What is pulmonary emphysema?
Emphysema
is a disease that is a violation of lung ventilation and blood circulation. It lasts quite a long time. Very often a person with such a disease becomes disabled.
Signs of emphysema
:
- chest expansion
- shortness of breath
- expansion of intercostal spaces
ICD 10 code
- J43.9.
Men are more susceptible to this disease. People over 60 years of age are also at risk. The risk of this problem also increases in those who have chronic obstructive diseases of the pulmonary system.
This disease is also dangerous due to complications that can lead to disability and death.
How is the study carried out, and what does the doctor see on an x-ray for pulmonary emphysema?
There is no preparation required before the procedure. To ensure a clear X-ray, the patient will be asked to undress to the waist and remove jewelry that hangs down the chest.
The examination is most often carried out in a standing position, using special equipment for x-ray diagnostics. The patient must stand as required by the doctor so that the image in the desired projection is clearly readable. The clarity of the radiograph is also affected by the immobility of the chest at the time of irradiation. The specialist’s requirement to inhale and hold your breath for a few seconds is based on the maximum expansion of the chest and lungs for a better view of the organs and their immobility.
For an accurate diagnosis, a specialist may ask you to take test images:
- irradiate during retention, inhalation and exhalation - in a sick person, the enlightenment remains the same;
- targeted images are carried out to examine areas with high pneumatization;
- cover part of the diaphragm with a screen to detect its reduced mobility.
Taking X-rays involves irradiating the body. If, due to the patient’s inattention to the doctor’s request, the picture is unclear, the procedure will have to be repeated, once again being exposed to hard rays.
Decoding
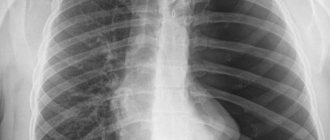
The areas of the lung affected by emphysema appear the most transparent in the image. This indicates increased pneumatization of these areas. In addition to clearing in the image, the doctor evaluates:
- Changing the shape of the chest. The barrel shape of the pulmonary region and the increase in anteroposterior size can only be seen in the lateral projection. With emphysema, the intercostal spaces become widened, and the ribs are positioned horizontally.
- Changes in the lung pattern and its redundancy. The size of the organ itself (pulmonary field) increases in relation to the physiologically normal one. Because of this, the outlines of the diaphragm dome change, and at a high degree of development of the process, it becomes like a tent: with a sharp, raised middle and steeply sloping sides.
- Transparent (enlightened) lungs. On an x-ray, the entire lung tissue is filled with air and transmits rays, creating a more or less pronounced “haze”. The affected areas appear even more transparent.
Classification of the disease
The classification of pulmonary emphysema is divided into several large sections.
By origin
:
- Primary - due to congenital abnormalities in the body. This type is very difficult to treat. It appears even in newborns.
- Secondary is a milder form of the disease. It may occur unnoticed by the patient himself. However, advanced stages can greatly impact a person’s ability to work. Occurs due to chronic lung diseases.
According to the nature of the flow
:
- Acute - a very rapid change in the lungs as a result of extreme physical exertion or asthma.
- Chronic - changes do not appear so quickly.
Due to the occurrence
:
- Laboratory - appears in newborns due to obstruction of one of the bronchi.
- Senile - due to age-related changes in blood vessels and impaired elasticity of the walls of the alveoli.
By prevalence
:
- Focal - changes in the parenchyma appear around foci of tuberculosis, the site of bronchial blockage, scars.
- Diffuse - tissue damage and destruction of the alveoli occurs throughout the lung tissue.
According to anatomical features and relation to the acinus
:
- Bullous (bubbly) - large or small blisters appear where damaged alveoli are located. The blisters themselves can burst and become infected. Also, due to their large volume, neighboring tissues are subject to compression.
- Centrilobular - the center of the acinus is damaged. A lot of mucus is released. Inflammation also appears due to the large lumen of the alveoli and bronchi.
- Panacinar (hypertrophic, vesicular) is a severe form of emphysema. Inflammation does not appear. However, there is significant respiratory distress.
- Interstitial (subcutaneous emphysema) - air bubbles appear due to rupture of the alveoli under the skin. Through the gaps between the tissues and the lymphatic pathways, these bubbles move under the skin of the neck and head.
- Peri-scar - occurs near fibrous foci and scars in the lung. The disease occurs with minor symptoms.
