Modern medicine has in its arsenal quite a lot of techniques with the help of which high-quality diagnostics of various diseases is carried out. The spine is the main axis of the body as a whole. The main load falls on it, so this structure is susceptible to various disorders that manifest themselves as a result of certain diseases or after injury.
Examination of this area is possible in various ways, but the most effective methods are computer scanning and nuclear resonance screening. Many people mistakenly believe that these methods are absolutely the same, so there is no significant difference which method to give preference to. In fact, this is not true; CT and MRI have striking differences. Despite the external similarity in the equipment with which the described types of diagnostics are carried out, as well as similar results in the form of black and white images, these methods are used for different pathologies and to solve different goals and problems.
The question of which method is better and more informative is posed incorrectly, since different types of tomography study different areas and structures. The choice of the best diagnostic method in each individual case always remains with professional doctors, since both methods have both their limitations and advantageous indications.
If we compare the two types of tomography in terms of cost, there are no significant differences. Both diagnostics are classified as expensive. The price in each clinic specializing in hardware scanning will be slightly different, since each institution has its own pricing policy. Much depends on the modernity and power of the equipment, on the technical characteristics, on the number and qualifications of personnel and medical staff, on the availability of related procedures and the quality of consumables.
What is CT (computed tomography)
To understand which is better - CT or MRI of the spine, you need to find out what these procedures are, how they are similar and how they differ.
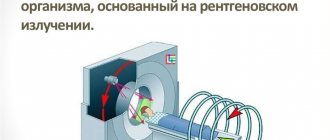
CT is the same X-ray, only improved and modified. Its feature is the minimum radiation load. The rays here are directed only at a certain area of the human body. Their source makes revolutions around the body and sends information to the receiver, which is located opposite.
A full rotation of the tube around the body occurs in just a couple of seconds. And in this short time, 1,000 X-ray signals are emitted from the device. In total, 30 revolutions occur in one scanning procedure. This allows you to get a high-quality picture of the small bone structures of the spine on the operator’s screen, for example, his lumbar region or neck.
A CT scan of the spine is most often prescribed for fractures of any part of the spine or for injuries to the vertebral arches. But this study is not able to detect diseases of soft tissues or intervertebral discs, for example, a hernia.
Another option is MSCT. This is a multislice computed tomography that allows you to see every millimeter of a bone or internal organ. Moreover, you can get a picture on the screen from different angles and perspectives.
In what cases is CT or MRI of the spine prescribed?
There are a number of indications that require immediate diagnostic clarity. Traditional radiography is often prescribed as an initial step to examine the condition of the spinal column and adjacent structures and tissues. It will help identify obvious problems. However, to clarify the picture of the disease or in case of ineffectiveness of classical medical methods, the patient is additionally sent to a CT or MRI of the spine. This is necessary to find out the root cause of the disease even in the early stages of its onset.
On a regular x-ray you can see only noticeable fractures and cracks, the general condition of the bones and vertebrae. Microscopic lesions and soft tissues, as well as nerve fibers, are not visible on x-rays. If the cause of the disease is not identified and symptoms persist even after treatment, the doctor will necessarily refer the patient to a CT or MRI.
Indications for undergoing a CT scan of the spine are the following pathologies:
- osteomyelitis;
- constant pain syndrome;
- stiffness in movements;
- curvature of the spinal column of varying severity;
- dislocations and fractures;
- osteochondrosis;
- bone tissue dystrophy;
- implantation of ferromagnetic systems to maintain the spinal column, monitoring their correct location;
- determination of bone density;
- monitoring the migration of metastases, the degree of their spread in oncology;
- identifying the source of deformation and compression of the bone marrow.
An MRI of the spine is required if the following disorders occur:
- hernias between the vertebrae;
- tumor processes of varying nature and degree of spread;
- vascular pathologies;
- formation of liquid-containing capsules and cysts in the area of the spinal column and coccyx;
- change in the diameter of the spinal canal towards narrowing;
- injuries of adjacent soft tissues;
- genetic or acquired disorders of the development of the skeletal system;
- monitoring the condition of internal structures after surgery;
- detection of cancerous processes in soft fibers;
- spinal brain degeneration.
