09/11/2020 319 Functional diagnostics
Author: Tatyana
FCS of the intestine is a gastroenterological study that allows you to determine the presence of pathological changes in the wall of the colon. The main advantage of colonoscopy compared to ultrasound is the ability to perform minimally invasive interventions directly during the examination.
- 2
The difference between FCS (fibrocolonoscopy) and FGDS (fibrogastroduodenoscopy) - 3
Colonoscopy with biopsy: what is it? - 4
The procedure for examining the intestines through a colostomy - 5
Indications and contraindications for examination - 6
Preparation for the procedure6.1
How to eat, recommendations
- 6.2
Enema or drug method of bowel cleansing
How is it done?
- 7.1
Colonoscopy under anesthesia
What the diagnostics will show: deciphering the results
Possible complications after FCS
Advantages and disadvantages
What is the price
Video
Comments and Reviews
What is the procedure
FCS is an examination of the entire length of the rectum and colon using a special probe.
The term "colonoscopy" is derived from:
- the Latin name for the large intestine is “colon”;
- Greek "skopiya", which means "I look";
- the “fibro” particle indicates the use of a flexible probe.
When performing a colonoscopy, the doctor has the opportunity to perform:
- taking tissue for biopsy;
- removal of tumors;
- coagulation of the source of bleeding;
- elimination of volvulus or intussusception.
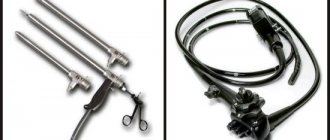
Fibercolonoscopes, which are used in medicine, are a long, flexible tube made up of many optical fibers that send images to an eyepiece. The colonofiberscope also has an instrumental channel, by controlling which the doctor can pinch off tissue and carry out other manipulations.
Fibercolonoscopy and how it is done, you can learn about this in detail from the video of the European Clinic channel.
What is this procedure
Fibercolonoscopy of the intestine is a diagnostic method that makes it possible to examine all parts of the digestive tract.
The procedure is carried out, as a rule, without the use of anesthetic drugs. To perform the examination, a special device is used, which is called a fibrocolonoscope. When it is introduced into the rectal area, it is possible to determine in a matter of minutes the condition of the large intestine.
Currently, this technique is one of the more effective types of diagnostic research, having significant advantages over X-ray or ultrasound examination.
Colonoscopy with biopsy: what is it?
To clarify the nature of the disease, the extent of the spread of the pathological process and the stage of development of neoplasms, a colonoscopy with biopsy can be performed:
- Sighting. Targeted collection of tissue from a pathological lesion that was detected before the start of the procedure.
- Search engine. A diagnostic examination of the intestine, which is used in the early stages of the disease, when the pathology itself is not yet visualized during colonoscopy.
Tissue samples obtained during biopsy are further examined under a microscope to identify abnormal cells, which will help make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment for the patient.
The procedure for examining the intestines through a colostomy
This option for examining the intestines is not fundamentally different from a colonoscopy performed through the rectal opening.
A colostomy is an anal opening formed during surgery to remove the rectum. The open end of the sigmoid or colon is brought out onto the abdominal wall on the left side. The doctor can use it for endoscopic examination.
Many patients fear that inserting a probe in this way and pumping air to straighten the folds of the mucous membrane can be traumatic. If the stoma heals without complications and is properly cared for, there is little risk of damage.
On the eve of the study, a special diet and bowel cleansing are required, as with the standard FCS procedure. It is important to provide the doctor who performs the colonoscopy with as complete information as possible about the nature of the operation undergone. This will increase the efficiency of the examination and help avoid misinterpretation of results.
How is the procedure done?
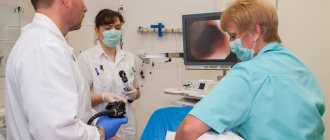
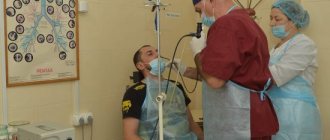
Is fibrocolonoscopy performed under anesthesia? Patient reviews of this nuance are very varied. Some say that local anesthesia is required, while others had this procedure performed without it. Experts say that this diagnostic method does not require anesthesia. Although in some cases anesthesia is still used (if the patient has fissures in the anus). So how is fibrocolonoscopy performed? First, the specialist examines the rectum using palpation. After this, he inserts the device tube through the anus. It is slowly moved throughout the intestine, and then air is supplied. This is necessary in order to straighten all the folds of the intestines. During air delivery, the patient may experience minor discomfort in the form of bloating and the need to defecate. In this way, specialists perform an examination, and if urgently necessary, they pinch off tissue or remove polyps, after which the tube is slowly withdrawn.