- Periacinar (distal, perilobular, parasepital) - occurs with tuberculosis. The extreme parts of the acinus near the pleura are affected.
Lifestyle correction for patients with emphysema
If persistent emphysema is detected on an x-ray, lifestyle changes should be made to improve overall well-being and improve quality of life. The following activities are recommended:
- Quit smoking, as smoking is the main cause of COPD.
- Change your work activity (if it is related to the chemical, coal, flour milling and other industries that increase the risk of developing obstruction and other respiratory diseases).
- Move to an ecologically clean region or at least undergo treatment in a sanatorium once a year; you need to choose a dry and warm climate.
- Follow a hypoallergenic diet, as sometimes food can cause bronchial asthma and lead to bronchial obstruction.
- For any diseases of the upper respiratory tract, follow the doctor’s recommendations and strictly adhere to the prescribed therapy.
Pulmonary emphysema is the logical conclusion of a chronic obstructive process. The pathology is accompanied by significant changes in the functional state of the lung tissue and is clinically manifested by signs of respiratory failure. As the process progresses and decompensates, cardiovascular disorders form. It is important to detect the first signs of emphysematous changes for timely lifestyle correction and prevention of serious complications.
Bullous emphysema
Bullous emphysema is a serious disorder of the structure of the lung tissue with subsequent destruction of the interalveolar septa. In this case, a huge air cavity appears.
Bullous emphysema
This form of the disease occurs due to purulent and inflammatory processes in the lungs.
With single bullae (blisters), the disease is very difficult to diagnose. It cannot be seen even with a regular x-ray. It is detected only when there are a large number of bullae throughout the lung tissue.
The biggest danger of bullous emphysema is that there is a high risk of blisters bursting. As a rule, it occurs due to a strong cough or during heavy physical exertion.
When the bulla ruptures, air from the lungs enters the pleural cavity. Thus, pneumothorax occurs. The accumulated air creates a lot of pressure on the lung.
If there is a large defect in the lung tissue, the lung will not be able to close. As a result, there is a continuous flow of air into the pleural cavity.
At the most critical level, air begins to enter the subcutaneous tissue and mediastinum. As a result, respiratory failure and cardiac arrest may occur.
Diagnosis of emphysema
If symptoms similar to pulmonary emphysema occur, you should consult a general practitioner or pulmonologist.
Percussion
Using percussion (tapping), a specialist can determine:
- “box” sound over emphysematous areas of lung tissue;
- limited mobility and drooping of the lower edge of the lungs.
Auscultation
During auscultation (listening with a phonendoscope):
- increased exhalation;
- decreased breathing;
- dry or moist wheezing due to bronchitis;
- muffling of heart sounds due to hyperairiness of the lung tissue, which absorbs sound;
- increased heart rate (tachycardia). In conditions of oxygen starvation, the heart tries to correct the situation;
- an increase in the frequency of respiratory movements, indicating respiratory failure.
Laboratory and instrumental diagnostics
From laboratory tests and instrumental research methods it is possible to use:
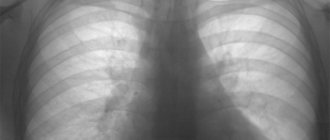
- plain radiography of the chest organs. It is a very important method for diagnosing emphysema. There will be areas of increased transparency, an increase in the volume of the lungs, a low location of the diaphragm, drooping of the lower edges of the lungs;
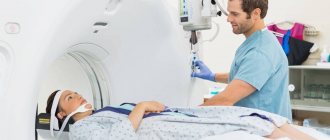
- computed tomography. The disadvantage is the high radiation exposure. But it allows you to examine the lung tissue layer by layer and identify airy areas, even of small sizes, bullae, their volume and location, areas of fused alveoli, changes in the roots of the lungs;
- magnetic resonance imaging. Allows you to determine areas of compression of the lung tissue, circulatory disorders, even in small vessels, the presence of pleural fluid;
- spirography. It is performed using a spirograph, which takes into account the amount of air exhaled and inhaled. With emphysema, an increase in residual volume, total lung capacity, a decrease in vital capacity and pulmonary ventilation are determined. Indicators are reduced by 25 - 30%;
- peak flowmetry. Determined using a device that allows you to determine the maximum expiratory flow rate. It will be reduced by 20%;
- general blood test. There is an increase in red blood cells, hemoglobin, hematocrit (the ratio of blood plasma to red blood cells), a decrease in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate below 2 mm/h;
When determining the gas composition of the blood, a decrease in oxygen in the arterial blood is noted below 60 mmHg, an increased level of carbon dioxide is above 50 mmHg.
