How MRI works
MRI works based on the principle of nuclear magnetic resonance. Its essence lies in the fact that the electromagnetic field that is present in the tomograph is capable of capturing the energy emanating from the nuclei of atoms. The computer, in turn, displays this energy and captures it in the form of an image.
Hydrogen nuclei have the highest concentration in the human body. It is on capturing the difference in their concentrations and the energy emitted by them that the construction of images of internal organs and tissues on a computer is based.
A special feature of MRI is that bone tissue is not displayed on the image, which allows you to carefully examine the structure of soft tissues. This is why MRI of hand joints has become so widespread. You can clearly see damage to any component of the joint, and the bones will not interfere with this.
Patient actions after MRI
After completing the procedure, the radiologist issues a description with which you need to go to a specialist. Which one exactly - you can see in the conclusion. This could be a surgeon, oncologist or rheumatologist.
If necessary, the attending physician will prescribe additional tests, make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment. If the patient is a candidate for surgery, an MRI will help track the recovery period.
The procedure for tomography of the wrist and hand is widespread in Western countries. Basically, the procedure is carried out in open machines so as not to expose patients to stress. In Russia, this examination is carried out both in public and private clinics.
When is an MRI necessary?
The traditional method for diagnosing hand pathology is an X-ray examination. However, this diagnostic method allows you to see only a violation of the structure of bone tissue, while joints and cartilage are left without attention. When should you get an MRI of the hand?
- Prolonged pain in the joints of the hand.
- Damage to hand muscles.
- Impaired movement in the wrist joint.
- Pinched nerves of the hand.
- For the diagnosis of arthritis, gout, osteomyelitis.
- Suspicion of the presence of a purulent inflammatory process of the soft tissues of the hand - phlegmon.
- Presence of neoplasms on the hand.
- Clinical signs of carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Lack of effectiveness of treatment measures that were carried out previously.
- When planning a surgical intervention and after it is carried out - to assess the effectiveness of the operation.
Indications for diagnosis
Scanning hands and joints using MRI is considered an effective non-invasive method, which is also absolutely harmless and painless. Most often, this procedure is prescribed to patients who have already undergone X-rays, ultrasound of joints, and computed tomography, but it was not possible to accurately determine the diagnosis.
MRI of the wrist and hand is prescribed in the following cases:
- Before and after surgery. The need for the procedure is due to the fact that the doctor evaluates the condition of the bones before the intervention and the result after the operation.
- For limb injuries (fractures, cracks, dislocations).
- For inflammatory joint diseases - arthritis, arthrosis, osteomyelitis and gout.
- If there is a suspicion of a tumor process. The specialist evaluates the development of metastases.
- Pinched tendons and nerves, including carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Pain of unknown origin with limited mobility of the limb.
Currently, the MRI procedure is becoming the most popular, as it differs significantly from other types of diagnostics.
For example, a computed tomography scan shows all the small bones in the hand, but does not evaluate the ligamentous-tendon system.
What can you see with an MRI?
In terms of diagnostic value, MRI of the wrist and hand is second only to arthroscopy. The latter is a surgical procedure in which the surgeon, using a special device, inserts a camera into the joint cavity and examines its structure. But this diagnostic method requires damage to the integrity of the skin, so you must first do an MRI.
What does an MRI of the hand show?
- Injuries to the hand and forearm.
- Inflammation of the tendons and tissues surrounding the joint – tenosynovitis.
- Rupture of hand tendons.
- Inflammatory processes in the joints: infectious in nature and autoimmune in nature (with rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus).
- Deposition of uric acid crystals in joints due to gout.
- Softening of tissues in osteoporosis.
- The presence of tumors in the tissues of the hand.
- Congenital abnormalities of joint structure.
- Impaired blood flow in the tissues of the hand.
What will a CT scan show?
Bone structures are best visualized on a CT image of the hand, since they are the densest and do not transmit x-ray radiation. To clarify soft tissue pathologies, a computed tomography scan of the hand with intravenous contrast is performed.
