In the conclusion to the ECG, after indicating the heart rate, the nature of the rhythm and the location of the EOS, you can find the line: “incomplete blockade of the PNPG (right bundle branch).” It is difficult for people not privy to the mysteries of cardiology to imagine what kind of leg there might be in the heart, where exactly it is located and how it affects its functioning. Let's figure out what the danger is of incomplete blockade detected on an ECG and what consequences await people with such a pathology.
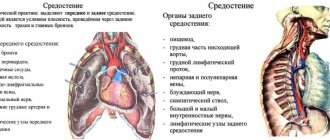
Location of the His bundle
Mechanism of development of deviation
Pathological deviation occurs gradually, suddenly - relatively rarely, we are talking about acute processes. To understand what underlies the development of pathology, you need to turn to anatomical information.
The heart is capable of autonomous operation indefinitely. This is the result of the presence of the so-called sinus node or natural pacemaker. It is responsible for generating an electrical impulse.
Excitation is transmitted through special fibers known as the bundle of His. It is a tree-like, branched structure.
As a result of previously existing inflammatory pathologies, congenital or acquired defects and other conditions, conduction disturbances occur, the electrical impulse slows down the movement (with incomplete blockade) or it becomes completely impossible (complete blockade).
As a result, the contractility of the myocardium on the right side (atrium and ventricle) decreases, and the movement of blood in the pulmonary circle is disrupted. Hence pulmonary problems as an early symptom of the pathological process.
Treatment tactics
If you suspect a pathology of the elements of the conduction system of the heart, you must consult with doctors: an arrhythmologist, a cardiologist and, in some cases, a cardiac surgeon. In the case of incomplete blockade of the branches of the His bundle, the main treatment should be aimed at the organ or organ system that provoked the abnormal functioning of the vascular bed and caused the development of the blockage.
There is no general treatment regimen for bundle branch blocks. If impulse transmission disorders are caused by angina pectoris, hypertension or heart failure, then basic treatment is based on taking antihypertensive and antiarrhythmic drugs, as well as cardiac glycosides. For proximal blockades, treatment with sympathomimetic agents: isadrin or subcutaneous injections of amiatropine is considered the most effective.
In case of incomplete blockade, if the patient does not experience discomfort and can lead a normal life, only control diagnostics and restorative therapy are required.
In case of genetic abnormalities or congenital defects, treatment of blockades is carried out surgically. The reasons for the operation are frequent fainting and life-threatening abnormalities of the heart. In modern cardiac surgery, to correct the functioning of the vascular branches of the cardiac conduction system, an electrical pacemaker is installed - a device that generates contractions and ensures a given heart rhythm.
With incomplete trochlear fasciculus, the width of the complex is greater than normal, so the disease is characterized by a slow impulse. As a rule, such a blockade is diagnosed on an electrocardiogram. An experienced cardiologist can hear splitting of the tone at the apex during auscultation. Partial disturbances in impulse transmission in the branches of the His bundle contribute to the development of chronic heart failure. To prevent the blockade from developing into a complete one, taking cardiac glycosides is contraindicated with this diagnosis.
Distal blockades are difficult to treat with medication. Electrical stimulation of the heart is considered the most effective method. For acute blockades that were provoked by myocardial infarction, temporary electrical stimulation is indicated. In case of persistent blockades, constant electrical stimulation is prescribed.
If a complete blockade suddenly occurs, an injection of “Euspiran” or “Isuprel” with a glucose solution (5%) will help relieve the patient’s acute condition. You can use the same drugs in tablet form. With prolonged exposure to medications on a neurovascular disease, complete heart block can turn into partial.
Complete heart block due to digitalis intoxication poses a danger to the patient’s life. In this case, to normalize the condition, stop taking glycosides. If complete blockade with a rhythm of 30-40 beats per minute persists, injections of Atropine intravenously and Unitol intramuscularly (2-4 times a day) are prescribed, and therapy can be supplemented with temporary electrical stimulation.
The main method for detecting bundle branch block is standard electrocardiography and its variations - transesophageal electrocardiography (TEE), rhythmocardiography, 24-hour ECG monitoring. To identify evidence of organic heart damage, echocardiography, MRI, MSCT, and cardiac PET are performed. If bundle branch block is detected, the patient must be consulted by a cardiologist, arrhythmologist or cardiac surgeon.