Causes
There are many causes of pulmonary emphysema. However, they can all be divided into two main types.
First type
, includes what leads to impaired elasticity and strength of lung tissue. The main one from this category will be a violation of the system responsible for the formation of enzymes. In this case, the properties of the surfactant change and a lack of A1-antitrypsin appears in the body.
The presence of gaseous toxic substances in the inhaled air significantly affects the body. Frequent incidence of infectious diseases reduces the ability of the lungs to protect. Therefore, they are more quickly exposed to harmful effects.
Smoking is the main reason why emphysema can develop. Plumes of tobacco smoke in the lungs accumulate inflamed cells, from which substances are released that can destroy the partitions connecting the cells. People who smoke are more vulnerable to the manifestation of this disease; emphysema in smokers has more complex forms.
To the second type
include factors that can cause an increase in pressure in the alveoli of the lungs. These include previous pulmonary diseases. For example, chronic obstructive bronchitis or bronchial asthma.
Since emphysema has two types, it can be primary or secondary. All factors lead to the fact that the elastic tissue of the lungs is damaged and loses the ability to fill the lungs with air and release it.
The lungs become overfilled with air, causing the small bronchi to stick together when exhaling. Pulmonary ventilation is also impaired.
With emphysema, the lungs increase in size and take on the appearance of a large-pored sponge. If you examine emphysematous lung tissue using a microscope, you can observe the destruction of the alveolar septa.
Briefly about the essence of the disease
Emphysema is considered the final stage of many chronic diseases accompanied by inflammation. In addition, an increase in the airiness of lung tissue is characteristic of bronchial asthma and occupational diseases of the organ parenchyma. Thus, there are factors for the development of emphysematous disorganization of the lungs:
- Long history of smoking.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
- Bronchial asthma.
- Chronic bronchitis, including with an obstructive component.
- Long-term professional contact with dust and other pollutants.
- The birth defect is alpha-antitrypsin deficiency, which is expressed in the weakness of the walls of the terminal structures of the respiratory functional unit.
Deficiency of this compound (congenital pathology) or chronic exposure to the above factors lead to the inability of bronchioles and alveoli to perform their functions. Their walls become deformed and expand. An air trap occurs - a condition in which air passes freely into the respiratory tract, but it cannot move back in the opposite direction. Vast spaces appear that are filled with air and are completely or partially excluded from the act of breathing. Emphysematous bullae may develop.
Symptoms of emphysema
Let's talk about the symptoms of emphysema. It should be said right away that this disease often has hidden initial forms. Therefore, a person may not even suspect that he is sick.
The presence of symptoms appears already at the stage of severe lung damage.
Usually, shortness of breath
observed at the age of 50-60 years. Initially, this symptom is noticed during physical work. And later it manifests itself even in a calm state.
During an attack of shortness of breath, the skin of the face becomes pinkish. Most often, the patient takes a sitting position and leans slightly forward. Constantly holding onto something in front of him.
Emphysema makes it difficult to breathe
. When exhaling, various sounds are heard, since this process is very difficult for the patient.
Inhalation occurs without difficulty.
However, it is difficult to exhale. Therefore, it is often observed that the lips are folded into a tube to facilitate the exhalation process.
Since the appearance at moments of shortness of breath is characteristic, such patients are called “pink puffers.”
After the onset of symptoms of shortness of breath, after a certain time the presence of cough
which is not too long.
A clear sign that will indicate emphysema will be a significant weight loss
. Indeed, in this case, the muscles become very tired, working exhaustingly to facilitate exhalation. If body weight has decreased, then this is an unfavorable sign of the course of the disease.
Patients also have an expanded chest
, having the shape of a cylinder. She seemed to freeze while inhaling. Its figurative name is barrel-shaped.
If you pay attention to the area above the collarbones, you will notice expansion here, and the spaces between the ribs seem to sink.
When examining the skin, a bluish tint is noted, and the fingers take on a shape reminiscent of drumsticks
. Such existing external changes are typical in the presence of prolonged oxygen starvation.
Subcutaneous emphysema of the face
Its appearance is often associated with fractures/cracks of the skull bones, namely the face/nose/paranasal sinuses, and rupture of the mucous membrane. Sometimes dental procedures can also be a cause if high-speed “blowers” are used.
