- Indications for tubal HSG
- Preparation for the procedure and procedure for its implementation
- Contraindications for the study
HSG (hysterosalpingography) of the fallopian tubes is a diagnostic research method that consists of conducting an X-ray examination of the fallopian tubes for patency. The main indication for the procedure is difficulties in conceiving or carrying a pregnancy (frequent miscarriages, ectopic pregnancies, inflammation in the pelvic organs, etc.). The procedure is carried out in a hospital setting and the patient is constantly under the supervision of a doctor. HSG causes discomfort and in rare cases provokes the development of complications, but the opportunity to get answers to many questions and identify the cause of infertility for women is a more powerful argument than the consequences.
What is hysterosalpingography and what does it show?
Hysterosalpingography, or HSG, is a way to diagnose the condition of the uterine cavity and its appendages (from the Greek “hystera” - uterus and the Latin “salpinx” - tube). Other names for the procedure are metrosalpingography (MSG), hysterosalpingosonography (HSG), ultrasound hysterosalpingography (US GHA).
All of them reflect the method by which the study will be carried out - ultrasound or radiographic. The reliability of the results ranges on average from 70 to 80%.
What are the normal results of hysterosalpingography?
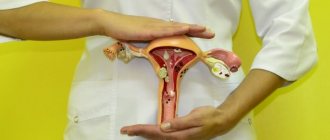
The doctor draws his conclusions based on the images obtained, providing the patient with a complete transcript of them. If everything is in order, then they will depict a uterus in the shape of a triangle, which has two fallopian tubes, which are thin branches. They open into the abdominal cavity, where the ovaries are located.
Spots may be visible on the x-ray. This is how the contrast agent appears, which was able to enter the uterine cavity and penetrate the fallopian tubes, and then exit into the abdominal cavity. This picture indicates absolute patency of the fallopian tubes.
If only one pipe is completely visible on the image, then only it is passable; if both are not fully visible, then they are diagnosed as completely obstructed. Usually the contrast stops at a certain area. In medical practice, there are cases of partial obstruction.
The accuracy of the result depends on the correct preparation of the patient and the choice of the day of examination, since HSG must be done in the first half of the menstrual cycle.
The study allows you to diagnose polyps, fibroids, hydrosalpinx, adhesions, including those pressing on the outside of the pipe.
In what cases is it prescribed?
Having an HSG is one of the primary tasks facing a woman who has problems conceiving and/or bearing a fetus. The procedure allows you to detect the causes of anatomical infertility - neoplasms, adhesions, abnormalities in the structure of the uterus and appendages.
The gynecologist prescribes one of the types of HSG before IVF, artificial intrauterine insemination and other methods of assisted reproductive medicine.
HSG will help to detect not only the causes that prevent pregnancy, but also the causes of various disorders associated with the menstrual cycle - pain, irregularity, spotting in the middle of the cycle.
The HSG procedure helps to detect:
- obstruction of the fallopian tubes associated with the presence of adhesions, polyps, tumors and other uncharacteristic structures;
- abnormal structure of the uterus and/or its appendages;
- inflammatory process caused by tuberculosis or other infectious disease;
- pathological growth of the endometrium;
- isthmic-cervical insufficiency.
A gynecologist may prescribe this procedure before surgery on the internal reproductive organs to exclude the presence of adhesions and other neoplasms.
Consequences and complications
Exacerbations of the condition when performing HSG of the fallopian tubes are very rare.
The most important of which are:
- Inflammation in the reproductive organs. Occurs in a situation if the study was carried out with a high number of leukocytes in the vaginal smear;
- Immunity to contrast components;
- Blood loss or disruption of the integrity of the uterine cervix due to incorrect examination methods.
Thus, we can say that side effects from fallopian tube HSG are associated, firstly, with careful preparation for the procedure - establishing all negative indications.
