For the treatment of many serious gynecological diseases or their diagnosis, the laparoscopic method is used. Menstruation after ovarian laparoscopy occurs in each woman depending on her individual characteristics. To prevent early complications, it is necessary to monitor changes in the body and possible menstrual irregularities that may appear after surgery. Laparoscopy rarely leads to adverse consequences, but if abnormalities are detected, consultation with a specialist is required.
Laparoscopy as a surgical treatment and diagnostic method of research
Laparoscopy is a modern, minimally invasive surgical method. Laparoscopic surgery is in great demand in gynecology for ovarian diseases. It can be used to:
- resection (removal of part of the ovary);
- adnexectomy (removal of the entire organ);
- ovarian cystectomy (husking of the cyst while preserving the organ).
Such operations are used to treat cysts, polycystic diseases, and other types of formations. Laparoscopy allows you to diagnose, identify the presence of the disease, and also take a biopsy.
Ovarian laparoscopy is a surgical operation that requires scrupulousness and attentiveness from the surgeon. Removal of pathological formations must be done using special medical equipment, and the integrity of the healthy part of the ovary must not be damaged.
What is laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is the main method of surgical intervention. The procedure is performed using a laparoscope. Manipulation happens:
- medicinal;
- diagnostic.
If necessary, a section of tissue may be taken during the procedure for further study. This is usually required if a malignant process is suspected. It is possible to examine the abdominal cavity and small pelvis.
During the intervention, an organ or part of it may be removed. Before the procedure, the doctor administers painkillers, so laparoscopy does not cause significant discomfort to the patient.
The advantages of the procedure include:
- minimum incision size;
- neatness of postoperative scars, which are almost invisible;
- speed of recovery;
Using special equipment allows you to make small incisions
- reducing the length of stay in a medical institution;
- reduced risk of infection;
- reduced risk of complications.
Laparoscopy is used not only in gynecology.
Laparoscopy during menstruation
It is strictly forbidden to perform laparoscopic intervention during endometrial desquamation (period of menstrual bleeding), because the woman’s coagulogram values change. Which means decreased blood clotting. During surgical procedures, due to damage to blood vessels, blood loss is inevitable. Therefore, in order to prevent large blood loss, against the background of such a physiological state, this procedure is unacceptable.
When is laparoscopy done during menstruation?
Most patients are concerned about the question of whether laparoscopy can be done during menstruation. In the absence of indications for emergency intervention, manipulations are not performed during menstruation. This is due to a violation of the blood clotting process and a high probability of sudden bleeding. However, to clarify the diagnosis in complex clinical cases, as well as for vital signs, the procedure can be performed during menstruation. Immediate surgery occurs when:
- rupture or torsion of an ovarian cyst;
- in case of acute appendicitis;
- with ectopic tubal pregnancy;
- if adhesive intestinal obstruction is diagnosed.
Changes in the menstrual cycle and the effect of laparoscopy on the female body
Each female body reacts differently to such an operation. There are cases when the procedure leads to the restoration of menstruation, in other cases no changes are observed. It all depends on the location of the operation.
On the first postoperative day, bleeding appears, the duration of which normally lasts two or three days. Further, the discharge takes on a yellow tint. In the absence of pain, the natural process is a shift, a delay in the menstrual cycle and heavy periods.
Cycle offset
According to experts, the first day of menstruation is the day of the operation. Most often, menstruation begins as during a woman’s normal cycle. The nature of the discharge is bloody and mucous, without obvious changes. Their duration can be from two to three weeks, which is a completely normal process. But if the discharge becomes green or brown, with an unpleasant odor, accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, then this is the beginning of inflammation or infection.
Delayed menstruation
If your menstrual cycle is delayed by two or three weeks, then there is no need to worry, as the cycle will recover and stabilize over time. The reason for this violation is the emotional overstrain of the patient before the operation itself, or after exposure to anesthesia. After laparoscopy of the ovaries and fallopian tubes, periods may not appear for a long period of time.
