Medicine has come a long way in recent decades. Many diseases are now much easier to treat than before. Previously fatal diseases have become easily treatable or preventable through vaccination. Such a common disease as sinusitis has been known for a long time. However, it was not so easy to treat him. With the development of pharmaceuticals and the chemical industry, many different types of antibacterial drugs have appeared, which greatly simplify the treatment of sinusitis.
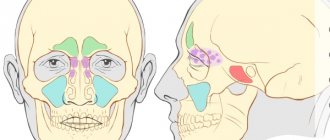
Sinusitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the air cavities in the facial part of the skull, which are called the maxillary sinuses. They are located on the sides of the nose, inside the upper jaw. They are also called the maxillary sinuses. Normally, the air inhaled by a person should be warmed and moistened in these sinuses. The paranasal sinuses play an important role in protecting the body from various diseases, however, they themselves are susceptible to certain ailments, one of which is sinusitis.
Inflammation of the maxillary sinuses is not the most dangerous disease today. The large number of effective antibiotics makes treatment of this disease relatively simple. However, if left untreated, sinusitis can cause serious complications. It is known that everything in the human body is interconnected. The source of infection and inflammation in the nasopharynx can spread to other parts of the head. The most dangerous are meningitis and cerebral edema.
Sinusitis can be acute or chronic. The acute form of sinusitis most often occurs due to infection entering the nasopharynx. The causes of this disease are viruses, bacteria or fungi. Most often, sinusitis occurs against the background of a viral infection. Inflammation of the maxillary sinuses caused by a fungal infection is difficult to treat.
In addition, inflammation of the paranasal sinuses can occur as a result of its injuries, which can lead to disruption of the anatomical structure of the bone walls of the nasal cavity and sinuses. Also, sinusitis often appears after a long allergic rhinitis.
Chronic sinusitis occurs in the absence of proper and timely treatment of the acute form of the disease. Treatment of chronic sinusitis requires much more time and effort. Therefore, it is better not to bring your body to such a state.
Main symptoms of sinusitis
The main and most well-known symptom of inflammation of the maxillary sinuses is headache. In some cases, pain can cause a lot of inconvenience; in rare cases, the pain reaches such heights that it is necessary to take painkillers. At the beginning of the disease it has a certain localization. With sinusitis, discomfort occurs in the forehead, nose and around the eyes. However, after some time the pain becomes irritating, affecting many areas of the head.
The pain of sinusitis can sometimes be very similar to the pain of a migraine. However, sinusitis also has other symptoms, which, coupled with headaches, allow the doctor to diagnose this disease quite accurately. To confirm the diagnosis, radiography of the paranasal sinuses is used.
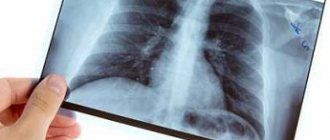
On x-rays with sinusitis, shadows are clearly visible, in which you can guess the fluid accumulated in the maxillary sinuses of the nose. This liquid is a mixture of mucus and pus. It is the accumulation of exudate in the maxillary sinuses that is responsible for the appearance of headaches, as it puts pressure on the inflamed mucous membrane and causes discomfort.
Headache with this disease can intensify when bending the body forward, as well as from sudden movements of the head. To minimize discomfort, the patient needs rest. There are also other symptoms of inflammation of the maxillary sinuses:
- nasal discharge,
- nasal congestion,
- swelling of the soft tissues of the face, eyelids,
- increased body temperature,
- weakness, irritability.
These symptoms are characteristic not only of sinusitis, but coupled with a severe headache, they indicate precisely this disease. If you suspect an inflammatory process in the maxillary sinuses, you should immediately consult a doctor and undergo an examination to confirm the diagnosis. Untreated sinusitis can have serious consequences for the body.
Features of radiography for sinusitis
The main way to confirm sinusitis today is still radiography. The procedure takes very little time and is available in most clinics in Russia.
On an x-ray of the paranasal sinuses with sinusitis, darkening in the area of the maxillary sinuses is clearly visible, indicating that there is an inflammatory process and there is excess fluid. Depending on the severity of the disease, the darkening can be local (small), subtotal and total.
Small darkening indicates that the disease began not long ago, the painful manifestations are not very pronounced, and drug treatment will be most effective.