It should not be surprising that if you suspect the same diagnosis, different specialists may refer you to different types of tomography. The root cause of the disease can be pathologies localized in tissues of different density and nature. The doctor, based on the collected medical history of the patient, as well as based on his individual health characteristics, refers for diagnosis in one way or another. It should be remembered that tomography is not prescribed simply for the sake of idle curiosity. If the doctor strongly recommends undergoing a hardware examination, then there are indeed good reasons for this. Under no circumstances should you ignore a full examination; your subsequent condition and health, and sometimes life, depend on it.
In some complex cases, it may be necessary to jointly study the area under study using both methods; this will give the most complete picture of the developing pathology and the most accurate result.
What is MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
MRI is based on the use of a magnet that produces radio waves. Under their influence, hydrogen ions in the human body vibrate in only one direction. This is captured by the device and converted into images on the operator’s screen. Moreover, such images can be obtained in any plane.
MRI is most often performed to diagnose diseases of the intervertebral discs of the lumbosacral region, nerve roots and spinal cord
Most hydrogen ions are found in soft tissues. Therefore, this study is used to diagnose diseases of this profile, after which the doctor prescribes therapy. Bones on MRI look like dark, homogeneous structures, which means it is not possible to identify their diseases.
Magnetic diagnostics is best suited for identifying diseases of the intervertebral discs of the lumbosacral region, nerve roots and spinal cord.
Therefore, in each specific case, the doctor makes an individual decision. And here everything will depend on what structures of the spine (soft tissue or bones) the specialist wants to see in as much detail as possible.
CT or MRI of the spine: advantages and disadvantages
Each technique has both its pros and cons. Thus, MRI is more effectively used to identify pathological processes developing in soft tissues, for example:
- degenerative processes in the bone and spinal cord;
- infectious lesions of a bacteriological or viral nature;
- protrusion and compression of cartilage tissue between the vertebrae;
- early stages of oncology, degree of tumor ingrowth and spread of metastases into soft fibers;
- changes in configuration and destruction of the walls of blood channels;
- disorders in soft internal organs.
Important advantages of MRI of the spine are:
- complete safety in use by a wide range of patients, the ability to repeat sessions in multiple quantities;
- high quality of acquired images at any depth and from different angles, the ability to compose images into multidimensional projections;
- qualitative assessment of the state of organs and structures of the studied area.
The disadvantages of this diagnostic method include:
- high price for the provision of services;
- long duration of the procedure, the need to remain in a stationary position for a long time to obtain the correct result.
CT scan of the spine allows you to quickly recognize such anomalies as:
- old and new fractures and cracks in bones;
- prediction of the possibility of subsequent damage as a result of compression effects;
- determining the degree of operability of the patient in the preparatory period before surgery;
- postoperative monitoring of the condition of internal structures;
- the ability to quickly see internal bleeding, hematomas, and complex injuries.
The advantages of CT scan of the spine include:
- maximum degree of visual assessment of bone fibers;
- high resolution and quality of photographic images;
- painlessness and high diagnostic speed;
- possibility of diagnosing for patients with implanted metal implants.
The disadvantages of computer examination are:
- low financial accessibility, high price;
- high degree of ionizing radiation, the impossibility of frequent use of CT.
Indications
CT differs from MRI not only in the examination method, but also in the indications for use.
| When to do a CT scan | When to do an MRI |
| Spinal osteomyelitis | Intervertebral hernia |
| Chronic back pain | Spondylitis |
| Limited mobility | Spondyloarthrosis |
| Scoliosis of various stages | Tumors (malignant and benign) |
| Ankylosing spondylitis | Spinal vascular diseases |
| Fractures of various parts of the back | Coccyx cysts |
| Osteochondrosis | Narrowing of the spinal canal |
| Degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the spine | Traumatic soft tissue injuries |
| The presence of metal structures for spinal alignment and monitoring their condition | Congenital or acquired developmental anomalies |
| Detection of bone metastases | Monitoring the condition of the spine after surgery |
| Bone Density Analysis | Detection of metastases in soft tissues |
| Determining the cause of spinal cord compression | Spinal cord infarction |
The difference between CT and MRI in the indications for performing it is clearly expressed. Therefore, it should not be surprising that the same doctor can prescribe a CT scan for one patient and an MRI for another.