Although, as practice shows, air cushions often move to the face area from the chest cavity.
to diagnose such emphysema, since the swelling is more than obvious, although it does not cause much discomfort. The eyelids especially suffer; they not only swell, but also droop, which does not look very aesthetically pleasing.
Diagnosis of the disease
Respiratory function tests are of great importance in diagnosing pulmonary emphysema. Peak flowmetry is used to assess how narrowed the bronchi are.
.
Peak flowmetry in the diagnosis of pulmonary emphysema
The patient should be at rest, inhale twice and exhale into the peak flow meter. He will record the degree of narrowing.
Obtaining this data will make it possible to determine whether a person really suffers from emphysema or whether he has bronchial asthma or bronchitis.
Spirometry
determine how much the tidal volume of the lungs changes.
This helps in identifying inadequate breathing. Spirometry
Carrying out additional tests that use bronchodilators
, makes it possible to say what kind of disease is present in the lungs. In addition, the effectiveness of treatment can be assessed.
With x-ray
, it is possible to identify the presence of dilated cavities that are located in different pulmonary sections. You can also determine increased lung capacity. After all, in this case the dome of the diaphragm moves, and it becomes denser.
Carrying out a computed tomography
will make it possible to diagnose the presence of cavities in the lungs, which will also be more airy.
Clinical picture and diagnostic methods
Emphysema of the lung at the initial stage of its development practically does not manifest itself in any way. Shortness of breath may occur after intense physical activity. Over time, it becomes constant and does not leave the patient even during rest.
With this disorder, there is a rapid shallow inhalation, which is replaced by a problematic exhalation. The skin on the cheeks takes on a pink tint. As emphysema progresses, the clinical picture becomes more pronounced.
Severe shortness of breath is accompanied by more and more new symptoms:
cyanosis of lips, nails and tongue;- the so-called emphysematous chest appears (against the background of an increase in volume, it acquires a barrel-shaped silhouette);
- widening the spaces between the ribs;
- the fingers on the hands become like drumsticks.
In some cases, patients with emphysema begin to rapidly lose weight. This symptom is caused by fatigue of the respiratory muscles, which experience enormous stress when exhaling. A noticeable weight loss indicates the aggressiveness of the pathological process.
Pulmonary emphysema has quite characteristic symptoms. However, the same signs may indicate other pathological processes in the body. If the patient has previously been diagnosed with bronchitis or asthma, he may not pay due attention to shortness of breath.
That is why emphysema is very often detected in the later stages of development, when the clinical picture is especially pronounced. Attacks of suffocation are now repeated so often that the patient develops a fear of death.
If you suspect emphysema, you should seek help from a physician. If necessary, he will refer you for additional consultation with a pulmonologist. For this disease, the initial examination includes a physical examination and listening to the pulmonary system. At the next stage, they move on to instrumental options for diagnosing emphysema.
First, the doctor tests your breathing functions. Using specialized instruments, he evaluates the severity of respiratory failure and narrowing of the bronchi, and the approximate volume of the lungs. These parameters are studied not only in a quiet position, but also after several deep exhalations.
In particularly serious cases, testing is carried out using so-called bronchodilator medications. Such a detailed diagnosis of pulmonary emphysema makes it possible to differentiate it from asthma and bronchitis.
A potential patient is always additionally prescribed a chest x-ray.
With its help, a qualified specialist will be able to determine the presence of defects, assess lung volume, and the degree of change in the vascular pattern. Downward displacement of the diaphragm helps confirm the diagnosis of pulmonary emphysema.
X-ray is considered the most informative examination method in this matter. It is second only to CT.
Treatment of emphysema
Now let's look at the main methods of treating pulmonary emphysema. It is worth saying that all treatment procedures should be aimed at facilitating the respiratory process. In addition, it is necessary to eliminate the disease whose action led to the development of this problem.
Surgical treatment of emphysema
Treatment procedures are mainly carried out on an outpatient basis. But there should be an opportunity to be observed by doctors such as a pulmonologist
or
therapist
.
Lifelong use of bronchodilators, in the form of inhalations or tablets, is recommended. If there is cardiac and respiratory failure, then oxygen therapy is carried out, after which diuretics are taken. Breathing exercises are also recommended.
If a person is diagnosed with an infection, he is hospitalized in the hospital. He may also be hospitalized if respiratory failure is severe or if any surgical complications arise.
Emphysema can also be treated surgically.
