is no treatment or it takes a very long time to be treated.
Reference! Depending on how the leukocyte count increases, doctors can determine the severity of the patient’s condition.
Leukocytes are not the only parameter that changes during leukemia; in parallel, red blood cells drop significantly, and ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) increases. The last coefficient can reach, and even much exceed, the figure of 20, and this is also one of the indisputable signs of the presence of pathology. These three changed CBC indicators will immediately make the doctor think about a serious illness.
Preparing for analysis
Material is collected from the patient for this analysis in the morning on an empty stomach.
It is recommended to start preparing for this type of study 1-2 days before the test. To do this, the patient should follow these recommendations:
- Eat food no later than 8-10 hours before the test.
- The day before the test, refrain from smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Limit physical, mental and emotional stress as much as possible.
- 1-2 days before the test, refrain from eating fried, spicy, fatty foods high in carbohydrates. Consumption of concentrated juices, coffee and strong tea is also undesirable.
- Do not use hormonal contraception.
- Do not take antibiotics or antibacterial medications.
- It is strictly forbidden to perform radiography and fluorography immediately before the examination!
- Refrain from physiotherapeutic procedures and instrumental examinations on the eve of the test.
- On the morning of the test, drink only still water. However, if you are shown a serological blood test, then it is better to refuse water or limit the amount of liquid consumed as much as possible.
Compliance with the above recommendations will ensure that you obtain extremely accurate test results.
Types of leukocytosis
The results of a detailed blood test include information on each type of leukocyte, which makes it easier for doctors to make a diagnosis. Taking into account their features, you can immediately search in a specific direction. Based on this, leukocytosis is divided into the following types.
Neutrophilic - characterized by a sharp increase in the number of cells of the same name, which, in turn, are divided into rod (young) and segmented (mature). The shift occurs due to the development of an acute long-term inflammatory process, bacterial infection, significant blood loss and intoxication of the body.
With these pathologies, both the so-called rods in the blood and mature neutrophils increase, since the former are intensively produced, and then their intensive maturation occurs. Increased leukocytosis of this type is observed with the appearance of malignant pathologies of the bone marrow, but such cases have been recorded quite rarely in medical practice.
Eosinophilic - also indicates the development of inflammation, but most often the growth of this variety is due to allergies, not excluding a reaction to certain medications. Basophilic – noted in diseases of the spleen, thyroid gland and digestive organs.
Lymphocytic – characteristic of severe infections, for example, tuberculosis and hepatitis. This variety is also greatly increased in measles, rubella and chickenpox. Monocytic - occurs during the recovery stage after severe infectious diseases. Often observed in patients undergoing long-term therapy for tuberculosis. Quite rare, but still happens in cancer patients.
Systemic diseases
Leukocytosis is often caused by chronic systemic inflammatory processes. The exact pathogenetic mechanisms of the increase in leukocytes in these pathologies are still unknown. It is assumed that mediators and cytokines produced during rheumatic inflammation stimulate the production of leukocytes in the bone marrow. This mainly concerns the following rheumatic diseases:
In arthritis and diffuse connective tissue diseases, leukocytosis is usually moderate. In systemic vasculitis with necrotizing inflammation in the vascular wall, leukocytosis can reach high numbers.
Increased rate in children
Leukocytosis in infants and slightly older children may not manifest itself in any way. It is diagnosed only by the results of a blood test. If, according to the examination materials, an increase in values was recorded in a newborn who is only a few days old, then he is diagnosed with congenital leukemia.
This condition is usually observed in cases of serious developmental disorders in infants: Down's disease, body defects, heart defects, and is a fairly rare pathology. The number of white cells in the blood of a baby over one year old can increase, just like in an adult, for physiological reasons:
- improper or unbalanced diet;
- excessive physical activity for the child’s body;
- psycho-emotional overstrain and stress.
Parents are obliged to be attentive to the health of their child and not subject him to unnecessary everyday and social difficulties. In addition, they must monitor the diet and quality of food, and also save the baby from unpleasant worries. Parental attention is especially important for teenagers who experience many negative moments due to hormonal changes.
The main pathological causes of high levels of leukocytes in children include leukemia and infectious diseases. Moreover, if these cells are slightly enlarged, then, in all likelihood, the developing disease is mild or moderate, whereas with very large growth, as a rule, the pathology is very serious and life-threatening. For example, with sepsis, leukocytes can reach a value of 100*109/l and higher.
Study of blood gas composition
Since acute bronchitis can provoke bronchial obstruction, another study is a blood gas analysis. The ratio of oxygen and carbon dioxide, as well as the acid-base balance, should indicate how severe the disease is. The testing procedure is painful because a puncture or catheterization of the artery is performed.
Obstructive bronchitis manifests itself in the following:
- Carbon dioxide – partial pressure above 35-45 mm. rt. Art.
- Oxygen – partial pressure below 80-100 mm. rt. Art.
- Decreased oxygen content and oxygen saturation. Normally they are 15-23% and 94-100%.
Oxygen therapy is prescribed if the partial pressure is clearly reduced, as are volumetric content and oxygen saturation. During a fever or when taking medications, gas levels may increase.
In adults
The reasons for the increase in white cells in adults are largely due to their gender differences.
Among women
What causes an increase in leukocytes in the fairer sex is, in most cases, normal physiology. This is the premenstrual period, pregnancy and consequences after childbirth (regular or cesarean section). Each of these situations is a significant burden on the body. Especially when carrying a child.
Pregnancy requires the mobilization of all capabilities, internal resources and hidden reserves of the body. In women during this period, the immune system works in enhanced mode, forcing the bone marrow to produce additional numbers of leukocytes.
At the same time, their ratio in the leukocyte formula does not change. An increase in the concentration of white cells is also directly related to hormonal changes, strong emotional changes or stress, since the expectant mother’s resistance to them decreases. In addition, physiological leukocytosis often occurs against the background of severe toxicosis.
By the end of the 3rd trimester, the number of these cells increases, and they concentrate in the uterus. In this way, the body prepares to protect the child who will be born in the near future. Physiological factors for increasing the level of leukocytes in non-pregnant women include regular bathing with hot water, visiting baths and saunas.
The most common causes of pathological elevation are:
- infectious diseases of various nature;
- injuries: bruises, fractures, internal injuries;
- anemia and excessive blood loss;
- cardiac ischemia;
- extensive burns.
In men
Increased neutrophils in the blood
The causes of pathological leukocytosis in men in most cases are:
- inflammatory diseases localized in the pelvis: prostate gland, seminal vesicles, bladder and rectum;
- kidney pathologies;
- diabetes;
- neoplasms.
Physiological growth factors for leukocytes include:
- playing sports and heavy professional activities associated with physical effort;
- prolonged and uncontrolled use of medications;
- irregular and poor quality nutrition.
In addition to all of the above, removal of the spleen leads to leukocytosis in both women and men.