07 Jun 2020 at 13:13 Other MRI studies 2589
Every patient faced with the need for magnetic resonance imaging wants to know how MRI differs from X-ray , and why the doctor prescribed this particular diagnostic procedure to him. Some citizens believe that there is no significant difference between these diagnostic methods. However, in reality this is not the case. Read below about the features and differences between MRI and radiographic examination.
Is MRI an X-ray or not?
Some patients do not see the difference between the methods, believing that they do not have significant differences. In fact, MRI is a modern and highly technical method of examination based on a magnetic field. It helps to scan the body without pain or danger to health, and does not change the structure of tissues at the cellular level. When developing the scanner, the features of X-ray radiation were not used.
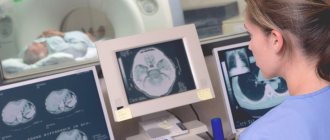
An MRI tomograph is a massive apparatus in which the patient is placed on a special retractable table. Powerful magnetic coils work around a person, generating a magnetic field. It easily passes through the body and completely illuminates the internal organs and tissues. Sensors located opposite pick up any signals and convert them into high-quality information.
The main difference between X-ray and MRI is the operating principle of the device. X-rays penetrate the patient's body, but are concentrated in the bone tissue. At the same time, shooting is carried out in 1–2 projections. The images show outlines of bones or hollow organs. They provide a better view of soft tissues, joints and cartilage, and visualize the circulatory and lymphatic networks.
It is impossible to say unequivocally which is better – time-tested X-rays or modern MRI. These are two completely different diagnostic methods. With magnetic resonance, hydrogen molecules are affected, so all tissues containing water can be visualized. This expands the possibilities of examination, allowing you to identify dangerous pathologies at an early stage.
Why do MRIs be done?
Considering the safety and clarity of the result, MRI is best done in the following cases:
- search for pathological foci in soft tissues and internal organs;
- preparation for surgery to remove lymph nodes, tumors, affected vessels;
- inflammation of nerve endings;
- determining the cause of pain or internal bleeding;
- suspicion of abnormal changes in organs.
Using MRI, it is easy to examine the brain and spinal cord and identify deformations and atrophy of cartilage tissue. It better identifies intervertebral hernias, pinching of large vessels, and helps determine the degree of damage after a stroke or heart attack.
MRI scans internal organs better. The device shows the structure of tissue, ducts and vessels, and identifies abnormal cell proliferation. Thin sections are no more than 1–2 mm thick and are projected from different sides. The doctor, based on a high-quality three-dimensional image, diagnoses the slightest neoplasms with an accuracy of 95–98%. This is important when searching for metastases and monitoring the effectiveness of treatment.
Why is x-ray done?
X-ray radiation is best used when examining bone tissue. The method helps to detect the following pathologies:
- consequences of cancer;
- the presence of abscesses, fistulas or ulcers;
- upper respiratory tract diseases;
- pneumonia;
- advanced tuberculosis;
- fractures of bones, spine;
- development of osteochondrosis.
Radiography is used to identify inflammatory foci in the human abdominal cavity. It is best used to examine organs with a hollow structure: stomach, intestines, lungs. The images reveal foreign bodies swallowed by the child, bullet fragments, and implants.
Specifics of methods
Magnetic resonance imaging is used to diagnose the presence of pathologies in tissues. With its help, you can assess the condition of internal organs, soft tissues and vascular structures, as well as identify various tumors of a malignant and benign nature. Its main difference from X-rays is the ability to obtain scans of organs in the required plane and in three-dimensional form.
Radiography is used to diagnose pathologies of the skeletal system, as well as diseases that occur in soft tissues. This method is used to examine the abdominal organs and detect stones in the kidneys and biliary tract, as well as diagnose lung cancer, pneumonia and edema.
Difference between X-ray and MRI
Once you understand the difference between an X-ray and an MRI, it is easier to understand the choice of doctors. These are different procedures in terms of methodology and technology, so the images differ in quality and visualization accuracy. In the first case, the bone structure and musculoskeletal system are better visible. The magnetic field ideally tracks changes in structure, which become the cause of pathology.
The difference between an MRI and an X-ray is shown better by the pictures. For example, if a spinal column examination is performed:
- X-ray images show the vertebrae, bone tissue, and large joints. Fracture cracks are clearly visible.