Indications and contraindications for examination
Absolute indications for colonoscopy include:
- bleeding from the lower intestines;
- Crohn's disease;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis;
- colon polyps;
- assumption of intestinal obstruction of unknown nature.
Relative indications are symptoms such as:
- stool disorders (frequent constipation or, conversely, diarrhea);
- chronic abdominal pain;
- the appearance of blood or mucus in the stool;
- weight loss with a normal calorie diet;
- anemia of unknown origin.
In addition to diagnostic purposes, FCS is also prescribed to perform various manipulations on the intestines (using local anesthesia or intravenous anesthesia).
The decision to perform fibrocolonoscopy in these conditions is made by the doctor, taking into account the general picture of the disease and the results of other studies.
Absolute contraindications for performing FCS include:
- acute myocardial infarction;
- stroke;
- atherosclerosis;
- aortic aneurysm;
- hypertension stages 2 and 3;
- the presence of an artificial valve on the heart muscle;
- peritonitis;
- intestinal perforation;
- ulcerative colitis in the acute phase;
- recovery period after recent surgery on the large intestine.
It is better to postpone colonoscopy if there are relative contraindications, including the following:
- poor intestinal preparedness for examination;
- pregnancy;
- stomach or intestinal bleeding;
- presence of hernias;
- history of multiple surgical operations on the pelvic region.
In the above cases, performing FCS can be dangerous for the patient or uninformative. The question of the advisability of performing a colonoscopy, if there are relative contraindications, is decided by the doctor individually.
What is fibrocolonoscopy?
Fibercolonoscopy of the intestine is an informative and effective endoscopic method for diagnosing organs using a fibercolonoscope. It allows you to examine and evaluate the condition of all parts, mucous membranes and mucous membranes from the inside and diagnose the disease at an early stage. Early treatment shortens the duration of therapy and avoids the development of serious complications.
Indications for the procedure
Fibrocoloscopy is prescribed for the diagnosis of secondary diseases:
- Hirschsprung's disease;
- polyps;
- Crohn's disease;
- diverticulum;
- colitis;
- foreign bodies;
- oncological pathologies.
The main indications for the procedure are considered:
- the occurrence of blood impurities in feces.
- Frequent abdominal pain associated with flatulence.
- Regular stool disorders.
Fiberoscopy of the intestines is a safe procedure and is usually performed under local anesthesia.
Contraindications to the procedure
Fiberoscopy is contraindicated in some cases. Manipulation is carried out only on vital parameters.
The procedure is not prescribed for the following pathologies:
- patients with pulmonary insufficiency;
- with severe ischemic colitis;
- with blood clotting pathology;
- peritonitis;
- with severe ulcerative colitis;
- with acute forms of infection.
In addition, the study will be conducted in cardiovascular failure.
How to prepare properly?
To obtain accurate results during fiber coloscopy, it is necessary to properly prepare the fiber coloscopy. It is recommended to follow a special diet for several days before the examination.
High fiber foods and foods that cause excessive gas should be eliminated from the diet. The day before the procedure, the patient must drink Fortrans, which has a laxative effect.
This product is approved from 15 years of age.
To obtain accurate results, fibrocoloscopy should be performed on an empty stomach and with a completely clean colon.
Carrying out fibrocolonoscopy
The procedure is performed using a fibercoloscope. The latter is presented in the form of a flexible small tube equipped with an eyepiece and illumination. The image is displayed on the monitor. The device also has devices through which air is supplied and various manipulations are performed.
During a fiber colonoscopy, specialists can:
- stop the bleeding;
- remove polyps;
- take a piece of material for research.
During the examination, the patient should lie on his left side. In some situations, the patient may be asked to bend their knees or lie on their back.
At the beginning of the procedure, the doctor performs rectal palpatation, after which a fibercoloscope is carefully inserted through the anus. The device slowly moves forward along with the air supply, which helps to expand the intestinal lumen. After the end of the manipulation, additional air is sucked from the intestine through the fibercoloscope. The latter is slowly sucked out of the anal canal.
Fibercolonoscopy is usually performed under local anesthesia. However, in some situations, when a person has inflammatory pathology of the rectum, general short-term anesthesia can be used. The duration of the procedure is from 15 minutes to half an hour, taking into account the anatomical structure of the body.
Rehabilitation period
After fibrocoloscopy, a person can return to their daily routine and diet. However, it is recommended to avoid fried and spicy foods on the first day after the procedure. For minor pain in the abdomen, the doctor may recommend taking an antispasmodic.