There is no specific therapy for bundle branch block; With this disorder, it is necessary to treat the underlying disease. For bundle branch block complicated by angina pectoris, arterial hypertension, heart failure, therapy is carried out with nitrates, cardiac glycosides, and antihypertensive drugs. In patients with AV block, indications for pacemaker implantation should be considered. In case of bundle branch block that occurs without clinical manifestations, dynamic observation is carried out.
Incomplete blockade of the right bundle branch is a fairly common problem. It can be detected during electrocardiography. The problem arises under the influence of congenital or acquired pathologies and requires timely diagnosis. This will prevent the condition from getting worse.
Description of the organ
The contraction of the heart muscles is ensured by the conduction system. It contains the sinus and atrioventricular nodes, the His bundle and Purkinje fibers.
The bundle of His consists of a right and left bundle. They ensure the movement of electrical signals to the tissues of the ventricles. If a blockade is diagnosed, this indicates that signals do not pass through it completely or do not arrive at all.
If a partial blockade develops, the electrical signal is not transmitted along one leg. This condition does not pose a threat to the patient's life. The conductivity of the heart slows down in this situation. Similar processes can be detected in people who do not have health problems. Therefore, the problem is often considered as a variant of the norm.
A great danger is the disruption of impulse transmission along the left leg, as this contributes to heart failure.
The pathology is most often diagnosed in men. Older women are more likely to suffer from left leg block.
Often the conduction of impulses slows down in childhood. If there are no pathologies of the heart, respiratory and circulatory systems, then this condition does not pose a danger.
Although the disease most often occurs without the slightest manifestations, it gradually disrupts the functioning of the ventricles.
Causes
Incomplete blockade of the right leg can occur under the influence of many diseases. Most scientists are inclined to think that such disorders are not associated with hereditary predisposition. Although if there are pathologies of the heart and blood vessels in close relatives, the likelihood of their development increases significantly.
Conduction disturbances along the right leg occur in different cases:
- for ischemic disorders in the heart;
- as a result of tumor processes;
- with abnormalities in organ development;
- with inflammatory processes in the endocardium or myocardium;
- if one pulmonary artery is blocked;
- with cardiosclerosis;
- if a long course of hypertension has led to an enlarged heart;
- with pathologies in the respiratory system that led to the appearance of cor pulmonale;
- after a heart attack;
- under the influence of bad habits;
- with constant emotional stress.
The electrical impulse is transmitted more slowly than it should if the person has taken large doses of antiarrhythmic drugs.
Incomplete blockade of the right leg of His occurs if the vagus nerve is in an overexcited state. This happens if a person is exposed to excessive physical activity.
Blockades also develop if surgical treatment of heart disease has been performed.
Symptoms
Most often, when the electrical signal does not travel completely down the right leg, the person does not notice any symptoms. Problems are identified during routine electrocardiography.
Patients may experience signs of an underlying pathology that has disrupted cardiac conduction. Wherein:
- have difficulty breathing;
- pain periodically appears in the chest;
- the rhythm of heart contractions is disrupted.
Therefore, treatment for such diseases should be carried out in a timely manner.
But, if the signal is blocked completely:
- dizzy;
- weakness is constantly felt;
- the patient periodically loses consciousness;
- there is pain in the heart;
- the organ works intermittently;
- headache;
- the heartbeat is clearly felt.
If such disorders appear, you should be examined urgently, as this can occur with dangerous chronic diseases.
Although with incomplete blockade, healthy people do not need specific therapy, since this condition is considered quite normal.
Establishing diagnosis
If diagnostic procedures are not carried out, then a suitable treatment option cannot be selected. Complete or even partial disruption of the electrical signal leads to a decrease in the number of ventricular contractions. To confirm such changes, electrocardiography is performed and the blood is examined for hormones.
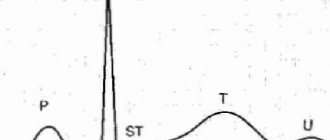
Incomplete blockade of the right bundle branch on the ECG is manifested by a slow passage of the electrical signal. In this case, there is a wave showing contraction of the atria, but there is no wave characteristic of contraction of the ventricle. This disorder is characterized by the appearance of small notches on the S wave and changes appear on the right.
If a person suffers from partial obstruction, then the QRS complex has a normal duration, but sometimes reaches 1.1 seconds.
General and biochemical examination of urine and blood.
- Heart examinations using ultrasound.