- The three-dimensional MRI image highlights the intervertebral discs, soft tissues and vessels adjacent to the spine. This allows you to assess the condition of the spinal cord, its blood circulation, and determine the risks for the patient.
Therefore, in case of osteochondrosis or a dangerous fracture of the cervical spine, MRI is better than X-ray in detecting ruptures, pinching and protrusion of discs. This is the only way to assess further complications, after which doctors decide whether surgery is necessary. Therefore, the use of magnetic resonance is mandatory in complex clinical cases.
A modern analogue of X-rays – computed tomography (CT) – is increasingly being used. The scanner uses high-power X-rays, but takes pictures in several projections. The information is informative; small lesions and metastases are well identified. But the cost of the method and the danger of radiation are several times higher than standard x-rays, so doctors use it only in special cases.
The difference and features of MRI and X-ray are contraindications. Magnetic resonance is prohibited with implanted metal prostheses, implants, and tattoos in the scanning area. It should not be carried out in the presence of foreign bodies in the patient’s body if they contain metal particles. Video: Difference between MRI and X-ray, indications and contraindications. Radiation diagnostics doctor Yakov Leonidovich Babenyuk answers
What causes more harm to the body – X-ray or MRI?
Many patients are interested in what is safer for examination: MRI or X-ray? When assessing the strength and danger of radiation, doctors clearly choose a magnetic field. Numerous studies have not proven its effect on tissue structure, the occurrence of cancer or other dangerous consequences.
The effects of X-rays are more ambiguous, so they are strictly not recommended for pregnant women. In terms of safety, radiography is significantly inferior to MRI in many respects:
- promotes changes in the structure of proteins in cells;
- can change structure at the molecular level;
- accelerates the aging of soft tissues;
- provokes abnormal cell growth in the irradiation zone.
The number of exposures per year is strictly limited. When used correctly, if an MRI is not possible, it is better to recommend an x-ray. The human body gradually removes accumulated radiation without harm. The images take several minutes, which is important for patients in serious condition, so the technique continues to be actively used in the treatment of various diseases.
What can you trust: X-ray or CT
CT and X-ray differ in the examination results. The latter method is a simpler procedure, which is performed when it is necessary to quickly examine the patient after an injury and confirm the fracture. Computed tomography better replaces ultrasound of the brain or internal organs when diagnosing oncology, internal bleeding or inflammation.
Each method is used only according to indications, helping to make the correct diagnosis. The quality of diagnostics is influenced by the qualifications of doctors, technical characteristics of equipment and other factors.
Harm from X-rays
The harm of x-rays is greatly exaggerated. But it cannot be said that it does not exist at all. To carry out this examination, there must be a doctor's authorization . The likelihood of oncological processes occurring is quite low, but it exists. Therefore, you need to weigh the benefits and harms, which only a professional doctor can do.
Also, computed tomography leads to even more radiation , but it is actively used as a replacement for radiography. After all, this research method is not done every day, so the harm is minimal.
If there is a medical indication, there are no people who should not have this procedure (unlike an MRI). The only case when it is necessary to weigh the pros and cons is pregnancy. And this will not be a contraindication in all cases. You need to approach this issue individually.
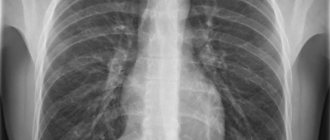
MRI or x-ray of the lungs: which is better?
There is a big difference and a number of features that differ between MRI and X-ray. When examining the lungs and upper respiratory tract, the doctor chooses a method based on the expected diagnosis:
- Radiography is indispensable when examining the pleural cavity, lungs, and trachea for infections and inflammatory diseases.
- MRI is best performed if tumors, fibroids, or metastases in the lungs are suspected. The procedure is often used if x-rays show shadows of an unclear nature. At the same time, it is possible to assess the condition of the lymph nodes and blood vessels that supply the respiratory organs.
X-rays are more affordable for patients, and hospitals of any level have the equipment. Therefore, it is often prescribed as the initial stage of diagnosis, later using MRI for clarification.
The difference is in the principle of operation
The principle of radiography is based on the ability of biological tissues, which differ in density, to transmit X-rays differently. Bones, for example, absorb them almost completely and appear white in photographs. Air-filled cavities freely transmit electromagnetic waves and appear black, while soft tissues appear gray. The examination takes a few seconds.