Diseases that can be detected using a CT scan of the hand and wrist are presented in the table:
| Disease | What can be seen on a CT scan of the hand |
| Arthritis is an inflammatory disease of the joint of an infectious or autoimmune (rheumatic) nature. | · CT scan of the hand allows you to determine the stage of inflammatory changes by the expansion or narrowing of the joint space. · In case of autoimmune damage, it is necessary to compare the CT findings of the hand on the right and left hand - the damage must be symmetrical. · Contrast-enhanced computed tomography confirms the severity of the process with the accumulation of pharmaceuticals in the area of the affected joints. |
| Arthrosis is destructive changes in the wrist joints associated with the natural processes of aging or metabolic disorders. | When comparing CT scans of the right and left hands, the presence of symmetry of the process is revealed. Based on the diagnostic results, the degree of the disease is determined (depending on the severity of the narrowing of the joint space, decalcification of the articular surfaces of the bones, the formation of osteophytes and ankylosis of the joints). |
| Osteoporosis is a destructive disease of the wrist bones due to aging. | On a CT scan of the hand, there are areas of clearing in places of greatest fragility of the bone structures. |
| Traumatic injury is damage to structures as a result of physical impact. | CT images of the hand visualize cracks, fractures, dislocations and subluxations of joints, of which there are up to 30 in the anatomical region. |
| Tumor-like formations. | Computed tomography of the hand allows for differential diagnosis of oncological lesions of bone structures. |
Osteoporotic changes are best diagnosed using CT densitometry. The study allows you to obtain spatial images of the spongy and cortical layers and determine the density of bone tissue. Based on the results, the degree of metabolic disorders and the risks of developing pathological fractures are revealed. The technique is recommended as a screening method for patients over 65 years of age.
The advantage of computed tomography of the hand over the usual x-ray is the reliability of the results and a more accurate determination of the affected area in case of fractures, bone destruction, and joint pathologies. For soft tissue lesions, the study is not very informative and is used if there are contraindications to MRI.
The price of a CT scan of the hand in St. Petersburg is about 3-4 thousand rubles. The cost of a CT scan of the hand in and “Medicine of the Northern Capital” is from 2,450 rubles. Photos on photo paper are paid separately (300 rubles). If necessary, it is possible to restore diagnostic data, since all results are stored in the archives of diagnostic centers.
Computer tomogram of the hand.
When is contrast needed?
MRI of the hand with contrast is a more informative method compared to classical MRI diagnostics. In this case, the drug “Gadolinium” is used, which is absolutely safe for the body. Before administering this substance, it is necessary to conduct a skin test to exclude the presence of allergies in the patient.
Contrast is necessary for rapid staining of blood vessels. It is mainly used when a tumor process is suspected, since in the area where the tumor appears, the blood supply is increased, so the contrast agent actively accumulates. It accurately shows the extent of tissue damage. This is especially valuable when planning surgery and monitoring its effectiveness.
MRI or CT: what to choose
Since magnetic resonance imaging is a highly accurate, but quite expensive study, it is often prescribed when radiography, ultrasound and computed tomography are insufficiently informative.
Each method has its pros and cons:
- X-ray is the cheapest method of examination and allows you to obtain information about the condition of the bone structure. Its disadvantage is the radiation exposure to the body;
- CT is also accompanied by radiation exposure, but unlike X-rays, it creates an image of the area under study in different projections. Computed tomography is usually ordered when abnormalities in bones and cartilage are suspected;
- Ultrasound, on the contrary, can only diagnose soft tissue pathologies. It is absolutely safe and painless, so it can be performed even on newborns. Ultrasound diagnostics are affordable. But despite all its advantages, it is not able to detect diseases of bones and joints.
Since there is no universal diagnostic method, in each case the rheumatologist or surgeon selects the technique individually, based on the patient’s complaints and the characteristic symptomatic picture.
Preparing for an MRI
To obtain more accurate results when performing a magnetic resonance imaging scan, you must adhere to a number of rules.
For example, you need to wear the right clothes. It should not contain any metal accessories: buttons, plaques, fasteners. It is also necessary to remove all jewelry.
If a person is extremely agitated and worried about a future examination, the doctor may prescribe sedatives (valerian infusion) or stronger tranquilizers.
Must remember! The use of sedative medications is possible only with the permission of a doctor.