- Computer and magnetic resonance imaging. These procedures are necessary in severe cases to obtain a complete picture of the condition of the heart.
- Transesophageal electrocardiography.
- daily monitoring of electrocardiography. This helps to identify transient disorders.
When undergoing a routine examination, a person may accidentally find out that the ECG reveals an incomplete block of the right bundle branch. Below we will try to talk in more detail about whether there is a danger to health and whether it is worth treatment.
The bundles of His are an important part of the cardiac conduction system. They are formed from special muscle fibers of the heart, which have the unique property of conducting impulses. Thanks to these nerve impulses, the heart is able to contract.
There are only two such bundles in the heart - left and right. They arise from a common trunk, which lies in the interventricular septum. Next, the legs of His go each to its own ventricle.
Passing deep into the walls of the ventricles, the legs branch into numerous small Purkinje fibers.
Each of these fibers conducts nerve impulses to the heart cells, as a result of which they are all able to contract almost synchronously.
Sometimes the conduction of impulses along the branches of His is disrupted, may slow down, or even disappear altogether. Then there is a complete or partial blockade of the legs. As a rule, such a conduction disorder does not manifest itself in any way and is an accidental finding on a routine electrocardiogram.
Classification
Classification and degrees
The blockade is classified for a number of reasons.
According to the nature of the flow:
- Intermittent form. Transitional. Develops in 15% of cases. Identified by intermittent movement of the defect. Deviation is present or not at any given time. It is difficult to catch the change; an ECG is required several times to record the results. Therefore, inpatient examination is recommended.
- Alternate variety. Determined by a different current. There are always deviations, but they move from one branch to another, which complicates early diagnosis.
- Permanent form. Develops in most cases. There are no difficulties in the examination. Changes are stable.
Based on the number of affected bundles:
- Single. The movement of an electrical impulse along one branch is blocked. Characterized by a minimal clinical picture. Since there are no symptoms, the patient does not pay attention to his own health, the process progresses. In most cases, it becomes complicated within 2-3 years.
- Double. Several legs are involved at once. Manifestations are present, they are sufficiently pronounced to warrant going to the hospital.
- Triple. The most dangerous variety. Characterized by generalized disorders of the organic type. Urgent recovery under the supervision of a cardiac surgeon.
Finally, depending on the degree of impairment of the functional activity of the fibers:
- Incomplete blockade of the right bundle branch. Determines the initial stage of a sluggish pathological process. Over time, the condition becomes more complicated, and generalized lesions of cardiac structures and other systems develop. In the case of severe etiological factors, this phase does not develop; the disease (relatively speaking) immediately moves to another stage.
- Complete block of the right bundle branch. Characterized by total non-conductivity of fibers. The electrical impulse does not reach the ventricles. Hence the compensatory mechanism, when other cardiac structures begin to generate a signal themselves. The situation is only getting worse. Bradycardia at the level of 30-40 beats per minute is replaced by ventricular fibrillation. This is a direct path to death from cardiac arrest.
Classifications are used to determine diagnostic and treatment tactics.
Causes of pathology
The table presents the main causes of the disease.
Table 2. Causes of the disease:
| Cause | Description |
| Narrowing of the LV outflow tract in the area of the aortic valve. The condition leads to difficulty in blood outflow from the LV and a sharp increase in the gradient between the LV and the aorta. |
| A pathological condition characterized by the production of too much thyroid hormone. |
| A pathological condition in which the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood decreases. |
| Chronic systemic pathology of connective tissue. The nature of the disease is autoimmune. |
| Organic and functional damage to the myocardium, provoked by a deficiency or cessation of blood supply to the heart muscle. |
| Disease of the heart muscle. It is characterized by the growth of connective scar tissue in the myocardium. Over time, valves deteriorate. Muscle fibers are gradually replaced. |
| An inflammatory process affecting the muscular lining of the heart. It has an allergic, infectious, or rheumatic nature. It occurs in acute or chronic form. |
| Site of ischemic necrosis of the heart muscle. Develops against the background of acute coronary circulation disorder. In the absence of timely assistance, the death of the patient occurs. |
| Chronic inflammatory process affecting the respiratory system. Characterized by the “birth” of various cellular elements. |
How dangerous is the blockade?
Complications can occur at any stage of the pathological process. However, there is no guarantee that death will not occur.