Heavy discharge during menstruation
Healing of a damaged ovary takes much longer than the skin. Therefore, heavy, bright periods without signs of inflammation, during the first menstruation after surgery, are not a violation.
If heavy periods are prolonged, this indicates internal bleeding. In this case, a visit to the doctor is necessary!
Menstrual irregularities as a result of laparoscopic surgery
After laparoscopy, a delay in menstruation is possible, and heavy menstruation and its atypical characteristics are sometimes observed. Changes in the cycle will depend on the specifics of the gynecological operation. This may include:
- removal of tumors or cysts;
- stimulation of ovulation in polycystic disease;
- infertility treatment;
- elimination of the adhesive process;
- extraction of endometriosis foci;
- permanent or temporary sterilization;
- fibroids in the presence of bloody discharge;
- treatment of the initial stage of uterine cancer.
The intervention may include partial removal of the uterus. If necessary, it is possible to remove the tumor along with the problem area of the tissue of the reproductive organ. There are also cases when the uterus or ovaries are completely removed. The complexity of the manipulation determines how much the menstrual cycle will be changed.
Menstruation after removal of formations
When tumors appear on the ovaries and female pathologies, laparoscopy is prescribed in most cases to reduce the risk of infertility or increase the chances of pregnancy. Thanks to this operation it is possible to treat:
- cystic formation;
- ovarian endometriosis;
- polycystic disease;
- adhesions and other pathological formations.
Treatment of endometriosis
Endometriosis is a disease that is diagnosed and treated by laparoscopy. After treating this pathology with this particular method, a feeling of pain and bleeding may appear, which women mistake for menstruation. If such symptoms are detected, the specialist will prescribe conservative treatment that will restore hormonal levels.
Treatment of other types of formations
Menstruation after surgery to remove an ovarian cyst or treatment of polycystic disease, with prescribed hormonal therapy, is restored and comes on time. If their appearance does not occur in the near future, the woman is recommended to conceive a child. This recommendation is used to prevent the formation of new cystic formations and to reduce the risk of relapse of adhesions.
On what day of the cycle is laparoscopy performed?
When planning laparoscopy, it is necessary to decide when is the best time to perform the operation. The exact date is selected depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle. For ovarian cysts, it is best to plan surgical intervention for the period after ovulation.
If it is necessary to check the patency of the fallopian tubes, then the operation is prescribed for the period before ovulation. This will eliminate the possibility of pregnancy.
If there are indications for emergency intervention, the surgeon will not focus on the day of the menstrual cycle. Laparoscopy is performed immediately after the patient is admitted to the hospital.
Is laparoscopy done during menstruation?
During menstruation, elective surgeries are not performed. During menstruation, blood clotting in women is impaired, so the risk of bleeding increases. If such a complication occurs, there is a possibility that the surgeon will be forced to make an incision in the anterior abdominal wall and completely remove the uterus in order to save the patient’s life.
Performing laparoscopy during menstruation is associated with the risk of developing an infectious and inflammatory process. If there are no indications for emergency surgery, then surgery is not performed during menstruation, it is postponed.
Laparoscopy during menstruation can be performed provided that the woman was admitted to the hospital with suspected one of the following diagnoses:
- cyst rupture;
- twisting of the pedicle of the cystic formation;
- ovarian apoplexy;
- development of a purulent-inflammatory process in the appendages.
If emergency intervention is necessary, the doctor focuses only on the patient’s hemodynamic parameters and test results.
On what day of the cycle is it best to do laparoscopy?
Planned laparoscopy is best performed after ovulation has completed. In phase 2, it is recommended to do diagnostic and treatment laparoscopy for infertility of unknown origin, cysts and polycystic ovary syndrome.
With a standard cycle lasting 28 days, the optimal period for its implementation is considered to be 15-24 days. It is better not to plan laparoscopy for the last days of the cycle.
For scheduled therapeutic and diagnostic laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes, day 5-7 of the cycle is selected. During this period, the functioning of the blood coagulation system is normalized, and the body will have enough time to recover before the start of the next menstruation.