MRI capabilities
MRI is a highly informative and safe method of radiological diagnostics. It allows you to detect changes in the spinal cord and its membranes, nerve roots and spinal nerves, intervertebral discs and paravertebral tissues.
Indications:
- Suspicion of herniated intervertebral discs,
- Assessing the degree of compression of nerve roots and spinal nerves,
- Spinal cord malformations
- Primary spinal cord tumors and metastases,
- Infarction and other vascular diseases of the spinal cord,
- Inflammatory damage to the spinal cord and its membranes (myelitis)
- Diagnosis of demyelinating diseases (multiple sclerosis, syringomyelia),
- Assessment of the spinal cord after injury,
- Monitoring the condition of the spinal cord after surgical treatment,
Advantages
- no radiation exposure;
- the possibility of early diagnosis of tumors (detects formations less than 2 cm in diameter);
- high information content even without contrasting;
- a completely safe method that allows you to examine children and pregnant women;
- high accuracy of information, three-dimensional image;
- can often be used for diagnosis, unlike CT;
- There are practically no errors during scanning;
- Contrast is not required to study blood flow;
- When examining intervertebral hernias, the assessment of damage to the central nervous system is highly informative.
Flaws
- The need to lie still for a long time;
- The study averages from 15 to 40 minutes. This complicates diagnosis in patients with claustrophobia, with severe deformation of the spinal column and pain syndrome;
- Absolutely contraindicated for people whose bodies contain metal elements and electronic devices (pacemakers, metal implants, hemostatic clips, foreign bodies, etc.);
- Even the slightest movements reduce the quality of images;
- High price for examination.
The main advantages of CT over MRI
Many doctors recommend CT scanning to their patients to identify back diseases. First of all, this study is good at identifying any pathologies of the bone structure of the vertebra at a very early stage of the disease. This means that pathology can be identified and treated even when there are no manifestations yet.
CT is an examination that is ideal for patients with artificial joint surfaces or metal structures in the body.
CT scanning takes minimal time and is somewhat cheaper. If you have claustrophobia, you can choose an open device, which is specially designed for those who are afraid of confined spaces.
What is the difference between MRI and MSCT?
The techniques have many similarities. Among them:
- non-invasive;
- short preparatory stage;
- use of contrast agent (MRI) to detail the results;
- obtaining thin sections;
- determination of pathology in the initial period of its development.
What are the differences between multislice computed tomography and MRI? For ease of perception of information, we present the distinctive characteristics of the methods in the table:
| Comparison criteria | MRI | MSCT |
| 1. Diagnostic principle | based on magnetic field | X-ray based |
| 2. Opportunities | most informative when examining soft tissues | highly effective when scanning hard tissues |
| 3. Allowed number of sessions | as needed (the procedure is harmless) | when prescribing the procedure, the specialist takes into account the radiation dose (the maximum permissible for the population is 5 mSV per year) |
| 4. Type of contrast used | substance based on the metal gadolinium | iodine-containing drug |
| 5. Duration of the study | about an hour | from a few minutes to half an hour |
| 6. Conditions of stay inside the tunnel | You must remain still throughout the entire scan | immobility is important, but not so essential |
Computed tomography (MSCT)
MRI
Among other differences in diagnostic methods are indications and limitations for examinations.
Main advantages of MRI over CT
But MRI also has its advantages, so it cannot be said that this method is worse or better than X-ray or CT.
Which doctor should you go to if your tailbone hurts?
The main advantage of MRI of the spine is that during the procedure the patient does not receive a dose of X-ray radiation, since the apparatus for carrying out the procedure uses a magnet. Therefore, if necessary, the procedure can be repeated several times a year or even several times a month.
This method can be considered ideal if the doctor needs to obtain images of cartilage, ligaments, intervertebral discs or nerves of the cervical, thoracic or lumbar back.
If you suspect a tumor of a malignant or benign nature, it is best to use this technique. The resulting images can reveal even formations of minimal size, which do not yet give any symptoms.