Equipment for MRI of the hand
For magnetic resonance imaging of the hands, devices with an open chamber are increasingly used. This is especially true for people suffering from claustrophobia or panic attacks. In addition, tomographs differ in the strength of the magnetic field. You should not save on your own health and take pictures with devices with a voltage of less than 1 Tesla, since the pictures will not be informative enough. For early diagnosis, 1.1-1.5 Tesla devices are sufficient. You can see what type of tomographs the clinic you choose uses on the website.
Preparing for an MRI with contrast
If an MRI is performed with contrast, that is, contrast is administered intravenously, you must follow a diet before the examination. The patient should refrain from eating at least 10 hours before the MRI of the arm joints, as the contrast may cause nausea and vomiting.
If the patient is allergic to the contrast agent, he should notify the doctor about this. In cases where the patient does not know whether he has an allergy, an allergy test is performed before the examination. To do this, the doctor injects the patient with a small amount of contrast subcutaneously, and then observes the reaction of the skin. If there are any signs of allergy (redness, itching, rash), you must refuse to administer the contrast or replace it with another substance.
Contrast is also contraindicated in diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract, since in these conditions it is difficult to remove the dye from the body. If the patient has any dysfunction of the urinary system, he should notify the doctor about this.
Preparation rules
Advance preparation for the procedure is not necessary, but you need to remember some features.
It is important to inspect your wardrobe and choose clothes that are free from metal structures. To do this, you should avoid wearing clothes with zippers, buttons, rivets and other metal accessories, as they distort the results of the study and cause damage to the device.
If this rule is ignored, the patient will be offered disposable medical underwear. Before starting the study, it is necessary to warn the diagnostician about possible pregnancy or diseases that could interfere with the procedure.
These include severe forms of parkinsonism, choreoathetosis with involuntary movements of the limbs, claustrophobia (fear of being in closed spaces).
If tomography with contrast is performed, despite the hypoallergenicity, it is worth warning the doctor about hypersensitivity to the components of the drug or about previous cases of allergic reactions to medications.
When using contrast, the last meal to avoid nausea and vomiting is recommended at least 3-4 hours before the start of the procedure.
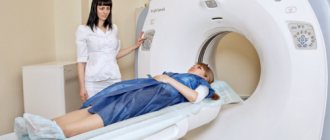
How is an MRI of the hand done?
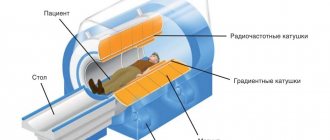
In order to see in detail all the soft tissues of the hand, a special device is used - a tomograph. The patient is placed on the tomograph table. His head, arms and legs are firmly fixed to the table. This is a necessary step to eliminate the slightest movements, as they degrade the image quality.
Next, the table slides into the tomograph, the patient’s hand is scanned, and the image is displayed on the operator’s computer. The tomograph ring rotates next to the hand, emitting a barely audible crackling sound. As a rule, the whole process takes no more than half an hour.
Magnetic resonance imaging with the introduction of contrast takes a little longer. After an allergy test, contrast is injected through a catheter into a peripheral vein. “Gadolinium” stains the vascular system of the entire body, which allows you to see tumor-like formations in the hand and accurately assess the extent of the damage. If there is oncology, the blood supply to the corresponding area of the hand will be increased.
The introduction of contrast when performing MRI increases the cost and duration of the examination by 2 times, but the informativeness of the diagnosis also increases.
After an MRI, the radiologist takes some time to decipher the results. At the end, the patient receives images and a detailed description of the diagnostician.
Important! The radiologist cannot make a final diagnosis, he only describes what he saw.
The clinical diagnosis must be made by the attending physician based on the patient’s complaints, medical history and, in fact, MRI results.
The patient can immediately return to his usual activities after the examination; there are no restrictions on further activities.
Is it possible to do a CT scan of the hand for children?
The use of radiographic techniques in childhood is limited, since radiation disrupts cell division and can lead to the formation of pathological changes.