Subtotal blackout
Subtotal darkening of the maxillary sinuses may indicate a severe inflammatory process. This suggests that the disease is in an advanced state. In such cases, in addition to antibacterial therapy, procedures may be prescribed to remove fluid from the inflamed sinus cavity.
Sometimes the inflammation spreads to other paranasal sinuses. Sinusitis can turn into frontal sinusitis or sinusitis. In such cases, the pathological process affects, respectively, the frontal sinuses or the ethmoid labyrinth.
Total blackout
Detection of total darkening on an x-ray is an alarming sign. However, modern medicine copes with such advanced cases. The most important thing is that treatment is started immediately.
If the sinuses are filled with pus and inflammatory processes are in full swing, then doctors prescribe fairly high doses of antibiotics to prevent the development of serious complications. Additionally, a puncture of the maxillary sinuses can be performed to remove accumulated exudate.
Classification of blackouts
Each problem has its own form of darkening in the image. This circumstance gives doctors the opportunity to make preliminary diagnoses before the upcoming examination, as well as most accurately give referrals to specialized specialists.
This saves time, which is very important when identifying and treating certain diseases, especially inflammation and tumors.
- Multiple opacities in the area of the apex of the lung. This location often indicates tuberculosis.
- Blurred spot boundaries. This indicates pneumonia. Additional signs include high fever and general weakness.
- Multiple blackouts. The spectrum is very wide - tuberculosis, inflammatory processes, tumors in other organs and systems. If such spots are detected, the examination will be lengthy and quite complex.
- Single clear spot. This is the most unpleasant option, since it speaks of a tumor. But in some cases, similar results are obtained with advanced pneumonia, foreign objects in the bronchi and heart problems, such as a heart attack.
When deciphering the results of fluorography, the doctor pays special attention to the geometric shape of the spots. It is she who speaks about suspected problems and allows us to adjust diagnostic measures.
Important! The most harmless cause of darkening is a defective film or a foreign object between the chest and the emitter. The subtlety is that a repeat shot to correct the result should not be taken earlier than six months later. You will still have to undergo the examination.
Possible complications of advanced sinusitis
Sinusitis in itself is not a dangerous disease. However, inflammation in tissues so close to the brain can have serious consequences, especially if not treated adequately and promptly.
Meningitis and meningoencephalitis
Meningitis is a dangerous disease characterized by an inflammatory process in the membranes of the brain. This disease can lead to disability and even death.
Meningoencephalitis is an even more serious disease. Inflammation in meningoencephalitis covers both the membranes and the substance of the brain.
The symptoms of these diseases are similar:
- headache,
- nausea,
- vomit,
- chills,
- elevated body temperature.
These diseases are very insidious. If there are prerequisites for their occurrence, they can develop in an acute form within just a few hours.
Both diseases are extremely dangerous and have a poor prognosis. High probability of death.
Chronic sinusitis
If acute sinusitis is treated incorrectly or not treated at all, the disease may become chronic. Chronic sinusitis is difficult to treat, and it is impossible to guarantee a positive treatment outcome.
Periodically, with a decrease in immunity, chronic sinusitis will worsen, causing a lot of inconvenience. In addition, a chronic inflammatory process in the maxillary sinuses is fraught with much more serious problems, including:
- chronic rhinitis,
- inflammation of bone tissue,
- inflammation of brain tissue.
You should take care of your health. Then the occurrence of a disease such as chronic sinusitis is unlikely.
What to look out for: Symptoms
Characteristic manifestations of an insidious maxillary exacerbation of a runny nose and nasal congestion include:
- heavy discharge of snot and mucus from the nose;
- runny nose with bloody streaks;
- pain in the frontal part of the head;
- state of heaviness and general headache;
- pain on the nose and bridge of the nose;
- periodic increase in temperature;
- difficulty breathing, particularly through the nose;
- pain behind the eyeballs;
- deepened voice;
- sleep disturbance.
Very often they lead to general fatigue of the body, frequent overwork, decreased performance and blues. The chronic stage of sinusitis can even provoke the development of conjunctivitis, chronic cough and runny nose, and constant migraines. Advanced stages of the inflammatory process of the nasal mucosa and complete blockage of mucus in the paranasal sinuses can lead to arbitrary infection in the brain and the development of meningitis, which is especially fraught for the child’s body.
