Purpose of colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is a medical way of examining the intestines and rectum. This procedure involves inserting a probe into the body through the anus, which is equipped with a camera and light. During the examination, the doctor pushes a tube into the intestine and examines its condition. Such diagnostics makes it possible to identify:
- oncological pathologies;
- the presence of polyps in the intestine;
- diverticula;
- inflammatory and infectious lesions of the mucous membrane;
- swelling of large veins.
The diagnostic test will take approximately 30 minutes. If necessary, during a colonoscopy, the doctor can take biological material for further examination in the laboratory.
Most patients who are prescribed such an intestinal examination are interested in whether there is an alternative diagnostic method for studying the internal organ. In addition to the unpleasant sensations that arise during the examination, many are confused by the technology of colonoscopy itself.
Anoscopy
This method uses an anoscope to examine the anus and identify diseases of the rectum.
This is a mandatory procedure before prescribing colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy.
Patient preparation is the same as for irrigoscopy. In the hospital, the patient lies on the couch on his side or takes a knee-elbow position.
The doctor inserts the anoscope to a depth of about 10 cm . If dangerous pathologies are found and basic diagnostics cannot be carried out, then they choose what to replace colonoscopy with.
Alternative diagnostic methods
In addition to the fact that colonoscopy causes discomfort to the patient, sometimes it is not enough or this procedure is not recommended due to the patient’s serious condition.
The development of medicine does not stand still, and today there are several analogue techniques that can provide all the necessary information about the state of the intestines:
- Irrigoscopy. The diagnostic procedure is carried out using x-rays. To determine the location and extent of the pathogenic area, before the study begins, the patient is given a cleansing enema, and then a contrast agent, usually barium sulfate, is injected into the intestine. Sometimes irrigoscopy is performed with double contrast. After the contrast is injected, air is pumped into the intestines. It will provide an opportunity to see all the outlines of the organ in more detail. This procedure is painless and safe.
- Sigmoidoscopy. Diagnosis in this way involves examining a small part of the intestine, up to 30 cm. For this, a sigmoidoscope is used, which is inserted into the body through the anus. At the end of the examination, if necessary, the doctor can take samples of biological material for laboratory histological examination.
- Virtual colonoscopy. Non-invasive diagnostic method of examination. The three-dimensional image of hollow organs created from the inside by the software of X-ray computed tomographs makes it possible to diagnose the presence of all deformations and pathological changes with high accuracy.
- Capsule technique. The endoscopic diagnostic method is carried out using a small capsule. All the patient needs to do is swallow the device like a pill. The device will move through the digestive system on its own and take all the necessary pictures. The shooting speed will depend on the intensity of movement of the swallowed object. All materials received by the capsule are not stored on a hard medium, but are transferred to a special protective device using electromagnetic waves. The duration of the diagnosis will be within 5-8 hours. During this time, the patient is not recommended to stay near strong magnetic fields. The object will leave the body on its own, naturally. Single use capsule.
- Ultrasonography. Allows you to detect tumors larger than 0.5 cm.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. It is considered one of the best diagnostic methods. It is painless and non-contact. All that is required of the patient is to lie down in the tomograph capsule and not move while the diagnosis is being carried out.
Modern methods for diagnosing the intestines are varied, and therefore it is possible to avoid such an unpleasant procedure as a colonoscopy. It should be borne in mind that the final word on the choice of examination method remains with the doctor. The type of diagnostic procedure is selected taking into account many parameters. Preference is given to the technique that will be as informative and safe for the patient as possible.
What diseases can be detected during diagnosis?
Using capsule endoscopy, you can evaluate the condition of all parts of the gastrointestinal tract, but the greatest diagnostic value is found when examining the small intestine . Diseases of other parts of the digestive tract (stomach, esophagus, large intestine) can also be detected in this way, but it is still inferior in information content to the conventional endoscopic technique and colonoscopy.
The small intestine is quite difficult to access for other research methods, but is perfectly visualized in pictures taken by the capsule camera. Each organ has its own capsule, and devices have also been developed that can record images from all parts of the gastrointestinal tract. Capsules vary in size: the smaller it is, the greater the safety of the procedure. The speed of recording images and the viewing angle of the camera are of - the diagnostic value of capsule endoscopy depends on these indicators.