Cycle disorders after laparoscopy
The main sign of normalization of the functions of the reproductive system is healthy menstruation that meets the norms. But not always and not all women, after such a minimally invasive method as laparoscopy, have normal menstruation. The cycle may be disrupted or completely absent. You should know the etiology of the disorder and the measures necessary for amenorrhea (absence).
Etiology of disorders
The causes of violations depend on the work done by the surgeon and his professionalism. The characteristics of the female body also play an important role:
- age;
- hormonal background;
- health status.
Features of restoring the menstrual cycle after the procedure
Each human body is individual. There are different reactions to any intervention, including laparoscopic surgery. This also applies to the restoration of the menstrual cycle. There is no clear standard. Some patients began menstruation immediately after laparoscopy, others recover over a long period of time. Most often during the recovery period the following manifestations are observed:
- Heavy or painful periods after laparoscopy;
- Prolonged absence of menstruation;
- Pathological vaginal discharge;
- Changing the timing of the cycle or its duration.
In most patients, such problems disappear over time, and the body returns to normal. You should not panic, these are features of postoperative recovery, you need to see a doctor and follow his recommendations. The time it takes to normalize the cycle also depends on the qualifications of the surgeon. Menstruation comes quickly after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, if the doctor was able to cut off the tumor with minimal damage to the organ tissue. Extensive cuts lead to hormonal changes that affect the condition of the female body and hormonal levels.
The effect of hysteroscopy on the menstrual cycle
When examining the female organs from the inside using hysteroscopy, various pathologies can be diagnosed and immediately removed. After examining and examining the woman’s genital organs, without damaging the membranes, the menstrual cycle will remain unchanged. If the purpose of hysteroscopy is the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome, then after hormonal therapy menstruation will be restored.
To treat endometrial hyperplasia of the uterus, surgical hysteroscopy is prescribed. After this, bleeding may occur, which should not be confused with the onset of menstruation.
The reasons for missing periods are not always related to the laparoscopic procedure. Menstruation is a complex process in the female body. Factors and disruptions in the body lead to shifts, delays, absence, and other changes in this process. We must not forget that treatment prescribed by a gynecologist will help to properly restore and even out the menstrual cycle.
What side effects may occur after the examination?
The most common side effect after laparoscopy is delayed menstruation. Other complications appear only if the manipulation was carried out incorrectly and serious mistakes were made. In this case, a woman may experience the following symptoms:
- swelling;
- vein damage;
- damage to internal organs.
After laparoscopy, blood may be released, which has nothing to do with menstruation. In this case, the woman discovers a bloody smear on her underwear.
The absence of menstruation is not always associated precisely with interference in the body’s performance. Sometimes the delay is the result of the stress that the woman experienced during the manipulation. If your period has completely disappeared, then this is normal, but only if the ovaries are completely removed.
The procedure is best performed on days 7-8 of the cycle. Manipulation should only be carried out by experienced specialists.
After the intervention, the woman feels significant weakness. Performance decreases and there is obvious drowsiness. There may be no appetite at first. All of these symptoms are normal and will soon disappear on their own.
Watch this video if you want to know how to recover after your period:
Possible complications
As mentioned above, laparoscopy, like any other surgical intervention, can be accompanied by complications. Among them, the most common are:
- Development of adhesive processes.
- The occurrence of inflammation in the organs of the reproductive system.
- Opening of bleeding.
- Menstrual irregularities (this complication occurs especially often during ovarian surgery).
- Infection.
Signs of complications developing after laparoscopy are the following conditions:
- Discharge of clots of dried blood.
- Temperature increase >38 degrees.
- Weakness.
- Sharp cramping pain in the abdomen.
- The presence of a specific odor from the intimate area.
- Discharge of pus.
If at least one of these symptoms appears on the second or third day after the operation, a re-examination is required. If the development of complications is confirmed, the woman will need to undergo another course of treatment, which will avoid serious consequences.
