An ECG is a procedure that allows you to track the rhythm of the heart. The paper tape displays a graph of cardiac activity at the time the procedure was performed. The necessary information can be obtained quickly.
The electrical field of a woman’s heart is analyzed, its rhythm and number of contractions are determined, disorders such as heart pathologies, non-cardiac diseases and much more are reflected.
Carrying out an ECG of the fetus
The study is non-invasive, there is no trauma to the skin, and patients do not experience pain. In cardiology, the procedure is considered informative. But despite this, there are also disadvantages. Many are of the opinion that the procedure does not detect heart defects, tumor formations, murmurs and much more.
What is ECG
Electrocardiography is a method of studying the electric fields generated during the work of the heart with subsequent recording of the results obtained on paper film.
The examination provides accurate information about the frequency and rhythm of the heartbeat, recording the speed of the electrical impulse.
When conducting a cardiogram, electrodes are attached to the patient's skin to obtain information using a special device that records the regularity of contractions.
Diagnosis records cardiac dysfunction, individual forms of arrhythmia and the presence of specific diseases associated with the functioning of the heart.
Pregnant women undergo electrocardiography at least twice during the entire gestation period if there are no problems with cardiac activity. If necessary, the procedure is performed more often.
Diagnostics are allowed for young children and developing fetuses to register their health status.
An ECG during early pregnancy is prescribed by a doctor to diagnose possible abnormalities and determine the correct treatment regimen.
Indications for use
In modern cardiology, ECG is often used. The procedure helps to identify pathologies in a child or mother at an early stage. There are many indications for this procedure, from the recommendations of the attending physician to the initiative of the woman herself.
Procedures may be prescribed based on the patient’s complaints, including:
- headaches, causeless fainting;
- shortness of breath, feeling of weakness;
- sudden rapid heartbeat that appears in a calm state;
- heart disease in close relatives;
- difficulty breathing, chest pain;
- disease of the nervous or endocrine system.
Example of electrode fixation
Important! During the first pregnancy, an ECG is a mandatory procedure. Other indications are a conflict of Rh factors, diastasis after the birth of a child.
There are other indications for the procedure not related to pregnancy, including:
- persons after forty years of age;
- women planning pregnancy;
- complications that appear during pregnancy;
- people who have had infectious diseases;
- abuse of bad habits;
- before the upcoming surgery.
In each case listed above, an ECG is mandatory.
ECG for pregnant women - can it be done?
Pregnancy is a condition in which the body adjusts to a new rhythm of work. For full gestation of the fetus, the necessary hormones are produced. An ECG is mandatory, some time after a woman registers at the antenatal clinic.
Position on a special couch
Frequency: at least once. Many doctors recommend having ECGs up to three times every nine months. To determine the health of the fetus and the expectant mother, the procedure is carried out in the first trimester. It is possible to identify existing deviations at an early stage of development.
During pregnancy, a woman's heart works for two, pumping a large amount of blood every day, the load increases several times. All these factors, together with hormonal changes, can cause the development of other pathologies.
Interesting! All women registered for pregnancy are sent for an ECG. As a supplement, studies are performed after the onset of chest pain or other symptoms.
To ensure that the life of the woman and child is not endangered, it is necessary to undergo the procedure, as well as treatment, if necessary.
Preparing for a cardiogram: about eating and drinking
Before starting diagnostics, you should pay attention to the following points:
- It is necessary to notify the doctor ahead of time about the medications you are taking. Ingredients in some medications may interfere with test results;
- before making a diagnosis, it is prohibited to apply cosmetic or medicinal creams to the skin surface due to the effect on conductivity;
- For the appointment, it is better to wear clothes that are easy to unbutton or take off;
- bracelets, pendants, chains and other jewelry from the neck and hands are removed in advance;
- drinking cold water is eliminated.
A number of common questions include: “Can I eat before an ECG?”
Eating is allowed two hours before the start of the procedure. Diagnostics on an empty stomach is not allowed, as this affects the results of the analysis.
Before performing an ECG, it is necessary to exclude physical activity.
Stages of the procedure
ECG or electrocardiography is a procedure aimed at studying the heart muscle; 12 graphs are displayed on the tape. Based on them, we can draw conclusions about the work of the body.
It is important to remain calm during the procedure
Is preparation necessary?
The expectant mother does not undergo special training before conducting the study. There are some recommendations to improve the passage of impulses.
These include:
- an hour before the procedure, ensure yourself peace, avoid physical activity;
- on the day of taking readings, it is prohibited to drink coffee and other energy drinks;
- the day before the procedure you cannot go to the sauna or steam bath;
- It is prohibited to lubricate the chest area with greasy cream.
By following the recommendations indicated above, you can obtain reliable research results.
Process description
An example of one of the deviations
The procedure can be performed by nurses working in a medical institution or specialized specialists.
The procedure is as follows:
- the woman will sit on a special couch;
- the chest area and other places where the sensors are attached are degreased with ethyl alcohol;
- to improve the conductivity of electrical impulses, a special gel is applied;
- Electrodes are attached to the hands, legs and chest area, the wires are attached to the sensor of the measuring device;
- to display the graph and record it on the tape, the cardiograph is turned on;
- At the end of the procedure, a tape with a graph of heart function is obtained.