If the tissue contrast is not well expressed, a contrast agent - barium sulfate or a preparation containing iodine - helps. It absorbs rays much more or less than nearby tissue, so the organs that accumulate it appear very light or dark in the picture.
MRI examinations do not use ionizing radiation. The method is based on the fact that all the hydrogen atoms in the body behave like tiny magnets. They react to an externally applied magnetic field, lining up along its lines. Additionally, the atoms are exposed to radio waves and absorb some energy. At the moment the stimulation stops, they return to their original position and release the accumulated energy, which is recorded by the computer.
The machine processes many individual signals emitted by atoms that are distributed differently in the body. As a result, three-dimensional layer-by-layer images are formed on the monitor screen. Images differ from two-dimensional radiographic images in that they can be rotated, which is why tomography is more informative than x-rays. To increase the contrast of tissues, take one of the gadolinium-based products. The patient lies inside the tube of the device for approximately 15–45 minutes.
Which is better: which method is more informative and safer?
Computed tomography is a much more informative research technique. It allows you to get a clearer picture of the changes occurring in the patient’s tissues. When different programs are included in the process of creating an image, the doctor can get a view of the organ under study from different sides or a section of it in different planes, movement (for example, the work of the heart).
The x-ray is devoid of such details and most often represents an overview image of the organ in the front (posterior) and side position. It is more difficult to see a small pathology on an x-ray than on a tomogram.
Thanks to high information content and improved equipment, CT is becoming an increasingly safe procedure. Doctors have the opportunity to quickly and thoroughly examine the patient in one session, and changes in organs during treatment or the development of pathology occur quite slowly. Frequent procedure is not necessary and is indicated only in difficult situations: when monitoring cancer patients or to identify possible complications after surgery.
Compared to traditional X-rays, tomography is becoming an increasingly safer and more informative technique. But the use of x-rays remains popular due to the relatively low cost and availability of this research method in any clinic in the country. CT equipment is not available everywhere.
Application comparison
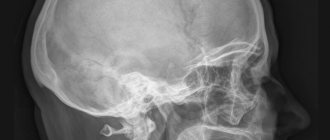
X-rays are used primarily for bone fractures, including skull fractures with brain damage, as well as joint problems and pulmonary diseases. Using this method, doctors detect bone cracks and foreign bodies. For example, a tumor on the lung appears as a shadow on the image. The method is used for osteoporosis, caries and the presence of neoplasms. Contrast agents make the organs of the digestive system, blood vessels, kidneys and ureters visible. To detect changes in breast tissue, a special X-ray machine is used - a mammograph.
Advantages and disadvantages of radiography
The advantages of performing radiography are:
- High speed of detection of pathologies of bones, vertebrae, their displacement, growth, etc.
- Possibility of emergency diagnosis of spinal injuries.
- Simplicity of the procedure, no preparation required.
- Cost-effectiveness and accessibility - radiography can be done in any clinic or emergency room.
X-rays also have many disadvantages:
- The procedure is definitely more harmful than MRI; it uses radiation. Radiation exposure in modern devices is reduced, but is still present.
- X-rays should not be taken frequently.
- X-rays are prohibited for use in pregnant and lactating women.
- The method is ineffective for diagnosing diseases of paravertebral tissues and does not allow accurately determining the type of tumors.
How is research conducted?
Before the procedure, your doctor will tell you how best to prepare for it. For example, a CT scan or abdominal x-ray may require a diet and an enema. But you won’t have to carry out complex manipulations.
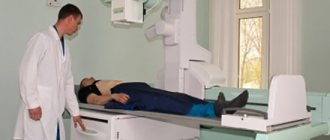
During radiography, the patient is placed on a couch under the emitter. The specialist takes a picture of an area of the body, then asks you to change position and takes a picture in the second projection. If necessary, more detailed pictures are taken (part of the chest, for example) or contrast is used.
When examined on a tomograph, the main requirement for the patient is to remain motionless. Belts are used for this purpose, which often frighten those undergoing the procedure for the first time: the doctor fixes the limbs and torso in order to eliminate involuntary movements that distort the scan image and force unnecessary radiation on the patient.
A CT scan is an x-ray that takes many quick pictures. The table and the ring with the X-ray tube move automatically. Sometimes the doctor asks you to hold your breath.