An operation is performed in which the volume of the lungs is reduced. The technique involves eliminating damaged areas of lung tissue, which leads to a decrease in pressure on the remaining part. After this procedure, the patient's condition improves significantly.
Emphysema - treatment with folk remedies
If you have emphysema, you should not miss out on treatment with folk remedies.
Treatment of emphysema with folk remedies
Here are some methods:
- Herbal medicine
. Some plants have expectorant and bronchodilator properties. For emphysema, they are used to prepare infusions and decoctions, which are later taken orally. Such plants include: licorice, caraway, fennel, thyme, lemon balm, eucalyptus, anise, sage and many others. - Potato
. Carrying out hot inhalations over boiled potatoes helps cough up and relaxes the bronchial muscles. - Aromatherapy
. The air is saturated with the help of medicinal components of essential oils of dill, oregano, wormwood, chamomile, thyme, sage and others. For spraying, you can use a diffuser or aroma maker (5 - 8 drops of ether per 15 square meters of room). This helps in improving the patient's condition. You can also apply a few drops of these oils to your feet, palms and chest. In 1 tbsp. l. Add 2-3 drops of vegetable oil or a mixture of several drops.
If a person has emphysema, he should periodically visit a pulmonologist. Folk remedies are used only as a supplement to the main methods of treatment. You should not use only them, as this will not bring the desired effect.
Use of oxygen therapy
To improve gas exchange at the very beginning of the disease, oxygen therapy is prescribed. During this technique, the patient inhales air with a reduced amount of oxygen for 5 minutes.
Oxygen therapy
Next, the same period of time is spent on the supply of ordinary oxygen. Such cycles are repeated 6 times during the session.
Treatment is carried out once every day. The course is 15-20 days.
If this method is not possible, then a nasal catheter is inserted into the patient. It is through this that oxygen is supplied to alleviate the patient’s condition.
Breathing exercises for emphysema
Good breathing exercises also help a lot with emphysema.
Breathing exercises for emphysema
Here are some exercises:
- You should inhale and hold your breath. Next, exhale sharply using the mouth opening. At the very end of exhalation, change the position of the lips to a tube.
- Also hold your breath. Next, exhale using small bursts, folding your lips in the form of a tube.
- Breathe in and don't exhale. Extending your arms and clenching your fingers into fists, move them to your shoulders, then stretch them to the sides and lower them back to your shoulders. Thus, do this a couple of times, and then exhale strongly.
- Inhale for 12 seconds, hold your breath for 48 seconds. and exhale for 24 s. Repeat this three times.
Drug treatment
If there is an exacerbation of the inflammation process, then drugs with an antibacterial effect may be prescribed.
Treatment of bronchial asthma or bronchitis occurs with drugs that dilate the bronchi. To facilitate the removal of mucus, mucolytic drugs should be taken.
Diet for emphysema
The diet for pulmonary emphysema should be balanced. It should contain many vitamin components and microelements. The diet must necessarily consist of vegetable and fruit dishes. In addition, these products should be consumed raw.
It is recommended to use a low-calorie diet, no more than 600 kcal per day. If the positive dynamics are stable, then the calorie content can be increased to 800 kcal. per day.
To select the correct menu for every day, I recommend using our calorie calculator.
Also, the main rule is to avoid nicotine. It's better to quit smoking right away. That is, do not stretch it out for a long cessation. In addition, you should not be in a room where other people smoke.
Application of massage
The use of classical, segmental and acupressure techniques leads to the fact that the sputum leaves faster and the bronchi expand.
In this case, preference is often given to acupressure massage, since it is more effective.
Therapeutic exercises for emphysema
Pulmonary emphysema is accompanied by the muscles always being in tension, which leads to their fatigue. To prevent muscles from becoming overstrained, you should do therapeutic exercises.
Here are some exercises:
- For example, exercises that create positive pressure as you exhale. To do this, take a tube. One end of it is placed in water. The second person takes it into his mouth and slowly exhales through it. An obstacle in the form of water puts pressure on the exhaled air.
- To train your diaphragm, you need to stand up and take a deep breath. As you exhale, point your arms forward and bend. When exhaling, the stomach should be pulled up.
- Another task: lie on the floor, put your hands on your stomach. When exhaling, press on the peritoneum.
Features of X-ray diagnostics of emphysematous changes
Emphysema is a pathology that contains not only signs of structural damage to the lung tissue, but also the functional failure of this organ. Intact areas of lung tissue do not take part in respiration and gas exchange. Therefore, a symptom of progressive respiratory failure occurs.