Many companies produce capsules. Some of them are Given Imaging (Israel), IntroMedic Co. (Seoul, South Korea).
Given Imaging capsule
Using the capsule, you can detect polyps in the intestines, neoplasms, hidden bleeding, Crohn's disease , establish celiac disease and other changes in the gastrointestinal tract that are difficult to see with other research methods.
What examination can replace intestinal colonoscopy?
Colonoscopy is one of the methods for examining the rectum, cecum and colon for various diseases, including cancer. However, due to the specifics of the research process, this method is not suitable for all patients. In modern medicine, there are several alternative procedures that can be used to check the intestines without a colonoscopy.
Advantages and disadvantages of colonoscopy
Alternative bowel examination methods
MRI and MR colonoscopy
Comments and Reviews
Irrigoscopy and colonoscopy: what to choose
Irrigoscopy and colonoscopy have similar indications and contraindications, but the differences are obvious, for example, in the difference in equipment. The advantage of colonoscopy over non-invasive methods is that during the procedure it is possible to obtain data and remove tumors, polyps, take tissue for biopsy, and cauterize bleeding. A 100% accuracy level makes colonoscopy more informative and effective. Unlike irrigoscopy, colonoscopy provides information from the inside.
The main disadvantage of colonoscopy is the risk of damage to the intestinal walls by the probe and intestinal perforation. The contrast agent during irrigoscopy also causes a side effect. However, the doctor must compare the effectiveness; in each case, an individual type of examination is preferable.
Advantages and disadvantages of colonoscopy
Positive aspects of this type of research:
- allows you to identify oncology;
- removes all polyps;
- cauterizes ulcers;
- reveals swelling of large veins;
- finds inflammatory processes;
- studies the mucous membrane more accurately.
It is better to check the intestines without a colonoscopy for people who have:
- liver, pulmonary or heart failure;
- with peritonitis;
- colitis;
- blood clotting disorders;
- acute intestinal infections.
During a colonoscopy, you can damage the intestinal wall, cause an infection, or cause an attack of appendicitis.
Alternative bowel examination methods
Most analogues are harmless and painless for humans, do not require special preparation and are carried out in a hospital setting.
The following are distinguished:
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging);
- CT (computed tomography);
- Ultrasound;
- irrigoscopy;
- capsule examination;
- anoscopy;
- sigmoidoscopy;
- PET positron emission tomography;
Replacing the procedure helps not only to facilitate the inspection process itself, but also to identify more serious lesions and obtain detailed inspection results.
MRI and MR colonoscopy
MRI is a full-fledged alternative to colonoscopy, but the cost is several times higher. This option is used in isolated cases; more often it is prescribed as an auxiliary examination of the sigmoid colon. Doctors include MR colonography here, during which about two liters of liquid with a contrast agent are injected into the rectum. The doctor then uses a special machine that examines the organs in three dimensions. The process lasts about an hour.
CT scan
Can be compared to an x-ray examination. Only in this case, the tomograph takes several pictures in a row, which allows you to painlessly check the lesion. Doctors say that this technique does not always help to detect cancer at the very early stages of development.
The procedure is used infrequently, since it can only determine the stage of appearance of tumors or a large tumor. Intestinal ultrasound is most often performed in patients with suspected diseases of the abdominal organs, mainly of an inflammatory nature.
Indications for ultrasound:
Capsule examination
It can become an analogue of a colonoscopy only if a person is unable to undergo the standard procedure due to individual anatomical features. The patient swallows a small enterocapsule, which, when it enters the gastric tract, begins to take photographs. This method is considered minimally invasive and allows you to examine every part of the digestive system.
Photos can be taken from 4 to 35 pictures per second, it all depends on the speed of movement of the capsule itself. The device is removed naturally. The examination may take from 4 to 8 hours. The procedure is indicated for hidden bleeding, suspected neoplasms and pathologies. Enterocapsule examination helps to detect stomach or intestinal cancer with probable accuracy.
Ultrasonography
Ultrasound diagnostic techniques are widely used in various branches of medicine. Examination of the intestines using an ultrasound probe is not a popular procedure, due to the presence of other ways to assess the condition of this organ. It is permissible to resort to the use of ultrasound only if it is impossible to perform a colonoscopy. The disadvantage of this method is that using ultrasound it is impossible to assess the condition of the intestinal mucosa and identify foci of erosive and ulcerative lesions and malignancy. In order for the information received to be reliable, the patient is recommended to refrain from eating 12 hours before the procedure, to cleanse the intestines with an enema several hours before visiting the ultrasound room, and not to empty the bladder 2 hours before the procedure.