The effect of laparoscopy on menstruation
Doctors prescribe such an operation almost at the beginning of the cycle, that is, after the next menstrual flow. In this case, the operation without complications will not affect the cycle in any way, and menstruation will proceed as scheduled.
But after the procedure, the nature of menstruation may change, and therefore many women mistake heavy menstruation for bleeding. In addition, a delay in menstruation is also possible, but in such a situation it is better to consult a doctor, because the absence of menstruation may indicate an unsuccessful operation or a hormonal imbalance.
It must be remembered that the speed of the recovery period after laparoscopy will largely depend on the patient herself. Of course, this method involves minimal intervention in the woman’s body, but even here complications may arise, the presence of which may be indicated by one or another vaginal secretion.
6 minutes Author: Lyubov Dobretsova 33797
Many women suffer from genital diseases. The consequences of such pathologies lead to infertility and other dangerous complications. In most cases, doctors have to resort to surgical intervention to save women from illnesses that bring physical and mental torment.
Thanks to the achievements of modern medicine and its evolution from abdominal operations to minimally invasive methods, most women were spared the inconvenience and lengthy recovery period. These techniques include laparoscopy (examination and surgery in the abdominal or pelvic area).
After laparoscopy, brown discharge instead of menstruation
Today, the medical industry has fundamentally new technologies for surgical interventions.
One of these achievements of modern science is laparoscopy - a safe, low-traumatic and short-term operation that does not require a long recovery period.
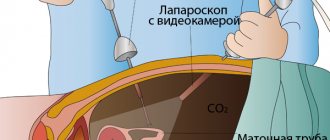
Laparoscopic interventions are carried out using probes that are equipped with a camera and special lighting that allows you to examine all the details of the operated area. They are inserted through small (no more than two centimeters) incisions on the skin.
This surgical technique is widely used in gynecology - after such an operation there are no noticeable cosmetic defects left on the skin of the abdomen, moreover, rehabilitation proceeds quickly and without any serious complications. In some cases, after laparoscopy, women note the appearance of discharge - this can be either a natural phenomenon or a sign of a pathological process.
In our article we want to talk about the specifics of laparoscopic surgery, the rules of preparation for the procedure, the characteristics of the rehabilitation period of the female body and explain whether brown discharge after laparoscopy is a pathology.
Practicing gynecologists use this minimally invasive diagnostic and surgical technique much more often than other medical specialists. Indications for laparoscopic and hysteroscopy (a method of examining the cervix and uterine cavity) are:
- endometriosis – growth of the endometrium (inner layer of the uterine walls);
- fibroids are benign neoplasms that form in the myometrium (muscular layer of the uterus);
- torsion of a benign ovarian tumor (cyst) or its rupture;
- ovarian apoplexy - a sudden violation of the integrity of its tissues;
- anomalies of the anatomical structure of the genital organs and malformations of their development;
- infertility;
- ectopic pregnancy - when the attachment of a fertilized egg can occur in the peritoneum, fallopian tube, cervix or ovary;
- initial stages of the malignant process.
Thanks to the capabilities of laparoscopy, the treatment of many pathologies of the female reproductive system has become much more successful.
Before any planned operation, the patient is pre-examined. After a conversation with a medical specialist and a physical examination by a gynecologist, the woman undergoes:
- general clinical urine and blood tests;
- biochemical blood test;
- coagulogram - assessment of coagulation system factors;
- determination of blood group and rhesus affiliation;
- fluorography;
- electrocardiogram;
- Ultrasound;
- serological tests for the presence of antibodies to HIV, syphilis, and hepatitis viruses.
The duration of recovery of the female body depends on the extent of the surgical intervention performed (for example, removal of an ovarian cyst requires rehabilitation of about 5 days).
After laparoscopy, patients note a feeling of discomfort in the abdomen.
This phenomenon is associated with the technique of manipulation - to increase the space for intervention, carbon dioxide is injected into the abdominal cavity.