An approximate list of consequences is as follows:
- Heart attack. The death of muscle organ cells and their replacement with scar tissue. The area of the lesion depends on the nature of the conduction disorder.
- Myopathy. Defect in the formation and development of the myocardium. It is determined for congenital reasons or as a consequence of alcoholism and other factors.
- Heart failure. Sudden, without prospects for restoration of cardiac activity.
- Stroke. As a result of a disruption in the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the brain.
- Respiratory failure of varying severity. Characterized by the impossibility of normal gas exchange.
- Pulmonary edema. Emergency condition. Requires urgent recovery in a hospital setting.
- Cardiac asthma. The attack may be isolated. In some cases, a group of episodes is identified over a short period of time.
- Death. As a result of the presented complications.
- Cardiogenic shock. Acute disorder, mortality approaching 100%.
The likelihood of consequences varies. It all depends on the degree of blockade.
Prevention
The patient is advised to quit smoking and alcohol, and avoid excessive physical and psychological stress. Adequate rest and sound sleep of at least 8 hours a day is necessary. You need to create a proper diet of foods containing potassium. Bananas and grapes are especially useful.
The patient should regularly undergo an ECG and contact a cardiologist if any pathologies are detected during the examination. If pain in the heart area or other unpleasant symptoms suddenly occurs, you should consult a doctor immediately. Preventive therapy is prescribed by a cardiologist based on the pathology that led to the occurrence of RBBB.
Causes
More than a dozen development factors can be named. This significantly complicates both self-diagnosis and examination under the supervision of a doctor.
An approximate list of the main and most common conditions leading to defects in the conductive structures of the heart:
Heart attack
Necrosis of cardiac formations. It is characterized by a total disruption of normal functional activity. Last but not least, right bundle branch block occurs. This is the result of the death of active tissues.
Recovery is basically impossible. The patient is prescribed lifelong maintenance therapy, the prospects for further biological existence are controversial, it all depends on the extent of the lesion, the age and state of health of the person.
Ischemic disease
Less active disturbance of blood supply to cardiac structures. Determined by severe coronary insufficiency or other conditions.
Recovery is carried out in a hospital on a regular basis. The prospects for a cure are minimal, especially if organic defects are present.
Pulmonary hypertension
Increased pressure in the pulmonary artery and anatomical changes in the myocardium in this form.
Potentially fatal, incurable condition. Requires regular assistance in a hospital setting.
Hypertension
In the early stages (0-1 stages of headache), minimal disruption of the conduction of the His bundle is determined, or there is none at all.
At stages 2 and, even more so, 3, generalized deviations arise not only from the movement of the electrical impulse, but also from the position of its generation in the sinus node.
General disorders require competent therapy under the supervision of a cardiologist. This is usually a lifelong impact on the underlying cause.
Rheumatism and other autoimmune pathologies
Accompanied by disruption of the normal functioning of the mitral valve and destruction of cardiac tissues in general. Treatment is long-term, using immunosuppressants and other drugs.
Inflammatory diseases of the heart muscle and pericardium
Accompanied by an intense clinical picture with symptoms of accelerated heart rate and severe chest pain. Tissue destruction is active and occurs in a short time.
Recovery in hospital, urgent treatment order. Without help, disruption of normal His bundle conduction is the least of the problems.
Complex prosthetics of the atria or other anatomical structures, including the mitral valve, will be required.
Metabolic disorders
First of all, calcification or deposition of inorganic salts in the structure of the heart.
Other development factors relate to congenital or acquired defects of cardiac formations, the aorta (narrowing of the lumen, aneurysm, deposition of cholesterol substances and other conditions).
The reasons for this condition and what is its danger
RBBB occurs due to two large groups of reasons; they are usually divided into congenital and acquired risk factors. If the patient has any of the following diseases or conditions, then he is at risk of developing incomplete blockade. Despite the benign nature of the process, without proper treatment, this slowdown in impulse transmission can cause serious heart disease over time.
Congenital risk factors include ventricular septal defect; Leva-Lenegra disease; atrial septal defect; pulmonary artery stenosis. Acquired risks leading to the development of the disease: chronic and obstructive pulmonary diseases, mitral valve stenosis, acute infarction, chronic ischemic heart disease, myocarditis, cardiosclerosis, hypertension, progressive dystrophy, bruises and other chest injuries, malignant processes, right ventricular hypertrophy, electrolyte disturbances ( especially hyperkalemia), drug overdose (beta-blockers, cardiac glycosides (digitalis), procainamide, quinidine).
