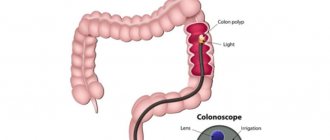
Colonoscopy is a diagnostic method that is used to assess the condition of the colon mucosa. The examination is carried out using a special instrument - a colonoscope. It is a thin flexible tube with a video camera at the end. The colonoscope is inserted into the intestines through the anus.
- Goals of performing a colonoscopy
- Preparing for a colonoscopy
- Diet before colonoscopy
- Indications and contraindications
- Diagnostic colonoscopy
- Therapeutic manipulations during colonoscopy
- Colonoscopy in a state of medicated sleep
- Colonoscopy technique
- Recording the procedure on video
- Recovery after colonoscopy
- Possible complications
- Alternatives to Colonoscopy
- Colonoscopy results
Goals of performing a colonoscopy
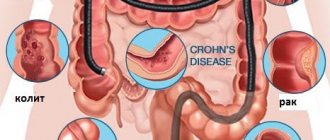
Using a colonoscope, the doctor can detect ulcers, polyps, foci of inflammation, tumors, and sources of intestinal bleeding. In addition, during a colonoscopy, tissue samples can be obtained from the intestines for histological and cytological examination, and polyps or other formations can be removed.
It is recommended to have your first colonoscopy at age 50. Further recommendations are given individually, depending on the results of the study. Unfortunately, most colon tumors are detected at late stages. There is only one reason here - late diagnosis of the tumor. The only way to detect a tumor at an early stage is regular examination of the colon, which allows us to identify pre-tumor pathology and remove it, or carry out other necessary treatment to prevent it from degenerating into cancer. The key to curing cancer is early diagnosis. Early diagnosis can be done using colonoscopy.
Diet before colonoscopy
An important part of preparing for a colonoscopy is proper diet in the preceding days and on the day of the examination. In general terms, the recommendations are as follows:
- A few days before the procedure, you need to switch to a low-fiber diet, reduce the consumption of fresh vegetables and fruits, dried fruits, nuts, and whole grains.
- 1–3 days before your colonoscopy and on the day of the procedure, you should avoid eating solid foods. Broths, clear fruit juices (for example, clarified juice from apples, white grapes), tea and coffee, and jelly are allowed. It is recommended to drink more fluid the day before.
- You should not eat or drink anything 2–4 hours before the procedure If with sedation, the patient must be on an empty stomach.
In parallel with the diet, in the afternoon before, the intestines are prepared for the procedure using laxatives. Recommendations regarding types of drugs and dosage regimens may vary from doctor to doctor.
Preparation for the procedure
It is necessary to carry out preliminary preparation in the form of diet and bowel cleansing so that nothing interferes with a good view of the surface of the mucous membrane.
It is the correct preparation of the patient for the study that is the key and guarantor of the reliability of the results.
Diet
Before the study, it is necessary to transfer the patient to a special menu.
| Prohibited Products | Authorized Products |
|
|
The day before the study, you must skip dinner (last meal before 6:00 pm); you should not have breakfast in the morning.
Read more: Nutrition before and after intestinal colonoscopy: basic principles, products and menu for the week
Drugs
Before the study, the patient is prescribed special medications against the background of decreased peristalsis.
| Brand name | How to cook | How to use |
| Lavacol | Dissolve a sachet (14 grams - 1 serving) in 200 ml of cold boiled water. | It is necessary to drink a total amount of 3 liters of solution (15 sachets), 200 ml portions, within three hours, 18-20 hours before diagnosis. |
| Fortrans | Dissolve 1 sachet of medicine in 1 liter of warm water. | 1 sachet is designed for 20 kg of human weight. You need to drink a glass (250 ml) at night every 15 minutes, the required amount of the drug. |
| Fleet Phosophosoda | Dissolve a bottle (45 ml - 1 serving) in 120 ml of cold boiled water. | The day before the test, the first portion should be drunk after breakfast (24 hours before diagnosis) and the second after dinner (12 hours before diagnosis). Wash down servings with two glasses of boiled cold water, 250 ml each. |
| Endofalk | Dilute 2 sachets in half a liter of boiled warm water, then add another half liter of cool water | Take 3 liters of the product (6 sachets) within five hours, 18-20 hours before the test. |
Purgation
If a person refuses to take drugs that cleanse the intestines, or if the patient has a history of severe constipation, it is necessary to enema the patient. The enema is carried out as follows:
- Take 1.5 liters of room temperature (25-28˚C) water into an Esmarch mug (enema).