There is no need to use iodinated contrast during the procedure in order to better identify the desired areas. MRI uses a different type of contrast agent that only causes an allergic reaction in very rare cases.
Comparison of the degree of danger of procedures and their possible side effects
MRI of the spine is considered a more harmless technique than CT, during which the patient receives a dose of X-ray radiation. It is worth considering, however, that the long-term consequences of exposure to a magnetic field on the body have not yet been fully studied, therefore it is not legitimate to call MRI an absolutely safe method.
MRI is dangerous for patients with metal in the body because it can heat up and become dislodged. Also, the magnetic field can disrupt the functioning of the pacemaker, so CT is recommended for this category of patients.
Radiation exposure during CT scans is dangerous for pregnant women and nursing mothers. After a CT scan, it is recommended not to breastfeed your baby for 48 hours. Then breastfeeding can be resumed.
Standard tomography does not cause any adverse reactions or discomfort. During an MRI, only a slight feeling of heating of the area being examined is possible.
Tomography with contrast is a more dangerous technique, since the contrast agent can disrupt kidney function and provoke an allergic reaction. It is important that contrast-enhanced MSCT often causes allergies, since it uses iodine contrast agents. Gadolinium contrasts used in MRI diagnostics are less allergenic.
Contraindications for CT scanning
Like any other medical test, computed tomography has its limitations. There are few of them, but you definitely need to know about them.
Both computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging have their limitations for performing
Absolute contraindications
There are few absolute contraindications. First of all, it is excess body weight. If it exceeds 120 kg, then it will be impossible to conduct the study, since the tomograph table is not designed for such loads.
The second absolute contraindication is pregnancy and even suspicion of it. Before the procedure, if a woman suspects it, she should visit a gynecologist and have an ultrasound of the uterus.
Allergic reaction to contrast injection during the procedure. In this case, the choice is made in favor of non-contrast CT.
And finally, mental illnesses in which the patient is agitated, does not understand where he is, and cannot follow the operator’s commands.
Relative contraindications
It is not recommended to do CT scans for children under the age of 12, however, if the life of a small patient depends on it, then this contraindication is removed.
Breastfeeding women after a CT scan should express breast milk for 2 days and not give it to the baby. During this period, the baby is transferred to artificial feeding.
CT scans are not done in patients with kidney disease, but only in the most advanced stages of chronic kidney disease. Before the study, it is recommended to consult a nephrologist.
Diabetes mellitus sometimes requires temporary discontinuation of insulin intake. Here you need to consult an endocrinologist.
Contraindications also include fear of closed spaces (claustrophobia), severe pain syndrome in which the patient will not be able to lie motionless for some time, and severe general condition.
In this case, CT scans are allowed to be done in the presence of any metal implants in the human body. This means that it is better for those patients who have bone fixators installed for fractures, a spinal implant, which is often installed for scoliosis, removable dentures, pacemakers, and hearing aids.
Radiography will not affect the operation of these structures in any way, which means that after the study they will remain safe and sound, and human life will not be in danger.
What does a spinal tomography show?
- osteochondrosis
- arthrosis deformans, spondylosis
- ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis)
- spinal lesions due to rheumatoid arthritis
- osteomyelitis
- tuberculous lesion
- rare inflammatory lesions (actinomycosis, brucellosis, echinococcosis)
- primary malignant pathologies
- metastatic tumors
- benign tumors
Changes in the normal axis of the spinal column:
- scoliotic curvatures
- lumbar hyperlordosis
- spondylolisthesis
- posterior, lateral, scalene and combined displacements of the vertebrae
Pathologies of the spinal cord, its membranes and roots:
- tumor lesions (malignant, benign)
- multiple sclerosis
- amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
| Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine will show: | A CT scan of the spine will show: |
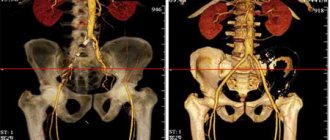
A CT scan of the sacroiliac joint shows its degenerative changes in the form of a narrowing of the gap, sometimes even to the point of ankylosis (complete fusion). A CT scan of the sacral spine also shows its injuries, features of shape and position. CT scanning of the coccyx is often used for fractures, since conventional radiography is often unable to visualize the fracture area. It can also be used to determine the cutaneous-coccygeal ducts. |
Contraindications for MRI
The main contraindication for magnetic resonance imaging is the presence of any metal structures in the human body. Not only can they affect the quality of the image, but they will literally be attracted to the magnet during the examination. This is very dangerous for human life.