In the centers of St. Petersburg, CT scans of the hand are allowed under strict indications with a doctor’s referral for children over 5 years old in the presence of parents. Diagnosis is possible only if the child is aware of what is happening and can withstand the time necessary for the study. The duration of the procedure is about 10 minutes, during which the patient must lie completely still in a confined space, accompanied by a characteristic knocking sound with which the emitter tubes move, otherwise the diagnosis will be useless.
Contraindications for MRI
MRI of the hand is not permitted in the following cases:
- pregnancy;
- age up to 7 years;
- the presence of metal objects in the body: pacemakers, prosthetic joints and limbs, insulin pumps, prosthetic heart valves, dental crowns, clips on blood vessels. Moreover, the presence of titanium plates and plastic dental crowns is not a contraindication;
- presence of mental illness;
- with hyperkinesis - a condition in which involuntary movements occur in various parts of the body;
- for claustrophobia - fear of closed spaces, with the exception of open-type tomographs;
- impossibility of transportation to the MRI room.
Severe renal or heart failure is a contraindication to contrast administration.
Children under 7 years of age are allowed to have a magnetic resonance imaging scan only if there are strict indications, when the expected benefit outweighs the possible harm.
Indications and contraindications for the study
The main indications for CT scanning of the hand are:
- various injuries to the area of the wrist joint, metacarpus, fingers - blows, dislocations, fractures;
- inflammation of the joints of a given anatomical region;
- discomfort, pain, limitation of movements in the wrist area;
- the presence of tumor-like formations located in the joint area or dense growths (the soft tissue component is better visualized on SCT or with contrast enhancement);
- control of prescribed treatment - to check the effectiveness of fracture healing, after therapy for degenerative diseases, oncopathology.
Computed tomography of the hand is contraindicated in pregnant women, as X-ray exposure can cause mutations in the fetus. During the lactation period, it is also recommended to refrain from CT scanning of the hand. According to the indications, the study is allowed, but after that it is necessary to express milk twice, and the child is briefly transferred to artificial feeding.
Due to the technical characteristics of the equipment, patient parameters such as a weight of more than 150 kg and abdominal and chest volumes of more than 150 cm are limitations for the study.
Advance preparation is carried out for a CT scan of the hand with contrast - a light snack 30-40 minutes before the procedure to prevent adverse autonomic reactions. Diagnosis with contrast is allowed only after determining the blood creatinine level. If the normal value is exceeded, CT with pharmaceutical enhancement is contraindicated, since the substance after intravenous administration is excreted by the kidneys, the functional state of which is reflected by this analysis.
Benefits of MRI
One of the undoubted advantages of diagnosing hand pathology using MRI is its high accuracy. Also, MRI of the hand for joint disease has a number of other advantages:
- complete absence of radiation exposure;
- the ability to obtain images of tissue covered by bones;
- better display of pathology by obtaining images in different planes;
- this is the only diagnostic method that is informative for damage to nerve tissue: with its help you can accurately see the location, type and level of nerve damage;
- informative when planning surgical intervention, as it accurately shows all the structures of the hand;
- Gadolinium contrast is safe and rarely causes allergic reactions;
- immediately after diagnosis, the patient can return to his business: there is no need for further observation in the hospital.
Using Contrast
Contrast MRI of the hand is intended to identify the degree of oncopathology, determine the size, location and nature of the tumor. To do this, gadolinium is injected into a vein, which is quickly distributed throughout the vascular network of the entire body. The tumor and metastases are visualized in the images as light spots.
The substance is toxic, but is excreted from the body immediately after examination along with urine. Therefore, the patient can immediately return to his usual activities: go to work, get behind the wheel. In rare cases, an allergy to metal is detected; to rule it out, an allergy test is performed before the MRI. Contrast is prohibited for pregnant women, children under 6 years of age, and patients with renal and heart failure.
Disadvantages of MRI
In addition to its undoubted advantages, MRI of the hand, like any other diagnostic method, has a number of disadvantages:
- it cannot be performed by people with foreign metal bodies;
- in the presence of hemorrhages in the tissue of the hand, a computed tomogram is more informative;
- the need to remain motionless for half an hour also limits its use in a certain group of people.
The risks to the patient are extremely low, but they do occur.
First, there is always the possibility of an anaphylactic reaction to the contrast agent.