- Drain water through the tube (squeeze out the air) so that it flows from the tip, and press the tube with a clamp.
- Lubricate the tip with Vaseline.
- Place the patient on a couch, previously covered with oilcloth, on top of which it is advisable to place a towel.
- Place the patient in a lying position on the left side with the left leg bent to the stomach.
- Hang the mug 1.5-2 meters above the patient's level.
- Spread the patient's buttocks with your hand.
- Insert the tip first towards the navel by 2-3 cm, then perpendicularly by 5-6 cm (in total, you need to insert the tip 7-8 cm).
- Open the valve on the tube extending from the mug.
- Slowly pour the contents of Emarch's mug into the patient's intestines and close the tube.
- Pull out the tip by squeezing the patient's buttocks.
- Ask the patient to be patient for 15-20 minutes (he can get up and walk).
Be sure to read:
Caecum: location, structure and functions
Read more:
- Colon cleansing with an Esmarch mug
- Colon cleansing with a syringe
After the patient has emptied his bowels, if necessary, the procedure can be repeated after an hour. It is advisable to carry out the procedure two evenings in a row before the study and the morning before the diagnosis.
Indications and contraindications
Indications for colonoscopy are:
- blood and mucus in the stool;
- presence of relatives with colon cancer;
- previous colon surgery;
- chronic abdominal pain of unknown etiology;
- suspicions of cancer, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease;
- elevated temperature for a long period of time, accompanied by anemia and weight loss.
Regular colonoscopy is also recommended for all people over 50 years of age for the early detection of tumors, polyps and other diseases of the colon.
Contraindications to colonoscopy are the active stage of Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis.
What is colonoscopy used for?
The procedure allows you to diagnose:
- Crohn's disease;
- inflammatory process;
- haemorrhoids;
- intestinal obstruction;
- polyposis;
- colon cancer;
- stenosis;
- organ tuberculosis;
- ulcerative colitis, etc.
Fiber colonoscopy and video colonoscopy are also used, which are modified and more modern research methods compared to conventional colonoscopy.
The procedure may also have a surgical focus and serve to excise a polyp, stop intestinal bleeding, or eliminate the causes of obstruction.
For the purpose of differential diagnosis, colonoscopy is often used in gynecology.
Diagnostic colonoscopy
A diagnostic colonoscopy is performed to identify certain pathological formations in the intestines. There are two special types of diagnostic colonoscopy:
- A screening colonoscopy is recommended for all people over 50, even if they have no symptoms. For some bowel diseases, screening may need to start at a younger age. This type of screening is used for early diagnosis of polyps that can develop into a malignant tumor and intestinal cancer.
- Control colonoscopies are periodically performed in people with a history of polyps, colon cancer, and inflammatory bowel diseases.
Having discovered a pathological neoplasm in the intestine, the doctor removes it using a special instrument inserted through a colonoscope and sends it to the laboratory for histological and cytological examination. This procedure is called a biopsy .
The European Clinic has a promotion “Gastro- and colonoscopy under intravenous sedation”. The cost of the complex service includes endoscopic examinations of the stomach and colon, light anesthesia (sedation, “medicated sleep”), a preliminary appointment with a specialist (candidate of medical sciences or doctor of medical sciences), a three-hour stay in a comfortable room. More details about the program.
Therapeutic manipulations during colonoscopy
During an endoscopic examination of the colon, the doctor may perform some therapeutic procedures:
- Remove polyp.
- Stop intestinal bleeding, for example, using electrocoagulation or clipping.
- Eliminate stenosis (narrowing of the intestinal lumen) caused by a malignant tumor or other causes. A special balloon is inserted into the narrowed area and inflated to expand the lumen, and then a stent is installed - a tube with a mesh wall made of metal or plastic (this procedure is called stenting ).
During the work of the endoscopy department at the European Clinic, more than a hundred endoscopic stenting of the colon was performed under the guidance of an endoscopist, Doctor of Medical Sciences Mikhail Sergeevich Burdyukov. This minimally invasive procedure helps restore intestinal patency in inoperable cancer.
Often, a colonoscopy is initially performed as a diagnostic procedure and, if pathological changes are detected, it becomes a therapeutic procedure.