In some situations, after the manipulation, the patient may have a feeling of fullness in the stomach. In such situations, activated charcoal and bed rest help.
After polyp removal or biopsy during fibrocoloscopy, slight bleeding may occur in the first two days, which should go away on its own. If this has not been done, you should consult your doctor.
What is a colonoscopy?
This diagnostic method helps evaluate the condition of the colon. For the study, a special drug is used - a colonoscope. The latter is presented in the form of a flexible probe equipped with a backlight, an eyepiece and a video camera. In addition, the drug contains tubes for air supply, as well as biopsy forceps. The length of the hardware coloscope is about 160 cm. This allows you to examine the intestine, taking into account its curvature.
Colonoscopy is not a painless procedure. For this reason, local anesthesia is used to prevent the patient from feeling unwell. Various ointments are suitable as painkillers, for example, wild ointment. The latter is processed with a colonoscope before manipulation.
Main indications
Colonoscopy is prescribed in the following cases:
- in case of regular bowel disorder: constipation or diarrhea;
- with nonspecific ulcerative colitis;
- for pain without specific localization;
- if you suspect Crohn's disease;
- with bloody, mucous or purulent discharge;
- to remove a foreign body from the intestine;
- for sudden exhaustion or anemia;
- for hemostasis in the colon;
- for neoplasms or polyps;
- for stenoses.
In addition, a biopsy is performed using a colonoscope for further examination.
How to prepare properly
To obtain accurate results, the bowel must be completely cleansed before diagnosis. To do this, it is recommended to follow a special diet for several days before the manipulation. A complete fast is prescribed the day before the colonoscopy and directly on the day of the colonoscopy. In addition, it is recommended to take drugs with a laxative effect, such as Endofalc.
Colonoscopy is performed for both diagnosis and treatment.
During the procedure, the doctor is able to:
- evaluate the surface of the mucous membrane, the presence of overlaps and its vascular pattern.
- to study the shade and presence of shine on the mucous membrane.
The duration of a colonoscopy is about 30 minutes.
Contraindications
Colonoscopy is contraindicated in some situations.
No manipulations are performed in the following states:
- with peritonitis;
- shock states of any origin;
- acute form of myocardial infarction;
- rapidly developing form of ischemic colitis;
- intestinal bleeding;
- pulmonary failure;
- large inguinal hernia;
- several operations in the pelvic area.
Even in patients with heart failure, surgery is not performed.
What is the difference between colonoscopy and fibrocolonoscopy procedures?
Fibercolonoscopy is considered a more modern diagnostic method and has recently been more often used in medicine than colonoscopy.
The structure of a fiber colonoscope is more complex. It consists of ultra-precise optical fiber, and the colonoscope is an ordinary rubber tube.
In addition, the colonoscope is not as flexible and is very thick. For this reason, the patient feels less uncomfortable with a fiberscope than with a colonoscopy.
Both methods are informative and have almost the same indications for use and contraindications.
In general, fiberoscopy and colonoscopy are endoscopic diagnostic methods. To obtain accurate test results, careful preparation is required before performing procedures.
You may be interested in: Polyps in the maxillary sinus: symptoms of the disease and treatment, diagnosis
Preparation for the procedure
FCS of the intestines is a study that necessarily requires cleansing of the colon. You need to start preparing for the procedure three days before it takes place.
How to eat, recommendations
There is no need to fast to prepare for a colonoscopy, but you should exclude from your diet foods that are difficult to digest and cause increased gas formation in the intestines:
- any fruits and vegetables;
- greenery;
- berries;
- nuts;
- legumes;
- porridge (oatmeal, pearl barley, millet);
- pasta;
- black bread;
- fatty meat, fish;
- sausages;
- whole milk;
- coffee;
- carbonated drinks.
The following products are allowed for consumption:
- wheat bread made from wholemeal flour;
- lean boiled meat (beef, poultry) or fish;
- fermented milk products (yogurt, kefir);
- low-fat broths;
- dry biscuits (biscuits).
The last meal before the FCS should be no later than 20 hours before the examination. Immediately before the procedure, you can only drink water or weak tea.
Enema or drug method of bowel cleansing
There are two ways to prepare the intestines before a colonoscopy: mechanically using enemas or using special medications.
The second option is more convenient for patients and does not create additional trauma if:
- anal fissures;
- hemorrhoids;
- other painful formations in the rectal area.
Cleansing with an enema
In the evening before the examination, the enema should be performed twice with an interval of 1 hour. To perform intestinal cleansing, one and a half liters of distilled warm water are used per procedure. The morning before the colonoscopy, you need to repeat the enema twice more. For better results, you can use mild laxatives or castor oil the day before you begin your colon cleansing.