With low-traumatic laparoscopy, a woman’s body recovers much faster than after exploratory laparotomy, a surgical operation in which the abdominal wall is cut to access the internal organs. Limiting physical activity and following the advice of your doctor speeds up recovery.
Within three weeks after surgery, there is a slight, transparent discharge from the vagina, with a slight splash of blood. This phenomenon is normal and should not cause any concern to a woman - it is associated with the healing of damaged tissue.
During this time, the patient must carefully comply with all personal hygiene requirements and refrain from intimate contact. Intense bleeding (especially with blood clots) is considered pathological - this is a signal of internal bleeding.
Leucorrhoea that is brown or yellow-green in color and has an unpleasant odor indicates a bacterial infection. White discharge, accompanied by itching and burning, may indicate candidiasis (or thrush) - the presence of yeast-like fungi Candida Albicans in the genital tract.
In the postoperative period, a woman takes antibacterial drugs that weaken the immune system - this provokes the active proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. Also very often, women notice changes in the menstrual cycle. In all of the above cases, the patient should contact the attending physician, who will take immediate action.
The following complications may develop after laparoscopy:
- adhesions;
- bleeding;
- inflammatory process;
- pathological discharge.
Laparoscopy is considered a safe and low-traumatic method of surgical treatment, which is why complete recovery of the female body occurs in no more than two weeks.
For many, menstrual function does not change; surgery is always scheduled on the eighth day of the monthly cycle, and by the beginning of the next menstruation, the woman’s body has time to fully resume its physical activity.
Isolation of exfoliated endometrium with blood from the vagina indicates rapid rehabilitation or a hormonal imbalance. As a rule, a small amount of discharge should not cause any concern.
As a rule, the first menstruation after surgery is very heavy and pronounced - this phenomenon is explained by the slow healing of internal organs.
There are other menstrual dysfunctions that are considered normal:
- "Shift" of the monthly cycle. The day of laparoscopy is considered the beginning of a new period; in this case, bleeding occurs after a certain period.
- The discharge of mucous-bloody leucorrhoea is noted immediately after surgical manipulation and lasts approximately 21 days. Their appearance should not be regarded as an alarming signal. If they have an unpleasant odor, you need to contact a laboratory center and have a smear from the genital tract analyzed.
- Long delay - it can be caused by psycho-emotional stress or the effect of anesthesia. The absence of discharge may be a consequence of a violation of the integrity of the tissues of the female reproductive glands (ovaries). If, during a delay in menstruation, a woman experiences abdominal pain and notices the release of blood clots, she must seek medical help, do an ultrasound and undergo tests.
In addition, it should be remembered that monthly bleeding is controlled by complex biochemical processes occurring in a woman’s body, taking into account the physiological and nervous system - the functional activity of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. Failure of the menstrual cycle can be associated not only with medical procedures, but also with any disorder in the female body. Only a qualified doctor can find and eliminate the cause of the absence of menstruation.
The first month after laparoscopy, the patient needs to limit sports activities and any physical activity - returning to the usual rhythm should occur gradually. Intimate life can be resumed 2 weeks after surgery.
Surgical intervention using the laparoscopic method is prescribed for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes in case of pathological processes accompanying infertility - fallopian tube adhesions, endometriosis, cysts, fibroids, polycystic ovary syndrome, etc. The successful completion of the recovery period indicates that it is already possible to plan the birth child.
When treating infertility, not only surgical but also conservative treatment is used - the use of medications that affect the functional activity of the female reproductive system.
That is why it is necessary to plan the birth of a baby after consultation with a practicing obstetrician-gynecologist, who has studied the patient’s medical history in detail.
If laparoscopy is successful, pregnancy planning can begin within a few months.
Side effects of this safe procedure are minimized. However, in addition to the appearance of pathological discharge, a woman may experience other symptoms:
- temperature increase;
- general weakness and fatigue;
- loss of consciousness;
- decreased appetite;
- bloating;
- frequent urge to empty the bladder;
- nausea, even vomiting;
- increased pain in the abdomen;
- swelling and hyperemia of suture areas;
- bleeding from wounds;
- pneumonia;
- stroke.