Preseptal inflammation involves only the eyelid, whereas postseptal inflammation involves orbital structures. In such cases, the patient should be evaluated by an otolaryngologist and an ophthalmologist. Purulent complications usually require operative surgical drainage. Patients who have changes in visual acuity or mental status or who do not improve within 24 to 48 hours require prompt surgery and drainage of the abscess.
Antibiotics may be changed if unacceptable when results of culture and susceptibility studies become available. In patients with altered mental status, neurosurgical consultation is indicated. Central nervous system complications such as meningitis and empyemas should be treated with either intravenous cefotaxime or ceftriaxone and vancomycin while awaiting the results of culture and susceptibility testing.
It is carried out under the supervision of an ENT doctor. Depending on the location and degree of development, the necessary courses of taking medications and undergoing physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed. Surgical intervention is possible only in the case of a long-term lack of effect from therapy and in the case of polyp growth against the background of exacerbation of sinusitis.
Accordingly, areas for future research include the following. Conduct increasingly large studies correlating clinical findings of acute bacterial sinusitis with sinus aspiration, imaging, and treatment outcomes. Develop noninvasive strategies to accurately diagnose acute bacterial sinusitis in children.
To correlate cultures obtained from the middle meatus of the maxillary sinus of infected individuals with cultures obtained from the maxillary sinus by puncture of the antrum. Develop imaging technology that distinguishes bacterial infection from viral infection or allergic inflammation.
When diagnosing, the patient is prescribed an X-ray examination of the nasal sinuses (in other cases, tomography) and tests. Using a fiber optic device in the ENT office, the doctor examines the condition of the nasal mucosa.
Treatment is carried out with medications that can relieve the exacerbation caused by the pathogen and provide further treatment for the entire sinusitis.
Develop rapid diagnostic methods for imaging sinuses without radiation. Determine the optimal duration of antimicrobial therapy for children with acute bacterial sinusitis. Identify the causes and treatment of subacute and recurrent acute bacterial sinusitis.
Determine the effectiveness of antimicrobial prophylaxis in preventing recurrent acute bacterial sinusitis. To determine the role of adjuvant therapy in patients with acute bacterial sinusitis based on the results of prospective randomized clinical trials.
In the case of parietal sinusitis, treatment can also be carried out with nasal medications, which relieve swelling of the mucous membrane and make it easier to breathe through the nose.
Nasal rinsing with flexible hoses is still relevant in the treatment of maxillary sinuses. It is recommended for all stages of the disease, except for the period of exacerbation. Within several procedures, the patient is completely relieved of ailments. Physiotherapy procedures are prescribed if there are no contraindications to them and there is an acute form of sinusitis. Physiotherapy in the treatment of persistent runny nose is ideal both for its prevention and for the restoration of the body.
Determine the role of complementary and alternative medicine strategies in patients with acute bacterial sinusitis by conducting systematic, prospective, randomized clinical trials. Assess the impact of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on the epidemiology of acute bacterial sinusitis.
Develop new bacterial and viral vaccines to reduce the incidence of acute bacterial sinusitis. This clinical practice guideline provides evidence-based recommendations for the treatment of bacterial rhinosinusitis in children aged 1 to 21 years. The guide provides decision-making strategies for treating sinusitis to help primary care providers diagnose and treat children with this common health problem.
Among other things, modern medicine makes it possible to enhance the effect of drug therapy using laser therapy. Treatment of sinusitis using similar methods can last from 2 weeks to 2 months. Everything will depend on the severity of the disease.
The Subcommittee would like to commend the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the New England Evidence-Based Medical Center for their work in developing the evidence report. Sinusitis Subcommittee.
American Academy of Family Physicians. American Academy of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery. Medical Liability Committee. Agency for Health Care Research and Institutes of Quality. Committee on Practice and Ambulatory Medicine.
National Association of Children's Hospitals and Related Institutions. Section on computers and other technologies. The recommendations in this statement do not indicate an exclusive course of treatment or serve as a standard of care. It is never, therefore, too much to turn our gaze on this subject from time to time, repeating it and illustrating it with new observations, in a palpable demonstration of how Otorhinolaryngology and its old sister Ophthalmology.
It is worth remembering that the risk of developing sinusitis is directly related to the lack of treatment for the first signs of viral and cold infections during hypothermia, colds and flu.