Non-cardiac causes
In addition to these factors, we can highlight:
- Long-term or improper use of antihypertensive, antiarrhythmic, psychotropic and other drugs, including glycosides.
- Smoking.
- Alcohol abuse. The duration until the blockade develops depends on individual resistance to ethanol and its metabolites.
- Poisoning with heavy metals and toxic substances.
- Endocrine pathologies: from diabetes mellitus to severe dysfunction of the thyroid gland or adrenal glands.
- Bronchial asthma, COPD, respiratory failure. The process moves in two directions: gas exchange disturbances aggravate the blockade and vice versa.
The cause must be identified in order to prescribe appropriate treatment. If the condition has not been identified, they speak of idiopathic blockade of the right bundle branch. Therapy is aimed at relieving the consequences.
The need for treatment for RBBB and what it consists of
Many patients underestimate this condition due to the absence of symptoms, and when they receive an ECG report, they are in no hurry to go to the doctor. But the danger of incomplete blockade is that without treatment it will sooner or later develop into a more serious pathology that is life-threatening. Therefore, there should be no doubt about the need for treatment - it is necessary!
Treatment is aimed at treating the disease that caused the blockade. There is no specific treatment for the blockade itself. Even in case of successful treatment, dynamic monitoring of the patient using an ECG is required.
To monitor treatment, a dynamic ECG is performed
Sometimes blockade occurs at a young age without objective reasons; this condition is considered normal and does not require treatment. However, it is necessary to undergo a full examination, and even if the cause of the development of RBBB has not been found, it is necessary to periodically perform an ECG.
Symptoms
Manifestations depend on the severity of the pathological process. There are no specific signs as such; they are caused by the underlying disease.
Complete RBBB
- Intense arrhythmia. According to the type of bradycardia, that is, weakening of the contractility of the heart muscle. Total deviation occurs at a late, advanced stage, when conduction disturbance covers 2-3 branches. Organ failure and sudden death are possible.
- Chest pain. Weak, unless an attack of angina occurs. Burning, pressing, radiating to the stomach, sore throat and arms. Treated with analgesics. In severe cases - narcotic drugs.
- Weakness, drowsiness and confusion. Especially if the brain does not receive enough nutrients and oxygen, disturbances in the functional activity of cerebral structures occur. Neurological deficit increases gradually or like an avalanche, depending on the nature of the underlying process.
- Dyspnea. In a state of complete rest. Even minimal physical activity becomes impossible.
- Cephalgia. The pain is localized in the occipital region or crown. Baling. Shooters. Regular. Accompanied by nausea, extremely rarely vomiting, this is not a typical sign. Vertigo. The patient cannot navigate in space and is forced to lie down for a long time until the condition normalizes and the function of the cerebellum is restored.
- Cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle. Blue discoloration of the perioral area. Develops as a result of any cardiac problem.
- Paleness of the skin. Occurs at the moment of acute hemodynamic deviation. Fainting, possibly repeatedly over a short period of time.
Incomplete RBBB
Partial blockade is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Mild arrhythmias. Slight weakening of heart contractions.
- Dyspnea. In a state of moderate intensity physical activity.
- Chest pain.
- Deviations in cognitive, mnestic functions.
Some situations are not accompanied by pathological signs at all.
In any case, incomplete blockade does not have specific symptoms, apart from arrhythmia of varying severity. More serious forms of disturbance of normal contractility are possible: from flutter fibrillation to extrasystole, which aggravates the overall prognosis.
Herbal infusions
Herbal mixtures are more effective because they simultaneously act “on all fronts”: they restore normal functioning of the bundle branch, reduce heart failure, and prevent complications. So, in Rus', herbalists most often recommended the following herbal mixture:
- Raspberry fruits – 20g;
- Birch leaves – 10g;
- Leonurus cordial herb – 10g;
- Herb or dill seeds – 10g;
- Periwinkle leaves – 20g.
Brew a tablespoon of this mixture with 0.5 liters of boiling water in a thermos, close the lid and leave for at least an hour. Every time 15 minutes before meals, drink half a glass of this drink. The course of treatment is from one month to a year (depending on the patient’s condition).