Medicinal cleansing
An alternative to enemas is the use of the drug “Fortrans” (or its analogues), specially created to cleanse the intestines before diagnostic procedures. The medication option for preparing for the examination should begin the day before the colonoscopy, 2 hours after the last meal.
The dosage of Fortrans should be selected individually by the doctor: approximately one sachet per 20 kg of the patient’s body weight. The drug must be dissolved in warm boiled water at the rate of one sachet per liter of water.
Since it is not possible to drink several liters of liquid at once, it is recommended to consume the solution in small portions over 2–4 hours. It is better to drink the drug quickly, without holding the solution in your mouth so as not to feel its taste. After a portion of Fortrans, you can take a sip of lemon juice - this will eliminate nausea.
Gastrocenter Ufa tells you more about proper preparation for the FCC examination.
Fibercolonoscopy and colonoscopy: what is the difference
12.06.2018
Colonoscopy and fibrocolonoscopy (FCS) are two identical diagnostic methods. Both allow you to examine intestinal segments, assess their condition, identify pathologies and perform minor surgical operations.
However, there are differences. In order to understand the difference between fibrocoloscopy and colonoscopy, it is necessary to study more deeply the structure of the devices and the principle of their operation.
What is fibrocolonoscopy
Fibercolonoscopy is a type of examination that allows you to assess the condition of the walls of the colon, take material for histological examination, cauterize bleeding, remove polyps and other tumors.
The procedure is carried out using a special probe - a fibercoloscope. Its length is from 135 to 145 cm. The device is equipped with:
- micro camera - it transmits the image to the monitor;
- optics - for illumination;
- air supply system - necessary for distribution of adhesive walls:
- with tweezers for tissue removal and surgical microsurgery;
- with aspirator - the device is designed to remove liquid
Fibrocoloscopy is an informative diagnostic method. Together with other endoscopic examinations of the intestine, FCC is the most effective examination in clinical proctology today. This inspection makes it possible:
- to assess the condition of the intestines, the appearance of the walls - color, shine, pattern of the mucous membrane of the blood vessels;
- to identify pathological processes - inflammation, bleeding, ulcers, scars, cracks, diverticula, neoplasms, foreign bodies;
- to confirm or refute the presence of diseases, identify their causes;
- to identify the provoking factor for defecation disorders and bleeding;
- for thermal coagulation (cauterization) of the bleeding area;
- for taking biopsy material;
- for the removal of polyps and tumors without malignant tumors.
Note! In fact, fibrocolonoscopy is an improved version of colonoscopy. The devices are similar in design and information content. But fibrocoloscopy is more modern and high-precision equipment.
Preparing for the FCC
The drug for fibrocoloscopy and colonoscopy is similar. Before the procedure, the intestines must be cleared of feces so that the probe can move easily and the mucous membrane can be examined.
Preparatory activities include
1st diet . Observed 3 days before the procedure. Products that take a long time and are difficult to digest and that lead to the formation of gas are prohibited. It is excluded from the diet:
- fruits, berries and vegetables in raw, pickled, steamed or cooked form;
- bakery products;
- sweets;
- nuts;
- sausages;
- fatty meat, fish, cheese;
- fast food;
- coffee. Allowed:
- porridge on water;
- light broth;
- dairy products;
- baked or cooked white meat;
- eggs;
- kisses, compotes, horses, free tea.
Eat your last liquid meal no later than 6 pm before your colonoscopy. It is forbidden to eat or drink in the morning before a colonoscopy.
Cleansing the second colon . Take a strong laxative with you. Usually you drink Fortrans, but you can prescribe analogues - Forlax, Lavacol. The drug is taken depending on body weight: 1 sachet per 20 kg. In the morning they take the last dose. Sometimes medications are replaced by enemas, but this is not advisable because they cannot clean out all parts of the intestines.
Important! Patients with hemorrhoids should only take liquid food once every 3 days. The doctor will be informed about the medications they are taking. Blood thinners and sorbents should be discontinued. The hospital should bring a towel, diaper, toilet paper and wet wipes.
Progress of the operation
Fibrocoloscopy is performed by a doctor/proctologist or endoscopist with the help of a nurse. In addition to a chamber with sensors, lighting and air supply, there are tweezers for various purposes - for removing tissue for histological examination or for minor surgical interventions.
The manipulations are performed step by step:
- The patient puts on a procedural nightgown, lies on his left side, and bends his legs.
- The doctor presses air into the intestinal cavity to expand it.
- He lubricates the anus with lidocaine anesthesia.