Even the harmlessness of the HSG procedure cannot promise that difficulties and consequences will not arise:
- The initial line in this list may be an allergic manifestation to contrast components. This occurrence is typical for women who have previously had similar “responses” in other tests. An allergic reaction may also occur in women with severe diseases of the respiratory system (asthma, tuberculosis).
- Bleeding, disease or damage to the uterus is still uncommon.
X-ray examination does not pose any threat to the patient at all, since its dose is 0.4-5.5 mGy, which is significantly lower than that which could lead to epithelial damage.
Contraindications
Hysterosalpingography is a procedure that is not prescribed to a woman without preliminary blood tests, a vaginal smear and other media and components of the body. This is necessary to identify pathological processes that can be detected already at the level of laboratory tests.
Some of them may be a direct contraindication to hysterosalpingography:
- inflammatory processes in the vagina, including the cervix (cervicitis), endometrium and fallopian tubes. The administration of a contrast agent may promote the spread of infection;
- allergy to iodine. Despite the fact that the contrast agent contains a negligible amount of iodine and does not penetrate into the bloodstream, HSG is not prescribed to patients with sensitivity to it;
- menstruation;
- pregnancy.
Preparation for tubal HSG
The HSG method is safe and low-traumatic, but it is an invasive procedure and therefore requires special preparation. Preparation for hysterosalpingography includes the following steps:
- it is necessary to undergo a general gynecological examination and undergo tests for hysterosalpingography: a bacteriological smear from the vaginal mucosa is necessary to ensure the absence of sexually transmitted infections;
- to diagnose other infectious diseases it is necessary to take blood tests;
- during the week before the examination, you should not use vaginal suppositories and suppositories, sprays, douching solutions and intimate hygiene products;
- you should abstain from sexual contact for two days before the study;
- sometimes the doctor prescribes allergy tests for the contrast agent used in x-ray examination;
- if the procedure is performed in the second phase of the cycle, a pregnancy test is performed.
Research methods and equipment
HSG is performed using both ultrasound and X-ray equipment. These techniques have varying effectiveness for different indications.
Ultrasound hysterosalpingoscopy (USGSS)
USGSS, or EchoGSS, is performed on an outpatient basis. The procedure is not traumatic, so anesthesia is not required. In some cases, a woman may feel painful sensations of varying intensity. This may be due to the presence of adhesions and neoplasms in the uterine cavity and tubes.
A woman on a gynecological chair has a catheter inserted into her vagina. Through it, a contrast agent enters the cavity of the reproductive organs. Usually this is a solution of glucose, furatsilin and sodium chloride.
Heated to +37°C in itself it does not cause any unpleasant sensations and is harmless to health. At this time, the passage of the substance is observed using ultrasonic equipment. The advantage of the procedure is that the visualization of the process occurs in real time.
During the diagnosis, the relief of the uterine cavity and the nature of its structure are clearly visible. The screen shows whether the substance comes out of the appendages or accumulates in them. The disadvantage of the procedure is that high-quality images will not be obtained, and visualization of the fallopian tubes is worse than with radiographic HSG.
HSG with x-ray
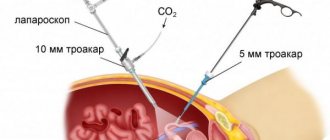
As in the case of ultrasound ultrasound, hospitalization is not required for this procedure. A radiopaque substance containing iodine compounds - cardiotrust, verografin, urografin and others - is injected into the vagina. Using a cannula, 2-3 ml of solution is injected into the vagina at a time. A fluoroscope is used for the procedure.
A small beam of radiation is supplied to the area being diagnosed, which, passing through the body, is reflected on a special film, or matrix. Due to the contrast agent, the image is clear and more detailed than with ultrasound HSG.
Diagnostic technique
Before the procedure, the woman must undergo a routine gynecological examination with speculum.
The procedure does not take too much time. After examination, a special tube (soft catheter) is inserted into the cervix. Through this tube, the doctor uses a syringe to inject a contrast agent for X-ray examination into the uterine cavity. After some time, when the contrast fluid penetrates the tubes, the doctor takes x-rays showing the condition of the fallopian tubes.