Seven Alternatives to Colonoscopy
Most health care professionals recommend using colonoscopy in screening tests for early diagnosis of colon cancer. However, the procedure can be perceived as expensive and too invasive, leading many people to avoid it.
As you know, colonoscopy is an endoscopic method for examining the large intestine. A flexible, high-tech hose called a colonoscope is inserted into the anus and moved up the entire length of the colon. The functional tip of the colonoscope is equipped with a transmitting video camera and microsurgical manipulators. If, for example, a polyp is discovered during the diagnosis, it is removed using a thin wire loop.
Why are colonoscopies avoided?
Although colonoscopy can be a life-saving diagnostic procedure for colorectal cancer—as demonstrated by the decline in mortality since its widespread use—some people avoid colonoscopy for the following reasons:
- A colonoscopy requires a full day of preparation, including diet, laxatives and, in some cases, a cleansing enema;
- the procedure requires sedation. Coming out of a state of medicated sleep, many feel increased pressure of intestinal gases;
- Along with the nervous anticipation of physical discomfort, many patients (with little or no health insurance) may be concerned about the high cost of a colonoscopy.
Alternative Methods
Currently, there are several procedures that can be an alternative to colonoscopy. They vary in diagnostic performance, and although colonoscopy remains the treatment of choice, alternative methods may still reduce the risk of colorectal cancer for individuals who are unwilling or unable to undergo a colonoscopy.
Fecal immunochemical test
The fecal immunochemical test (FIT) is a common screening method in many regions of the world; it is also certified by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) throughout the United States. The test uses antibodies to detect occult blood in the stool, which is seen in internal gastrointestinal bleeding. And only if any anomaly is detected, a colonoscopy is recommended for a more thorough examination. When used annually, FIT can be as effective as colonoscopy in early cancer detection.
Irrigoscopy with double contrast
It is a modified version of an x-ray examination of the colon. Can be effective in detecting polyps that are large enough, but smaller ones may be missed. Like colonoscopy, the method requires complete cleansing of the intestines, and if suspicious formations are detected, colonoscopy is also indispensable.
Fecal occult blood test
This analysis (FOBT, Fecal occult blood test), for a reliable diagnosis of colorectal cancer, should be used annually in combination with FIT, which is an effective alternative.
Cologuard (“Colorectal Guard”)
Also a stool test that can be used instead of a colonoscopy. This relatively new test is more expensive than FIT, but should be taken every three years for screening purposes.
DNA analysis of stool
This test can be done at home. Its purpose is to detect blood and certain DNA molecules that are indicators of colorectal cancer, and if such signs are found, removal of the malignant growth will require colonoscopy.
CT colonoscopy
CT colonoscopy uses X-rays to examine the large intestine. As with a colonoscopy, the intestines must be emptied first.
No premedication is required in this case. The colon is filled with air during the procedure to ensure the best possible visualization.
Sigmoidoscopy
The procedure is similar in every way to a colonoscopy, but a much smaller part of the large intestine is examined. In fact, this is the only advantage - since the preparation and discomfort are no different from those of a colonoscopy - and recommending sigmoidoscopy to patients as an alternative is often inappropriate.
conclusions
Colorectal cancer is a “slow” type of cancer process and can be successfully cured if detected early. Colonoscopy, the only disadvantages of which can be considered relatively high cost and invasiveness, is today the most effective method for the early detection of cancerous and precancerous tumors, and in most cases there is no need to undergo such an examination more often than once every ten years.
How to check the intestines without colonoscopy: alternative methods and their disadvantages
If a person complains of chronic pain in the umbilical, right or left iliac region, stool disorders, discharge of mucus, pus or blood from the rectum and other pathological symptoms, then he is usually prescribed a visual examination of the lumen of the large intestine through colonoscopy.
This method allows you to assess in real time the condition of the intestinal mucosa, identify benign or malignant neoplasms, polyps, as well as erosions and ulcers. Despite the high information content of the method, there is a whole list of contraindications, in the presence of which they try to replace this method with alternative diagnostic methods.