- Etiology of sinusitis Pathogenesis of the process
- Clinical signs
- Diagnostic criteria
- Principles of therapy
For parietal sinusitis, treatment is aimed at relieving the main symptoms and protecting the patient from the development of possible complications. Parietal sinusitis is a chronic disease that occurs due to inflammation of the maxillary (maxillary) sinuses. As a result of the action of certain causes, inflammation of the mucous membrane lining these sinuses occurs, the formation of pus and the development of the corresponding clinical picture. Sinusitis itself is not so much dangerous for its clinical manifestations as for its complications. In advanced forms of the disease, pus from the maxillary sinuses can move into the frontal sinuses, which can then lead to the development of purulent damage to the brain structures, up to a brain abscess or rhinogenic meningitis.
Although, however, it is not common to encounter cases where in patients diagnosed with eye trauma, iritis or choroiditis, and who have long challenged the patience and therapy of the optician, the diagnosis of which is often supported by Wasserrann positive is only clarified when another, unforeseen cause, sinusitis, manifests alarming symptoms.
The situation in the orbit in relation to the chest of the face explains, in particular, the consequences for it of inflammation of any of them. All have a more or less close relationship with the orbit. When examining the walls of the orbit in a skull whose facial cavities are well developed, it is clear that its upper wall is not a layer of the frontal sinus; its inner wall is formed by ethnoidal cells; the inferior wall corresponds to the roof of the maxillary sinus, and its apex is often surrounded by an extension of the spherical sinus.
Treatment of advanced sinusitis
After developing radiographs, one can judge the severity of the inflammatory process occurring in the maxillary sinuses. In case of total blackout, the doctor may prescribe a shock course of antibiotics and antihistamines to suppress inflammatory processes and reduce the severity of some symptoms.
In the most severe cases, surgical intervention may be indicated - puncture of the sinuses. This procedure has been known for a long time and is widely used in many countries around the world. Using a special syringe, excess fluid and pus are pumped out of the maxillary sinus. Then the sinus is filled with a special solution containing antiseptic drugs. This is done to reduce inflammation of the mucous membrane. Then the solution is pumped out of the sinuses. That's it, the procedure is completed.
This type of surgery is not dangerous, but it can speed up recovery and reduce the appearance of major symptoms, such as headaches.
For more effective treatment of sinusitis, the pus obtained after puncture can be sent for culture to identify the pathogen and determine which antibacterial drugs it is most sensitive to. Along with antibiotics, antihistamines are often prescribed to help reduce swelling, nasal congestion and other manifestations of the disease.
Some traditional medicines can be used to treat sinusitis. Such remedies should not replace the primary treatment prescribed by a doctor. They can only complement it. Moreover, before using any means, you should consult your doctor.
Using exclusively traditional medicine to treat sinusitis can lead to disastrous results. Untreated sinusitis will become chronic and will periodically trouble the patient throughout his life.
How to determine fluid in the maxillary sinuses
To determine the presence of liquid, it is enough to remember how milk behaves in a glass. It always has a horizontal liquid level even when changing body position.
An X-ray of the nose and paranasal formations also shows the need to perform a diagnostic puncture to remove pus, which cannot be eliminated with medications.
The pus can be clearly traced in a negative photograph of the nose and paranasal formations. The X-ray picture is enough for the ENT doctor to diagnose sinusitis or frontal sinusitis and begin immediate treatment.
X-ray photo: fluid level in the right maxillary sinus
The harm of self-medication
The most obvious harm of self-medication is the lack of positive results. People often take medications until they feel better. However, this approach is wrong. Antibacterial drugs should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor. Strictly in the volumes and within the time frame that he announced at the reception. Otherwise, the symptoms will go away, but the source of infection will remain. Inflammation in the maxillary sinus will become chronic.
Or, if the drugs were chosen incorrectly, there may be no improvement at all. The disease will become advanced, the pain due to overcrowded sinuses will become unbearable, and inflammation will have a chance to spread to the organs and tissues closest to the sinuses, causing all sorts of complications.
Another risk of self-medication is the medications that must be taken for sinusitis. If the dosage is incorrect, taken too often, or if there are problems with internal organs, antibacterial drugs can do more harm than good. Cases of drug-induced liver damage from uncontrolled use of antibiotics are not so rare. What can we say about gastrointestinal tract disorders, dysbacteriosis, and so on.