- Insert the fibercolonoscope, pushing it through the intestines one by one. If necessary, provide air flow to straighten the walls and facilitate passage of the endoscope. As the nursing assistant approaches the bowel folds, she presses on the patient's abdomen. The probe is flexible enough that it can be easily adjusted in this way.
- The endoscopist monitors the movement of the device and records data. If it is necessary to stop the bleeding, he cauterizes the ulcers. The doctor can also remove material using special biopsy forceps or remove tumors.
- At the end of the colonoscopy, the air is pumped out and the probe is removed from the intestine.
Fiberoscopy takes from 10 to 1.5 hours. The duration depends on the purpose of the procedure, the presence of complications and the need for additional manipulations. If a colonoscopy is performed for diagnostic purposes, it takes no more than 20 minutes. However, if it is necessary to remove polyps or stop bleeding, the duration of the procedure increases many times. The withdrawal is made in 1 - 3 days.
Note! If FCC was performed in the presence of bleeding or polyps were removed during the procedure, feces can be removed with low levels of blood contamination. This is considered the norm. However, in case of severe bleeding, you should go to hospital immediately.
Features of carrying out using anesthesia
Fiberoscopy and colonoscopy are unpleasant procedures. They are associated with discomfort (physical and mental) and pain.
The degree of pain depends on the individual sensitivity of the patient and the presence of pathologies in the intestines. Therefore, some patients insist on anesthesia.
This increases the cost of the procedure, its time and the length of recovery after the procedure. But this makes the FCC painless.
Fibrocoloscopy under anesthesia is mandatory:
- general serious condition;
- adhesions;
- enteritis;
- prostate adenoma.
Important! Doctors prefer not to use anesthesia, since the patient's reaction (to pain, discomfort) helps to conduct a more accurate colonoscopy. As a compromise, you can use a sedative, light sleep, which maintains the connection between the patient and the doctor.
Contraindications to the procedure
As with any diagnostic examination, there are indications and contraindications for colonoscopy. They are common in colonoscopy and fiberoscopy.
The procedure is performed if a colonoscopy is suspected:
- haemorrhoids;
- polyps, tumors, condoms, other neoplasms in the intestines;
- oncological pathologies;
- ulcerative colitis;
- inflammatory processes of the mucous membrane;
- internal hemorrhages.
Colonoscopy is prohibited if it is diagnosed:
- acute intestinal diseases;
- obstruction;
- hernia;
- acute infection - local and systemic;
- adhesions;
- mental disorders that make colonoscopy impossible;
- a sharp narrowing of the intestinal lumen or rupture of its walls;
- severe weakening of the body;
- pathology of the cardiovascular system: heart attack, stroke, atherosclerosis, ischemia, heart failure;
- peritonitis;
- pulmonary failure;
- pregnancy;
- blood clotting disorder.
Additional Information! In the above cases, fibrocoloscopy is replaced by a less significant but safe diagnostic method: capsule colonoscopy, MRI, CT.
You may be interested in: Laser removal of a polyp of the cervical canal: preparation for the operation and its course
What is the difference between FX and colonoscopy?
The procedures for FCS and colonoscopy are similar. The differences between diagnostic methods are small:
- - this is the main thing that distinguishes a fiber colonoscope - the structure of the equipment, roughly speaking, a colonoscope is a simple rubber tube, and a fiber colonoscope is a probe made of durable optical fiber;
- Another distinctive feature of fibrocoloscopy from colonoscopy is the best equipment; the devices are equipped with high-precision instruments for removing biopsy material, coagulation and extraction of tumors, improved optics and a video camera;
- for the patient, the main differences are less discomfort - the fibrocoloscope is thinner and more flexible, which facilitates passage through the walls and curvatures of the intestine, minimizing discomfort;
- for doctors, plus fibrocoloscopy - the accuracy of the equipment - it improves diagnostic and treatment methods, allows you to identify pathologies at an early stage, even minor deviations from the norm.
The doctor should explain what colonoscopy and fibrocoloscopy are, how they are performed, and how the two methods differ. Patients prefer FCS due to the greater significance of the study and less pain. Moreover, the difference in price is small - 1 - 2 thousand rubles. On average, you will have to pay from 5 to 10 thousand rubles for each type of procedure.
How is it done?
During a colonoscopy, a person lies on a couch on his left side with his knees pressed to his stomach. The anal area is treated with an antiseptic and lubricated with a special anesthesia gel, then the doctor carefully inserts the fibrocolonoscope probe into the rectum. At the next stage of the procedure, the doctor begins to slowly push it into the intestines to examine the walls. To make the study more informative, you need to straighten the folds of the colon: for this, air is pumped into it.