Colonoscopy in a state of medicated sleep
Colonoscopy is usually painless, but the patient may experience discomfort from a feeling of bloating (this goes away immediately after the procedure) and the probe moving through the loops of the intestine. In the European clinic it is possible to carry out the procedure in a state of medicated sleep. In this case, the patient is given a special sedative, under the influence of which he is plunged into deep sleep. After approximately 40 minutes, the effect of the drug ends, and within 5-10 minutes after waking up the patient can walk and talk, and after an hour he can go home.
Absolute contraindications
These contraindications imply the complete impossibility of carrying out the procedure. They are associated either with the general serious condition of the patient or with diseases of the abdominal organs.
General diseases
One of them is acute heart failure, usually caused by myocardial infarction. The stress that the patient experiences during the study can lead to further deterioration of heart function.
On this topic
- Other diagnostic methods
What is the difference between histology and cytology
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 4, 2020
A sharp drop in blood pressure, which is associated with a state of shock, also becomes an obstacle to colonoscopy. In this condition, the patient is indicated for resuscitation measures; diagnostic procedures are postponed until relatively normal vital signs are restored.
Another condition in which endoscopic examination of the intestine is contraindicated is pregnancy, since such an intervention can lead to its interruption.
Abdominal diseases
The development of peritonitis in the patient - acute purulent inflammation of the abdominal cavity - makes this diagnostic procedure impossible. The infectious process must first be eliminated.
Severe forms of colitis, inflammatory processes on the mucous membrane of the large intestine, after colonoscopy can be complicated by bleeding.
It is impossible to conduct an examination of the intestines in the case of already confirmed penetrating damage to the wall of this organ. The first priority is to normalize the patient's condition.
Colonoscopy technique
A diagnostic colonoscopy lasts on average 30 minutes. If therapeutic manipulations are required, the procedure time increases.
In order for the patient to undergo the procedure without pain and discomfort, the European clinic uses sedation - the patient is immersed in a state of “medicated sleep.”
The patient must be completely undressed from the waist down. He is placed on his left side, with his legs bent and knees brought to his stomach. The doctor lubricates the colonoscope with Vaseline, carefully inserts it through the anus and slowly advances it, examining the intestinal mucosa. In this case, the intestines are inflated with gas to provide a better view. In the European clinic, carbon dioxide is used because it acts as an antispasmodic, is absorbed through the intestinal walls and eliminated from the body faster than oxygen and nitrogen.
The image from the colonoscope camera is transmitted to the device screen. Videos of the study are recorded and saved on a computer.
After the intestines are examined, the doctor carefully removes the colonoscope. The study is completed.
How to do a bowel colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is a diagnostic procedure that is not classified as a complex procedure, but is unpleasant. In standard situations, it is performed by a doctor and a nurse.
Colonoscopy is performed in a specially prepared room. The patient must remove all clothing below the waist and lie on his left side on the medical couch. Legs need to be bent at the knees and pressed to the stomach.
Methods of pain relief
The use of anesthesia during the procedure depends on the indications. The doctor may prescribe local anesthesia, general anesthesia, or use sedation.
Typically, local anesthesia is used. For this purpose, medicines based on lidocaine are used in the form of a gel or ointment. The drug is used to lubricate the tip of the colonoscope, as well as the mucous membranes of the small intestine. With the help of anesthesia, local anesthesia is achieved, leaving the patient's consciousness clear. Local anesthesia can be administered by intravenous injection of an anesthetic solution.
General anesthesia allows the patient to be put into deep sleep with complete loss of consciousness. Even taking into account the fact that modern medicine has a high level of development, general anesthesia has a number of contraindications and carries some risks. In addition, after anesthesia, a person needs a certain time to recover.
General anesthesia is used for colonoscopy in children under 12 years of age, people suffering from mental disorders, and also with a low pain threshold.
Sedation is rarely used. With the help of drugs such as midazolam and propofol, the patient is put into a state of light sleep and does not feel pain. Consciousness does not turn off.
Progress of the study
Once the anesthesia has taken effect, the doctor inserts a probe into the anus to examine the condition of the walls of the large intestine. Directing the colonoscope forward, the doctor controls its movement by palpating the surface of the abdomen. To make the examination reliable and objective, a stream of air is supplied to the intestines.
The trapped air causes discomfort and bloating in the patient. The inconvenience is compounded by the fact that you cannot move during the study. Therefore, many patients choose general anesthesia or sedation during a colonoscopy.
The study usually lasts from 15 to 30 minutes. The movement of the colonoscope through the colon is recorded by a built-in video camera. If necessary, material is taken for a biopsy. At the end of the procedure, gas is removed through the outlet tube of the probe and the colonoscope is carefully removed from the anus.