To relieve pain, painkillers are prescribed; medications containing Simethicone can eliminate flatulence.
At the end of all the above information, I would like to add that in order to avoid all the unpleasant manifestations of the postoperative period, the patient must follow all the recommendations of the attending physician.
In addition, approach the choice of a medical institution and specialist who will perform laparoscopy with all responsibility. And if all the rules of the rehabilitation period are followed, the woman will quickly return to her previous shape and active life without consequences for her health.
source
If you did not find the information you need among the answers to this question, or your problem is slightly different from the one presented, try asking an additional question to the doctor on the same page, if it is on the topic of the main question.
You can also ask a new question, and after a while our doctors will answer it. It's free. You can also search for the information you need in similar questions on this page or through the site search page.
We will be very grateful if you recommend us to your friends on social networks.
Medical portal 03online.com
provides medical consultations via correspondence with doctors on the website. Here you get answers from real practitioners in your field.
Currently, on the site you can get advice in 48 areas: allergist, anesthesiologist-resuscitator, venereologist, gastroenterologist, hematologist, geneticist, gynecologist, homeopath, dermatologist, pediatric gynecologist, pediatric neurologist, pediatric urologist, pediatric surgeon, pediatric endocrinologist, nutritionist, immunologist a , infectious disease specialist, cardiologist, cosmetologist, speech therapist, ENT specialist, mammologist, medical lawyer, narcologist, neurologist, neurosurgeon, nephrologist, oncologist, oncourologist, orthopedist-traumatologist, ophthalmologist, pediatrician, plastic surgeon, proctologist, psychiatrist, psychologist, pulmonologist, rheumatologist, radiologist , sexologist-andrologist, dentist, urologist, pharmacist, herbalist, phlebologist, surgeon, endocrinologist.
We answer 96.6% of questions.
source
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical method that is used in various medical fields, including gynecology.
In the latter case, such an operation is used to remove tumors in the uterine cavity and ovaries, terminate an ectopic pregnancy, treat endometriosis, etc.
Despite the fact that this procedure is considered minimally invasive, it still causes damage to the mucous membranes of the reproductive system, and therefore bloody discharge after laparoscopy is completely natural.
But do not forget that laparoscopy is an operation, after which various complications can also arise. And here it is very important to know in which cases vaginal discharge indicates a normal course of recovery processes, and when it is complicated.
The laparoscopic method of surgical intervention in gynecology is used for:
- The development of an ectopic pregnancy (when the fertilized egg attaches to the fallopian tube and not to the uterus).
- Torsion of adnexal cysts.
- Cyst rupture.
- Polycystic disease.
- Apoplexy of the ovary.
- Uterine fibroids.
- Fibromatous node of the uterus and its torsion.
- Endometriosis.
- Infertility due to tubal obstruction.
- The appearance of polyps and other neoplasms in the uterine cavity that can degenerate into cancer.
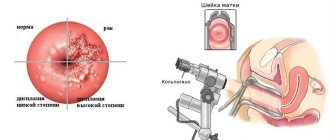
It should be noted that laparoscopy is used not only as a therapeutic therapy for certain diseases, but also for their diagnosis. This operation is performed if it is necessary to take tissue for biopsy or histological examination.
In some cases, laparoscopy is used both as a therapeutic and diagnostic method. For example, when acute abdominal syndrome occurs, accompanied by severe pain in the abdominal cavity, arising against the background of various pathologies of internal organs, injuries and effusion in the pelvis.
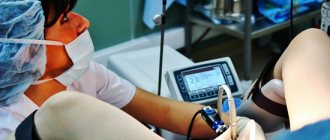
Laparoscopy is performed in a hospital setting under general anesthesia. If the operation is minor and takes place on the organs of the reproductive system, then all manipulations are carried out through the vagina.