Such contraindications include:
- A state of shock in which blood pressure drops to 70 mmHg or below.
- The presence of a purulent-inflammatory process in the abdominal cavity (peritonitis).
- Acute ischemic processes in the myocardium, as well as infarction.
- The period of bearing a child.
- Perforated changes in the intestinal wall, accompanied by the release of fragments of digested food and blood into the abdominal cavity.
- Severe course of ulcerative and ischemic colitis.
- Heart and pulmonary failure in the stage of decompensation.
Along with absolute indications, there is a list of relative contraindications for intestinal colonoscopy. These include:
- Previously installed artificial heart valve.
- Intestinal diverticulitis, complicating the advancement of a colonoscopic probe through the intestinal lumen.
- Recent surgery on the abdominal organs.
- Presence of signs of intestinal bleeding.
- Acute intestinal obstruction.
- The presence of an umbilical or inguinal hernia.
If the patient has one of the above contraindications, then he is individually prescribed one of the alternative methods for assessing the condition of the large intestine.
Finger method of intestinal examination
During a consultation with a proctologist surgeon, each patient undergoes a digital examination of the rectal area. The disadvantage of this method is that through digital examination it is possible to assess the patency of a small segment of the large intestine, and not the entire organ along its length.
Before performing this manipulation, the medical specialist puts on a disposable sterile latex glove and, after inserting one or two fingers into the lumen of the rectum, performs a palpation assessment.
During palpation, the patency of the organ, the presence or absence of neoplasms, diverticula and fissures are assessed. To increase the information content of the examination, the second palm of the medical specialist is placed on the patient’s lower abdomen.
The finger method does not provide information about the condition of the mucous membrane, the presence of erosive and ulcerative lesions and polyps.
Capsule diagnostics
The capsule bowel examination technique is based on the oral administration of a miniature device made in the form of a capsule and containing a small chamber. Passing through the intestines naturally, the built-in camera takes a series of pictures, based on which medical specialists make a clinical diagnosis.
The advantage of this method is absolute painlessness and lack of discomfort. The disadvantages include the minimal risk that the diagnostic capsule will not be excreted naturally. The probability of such a situation does not exceed 2%. In all other cases, the capsule with the camera comes out during the act of defecation.
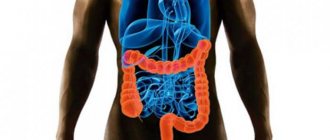
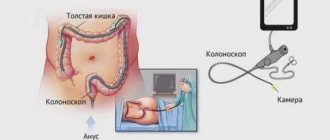
What is a colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is an instrumental examination that allows diagnosing pathological conditions of the rectum and colon. The examination is carried out using a colonoscope - a long flexible probe, at the end of which there is an eyepiece with a tiny video camera and backlight. The kit also includes biopsy forceps and an air supply tube. The probe is inserted through the rectum.
The resulting image is transmitted to the monitor and allows the specialist to assess the condition of the intestines along its entire length, which is about two meters. The camera takes high-expansion images that are magnified tens of times. In the images, the coloproctologist examines the mucous membrane and notes possible pathological changes.
In addition, during the examination, a number of interventions can be carried out to avoid additional surgical intervention.
These include:
- expansion of the intestinal area due to scarring;
- tissue sampling for histological studies;
- removal of a foreign body;
- elimination of polyps or benign tumors;
- elimination of bleeding.
Thanks to its additional capabilities, colonoscopy is considered the most informative and effective diagnostic method.
Differences from colonoscopy
Irrigoscopy or colonoscopy - which is better for the intestines? Before answering this question, it is necessary to highlight their main distinguishing features. This:
- Execution method
. Colonoscopy does not require the use of contrast or x-rays. Unlike competitive medical manipulation, it only uses a flexible probe with a camera. - Purpose
. Irrigoscopic examination is used exclusively for diagnostic purposes (except for intussusception in children), and during colonoscopy, polyps can be removed, bleeding can be stopped, or a biopsy can be taken.
How is a colonoscopy performed?
A few days before the examination date, preparations for a colonoscopy begin. It includes diet and proper bowel cleansing. So, for 2-3 days the patient must follow a slag-free diet: exclude vegetables, fruits, nuts, meat, cereals and baked goods. 20 hours before the test, only water and weak tea are allowed. For the study to give maximum results, it is necessary to remove all feces from the body. An enema or special medications are used for this, which are used a day before the procedure: Fortrans, Lavacol.