In an ancient French herbal medicine reference book we found the following recipe:
- Sage herb – 50g;
- Dill seeds – 50g;
- Medicinal cap herb – 50g;
- White mistletoe – 30g;
- Fragrant rue herb – 10g;
- St. John's wort herb – 10g.
Combine all ingredients. Take a liter of water for 2 tablespoons of the mixture, bring the mixture to a boil, and immediately remove from the heat. Let the drug brew for half an hour, then strain it and drink a glass 4 times a day. In severe cases of heart failure, the dosage is halved.
The following collection provides an excellent therapeutic effect:
- Blood red hawthorn flowers – 30g;
- Small periwinkle leaves – 30g;
- Melissa leaves – 10g;
- Spring adonis herb – 10g;
- branches of lavender spikelet – 10g.
Take a heaping tablespoon of this mixture, pour a glass of cold water and leave for half an hour. Then put the medicine on the fire, boil for 5 minutes and cool. Drink the resulting medicine in small portions throughout the day. The course of treatment must last at least 2 months for you to feel a stable effect.
Diagnostics
It is carried out under the supervision of a cardiologist, a specialized surgeon, in case of suspected pathologies that can only be eliminated by radical methods.
The approximate scheme includes the following activities:
- An oral interview with a person, collecting anamnesis to establish the clinical picture and the origins of its occurrence.
- Measure blood pressure several times. Also heart rate.
- 24-hour Holter monitoring to record blood pressure and heart rate for 24 hours. Repeated use is possible. It is better if the patient is outside the hospital, in natural, familiar conditions.
- Electrocardiography. Detects functional disorders. Considered the gold standard.
- Echocardiography. Visualization of heart tissue and surrounding structures. It is used to diagnose organic abnormalities that developed before or after the blockade. Cause and effect are established based on objective data.
- MRI or CT. To clarify the nature of anatomical defects.
Third party specialists are involved as necessary. Mainly in the field of endocrinology. Variations are possible. Extended activities are required to establish the origin of the process.
Establishing a diagnosis
First of all, the doctor refers the patient to an electrocardiogram. Additional diagnostic methods are presented in the table.
Table 5. Establishing a diagnosis.
| Diagnostic method | Description |
| The most informative diagnostic method. Helps identify transient blockade within 24 hours. |
| Detects rhythm disturbances. It is carried out if the “classical” ECG does not produce results. |
| Helps detect organic heart damage and evaluate myocardial contractility, as well as ejection fraction. |
| It is carried out if the clinical picture after the examination is still unclear. |
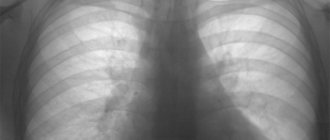
Signs on ECG
| Full | Incomplete |
|
|
Right bundle branch block on ECG is relatively difficult to detect. There are few typical signs; differential diagnosis is carried out with other pathologies. Significant qualifications are required to decipher the cardiogram and understand the type of process.
What is a “bundle of His” and why is it needed?
This bundle is responsible for conducting impulses through the ventricles of the heart. There are several legs in the bundle, each of which is responsible for certain sections. The posterior leg (there is only one) is responsible for the left ventricle (specifically, its lower wall) and the posterior left region of the interventricular septum. There are two anterior legs in the bundle of His: right and left. The left is responsible for the anterior lateral wall of the left ventricle and the anterior-left section of the septum. The right leg, which interests us, is responsible for excitation of the right ventricle and the right half of the interventricular septum.
Why is the blockade called incomplete? The fact is that with complete blockade, the excitation of the right ventricle and the right part of the interventricular septum does not occur in a completely adequate way, namely: the depolarization wave seems to spread from the left ventricle and the left side of the interventricular septum, which were “charged” by the impulse of the left leg. Incomplete blockade is simply an increase in the time of excitation along the right leg.
Treatment methods
Remedial measures depend on the nature of the deviation.
Against the background of long-term conduction disturbances without a pronounced clinical picture, organic defects on the part of the systems, and if the condition was discovered by chance, long-term follow-up is indicated. Control every 3 months. Then less often (once every six months).
In case of two or three-bundle blockade against the background of a hypertensive process, the use of a group of pharmaceuticals is indicated:
- To lower blood pressure (classic regimen: Diltiazem + Perindopril + centrally acting drug, for example, Moxonidine).
- Glycosides.
- Statins, in case of the presence of an atherosclerotic component.