You cannot worry while the research is being conducted, otherwise the research will be interpreted incorrectly. All you need to do is relax and breathe calmly.
Equipment used for the procedure
Interesting! The process of digesting food can increase the work of the heart; therefore, it is not recommended to eat within two hours.
ECG leads
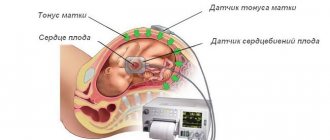
There are several ways to record an ECG: on the chest and in the heart area. To take readings from the fetus, special devices are attached to the abdomen of a pregnant woman.
Based on where the electrode is located, a graph will be displayed. Now, as for the lead, this is a method that records readings with different electrodes. It can be reinforced or standard.
As for the second method, the devices are connected in pairs, namely:
- First position . The potentials between the right hand and the left are measured.
- Second position . The difference between the right hand and, accordingly, the left leg is measured.
- Third position. Difference between left hand and right foot.
Fixing sensors on the belly of a pregnant woman
With enhanced abduction, the electrodes are located at certain points, namely:
- Electrode location on the right hand. The left arm and leg are connected to the passive electrode.
- The active one is located on the left arm, the passive one on the opposite arm and leg.
- Separation from the left leg. The hands are connected together, the active electrode is placed on the left leg.
The doctor decides which method to use.
How to do an ECG for pregnant women
This process for pregnant women is identical to the usual electrocardiography procedure. The patient is asked to lie down on the couch.
The doctor takes time for rest and relaxation - worries before the upcoming diagnosis affect future results.
Before fixing special equipment to individual parts of the body, the skin is degreased using alcohol or gel to conduct the impulse.
The doctor places four multi-colored electrodes in the chest area. Plates are attached to the wrists and shins:
- red and yellow electrodes are alternately installed on the right and left hands in accordance with medical standards;
- Electrodes of two colors are placed on the lower limbs: green on the left, black on the right. The black electrode is used to prevent electric shock in the event of sudden failure of special equipment.
Images of cardiac impulses are displayed on paper film. When carrying out the procedure, you must remain calm, come cheerful and rested.
Time: 10-15 minutes.
Effect of ECG on the fetus
An important question for an expectant mother is: “is it possible to do an ECG during pregnancy?” and “what impact does it have on the baby?”
It is known that ECG is harmful to the child and is strictly prohibited for pregnant women. However, this judgment has been refuted by doctors - a cardiogram is recognized as a safe, painless procedure and cannot have a detrimental effect on the developing embryo.
The impulses are not reflected negatively on the placenta, organs and tissues, or on the milk of the expectant mother.
The procedure has no contraindications.
What types of arrhythmia occur during pregnancy?
Arrhythmia is a serious medical problem. Heart rhythm disturbances pose a threat to the formation of the fetus and the course of gestation. Complications may develop:
- spontaneous miscarriage;
- gestosis;
- premature birth;
- chronic hypoxia and fetal malnutrition.
Practice shows that the risk of complications is higher with previous cardiovascular pathology.
Let's take a closer look at what forms of arrhythmia are detected during gestation. and how to recognize them by their characteristic features.
Extrasystole
Extrasystolic arrhythmia is the most common type of cardiac dysfunction in pregnant women. It occurs predominantly in the third trimester and is often asymptomatic. Accompanied by interruptions in cardiac activity and other nonspecific symptoms.
Short-term extrasystole is not dangerous to the health of the mother and fetus. The resulting hemodynamic disturbances do not interfere with the course of pregnancy. As the pathology progresses, fetal hypoxia develops. The risk of complications is higher with concomitant heart disease.
Sinus arrhythmia
With this option, the normal rhythm of the heartbeat is disrupted and becomes chaotic. At first it may become more frequent, then slow down with subsequent normalization. The intervals between individual contractions take on different lengths.
The cause of the pathology is a malfunction of the sinus node. It is through it that the impulse passes with a certain periodicity. But if the rhythm is disrupted, the node sends signals at various intervals. All parts of the heart contract sequentially, but without a clear rhythm. This is how sinus arrhythmia develops.
In clinical cardiology, it is customary to separately distinguish respiratory arrhythmia. Here, disorders are associated with movements of the chest during inhalation and exhalation.
Sinus arrhythmia during pregnancy is usually not dangerous for the mother and fetus. Such attacks do not affect the general condition of the body and have a short duration. But, if a woman’s well-being worsens, the fetus suffers, a consultation with a cardiologist and selection of therapy is indicated. Progressive sinus arrhythmia during pregnancy threatens the development of fetal hypoxia and premature birth.
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
WPW syndrome is a form of supraventricular tachycardia. Observations show that this form of arrhythmia in pregnant women is rare and is usually associated with previous heart pathology. The anatomical substrate of the disease is the formation of additional atrioventricular pathways (“bridges”). The bioelectric impulse from the sinus node spreads abnormally quickly and can move in a circle.