In the office, the patient is placed on his left side, with his knees pressed to his stomach. The anal area is treated with an antiseptic liquid, and if necessary, ointments and gels with an anesthetic are added. The probe is inserted into the rectum and slowly moves into the intestines. At this time, the specialist assesses the condition of the mucous membrane as shown on the monitor. If it is necessary to straighten the intestines, air is pumped into the body.
The essence of colonoscopy and additional options
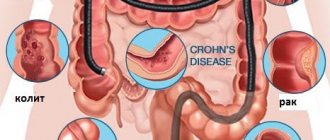
Colonoscopy is an examination of the inner lining of the intestine, which is carried out using a special probe (endoscope) through the rectum. At the tip of the instrument there is a small video camera, a light source. The doctor pushes the tube through the entire organ and examines its walls only on the way back. How long does an intestinal colonoscopy take? As a rule, no more than half an hour. With its help, you can identify pathologies such as:
- oncological diseases;
- polyps;
- diverticula (specific neoplasms on the internal mucous membrane of different parts of the intestine);
- infectious diseases, inflammatory processes;
- hemorrhoids (swelling of large veins).
This procedure will also help you take a tissue sample for laboratory testing (biopsy).
How to prepare for a colonoscopy at home? The conditions are simple. You need to follow a slag-free diet, cleanse the intestines (the evening before the procedure and the morning before it) with an enema or with the help of special medications (for example, Fortrans, Duphalac).
Advice: Before the test, every patient should know what to eat before a colonoscopy. For a week, muesli, wholemeal bread, cucumbers, tomatoes, and grapes are excluded from the diet. For three days, it is better to abstain from mushrooms, onions, lettuce, and spinach. Prefer easily digestible foods, such as soups, potatoes, rice, wheat pasta.
A slag-free diet will help you properly cleanse your intestines
A special menu must be followed before surgery. Liquid food and bowel cleansing minimize the risk of complications. Your temperature may rise slightly after bowel surgery, and this is normal. But if the symptom does not disappear after 2-3 days and the reading rises above 38.2°, the patient should immediately inform the doctor. This may indicate the development of complications.
Colonoscopy can be supplemented and sometimes replaced with alternative methods for examining the large intestine, which do not cause discomfort to the patient, are almost always accessible and are very informative:
- magnetic resonance imaging or MRI, that is, examination using magnetic waves;
- computed tomograph - CT (work is based on X-rays);
- irrigoscopy;
- anoscopy;
- sigmoidoscopy;
- capsule examination;
- Ultrasound.
Advice: You should not eat after midnight before the procedure. Such restrictions are important for conducting a high-quality examination, because the examination of tissues depends on the cleanliness of the intestines. It is also necessary to drink a lot to help cleanse the body.
Possible contraindications
Contraindications to colonoscopy can be absolute or relative. In addition, for most patients, the study causes negative emotions, and they begin to look for a variety of alternatives. If there are absolute contraindications, colonoscopy cannot be performed. These include:
- peritonitis;
- pregnancy;
- heart and pulmonary failure;
- ischemic or ulcerative colitis;
- myocardial infarction;
- severe internal bleeding in the intestines.
In the case of relative contraindications, the appropriateness of the study is assessed by the attending physician. In some cases, colonoscopy is postponed, but for certain indications it is performed with some caution.
Relative contraindications include:
- improper preparation;
- low blood clotting;
- bleeding;
- serious condition of the patient.
If necessary, the examination is carried out under general anesthesia, but in most cases anesthesia is not used.
Is there an alternative?
There are alternative ways to examine the condition of the large intestine, which in some cases can replace colonoscopy. They do not cause significant discomfort and are quite accessible; only the degree of information content differs.
In most cases, magnetic resonance imaging is an additional examination method: with its help it is impossible to obtain complete information about the internal state of the mucosa.
They usually check with a tomograph:
- mid intestine;
- pelvic area;
- terminal parts of the colon.
CT scan
CT scans provide detailed images of the intestines using X-rays. In some ways, this is a better alternative to a colonoscopy: the final image is quite detailed and clear. According to the results, computed tomography is the most approximate research method.