Also, the procedure is not recommended for patients with:
- Pacemaker.
- Hearing aid.
- Insulin pump.
- Metal dental crowns.
- Built-in defibrillator.
- Ilizarov apparatus.
- Hemostatic clips.
- Metal fragments in fabrics.
Wearing a hearing aid is a contraindication to MRI.
Therefore, to the question of what is better, CT or MRI of the spine in the presence of any medical devices in the human body, the answer will only be this: it is better to conduct only CT.
At the same time, the presence of an intrauterine device or pregnancy at 4 months and beyond is not a contraindication for MRI. The same applies to plates and other titanium metal structures that are installed for fractures.
Also, an MRI is not performed if there is a spinal fracture immediately after an injury - the procedure is quite lengthy and can take up to half an hour. The best option here would be a CT scan. The fracture itself will be clearly visible on the images, and the procedure takes only a few minutes, after which the patient can be immediately sent to the operating table.
Therefore, MRI scanning cannot be considered the best solution for identifying acute conditions and diseases that require emergency care.
Description of methods: diagnostic principles
Magnetic resonance imaging is based on obtaining three-dimensional images of tissues and organs using equipment that organizes vibrations of atoms of electromagnetic waves.
MRI is a safe diagnostic method
We are talking about a safe non-invasive diagnostic method, since when examining a patient, radiation exposure to the patient’s body is excluded. The quality of the research results depends on the capabilities of the device used, and the duration of the procedure depends on the area being examined.
Multislice computed tomography is based on the method of scanning the human body by transmitting x-rays, transforming the received data into electrical signals.
The most harmful diagnostic method
Mistakes that patients make when choosing
Only the doctor, not the patient, should choose between CT and MRI. Both procedures are performed when there is a suspicion of a serious illness or when diagnosis is difficult. Otherwise, for a good neurologist or neurosurgeon it is enough just to examine the patient, his complaints and x-rays.
Therefore, these procedures should not be performed without reason or need. If after a CT scan the patient does not plan to visit a doctor and does it only out of curiosity, this is the biggest mistake. As for MRI, it is most often prescribed before surgery, as well as after it, in order to monitor the condition over time.
Indeed, the difference between these studies is large, and it is not recommended to carry them out unless necessary. But if the doctor has prescribed an MRI or CT scan, you should not be afraid of this. In most cases, this allows the disease to be identified at an early stage. This means that the disease can be completely cured even before it begins to manifest itself.
Comparison of availability (prevalence) and cost of MRI and CT
The availability of tomographic diagnostics in Russia is growing every year. Today, CT is considered a more accessible tomography method. This is due to the widespread use of devices of this type in public medical institutions. Unlike CT scans, MRI machines are usually purchased by private companies - this examination is often carried out for a fee.
The difference in cost between a CT and MRI procedure depends on the resolution of the device: the higher it is, the more expensive the service. If we compare devices with high power, for example, a multislice computed tomograph and a 1.5 Tesla magnetic tomograph, then the study of one part of the spine with the latter will be approximately 800–1000 rubles more expensive.
However, it must be borne in mind that the need for an MRI or CT scan should be determined not by price and availability, but by the specific diagnosis and prescription of the attending physician.
Choosing a research method and what the specific difference is
Since computed tomography works on the principle of illuminating the insides with an x-ray beam, this method is always given greater preference in the presence of serious spinal injuries. A modern computed tomograph is able to perfectly examine the bone structure, and so accurately that all other methods cannot compare with it. In addition, a tomograph can be used to illuminate tumors on the surface of bones or in their internal structure. If the patient has already undergone a CT scan before, when the procedure is repeated, the doctor can conduct a comparative analysis and draw conclusions about the effectiveness of the treatment as a whole.