- Mild diuretics. Selection, especially against the background of antihypertensive therapy, is carried out only by a doctor. Incorrect combinations lead to myocardial arrest or degeneration and renal failure.
- Antithrombic to restore the rheological properties of blood.
Autoimmune diseases are treated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, and less often with other drugs.
The symptoms of arrhythmia are relieved with the use of Amiodarn in small dosages. It is possible to prescribe beta blockers (the best of its kind is Anaprilin).
Surgical treatment of RBPN is indicated in extreme cases, if there is a violation of the anatomical integrity of the organ, the need for prosthetics arises.
Against the background of atrioventricular block and generalized rhythm deviations, implantation of a pacemaker is possible. The measure is controversial, it is resorted to in exceptional cases, not all cardiologists support this treatment tactic.
If the pathological process is caused by subjective factors, giving up smoking, alcohol, bad habits in general, changing the diet towards reducing the amount of animal fats, and optimizing the drinking regime (2 liters per day, if there are no contraindications) are indicated.
Treatment
If incomplete blockade of PNPG is detected on the ECG, it is necessary to understand that this condition does not require therapeutic measures. Patients suffering from various diseases require adequate correction of the underlying pathology.
For this purpose I use various groups of drugs:
- Anti-ischemic.
- Antihypertensive.
- Antiplatelet agents.
- Statins.
- Diuretics.
- Cardioprotectors.
- Drugs intended for the treatment of diseases of the bronchopulmonary system.
- Antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for myocarditis.
If necessary, surgical correction is performed, which is carried out based on the underlying disease, severity of the condition, and individual characteristics.
Forecast
Depends on a number of factors. Favorable points associated with good survival:
- Complete or predominant absence of symptoms and clinical picture.
- Normal state of health (without somatic pathologies).
- High-quality response to treatment.
- Young age.
- Good family history.
- No bad habits. Incidental detection of an abnormality on electrocardiography.
Mortality is maximum with complete three-bundle blocks and reaches 80%. Bradycardia is the main factor in cardiac arrest. Heart attacks and strokes occur less frequently.
The prognosis for restoration of working capacity is relatively favorable. But you can safely forget about physical work. The likelihood of death due to mechanical overload increases sharply.
Treatment of complete and incomplete blockade of PNPG
If such a pathology is not combined with dysfunction of the heart or other internal organs that negatively affect its condition, medical intervention is not required. In the presence of provoking diseases, complex therapy for PNPG blockade using the following drugs is recommended:
- sedatives of natural origin - “Motherwort”, St. John’s wort, “Novopassit”, “Gerbion”, “Fitosedan”,
- B vitamins, nicotinic acid (vitamin PP),
- antithrombosis medications (antiplatelet agents) - “Cardiomagnyl”, “Magnikor”, “Thrombo ACC”, “Curantila”, “Pentoxifylline”,
- drugs to lower blood pressure - Atenolol, Losartan, Verapamil, Lisinopril, Valsartan,
- lipid-lowering drugs to reduce cholesterol levels in the blood - “Vazilipa”, “Simvastol”, “Traykor”, “Atorvastatin”,
- antioxidants - “Ubiquinone”, “Carnitine”, “Cratal”, “Mexidol”.
Adverse and dangerous consequences of underlying diseases should be treated using appropriate groups of medications. If, against the background of bronchopulmonary pathologies, “pulmonary heart” syndrome occurs (its right sections have expanded), the doctor prescribes glucocorticosteroids (Spiriva beclazone, Berotec), inhaled adrenergic agonists. For inflammatory processes in the membranes of the heart, antibiotics and NSAIDs (Diclofenac, Nimesil) are prescribed. The development of heart failure requires the use of diuretics (Chlorthalidone, Indapamide) and cardiac glycosides Celanide, Strophanthin, Ditoxin.
If conservative methods are ineffective, installation of a pacemaker or surgical treatment of the blockade is used.
Important: A patient with an installed pacemaker should not come within 20 cm of working electrical and wave devices. This applies to a TV, laptop, mobile phone, and hair dryer.
The question is often asked: does incomplete blockade of the right leg of the PG allow for sports training? You can play sports only in the absence of cardiac or pulmonary diseases that provoke deterioration of conductivity. If such pathologies exist, physical activity should be reduced. Restrictions apply to strength sports: kettlebell lifting, weightlifting, powerlifting, arm wrestling, power yoga. The intensity of the load and types of exercises should be selected by a specialist with a medical education.