During the examination, the patient simply lies on a special table, and the tomograph platform rotates around the body. The detectors of the device “catch” X-rays passing through the tissues of the body. The resulting sections are processed by a computer station, resulting in a detailed image of the organs.
Irrigoscopy
Irrigoscopy also refers to x-ray research methods that use a contrast agent. Most often, specialists use barium sulfate, which is introduced into the body through the rectum. You can evaluate the elasticity of the walls, the functions of the folds, the condition of the mucosa and the functional indicators of the organ parts.
Preparation for the procedure includes diet and bowel cleansing. During the examination, a special device similar to an enema is inserted into the colon. Using this device, the intestine is filled with contrast, after which the first overview image is taken. The patient must change position several times to obtain a series of targeted and overview images.
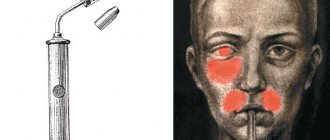
Anoscopy
Anoscopy is an instrumental examination method, thanks to which it is possible to evaluate a certain part of the intestinal surface - a maximum of 15 centimeters. An anoscope, a smooth hollow tube, is inserted into the intestine. The lumen is filled with a removable rod, through which the study is carried out.
Anoscopy is a good substitute and is prescribed not only for diagnosing the condition of the mucous membrane: using the device, you can take tissues or smears for analysis, administer medications, or perform minimally invasive surgical procedures, which are also performed during colonoscopy.
Sigmoidoscopy
Using sigmoidoscopy, a visual inspection of the surface of the lower part of the large intestine is performed. A special device is used for this - a hollow metal tube equipped with an air supply system and a lighting system.
In addition to examination, sigmoidoscopy allows you to perform a number of invasive manipulations - cauterize tumors, take tissue, get rid of polyps or stop minor bleeding. The procedure has the same contraindications as colonoscopy. In addition, preparation is required, including diet and bowel cleansing.
Capsule endoscopy
Capsule endoscopy is similar to colonoscopy, but the data is obtained not through a probe, but from a special miniature capsule. It is equipped with a video camera and a transmitter that allows it to receive signals in real time. The method allows you to examine not only the distal and upper parts of the intestinal tract, but also the ileum and jejunum.
The day before the examination, the patient is advised to refuse hard-to-digest foods, only semi-liquid foods are allowed, and it is advisable to cleanse the intestines through an enema or special medications.
Irrigoscopy
This procedure is performed by doctors using conventional x-rays. Before this procedure, it is necessary to carry out certain preparatory measures:
- Perform bowel cleansing using an enema and special medications;
- You are not allowed to shower before the event;
- Before the examination, a special liquid with a radiopaque substance, that is, barium sulfate, is taken.
The drunk substance passes throughout the intestine, gradually filling its area. Thus, a medical employee receives a full-fledged image with the simultaneous ability to determine the contours and lumen in the intestine. Using the images obtained as a result of the examination, the doctor not only determines the presence of pathology, but also identifies the degree of its development and, based on the data obtained, prescribes treatment. In certain cases, the irrigoscopy procedure is performed using a special double contrast. In this case, immediately after the dye leaves the intestine, air is introduced into it to clearly see the outlines of different parts of the intestine.
With this examination method, you can study the relief of the colon lining. This is an ideal alternative to intestinal colonoscopy, which makes it possible to detect congenital developmental anomalies, scar formations, fistulas, ulcers, various neoplasms, and the presence of diverticulosis. This is a fairly effective and at the same time painless procedure, which is completely safe. It is with this method that you can examine not only the rectum, but also the sigmoid colon.
What examination can replace intestinal colonoscopy?
Colonoscopy is one of the methods for examining the rectum, cecum and colon for various diseases, including cancer. However, due to the specifics of the research process, this method is not suitable for all patients. In modern medicine, there are several alternative procedures that can be used to check the intestines without a colonoscopy.
Advantages and disadvantages of colonoscopy
Alternative bowel examination methods
MRI and MR colonoscopy
Comments and Reviews
CT scan
When deciding how to examine the intestines without a colonoscopy, many use an analogue of a medical examination, such as computed tomography. Such an event allows you to examine the large intestine without any discomfort. The main advantage of the procedure is that this method is non-invasive, but at the same time quite effective. To carry out this activity, a standard tomograph is used. The colon in this case is checked using x-rays. The only drawback of the procedure is its fairly high cost.