The research liquid is absolutely safe for health. It is eliminated from the patient’s body without a trace, absorbed into the blood, without requiring any additional procedures to clean the uterus.
Is it painful to have a tubal HSG procedure?
Many women are interested in whether the examination will be painful. The procedure is considered a painless, minimally invasive diagnostic method, so no anesthesia or local anesthesia is required before the procedure. In some cases, local anesthesia with lidocaine is used if the patient does not have individual intolerance to the anesthetic.
During the procedure, you may experience unpleasant sensations reminiscent of menstrual pain in the lower abdomen. An hour after the end of the examination they disappear.
Video: “How is hysterosalpingography done and what are the advantages of diagnosis?”
Tests for HSG
Hysterosalpingography is prescribed after a gynecologist has examined your medical history and taken a smear from the vagina and cervix - this is the first necessary condition. Microscopic examination of the vaginal microflora is important for the timely detection of infectious and inflammatory processes. Cytological analysis of the cervix will detect benign and malignant diseases.
If necessary, the doctor gives a referral for a number of additional tests:
- general urine analysis. Already at this stage it is possible to identify diseases of both individual organs and systems. For example, cystitis, urethritis or kidney disease may be a contraindication to the HSG procedure;
- general blood analysis . Shows the status of the main blood parameters - hemoglobin, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, leukocytes;
- blood chemistry. Reveals changes in components characteristic of diseases of certain organs - liver, pancreas, cancer;
- analysis for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis B and C.
If pathological processes are detected, the patient is prescribed treatment, and HSG is postponed until recovery. Or methodologically adjusted to reduce the risk of possible complications.
Features of the GHA
Hysterosalpingography can be performed on an outpatient or inpatient basis. Often, HSG is prescribed in the first half of the menstrual cycle (before ovulation), when the uterine mucosa is at its thinnest.
The procedure for performing GHA is as follows:
- The patient is positioned on a gynecological chair, on which an x-ray can later be taken.
- The doctor treats the perineum with an antiseptic and examines the genitals with a mirror.
- Then a cannula is inserted into the uterus, through which contrast is supplied (Cardiotrast, Triombrast).
- Contrast in a volume of 2-3 ml fills the uterine cavity, after which an image is taken.
- Next, another 3-4 ml is injected, which allows the contrast to move further through the tubes.
- A repeat photo is taken.
- If necessary, the doctor can inject up to 10-15 ml of contrast agent and take several more pictures.
- After the procedure, the cannula is removed.
How is the patency of the fallopian tubes checked?
Conducting metrosalpingography and echoHSG are in many ways similar. Only the methods of visualizing the pelvic organs are different.
On what day of the menstrual cycle is it prescribed?
Carrying out HSG is most effective in the first few days after menstruation. At this stage, the endothelium becomes thinner, which makes it possible to more clearly visualize deviations from the norm.
Most often, hysterosalpingography is prescribed in the first phase of the menstrual cycle, until the onset of ovulation. However, if you suspect, for example, isthmic-cervical insufficiency, it is advisable to diagnose in the ovulatory phase, and for submucosal fibroids - any day before or after menstruation.
Preparation
From the first day of the menstrual cycle, during which HSG is planned, the use of contraception is mandatory. This is necessary in order to eliminate the possibility of becoming pregnant. In the case of an unknown pregnancy, a fertilized egg under the pressure of a contrast agent may be released into the abdominal cavity, leading to an ectopic pregnancy.
Also recommended:
- abstain from sexual intercourse for 2-3 days before the procedure;
- do not use vaginal preparations, douching and hygiene products 5-7 days before HSG to avoid microflora disturbance (only if they are not prescribed by the attending physician);
- the procedure is carried out on an empty stomach, so 1.5-2 hours before it you are allowed to drink only a glass of still water;
- You will need a robe, slippers and a light snack;
- immediately before HSG, you should empty your bladder, and, if necessary, give an enema to cleanse the intestines.