MRI has significant differences. A logical question arises - how is CT MRI different? The main factor in which these methods are different is the principle of operation. Magnetic resonance imaging is poorly suited for diagnosing bone conditions. However, these types of equipment differ in their ability to diagnose spinal nerve strains, spinal cord problems, and so on. In other words, MRI makes it possible to become more familiar with the structure of the tissue and its condition as a whole.
Which method to choose
What is better MSCT or MRI of the brain? It is impossible to give a definite answer to this question. Because these two methods are applicable in various clinical situations. Both procedures are of particular importance in identifying tumors; they help determine the extent of damage, the spread of the tumor to organs and tissues, and the condition of the lymph nodes.
Magnetic tomography will be the most informative when diagnosing soft tissues. MSCT is suitable for examining bones.
Due to the high speed of obtaining results after MSCT, this method is used for injuries, acute bleeding, and in emergency cases.
The multispiral device is less sensitive to the movements of the person being examined. The specialist can get a picture of the organs in real time. But the fact that magnetic tomography is harmless puts it one step higher than alternative diagnostics.
To summarize, it can be argued that both methods represent a type of diagnostics that provides maximum visualization of internal organs, tissues and systems, and each research method has individual advantages.
Magnetic resonance imaging provides accurate data when necessary to diagnose pathologies of the nervous system, soft tissues, joint apparatus, and blood vessels, without adversely affecting the patient’s body.
MSCT is not such a safe, but informative diagnostic method for bleeding, ailments of the gastrointestinal tract, genitourinary and respiratory systems.
In addition to direct indications for diagnostics, the following factors should be taken into account:
- age indicator;
- psychological condition;
- presence/absence of metal objects in the body;
- results of previous procedures;
- clinical symptoms;
- medical history data.
It is impossible to answer the question of which is better (MSCT or MRI). Diagnostic methods are similar (non-invasiveness, minimal preparation, early diagnosis of diseases and the use of a contrast agent, obtaining results in the form of sections of the examined organ).
The distinctive features of the methods are the main criteria for choosing a specific diagnostic method. The area of research and the circumstances under which the diagnosis is planned are taken into account (age of the patient, speed of obtaining the result, etc.). The cost of the study plays an important role. The final decision on the advisability of conducting a particular type of scan is made by a specialist.
Features of the preparatory stage
Special preparatory measures in the case of MRI are necessary only when examining the abdominal and pelvic organs:
- The patient should exclude from the diet foods that stimulate gas formation (bread, beans, cabbage, vegetables, fruits, etc.).
- You should not eat or drink for several hours before the scan.
- Before the test, you can take medications that reduce gas formation.
- If you are going to have your pelvic organs examined, you will need to fill your bladder before the MRI.
Preparation on the eve of MSCT is also insignificant and includes the following points:
- A few hours before the scan, it is not recommended to drink or eat if a contrast agent is to be administered.
- The doctor does not advise the patient to drink liquids immediately before MSCT if the patient is under the influence of sedative medications.
Operating principle of CT
Computed tomography is a modified, improved type of fluoroscopy. The radiation intensity in this case is reduced. X-rays collected in a beam are directed and are able to “illuminate” a smaller area.
With the correct beam direction, it is possible to obtain a complete “picture” of the organ. The larger the area to be scanned, the greater the x-ray dose.
To form a three-dimensional image, the beam will have to pass around the human body several times. A fraction of the radiation is absorbed. In the case of dense tissues, you need to expect a higher radiation dose.
The diagnostic result is an image with darkened and lightened areas. The equipment processes the received information and produces a 3D image of the area under study.
CT
In what cases is it advisable to prescribe an MRI?
Since MRI and CT have different mechanisms of action, each type of diagnosis will be effective for certain diseases. Thus, MRI can provide maximum information in the following cases:
- for any lesions of the spinal cord;
- with the development of tumors, benign and malignant neoplasms;
- when it is necessary to determine the condition of muscle tissue;
- for various diseases of the spine;
- when you need to obtain information about the condition of ligaments and joints;
- if necessary, determine the stage of cancer;
- MRI is indicated for intolerance to radiocontrast agents;
- for strokes, inflammation and brain tumors;
- to identify problems with intracranial nerves;
- to diagnose the state of the brain and its parts.