Performing a colonoscopy
Typically, a total colonoscopy takes no more than 15 minutes, but if the doctor has identified any pathologies or surgical manipulations are necessary during the procedure, it may take longer.
The channel “Mikhail Valivach” tells more about the FCC procedure.
Colonoscopy under anesthesia
Colonofibroscopy is also performed under intravenous anesthesia (drug sleep).
This type of diagnostic procedure is used for such categories of patients as:
- adults with a low pain threshold;
- children under 12 years of age;
- persons suffering from adhesive obstruction.
After FCS using anesthesia, you need to stay in the clinic for some time under the supervision of specialists.
How is fibrocolonoscopy performed?
The first and main rule of the FCC is that it can only be done on an empty stomach. The procedure looks like this.
- The patient takes off all clothing below the waist (you can wear special underwear) and lies on the couch on the left side, bending his knees. The anal area is treated with a gel containing lidocaine to minimize discomfort.
- The specialist carefully inserts the probe into the rectum, periodically straightening the intestines with gas. This makes the device move faster.
- The doctor watches the movement of the tube on the monitor. If a polyp or other formation is detected, he can immediately remove it or take tissue for laboratory testing.
FCC is not the most pleasant procedure. To make it more comfortable, specialists use anesthetics and sedatives to help the person relax. You can start taking them in advance by choosing the drug together with your doctor.
But there are situations in which a person cannot undergo intestinal endoscopy, for example, when he is in serious condition, or there is inflammation and adhesions in his organ. In such cases, it is advisable to perform FCS under anesthesia.
Colonoscopy with sedation is essentially no different from the usual procedure. When the patient takes the desired position, he is immersed in medicated sleep.
Medium-grade drugs without analgesic effect are used for the examination. This allows us to not reduce the accuracy of diagnosis. After waking up, a person will not remember a single unpleasant moment, pain will be forgotten.
Technique for examining the intestines through a colostomy
There is no fundamental difference between such diagnostics and classical FCS.
A colostomy is an artificially formed anal opening on the left side of the abdominal wall, created during the process of extirpation of the rectum. The doctor removes part of the sigmoid or colon into the resulting hole, through which an endoscopic examination can be performed.
Most patients are afraid of such a diagnosis, believing that inserting a tube in this way, as well as pumping air into the intestines, can cause injury. If the colostomy heals without problems with proper care, then the risk of damage to it is quite low.
To prepare for the examination, it is recommended to follow a special diet and cleanse the intestines, as before the classic procedure. It is important that the specialist performing the FCS receives detailed information about how the operation took place. Thanks to this information, the examination will be more effective, and the likelihood of incorrect interpretation of the results will be minimized.
How is a colonoscopy with biopsy performed?
Sometimes the doctor needs to clarify the nature of the pathology, the extent of its spread, and also find out the cellular structure of the developing tumor. In this case, it is advisable to perform FCS with a biopsy. There are two types of manipulation:
- targeted - tissue from the site of the disease detected before FCS is taken purposefully;
- search - the pathology has not yet been visualized, but there are suspicions.
Samples obtained by biopsy are examined in the laboratory under a microscope. They try to detect harmful cells in order to make a correct diagnosis and begin adequate treatment.
Duration
The examination time is no more than an hour, on average – from 20 to 40 minutes. The patient can go home immediately after the procedure is completed. The exception is FCS under anesthesia - you will have to wait until the effect of the drug wears off and remain under the supervision of doctors all this time.
How does the patient feel?
FCS, along with similar endoscopic techniques for examining the intestines, can hardly be called a pleasant procedure. Physical discomfort, stress and anxiety – the patient has to endure all this.
It's no wonder that most patients are afraid of colonoscopy. However, all worries are in vain. Diagnostics causes almost no pain - only some discomfort when inserting a probe into the rectum. But thanks to the examination, life-threatening pathologies can be identified.
Unpleasant sensations are caused by air, which is pumped in and out using a colonoscope.
If you can’t get rid of your fear, you can ask your doctor to administer local anesthesia or undergo a procedure with sedation. You should not refuse an examination, since it will help detect the disease on time, and, therefore, treatment will be quick and effective.
Could there be consequences?
Complications after FCS are quite rare, but possible. The most serious of these are bleeding or perforation of the intestine.
Some patients complain of discomfort in the intestinal area. It’s easy to get rid of them - you just need to lie on your stomach for a while, then there will be no trace of discomfort.