During a preliminary consultation with a gynecologist, the need for painkillers and antispasmodics is discussed. The latter are most often prescribed to prevent spontaneous contractions of the uterus and its appendages, which may interfere with an accurate diagnosis.
Progress of the examination
Hysterosalpingography is a non-invasive procedure that takes no more than 15 minutes. The patient lies down on the gynecological chair, as during a standard examination. The external genitalia are treated with a disinfectant solution. Then speculum dilators are inserted into the vaginal cavity for further sanitation of the walls, including the cervix.
To supply saline or radiopaque liquid, a catheter is used, which is inserted into the cervical canal. The supply of the substance is controlled by a nurse or gynecologist. During metrosalpingography, 3-5 ml are given, since the first time the liquid may not fill all the cavities and the results on the pictures will be erroneous.
With ultrasound HSG, the movement of the substance can be observed in real time, so first a few ml of the substance is injected, and then the remaining volume. No more than 15-20 ml is administered per procedure. Upon completion of the procedure, the woman can immediately go home.
Sensations during and after hysterosalpingography (pain, etc.)
When a contrast agent enters the uterine cavity, cutting or bursting sensations may occur. Often, pain symptoms are similar to those during menstruation. They have different intensities and depend on the characteristics of the body.
Rest is recommended after HSG. Walking and physical activity can trigger spasms and severe pain in the lower abdomen. During the day, a contrast agent may come out of the vagina. It may contain small amounts of blood, which is normal.
Essence of the GHA
Today, many are interested in what hysterosalpingography is, since the problem of infertility is relevant. This is an examination method that checks the condition of the fallopian tubes and uterine cavity .
The research process itself consists in the fact that the listed organs are filled with a special substance, which enters there through the vagina when using a catheter. After this, either an X-ray or an ultrasound is used, with the help of which the specialist can study in detail the position of the organs.
A special substance helps to see formations, inflammation, and adhesions. This method also helps to determine whether the contrast agent can exit into the abdominal cavity through the fallopian tubes. If a special fluid can pass through the fallopian tubes, this means that their condition is normal and the patency is not impaired .
There are two types of HSG:
- x-ray,
- echohysterosalpingoscopy.
If it is decided to use an x-ray, then contrast liquid is introduced in specially designated portions, and the specialist gradually takes several pictures. During an ultrasound, a saline solution is injected into the organ , with the help of which an additional action is carried out, which consists in breaking small adhesions. This leads to the fact that after this type of HSG, a woman can become pregnant. But this only happens if the problem was a minor pathology.
It is quite difficult for patients to understand what kind of diagnostic method this is, so before deciding to undergo HSG, you should consult a doctor, since the procedure has a number of contraindications.
Norms of hysterosalpingography indicators
The results obtained during the procedure are interpreted based on the average statistical indicators of a healthy patient:
- The shape of the uterus is an isosceles triangle, with its apex down. It ends with the uterine os, which passes into the isthmus and cervix. The normal depth of the isthmus is 0.8-1.0 cm;
- uterine wall - even, smooth. The contrast agent evenly follows their contours;
Hysterosalpingography - Fallopian tubes - have the form of thin canals, widened at the ends. The interstitial section of the tube extending from the uterus has the shape of a short cone. It abruptly turns into the isthmic section - the longest section with a narrow lumen, often very convoluted. At the ends of the pipes, expansions are visible - ampoules. Normally, the contrast fluid should flow freely from them into the abdominal cavity. This is especially clearly visible during metrosalpingography.
- the contrast agent completely exits into the peritoneum without lingering in any part of the tubes.
Research results
On X-ray images, if there are no adhesions, the outlines of the uterus filled with solution, thin pipe ducts and contrast flowing into the abdominal location are clearly visible. With such an image, a specialist can talk about the permeability of the fallopian tubes.
However, when the liquid stops on any fragment of the pipe, there is an assumption that it is impenetrable.