If local anesthesia was used, the patient is allowed to go home. If general anesthesia was used, then the person is observed for some time until consciousness is fully restored.
You are allowed to return to your normal diet immediately after the procedure is completed. If you still feel bloated, it is recommended to take activated charcoal and massage your abdomen.
Recovery after colonoscopy
Hospitalization is not necessary, and colonoscopy can be performed on an outpatient basis. The patient can leave the clinic as soon as he recovers from anesthesia. But you are not allowed to drive on your own on this day. You need to take one of your relatives to the clinic so that you can be escorted home.
Notes and recommendations regarding the recovery period after colonoscopy:
- When the effect of sedation wears off, a feeling of cramping and fullness of the intestines may appear. It will soon pass. In order for the gas to leave the intestines faster, it is recommended to walk.
- For 24 hours after the procedure, you should avoid drinking alcohol, driving vehicles, and doing work that requires concentration.
- Unless otherwise advised by your doctor, you can begin eating as usual immediately after the sedation ends. A special diet is prescribed after removal of polyps and other surgical procedures.
- It is recommended to rest for one day after the study, then you can do all your usual activities without restrictions, and go to work.
- If a biopsy was performed during a colonoscopy, you may notice some blood in your stool for 1 to 2 days afterward.
- If you need to take blood clot preventative or other medications continuously, ask your doctor how long after your colonoscopy you can start taking them again.
- Because your bowels were cleaned before the colonoscopy, another bowel movement may take a few days. It depends on your diet. If you do not have stool for a very long time after the procedure, consult your doctor.
You should immediately seek medical help if symptoms such as high fever, bleeding from the anus, or abdominal pain appear.
Possible complications
Colonoscopy is a safe test. The risk of complications during a diagnostic examination of the colon is minimal. The risks of surgical endoscopy of the colon are less than one percent, which allows us to speak with confidence about its safety. Complications during endoscopic examination of the colon are very rare, including:
- Allergic reactions to sedative medications.
- Bleeding after biopsy, polyp removal.
- Perforation (rupture of the wall) of the intestine.
Alternatives to Colonoscopy
In addition to colonoscopy, other tests may also be used for the early diagnosis of malignant tumors of the colon:
- Fecal occult blood test (annually). The accuracy of the study is 62–79%. Out of 10 people with colon cancer, only 6-8 will test positive. False-positive results are possible if the patient has recently eaten red meat, foods rich in vitamin C, or is taking drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. If the test shows a positive result, a colonoscopy is required to clarify the diagnosis.
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy (every 5 years) is an endoscopic examination of the rectum and lower third of the colon. It is performed in the same way as a colonoscopy, but during it, a smaller part of the intestine is examined. Helps identify 70–80% of polyps and malignant tumors in the rectum and lower colon.
- Fecal DNA testing combined with stool occult blood testing (every 3 years). Can detect up to 92% of malignant tumors and up to 42% of precancerous conditions.
- Virtual colonoscopy (CT colonography) (every 5 years) - multislice computed tomography (MSCT), during which the colon is filled with air. The detection rate of tumors larger than 1 cm using this study is 94%, polyps measuring 6–9 mm is 65%. Polyps smaller than 6 mm are not detected. If a polyp is found during CT colonography, a colonoscopy will still have to be performed to remove it.
Thus, colonoscopy is the most accurate and informative method of screening for colon cancer, while it makes it possible to immediately carry out a biopsy and some therapeutic manipulations.
About the pain of the procedure and indications for anesthesia
The procedure is often painful and causes significant discomfort. Patients often refuse the study; on the eve of diagnosis, some experience panic attacks, increased blood pressure, tachycardia, and so on. This indicates increased emotionality.
In some cases, general anesthesia is used. It is indicated in the following cases:
- children under 12 years of age;
- patients with certain psychiatric diagnoses who may harm themselves or staff during the examination;
- high threshold of pain sensitivity of the patient;
- adhesive intestinal disease and the presence of intestinal strictures (narrowings) (according to the results of irrigography) - general anesthesia allows you to relax the intestinal walls and abdominal muscles as much as possible, thereby facilitating the advancement of the fiberscope.
In some cases, it is enough to premedicate 30-40 minutes before the test. The main medications used are sedatives: propafol, midazolam, and so on. Consciousness is preserved, but the person is put into a kind of sleep, while pain sensations are reduced and emotional lability is eliminated.
Be sure to read:
Location and functions of the appendix