Secondly, if the doctor ignores the presence of metal objects in the patient or forgets to ask whether he has them, it is possible not only to distort the final results, but also to damage the device.
Breastfeeding mothers should stop breastfeeding for several days after an MRI with contrast, as it can pass into the baby's body through breast milk.
Contraindications and restrictions
When carrying out the procedure, you must follow all the doctor’s recommendations, then the examination will be safe and easy. But in some cases MRI is contraindicated or has special limitations. It is prohibited to conduct research in the following cases:
- Pregnancy at any stage and lactation. When breastfeeding, when a decision has been made to undergo an MRI, milk should not be given to the baby for 24 hours.
- Children's age up to 6 years. The examination requires complete immobility during the examination, and children cannot lie still. In rare cases, when there is an urgent need, an MRI is performed on children under general anesthesia.
- People with metal objects in the body - pacemakers, metal valves, prostheses, vascular clips, platinum prostheses, hearing aids, etc. Insert implants made of ceramics and plastic are not contraindications for examination.
- Patients who do not control their body movements (hyperkinesis).
- People whose weight exceeds 120 kg.
- For claustrophobia (exception: MRI in an open tomograph).
- In case of an allergic reaction to a contrast agent, heart or kidney failure.
- Mentally unbalanced people. In severe cases, patients are given sedatives.
Before agreeing to a magnetic resonance imaging scan, you should tell your doctor about all your features.
Where can I get an MRI of the hand?
There are many private diagnostic centers where you can get an MRI. Prices for MRI in Moscow range from 4,000 rubles. up to 8,000 rub. Below is a list of such centers:
- “MRT Tushino” – Voloklamskoe highway, 95;
- "European Diagnostic Center" - st. Nagatinskaya, 1;
- “Kuntsevsky Treatment and Rehabilitation Center” – st. Partizanskaya, 41;
- “MRT-Center” – Kurkinsoke highway, 30;
- "RAMSI Diagnostics" - st. Malaya Pirogovskaya, 13; st. Krasnoproletarskaya, 16;
- "MRT 24" - st. Ordzhonikidze, 11; st. Kalanchevskaya, 17.
Thus, MRI of the hand is an informative and highly accurate examination that allows you to find out almost any reason for the violation of the structure and function of the upper limb.
Stages of the survey
MRI of the wrist is performed using a special device - a tomograph. This device consists of a retractable table and a chamber. The patient is placed on the table, while the limb itself is securely fixed. Subsequently, this will help to avoid receiving low-quality images, which often happens. Then the table automatically moves inside the device.
The tomograph ring continuously rotates near the part of the arm being examined, creating a resonant flow. It can make a cracking sound without causing harm or discomfort to the patient inside. The entire MRI procedure takes no more than 30 minutes. If a contrast agent is used, it takes longer. After the scan is completed, the doctor begins to decipher the results. During the procedure, the tomograph takes many pictures of the limb. Now the specialist needs to combine the images in a three-dimensional projection.
What does an MRI of the hand joints show?
Rare nosologies are determined clinically. MRI scanning allows us to establish the etiology of atypical diseases.
MRI of the hands allows us to identify rare nosological forms:
- De Quervain's disease;
- Styloiditis (inflammation of the styloid process of the ulna);
- Carpal tunnel syndrome;
- Arthrosis and arthritis of the joints of the beam;
With De Quervain's disease, there is a clinical manifestation of pain in the area of the wrist joint, which intensifies with movement of the thumb. The cause of the symptoms is inflammation of the ligaments with fixation to the styloid process.
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs due to a pinched nerve within the fibrous tunnel formed by the tendon fibers of the palmar surface of the hand.
Post-traumatic arthrosis of the wrist joint occurs rarely. The main cause of the disease is a hand injury with a fracture of the wrist bones.
Types of wrist tunnel arthritis:
- Rheumatoid;
- Gouty;
- Specific (tuberculosis, syphilitic, chlamydia);
- Nonspecific (purulent, serous).
Nonspecific inflammation of the joints affects the upper and lower extremities, so MRI of the legs and knees is rational.
Timely diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome and De Quervain's disease helps prevent the irreversible development of nosologies through competent treatment.