Based on the results of HSG, it becomes possible to establish not only the presence of a lumen in the fallopian tubes, but also to identify such pathologies as: polyps in the uterine body, uterine fibroids, hydrosalpinx, adhesions that exert pressure from the outside onto the tube, or adhesions in the uterus itself.
Even a successfully performed procedure can sometimes mislead specialists. Studies that were carried out to identify the ability to qualitatively detect abnormalities in the condition of the uterus and fallopian tubes are 65%, and the specificity is 80%, which means identifying a certain disease from the probable ones. To examine the condition of the uterine body, hysteroscopy is prescribed as an additional diagnosis.
Decoding the results
Hysterosalpingography is the most effective diagnostic method. With its help, you can detect even those diseases of the reproductive organs that are asymptomatic.
| Character of filling | What does it mean |
| The substance evenly filled the uterus and appendages, taking on their outlines. A haze of contrast agent leaves the ampullary part of the tubes and disperses throughout the abdominal cavity. | Patency is normal |
| The substance accumulates in the ampullary part of the pipe, expanded to atypical sizes, and does not come out (or partially comes out). | A sign of an inflammatory process (sactosalpinx) in the tubes. Leads to the accumulation of exudate in the terminal part of the canal and narrowing of the lumen of the ampoule. |
| Fluid has filled the uterus, but does not pass into the tube (one or both). | Inflammation or tuberculosis of the genital organs. |
| The contrast agent accumulates in the abdominal cavity in the form of clearly defined individual formations. | An adhesive process in the pelvis, which can cause infertility. |
| The uterus is deformed, its size is smaller than normal; pipes can be expanded, with thickenings at the ends. The substance fills the cavities of the uterus and appendages. | Obliteration caused by inflammatory processes. For example, endometritis, or salpingitis, arising against the background of tuberculosis. |
| The substance passes through the uterus, staining only its lateral sides. | A malformation of the uterus caused by the formation of a septum inside it. It can be expressed weakly – saddle-shaped uterus and strongly – bicornuate, unicornuate uterus. |
| The liquid fills the uterus completely, but with varying color intensities. | Hyperplasia, or endometrial polyposis. |
The results shown in the table are generalized and may have a different interpretation depending on the medical history and accompanying tests. Only a gynecologist can make an accurate diagnosis.
Estimated cost of hysterosalpingography
It is best to find out how much HSG of the fallopian tubes costs directly at the medical institution where hysterosalpingography is performed. On average, the cost of the procedure varies between 4000-8000 rubles (150-250 dollars), depending on the clinic.
Today, X-ray HSG of the fallopian tubes is considered an outdated technique, which is increasingly being replaced by high-tech ultrasound and computer. In combination with other diagnostic methods, the procedure allows you to quickly and effectively diagnose and determine the physiological state of a woman’s reproductive organs.
Recommended Articles
“Chocolate” or endometrioid ovarian cyst
“Harmless” cyst of the corpus luteum of the ovary
Fallopian tube laparoscopy - the path to a long-awaited pregnancy
Possible complications
Hysterosalpingography is a relatively safe procedure that, if followed correctly, does not pose any health risks.
But in rare cases, complications may occur:
- penetration of the contrast agent into the vascular bed through the capillaries and venules of the uterus;
- penetration of the substance into the broad ligament of the uterus, or lymphatic vessels;
- rupture of the wall of the uterus or appendages under strong pressure of the solution;
- allergic reactions. In particular - for iodine-containing substances;
- introduction of infection, or complication of an existing one, not detected during preliminary examinations.
Such risks are due to the specifics of diagnosis and are typical for all intrauterine manipulations.
Consequences of the procedure
After the procedure, there may be slight discomfort in the lower abdomen and mild bleeding, which disappear after a few hours.
The following complications can occur extremely rarely:
- vascular reflux, which involves the penetration of contrast into the veins of the uterus;
- lymphatic reflux (drug entering the lymph vessels);
- perforation of the uterine wall;
- allergic reactions to contrast agent;
- rupture of the fallopian tubes due to their “tight filling” with contrast.