What the diagnostics will show: deciphering the results
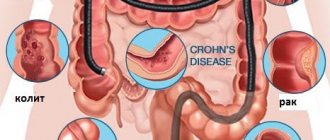
With fibrocolonoscopy, the doctor can see signs of the following diseases:
- Polyposis of the large intestine. The formation of benign growths (polyps) on the intestinal walls. They can transform into malignant tumors and therefore require removal. In most cases, polyps can be removed without surgery, during a colonoscopy.
- Nonspecific ulcerative colitis. Inflammatory bowel disease, the etiology of which is unknown. Usually the process begins in the rectum and spreads higher. A timely examination helps to identify nonspecific ulcerative colitis in the early stages of development. The doctor may also prescribe a repeat colonoscopy during treatment to monitor the healing of the ulcers.
- Colon cancer. A malignant tumor growing from its mucous membrane. FCS is one of the main methods of screening for colon cancer, recommended for preventive purposes every five years.
- Crohn's disease. A chronic inflammatory disease that can affect the gastrointestinal tract throughout its entire length, including the colon. Colonoscopy in this condition can determine the degree of inflammatory changes, the presence and number of ulcers, and identify sources of bleeding.
- Intestinal tuberculosis. Usually, it is a secondary disease, that is, this microbacterium develops in the primary focus (most often in the lungs), and then spreads to other organs. During fibrocolonoscopy, the doctor will see characteristic inflammatory changes, and will also be able to take a biopsy sample and send it for analysis to confirm the diagnosis.
Differences between colonoscopy and fibrocolonoscopy
- In the first stage, 1 liter of water is introduced, after 60 minutes another 1.
- This procedure is also recommended in the morning of FCC day.
Use of laxatives:
- Your doctor may recommend using Duphalak, Fortrans, or Magnesia.
- The dosage is calculated individually for each patient, taking into account body weight.
- Laxatives are administered 24 hours before fiberoscopy, at noon.
- The patient receives a light lunch at 12:00. The last laxative is taken at 18:00.
How is fiberoscopy performed?
The procedure goes through several important stages. The doctor must first explain to the patient how FCS should be performed in order to avoid psycho-emotional disorders in the diagnostic process.
| I |
|
| II |
|
| III |
|
| IV |
|
| V |
|
| VI |
|
The initial diagnosis can take up to half an hour. If FCC is performed two or three times, the process is much faster. If polyps are found, they are immediately removed. The patient will not experience any discomfort or pain, and the duration of manipulation can be increased to 35 minutes.
Differences between colonoscopy and fiberoscopy
Colonoscopy and fiberoscopy are similar procedures in modern medicine, the main purpose of which is to obtain information about the condition of internal organs using the least invasive methods. The list of indications, contraindications, and recommendations for preparing both procedures is similar. However, there is a certain difference between these research methods:
- Fibroscopy is a more modern technique that doctors often use when examining patients.
- Fibrocoloscopy has a more complex structure and allows you to obtain more detailed information about the condition of the internal organs.
- The colonoscopy device is a thin rubber tube, and the fiberscope uses heavy-duty optical fibers.
- The colonoscope is less flexible.
- Both procedures are informative and convenient for examining the patient.
Important! The use of more modern technologies can minimize the possibility of unwanted reactions and discomfort.
Recovery period after FCS - what to do?
It is also necessary to follow your doctor's instructions during the recovery period after FCS to avoid complications.
| General recommendations |
|
| Performance |
|
Cost of the procedure
The cost of the FCC ranges from 5,000 to 7,000 rubles and depends on a number of factors:
- Clinic operated by FCC: public, private.
- Type of hospital: 24 hours a day, throughout the day.
- Emergency or planned type of study.
- What drug was used to achieve the analgesic effect.
- What equipment was used.
- Availability of additional services.
Important! The price of TCS performed on an outpatient basis in a day clinic will be lower than if the study was performed at night.
Patient reviews
Feedback from patients with intestinal fibrocoloscopy is predominantly positive.
A number of patients recommend FCS as a means of prevention and timely detection of gastrointestinal diseases, while others note that this type of diagnosis is one of the most indicative.
It is recommended to perform FCS under anesthesia, sedation or intravenous anesthesia. Otherwise, you may experience psychological and physical discomfort, pain during a doctor’s examination of the gastrointestinal tract.
In accordance with reviews, it is necessary to ask the doctor all clarifying questions about compulsory medical insurance and the video colonoscopy algorithm before starting FKS. The doctor remains in touch throughout the entire procedure.
FCS is performed for at least 20 minutes while the doctor examines the colon. It must be prepared with extreme care to obtain the clearest and most reliable decoding results.
Preference should be given to good hospitals with highly qualified specialists.