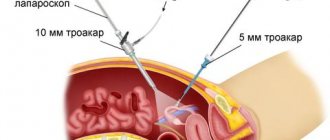
If more serious measures are required, for example, removing a cyst or opening the lumen of the fallopian tubes, then access to the affected organs is obtained by puncturing the abdominal wall in several places, into which all the necessary instruments are then inserted.
Surgery is performed using a special optical device that displays an image on a computer monitor, allowing doctors to monitor the progress of the operation. Once all the necessary measures have been completed, small sutures are placed at the puncture sites.
The operation itself is minimally invasive, and therefore recovery occurs in a very short time. However, despite this, the risks of complications after it remain, and therefore, in order to prevent them, an examination must be carried out before surgery, which includes:
- Gynecological examination.
- Ultrasound of the reproductive organs.
- Biochemical analysis of urine and blood.
- Coagulogram.
- Analysis to identify blood group and Rh factor.
- Tests for STDs.
- Fluorography.
Source: https://folkmap.ru/mesyachnye/posle-laparoskopii-vmesto-mesyachnyh-korichnevye-vydeleniya/
Pathological secretion after laparoscopy
Some types of vaginal discharge should alert a woman and cause a quick visit to the attending physician:
Yellow secretion
Dark green, yellow-green discharge indicates infection in the body. This could happen during the procedure or unprotected sexual intercourse, which, by the way, is prohibited in the first month after the operation. Additional symptoms of infection are considered to be general weakness, malaise, high body temperature, systematic headaches, and pain in the lumbar region.
White curds
Such secretion can appear while taking antibiotics, which create optimal conditions for the proliferation of fungi. Also, this discharge may be bloody and accompanied by itching and burning.
Brown discharge
Let us immediately note that they may be normal (indicate residual bleeding), but there should not be a lot of them, and an unpleasant pungent odor should not be allowed. In other cases, secretion of a similar color may be associated with infection or a complication after surgery.
In all these cases, it is better to undergo additional diagnostics (ultrasound of the fallopian tubes, various smears, routine gynecological examination).
When will the discharge disappear and the cycle will be restored?
The following complications may develop after laparoscopy:
- adhesions;
- bleeding;
- inflammatory process;
- pathological discharge.
After surgery for an ectopic pregnancy, women complain of bleeding that continues for a week.
Laparoscopy is considered a safe and low-traumatic method of surgical treatment, which is why complete recovery of the female body occurs in no more than two weeks. For many, menstrual function does not change; surgery is always scheduled on the eighth day of the monthly cycle, and by the beginning of the next menstruation, the woman’s body has time to fully resume its physical activity. Isolation of exfoliated endometrium with blood from the vagina indicates rapid rehabilitation or a hormonal imbalance. As a rule, a small amount of discharge should not cause any concern.
If the frequency of the menstrual cycle is not restored within three months, gynecologists assume a hormonal disorder and offer the patient the use of replacement therapy
As a rule, the first menstruation after surgery is very heavy and pronounced - this phenomenon is explained by the slow healing of internal organs.
There are other menstrual dysfunctions that are considered normal:
- "Shift" of the monthly cycle. The day of laparoscopy is considered the beginning of a new period; in this case, bleeding occurs after a certain period.
- The discharge of mucous-bloody leucorrhoea is noted immediately after surgical manipulation and lasts approximately 21 days. Their appearance should not be regarded as an alarming signal. If they have an unpleasant odor, you need to contact a laboratory center and have a smear from the genital tract analyzed.
- Long delay - it can be caused by psycho-emotional stress or the effect of anesthesia. The absence of discharge may be a consequence of a violation of the integrity of the tissues of the female reproductive glands (ovaries). If, during a delay in menstruation, a woman experiences abdominal pain and notices the release of blood clots, she must seek medical help, do an ultrasound and undergo tests.
In addition, it should be remembered that monthly bleeding is controlled by complex biochemical processes occurring in a woman’s body, taking into account the physiological and nervous system - the functional activity of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. Failure of the menstrual cycle can be associated not only with medical procedures, but also with any disorder in the female body. Only a qualified doctor can find and eliminate the cause of the absence of menstruation.