3-5 days after HSG, an exacerbation of existing inflammatory diseases of the reproductive organs is possible. Some patients also experience delayed menstruation. After a couple of months, the cycle is restored.
Conception and pregnancy after the study
HSG, in addition to its main diagnostic function, also has a therapeutic effect. A contrast agent supplied under pressure can clear the cavity of the fallopian tubes from adhesions and other neoplasms.
Therefore, in the first months after the procedure, the chances of getting pregnant may increase if the problem was a narrowing of the lumen of the appendages. However, in some cases, after X-ray HSG, doctors strongly recommend sexual rest for 2-3 months.
Types of research
Instead of a conventional X-ray examination, the doctor may prescribe an alternative method using ultrasound. In this case, instead of a contrast agent, normal saline solution is used. Ultrasound MSG in gynecology is used in cases of intolerance to standard imaging compositions, or in the presence of other contraindications.
Sometimes doctors prescribe selective metrosalpingography. Using special tubes, the contrast solution is injected directly into the tubes. This method is considered more gentle than conventional metrosalpingography.
When using it, women experience almost no discomfort. Selective examination is often performed simultaneously with tubal reconalization.
In this case, the procedure is diagnostic and therapeutic in nature. It allows you to get rid of obstruction of the fallopian tubes in places adjacent to the uterus, with mild pathologies.
Cost of the procedure
The price of GHA in government institutions ranges from 1500 to 3500 rubles. In private clinics – up to 15,000 rubles.
For women suffering from infertility and spontaneous abortions, hysterosalpingography is an opportunity to identify the problem when all other diagnostic methods have not yielded positive results. In addition, the procedure allows you to detect various pathologies and neoplasms and give them an objective assessment.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Question: Is it possible to have sex after HSG?
The site provides reference information for informational purposes only. Diagnosis and treatment of diseases must be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. All drugs have contraindications. Consultation with a specialist is required!
Is it possible to have sex after hysterosalpingography?
After the hysterosalpingography procedure, it is recommended to abstain from sexual intercourse for two to three days. After these 2 - 3 days have passed after the manipulation, you can safely engage in sexual intercourse if you wish. However, you should carefully protect yourself until the next menstrual cycle.
The need to abstain from sexual intercourse for 2–3 days after hysterosalpingography is due to minimizing the risk of infection through the cervix, which has undergone dilation during the manipulation process. Within 2 to 3 days, the cervix will collapse again, that is, completely close, and then it will be possible to have sex without the risk of infection entering the uterine cavity, fallopian tubes and ovaries.
Reading time: min.
The postoperative period begins from the moment the operation is completed and lasts for several months, until complete recovery – six months. And throughout this period, you must adhere to these recommendations by your doctor and lead an appropriate lifestyle. Certain restrictions also apply to the sexual sphere.
What is MSG
Another name for metrosalpingography is hysterography. The main reason for resorting to this procedure is infertility (to identify the causes). Manipulation is carried out only for gynecological indications and after special training. MSG is usually done in a clinic, but in special cases, diagnostics in a hospital setting are indicated.
Infertility, as a rule, occurs against the background of adhesions, obstruction of the fallopian tubes, which are provoked by previous surgical operations in the pelvis, herpes, chlamydia and other bacterial infections. After the MSG procedure, it becomes possible to prescribe the most appropriate treatment.
The picture shows the procedure for tubal MSG.
Contraindications to the procedure
Metrosalpingography cannot be performed in the following cases:
- suspicion of pregnancy;
- individual intolerance to iodine and contrast agent;
- heart and blood vessel diseases;
- bleeding;
- lactation;
- bacterial and viral infections in the acute stage;
- violations of the vaginal microflora;
- chronic pathologies of the reproductive system;
- any inflammatory processes.
The main goal of the diagnostic procedure is to identify the adhesive process or ensure its absence. You should know that it is impossible to assess the condition of the endometrium using MSH.