There are two groups of signs of pathology during X-ray examination:
In order to appreciate and see them, one photo will not be enough. It is necessary to conduct a study in two projections, because it is the lateral projection (laterogram) that will be informative in terms of visualizing X-ray morphological signs.
Radiography using the Sokolov method provides a lot of information.
This is an x-ray method that allows you to assess the functionality of the lungs. That is, the patient is forced to inhale as much as possible, hold his breath, and then forcefully exhale as much as possible. At all these stages, images are recorded. With the help of a tunnel cassette, it becomes possible to examine the lung tissue, pulmonary pattern and other signs in the context of the functional state.
Complications of the disease
This disease sometimes leads to various complications. Among them:
- Infectious complications
. Pneumonia often develops, and lung abscesses occur. - Inadequate breathing. Because there is a disruption in the exchange process between oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs.
- Heart failure
. In severe cases of the disease, an increase in pulmonary pressure is observed. In this regard, there is an increase in the right ventricle and atrium. All parts of the heart gradually change. Therefore, there is a disruption in the blood supply to the heart. - Complications of the surgical plan
. If the cavity, which is located near a large bronchus, ruptures, then air can enter it. Pneumothorax forms. If the septum between the alveoli is damaged, bleeding will occur.
Diagnosis of functional disorders
Carrying out functional tests during radiography is necessary for the differential diagnosis of irreversible changes in lung tissue.
With emphysema in the lungs, despite the increased volume, there is no functional exchange of used air. The dilated alveoli contain the same air. This leads to decreased blood oxygenation and clinical signs of hypoxia. To determine radiological symptoms of irreversible functional changes, the following tests are used:
- Sokolov’s method: a series of sequential photographs are taken on 13x18 cm X-ray film in different phases of the respiratory cycle, and then the excursion of the diaphragm is compared using a ruler;
- The method of targeted images is a aimed diagnosis at the area of local emphysema: several images are taken while inhaling deeply, then exhaling, while holding the breath, then the results are compared;
- Method using a shield: close the right lung so that the dome of the diaphragm is under the lower edge of the shield. Then a series of photographs are taken; the excursion of the lung is determined by the distance from the barrier to the diaphragm during the phases of inhalation, exhalation, and breath-holding.
Emphysema - life prognosis
What is the prognosis for life with emphysema? It is impossible to say exactly how long they live. It all depends on the nature of the disease and its treatment.
However, it should be said right away that it is impossible to completely recover from this disease. The peculiarity of the disease is its constant progression. Even if treatment is being carried out.
If you seek help from a medical facility in time and follow all procedures, the disease will be slightly slowed down. The condition improves, and disability is postponed.
If emphysema developed due to the fact that there was a defect in the congenital enzyme system, then no one can give a positive prognosis.
Favorable outcome factors
:
- Detection of the disease at an early stage
- The disease passes in a moderate form
- The patient strictly follows the diet prescribed by doctors
- Complete smoking cessation
X-ray symptoms
Respiratory failure is also reflected in the X-ray diagnosis of the disease. Usually, during fluoroscopy of the lungs, a specialist in this imaging technique very clearly sees a decrease in the mobility of the diaphragm. In a healthy person, the amplitude of movements performed by this muscle is sufficient. With emphysema, this value progressively decreases.
According to the previously described method Yu.N. Sokolov, you can assess the functional state of the lung tissue. Normally, the intensity and contrast of structures during imaging varies greatly depending on the phases of breathing. At the same time, the opposite picture is typical for emphysema. These indicators do not change significantly. This is a rather specific sign of emphysematous disorganization of lung tissue.
Prevention of emphysema
To prevent emphysema, you should do the following:
- Stop consuming tobacco products.
- Treat pulmonary diseases in a timely manner to prevent the development of the disease.
- Leading a healthy lifestyle helps to improve the condition and maintain the body in healthy shape. Playing sports, performing breathing exercises, walking in the fresh air, visiting the bathhouse - all this contributes to the normal functioning of the bronchi and lungs.
- In order for your lungs to be healthy, you need to be in the forest more often, inhaling the healing aromas of pine needles. Sea air is also beneficial. Such places help open the lungs and saturate the blood with oxygen.
- Watch your diet. It must contain fresh fruits. There should also be foods with a high amount of vitamin elements and nutrients.