Symptoms of WPW are nonspecific. Pathology is detected on an ECG. During an attack, heart rate reaches 200 beats/min. Atrial fibrillation and cardiac arrest are possible.
Paroxysmal tachycardia
Paroxysmal conditions rarely occur during pregnancy without a previous background. They usually complicate myocardial ischemia. By localization they can be atrial and ventricular.
An attack of paroxysmal tachycardia occurs suddenly. Heart rate increases to 200 beats/min. There may be complaints of tinnitus and dizziness. In pregnant women, an attack often occurs against a background of nausea. Possibly reversible speech impairment.
A prolonged attack of paroxysmal tachycardia is dangerous for the mother and fetus. Termination of pregnancy is possible.
Diseases identified during diagnosis
The cardiogram detects the following diseases:
- arrhythmia;
- tachycardia;
- bradycaria;
- blockade;
- hypertrophy;
- pericarditis;
- myocarditis.
It is possible to detect low levels of potassium and calcium in the blood, the causes of symptoms of difficulty breathing, dizziness, rapid heartbeat, and pathology of the heart muscles.
Norms and acceptable features of the cardiogram
Interpretation of ECG in pregnant women during the gestational period is associated with the physiological characteristics of the body. So, the norm for contraction frequency readings is 60-80 beats/min.
During pregnancy, due to increased blood circulation and changes in hormonal levels, the quantitative level of heart rate may increase, but ideally should not exceed 80 contractions.
The position of the heart is expressed by axis values. Normal value: 30-70, but during pregnancy a level from 70 to 90 is acceptable.
The location of the diaphragm is likely to change; the movement occurs along the sagittal axis. After the baby is born, the previous values are restored.
During pregnancy, the presence of other extrasystoles (contractions of the heart muscles) is permissible, since changes occur in certain parts of the heart.
Establishment of atrial or ventricular rhythm must be further examined by a doctor.
Before finding and recording possible pathologies with a negative cardiogram result, diagnostics are performed several times.
The doctor determines the differences between the two results, and if deviations from the norm are found, the patient is prescribed an ultrasound of the heart to identify anatomical disorders.
In the conclusion, the nature of the heart rhythm, heart rate and EOS (electrical axis of the heart) are indicated and the disorders found during the study are described.
The diagnosis is established based on the results of the cardiogram, taking into account the symptoms and characteristic signs of a particular disease, and the patient’s complaints.
Decoding the information received about the patient’s condition takes from 5 to 10 minutes.
Causes
Pregnancy is a risk factor for heart rhythm disturbances. There are explanations for this:
- Hormonal changes. The natural increase in progesterone and estrogen has a proarrhythmic effect on myocardial tissue.
- Increase in circulating blood volume by 20-30%. This leads to stretching of the atria, and the rhythm is disrupted.
- Physiological increase in heart rate. On average, heart rate increases by 15-20 beats per minute compared to the initial data. Against the background of natural tachycardia, cardiac output increases and arrhythmia develops.
Heart rhythm disturbances are detected in 10-12% of all pregnant women (according to some authors - up to 20%). The prevalence of pathology among expectant mothers is higher than among women outside the gestational period. Arrhythmia may be newly identified or formed before conception. Often the exact cause cannot be determined.
It is important to understand: not all heart rhythm disturbances in pregnant women are associated with organic damage to the myocardium. In practice, we often see that failure of the heart is caused by various conditions, including endocrine pathology, diseases of the nervous system, etc. The medical literature indicates that up to 45% of gestational arrhythmias are of functional origin and occur even in healthy women.
The following causes of arrhythmia are distinguished:
- functional states: consumption of certain products (tea, coffee), smoking, stress, physical activity;
- organic damage to the heart muscle: ischemic heart disease, heart defects, myocarditis, pericarditis, neoplasms;
- autoimmune diseases;
- bronchial asthma, bronchitis;
- cerebrovascular accident;
- pathology of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands;
- intoxication with alcohol, drugs.
Arrhythmia in pregnant women often develops when carrying a large fetus, multiple pregnancy, and polyhydramnios.
Disadvantages and Limitations
The cardiogram, along with other diagnostic methods, has its own shortcomings. Eg:
- some diseases can be displayed as normal values when displaying the result;
- this technique is static and does not indicate heart problems if there are no symptoms;
- pathological changes are observed in specific diseases. In such cases, an additional examination is prescribed to fix an accurate diagnosis.
Before attending the procedure, it is important to consult with the gynecologist leading the pregnancy and specialists.
Based on the diagnosis and tests obtained, the doctor will prescribe a competent treatment regimen and draw up a labor management plan.
Is ECG harmful for mother and baby?
Pregnant women can have an electrocardiogram at any stage, since the procedure does not cause any side effects. There are no contraindications to the study.
The following factors can cause difficulties in performing a cardiogram:
- chest injury;
- excessive excess weight;
- presence of a pacemaker;
- the presence of metal implants in the body.
There are several electrocardiogram methods. Each technique has its limitations, so before the procedure, the specialist studies the pregnant woman’s chart to determine possible limitations.