»
In medical practice, there are two identical terms: “colonoscopy” and “fibrocolonoscopy”. They are synonymous and refer to the most common examinations performed by a proctologist or endoscope, but there is a difference, so they cannot be called identical at all. But to understand the differences between fibrocoloscopy and colonoscopy, it is necessary to understand the nature of these methods of examining the colon.
Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is a method of visualizing the colon to evaluate its condition.
A colonoscope is a fairly flexible probe equipped with a light, a small video camera, an eyepiece, tubes needed to supply air, and a pair of pliers to remove tissue for examination.
You may be interested in: Polyps in the bladder in men: symptoms and treatment, surgery
The length of such a device is about 160 cm, which, combined with its flexibility, allows for easy examination of the intestine, taking into account its anatomical curves.
However, the procedure is not painless, so such manipulations require the use of local anesthesia using various gels or ointments, for example, wild ointment. Before the examination, it is processed by the device. Preparing the patient for the procedure involves cleansing the intestines.
To do this, a person must follow a special diet 3-4 days before the procedure, and the day before and on the day of the procedure, instead of a diet, a complete hunger strike must be declared. Laxatives such as Endofalka are also used.
Since the colon is the last part of the human digestive tract, the doctor performing the procedure records all data from all parts of the colon. This is the only way he can get a complete picture of the state of the intestines.
The procedure can have both therapeutic and diagnostic purposes.
During the transition from the rectum to the large intestine and to the initial part of the large intestine - the appendix - a specialist’s note:
- color and presence of mucous sheen;
- what is the surface of the mucous membrane and its vascular structure;
- what is mucous membrane.
In addition to taking written notes, the specialist may take photographs of certain areas of the colon to highlight pathology. The duration of the entire procedure usually does not exceed half an hour.
Indications and contraindications
Colonoscopy can be used for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. About the indications for the procedure:
differentiation of colonoscopy from sigmoidoscopy
- pain in the colon in a specific location or without a specific location;
- bowel disorders (diarrhea, constipation);
- suspected Crohn's disease;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis;
- pathological separation from the intestines, such as blood, mucus or pus;
- sudden weight loss in the patient, sudden anemia;
- foreign body in the colon;
- you need to stop bleeding in the colon;
- you need to remove a polyp or tumor;
- it is necessary to restore intestinal permeability during stenosis;
- you need to do a biopsy for examination in a histology laboratory.
There are also a number of contraindications for this manipulation; they should be divided into absolute and relative.
The absolute includes shock of any etiology, acute myocardial infarction, peritonitis and ischemic colitis in flash form.
Relative contraindications again include intestinal bleeding, frequent pelvic surgery, the presence of a large hernia, heart or pulmonary failure.
Heart failure is a relative contraindication to manipulation
Fibercolonoscopy
Fibercolonoscopy is also an examination of the colon that uses a fibercoloscope.
The kit with the device itself contains tweezers for various purposes, brushes for cleaning, valves for the cylinders and eyepieces for visualizing the type of bowel as the procedure progresses.
The length of the device may vary depending on the part of the intestine being examined.
The preparation, procedure, indications and contraindications for FCS are similar to classical colonoscopy.
First of all, the difference between fibrocolonoscopy and colonoscopy is that the first procedure is more modern and is used more often. Unlike a colonoscope, a fiberscope has a more complex structure. A colonoscope consists of a simple rubber tube, while a fibercoloscope is made using extremely strong optical fiber.
In addition, the colonoscope is quite thick and less flexible. Therefore, if the procedure is performed using a modern device, the patient feels less uncomfortable than using a classic device.
Apart from the design features of the instruments used for colonoscopy and fiberoscopy, there are no other differences in these diagnostic methods.
They are both quite informative and convenient for medical personnel during the examination.
Advantages and disadvantages
Intestinal FCS has advantages and disadvantages:
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Direct visual examination of the mucous membrane, which can reveal the most minor defects | According to patients, the procedure is extremely painful |
| It is possible to perform endoscopic manipulations (stop bleeding, remove polyps) and/or take tissue for biopsy | Uncomfortable for the patient, long preparatory period |
| The study lasts no more than half an hour | A fiber colonoscope cannot always overcome areas of stenosis and examine some hard-to-reach areas |
Video
Doctor Maryana Abritsova answered the most frequently asked questions about FCS from patients in her video.
Do you have any questions? Specialists and readers of the HROMOSOMA website will help you ask a question
Was this article helpful?
Thank you for your opinion!
The article was useful. Please share the information with your friends.
Yes (100.00%)
No
X
Please write what is wrong and leave recommendations on the article
Cancel reply
Rate the benefit of the article: Rate the author ( 2 votes, average: 5.00 out of 5)
Discuss the article: