Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are considered high-tech, expensive research methods. Only the attending physician can correctly select the method of examining the kidneys, taking into account the purpose of the diagnosis, and decide which is better suited in a particular situation: CT or MRI. Let us consider in more detail in which cases it is necessary to undergo a CT scan, and when it is necessary to perform an MRI of the kidneys.
Differences between procedures
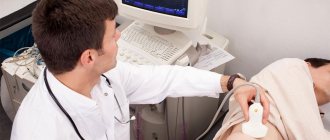
Ultrasound is a method of visualizing organs and tissues using high-frequency sound , which is not perceived by the human ear. It is produced by a sensor that the doctor places on the surface of the body. Ultrasound penetrates most tissues of the human body, and is partially reflected depending on their density. This part is picked up by the same sensor. It sends the received data to a computer, where it is processed and displayed on the screen in the form of an image.
Ultrasound allows you to study the abdominal aorta and blood vessels in Doppler mode. In it, the device detects different directions of blood flow. This allows it to be used for diagnosing the heart cavity and large vessels. Sometimes diagnostic interventions (punctures, biopsies) are performed under ultrasound control.
Ultrasound of the stomach
Computed tomography (CT) is an X-ray examination method that uses ionizing radiation. The patient takes a series of images in the device, which are processed using special software and displayed in the form of a three-dimensional image.
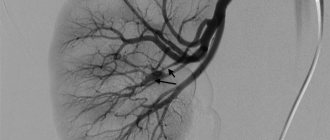
To increase the information content of CT, contrast agents are used that absorb X-ray radiation and selectively accumulate in different types of tissue. This allows the technique to be widely used for detecting vascular pathologies and oncological processes.
CT principle
Briefly about kidney functions
The kidneys, which are part of the genitourinary system, are a paired organ and perform the following functions:
- excretory;
- concentration;
- hematopoietic;
- metabolic;
- endocrine;
- ion-regulating;
- osmoregulatory.
The kidneys remove harmful and toxic substances from the body (for example, many drugs or alcohol), excess organic and inorganic compounds, take part in the metabolism of carbohydrates and proteins, and in the formation of biologically active substances: renin, erythropoietin, which regulate blood pressure and the rate of red blood cell formation.
Contraindications
Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity has no contraindications , except for situations that would make the procedure uninformative.
An ultrasound cannot be performed if the skin in the area of contact with the sensor is severely injured, for example, there are wounds, burns or an inflammatory process.
Abdominal tomography has a more extensive list of contraindications:
- Pregnancy period. X-ray radiation can negatively affect a child's development.
- Excessive body weight. A patient weighing more than 180 kg cannot be placed in the device.
- It is prohibited to use contrast if you are allergic to it, or if you have kidney failure, diabetes, or thyroid disease.
- Childhood and inability to lie still.
- Claustrophobia, high anxiety.
- Presence of seizures.
It makes no sense to carry out both ultrasound and CT as planned if the patient has eaten enough before the procedure, or there is increased gas formation in the intestines, which worsens the informativeness of the diagnosis. But in an emergency situation, with a sharp deterioration in the patient’s well-being, this can be neglected.
Do you need preparation for examinations?
For many kidney diseases, the use of a contrast agent is strictly contraindicated. This drug, based on iodine or gadolinium metal particles, is distributed throughout the circulatory system and is gradually eliminated by the human excretory system. Therefore, an additional burden is created, blood pressure increases, and there is a risk of exacerbation of renal failure.
Without the use of a contrast agent, preparation for the examination in any way is not required. The patient only needs to prepare a set of clothes and a direction indicating the expected diagnosis. If you need to track kidney disease over time, you should provide the diagnostician with the results of past CT or MRI procedures.
If the disease is associated with the need to diagnose a tumor, a contrast agent is used in the absence of contraindications. In some patients, it causes discomfort and nausea, so before the procedure it is recommended to abstain from food and not drink water or tea 6 hours before the procedure. Thus, unpleasant sensations are observed only in the first seconds after administration of the product and quickly disappear without consequences for health.
For some patients, undergoing an MRI becomes an unpleasant experience. When the tomograph is operating, the magnetic coils produce sharp knocking and humming noises, which unnerves you and makes it difficult to relax. In this case, it is recommended to discuss the possibility of taking a sedative. Video: General information about the differences in CT and MRI diagnostics is explained by radiologist Natalya Igorevna Petrovskaya.
Safety
Computed tomography uses ionizing radiation. In high doses, it can lead to cell destruction, DNA mutation and disruption of important body systems. In patients after massive irradiation, inhibition of the maturation of blood cells in the bone marrow, decreased resistance to infectious agents, and ruptures of the walls of blood vessels are observed. In the long term, oncological processes develop much more often.
Important It has been reliably established that X-ray radiation can harm the development of the fetus. Therefore, CT scanning during pregnancy is possible only for health reasons.
The radiation dose that a patient receives during a CT scan is presented in the following table:
| Rib cage | 11mSv |
| Abdominal organs | 14mSv |
| Pelvic organs | 9.5mSv |
| Head | 2mSv |
| Limbs | 0.5mSv |
| Thoracic or lumbar spine | 5mSv |
The maximum safe dose for humans is considered to be 20 mSv. In the presence of oncological pathologies, this figure increases to 50 mSv. Therefore, it is not advisable to do a CT scan of the abdominal organs more than 2 times a year.
Ultrasound diagnostics is considered absolutely safe for the patient. It can be performed without restrictions during pregnancy or breastfeeding, in the presence of concomitant pathologies. There is no evidence that it causes complications or provokes the development of new diseases.
Ultrasound certificate can be performed an unlimited number of times
. It does not provoke the development of new diseases, and does not aggravate the course of old ones. For safety reasons, an ultrasound procedure is performed on children to diagnose gastrointestinal diseases.
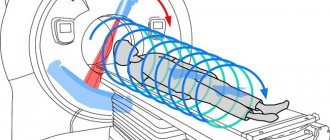
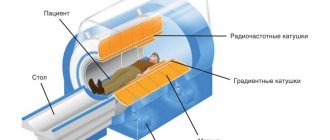
The operating principle of tomographs
The essence of both methods is layer-by-layer scanning of the body. As a result, tomograms are obtained (hence the name of the techniques). After which they are processed by a computer, which forms a 3D model of a particular part of the body from them.
The differences lie in the method of creating tomograms:
- With CT, they are formed by passing x-rays through the body. Thanks to the design of the device, a circular motion is ensured. Therefore, the rays scan the body from all sides, which helps the computer create a three-dimensional model.
- In magnetic resonance imaging scanners, layer-by-layer sections of the body are formed due to a magnetic field. It leads to the alignment of atomic nuclei in one direction or another along magnetic rays. The computer processes the received information and generates a tomogram of the body.
What to choose?
What to choose, ultrasound or computed tomography, is decided by the attending physician based on the clinical picture and previously performed tests. The specialist evaluates the medical history and symptoms, which helps to suspect negative changes in the body.
Ultrasound is often initially prescribed as a simpler and more accessible method. If the information received is not enough, then the patient is referred to a CT scan.
Ultrasonography
Ultrasound is chosen if the following diseases are suspected:
| Organs | List of diseases |
| Stomach |
|
| Spleen |
|
| Intestines |
|
| Liver |
|
| Gallbladder and bile ducts |
|
| Pancreas |
|
| Retroperitoneal space |
|
Whether stomach cancer is visible on an ultrasound is written in a separate article.
Computer tomogram
CT is better to choose for the following diseases:
| Organs | List of diseases |
| Stomach |
|
| Spleen |
|
| Intestines |
|
| Liver |
|
| Pancreas |
|
| Large vessels |
|
| The lymph nodes |
|
| Retroperitoneal space |
|
Diagnostic research methods
Before choosing which is better: kidney ultrasound or MRI, you should learn more about each technique. Perhaps in a certain case more CT will be used.
Ultrasound is an ultrasound examination, the principle of which allows you to identify pathology or its absence, as well as visually determine the structure of organs, their location and presence in the proper quantity. Conclusion The ultrasound is a table in which indicators of the condition of the kidneys identified during the procedure are noted, and normal indicators are noted next to them, as a comparison with the result. It is worth noting that abnormalities in the structure of organs may not be detected by ultrasound, but pathology may be present. For example, the functionality and performance of the kidneys may be reduced, which an ultrasound examination will not show. Thus, it is not entirely correct to choose which study is better than kidney ultrasound or MRI, since MRI is a more informative examination method.
Price
It should be noted that CT is much more expensive than ultrasound.
In Moscow, the cost of computed tomography is 4,000 (“Health Clinic”) - 25,900 rubles (“European Medical Center”). If contrasting is required, the price increases by another 4-10 thousand rubles.
In St. Petersburg, the cost of a CT scan in private medical centers is from 2,900 rubles. (“Magnit”, “North-Western Medical Center”). In Kazan, the price of an examination is 2400 (“Expert+”, “Maya Clinic”) - 8500 rubles (“Be Healthy”), in Yekaterinburg it ranges from 1900 (City Hospital No. 20) to 4200 rubles (“Heart Clinic” ).
An ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs in Moscow costs 1,200 (MedFord) - 17,600 rubles. (“European Medical Center”). In St. Petersburg, its price is slightly lower, and amounts to 900 (“International Diagnostic Center”) - 2900 rubles (“SM-Clinic”).
In Kazan, an ultrasound costs about 500 rubles at City Hospital No. 11, MKM Clinic and Nezhla. In Yekaterinburg, the price for a study starts from 650 (“ASK”), in Krasnodar – from 900 rubles.
Help In Russia, under the compulsory medical insurance policy, a patient can undergo both studies free of charge upon referral from a doctor (within 3 months). Its presence must be reported to the staff when making an appointment for diagnostics. In some clinics, there may be queues for several weeks in advance (especially for CT scans).