Advantages and disadvantages of colonoscopy
Positive aspects of this type of research:
- allows you to identify oncology;
- removes all polyps;
- cauterizes ulcers;
- reveals swelling of large veins;
- finds inflammatory processes;
- studies the mucous membrane more accurately.
It is better to check the intestines without a colonoscopy for people who have:
- liver, pulmonary or heart failure;
- with peritonitis;
- colitis;
- blood clotting disorders;
- acute intestinal infections.
During a colonoscopy, you can damage the intestinal wall, cause an infection, or cause an attack of appendicitis.
Alternative bowel examination methods
Most analogues are harmless and painless for humans, do not require special preparation and are carried out in a hospital setting.
The following are distinguished:
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging);
- CT (computed tomography);
- Ultrasound;
- irrigoscopy;
- capsule examination;
- anoscopy;
- sigmoidoscopy;
- PET positron emission tomography;
Replacing the procedure helps not only to facilitate the inspection process itself, but also to identify more serious lesions and obtain detailed inspection results.
MRI and MR colonoscopy
MRI is a full-fledged alternative to colonoscopy, but the cost is several times higher. This option is used in isolated cases; more often it is prescribed as an auxiliary examination of the sigmoid colon. Doctors include MR colonography here, during which about two liters of liquid with a contrast agent are injected into the rectum. The doctor then uses a special machine that examines the organs in three dimensions. The process lasts about an hour.
CT scan
Can be compared to an x-ray examination. Only in this case, the tomograph takes several pictures in a row, which allows you to painlessly check the lesion. Doctors say that this technique does not always help to detect cancer at the very early stages of development.
The procedure is used infrequently, since it can only determine the stage of appearance of tumors or a large tumor. Intestinal ultrasound is most often performed in patients with suspected diseases of the abdominal organs, mainly of an inflammatory nature.
Indications for ultrasound:
Capsule examination
It can become an analogue of a colonoscopy only if a person is unable to undergo the standard procedure due to individual anatomical features. The patient swallows a small enterocapsule, which, when it enters the gastric tract, begins to take photographs. This method is considered minimally invasive and allows you to examine every part of the digestive system.
Photos can be taken from 4 to 35 pictures per second, it all depends on the speed of movement of the capsule itself. The device is removed naturally. The examination may take from 4 to 8 hours. The procedure is indicated for hidden bleeding, suspected neoplasms and pathologies. Enterocapsule examination helps to detect stomach or intestinal cancer with probable accuracy.
Pros and cons of capsule diagnostics. Video provided by the program “Live Healthy”!
Irrigoscopy
Irrigoscopy is one of the safest methods and helps to identify the following diseases:
- bowel cancer;
- polyps;
- ulcerative colitis;
- Crohn's disease;
- diverticula.
The patient is given a barium enema and then x-rayed. Irrigoscopy should be performed when it is not possible to examine a person with a colonoscope, or when these results do not provide a complete picture. Experts strongly recommend irrigoscopy if cancer is suspected, since this examination most accurately finds tumors in the intestinal lumen.
Anoscopy
Allows you to painlessly examine the rectal cavity to a depth of 10-15 cm. A proctologist can independently carry out this procedure in his office by inserting an anoscope through the anus. Using anoscopy, doctors visually evaluate the inner surface of the anus and distal intestine. In addition, at the very initial stage it is possible to identify any pathologies of the lower intestine.
More detailed information about anoscopy is presented in the video. Photographed by Maryana Abritsova.
Sigmoidoscopy
Rectomanoscopy is not an analogue of colonoscopy; it is not performed unless absolutely necessary. During the procedure, it is possible to examine about 30 cm of the large intestine. If there is a tumor, a piece is plucked off from it for analysis. The technique does not give a broad picture of whether a person has a disease or not, and at what stage it is. Proctologists recommend being examined in other ways.
Endorectal ultrasound
The procedure is done according to the principle of ultrasound, but the sensor is inserted into the patient’s rectum. Ultrasound allows you to reveal the source of damage to the organ itself. The main advantages are simplicity and safety, absence of contraindications. The sensor technique can be used during pregnancy and for examining children.
Positron emission tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) in proctology is used to diagnose malignant tumors of the colon at the initial stage. PET is combined with CT to obtain reliable data on the exact localization of the detected tumor. During the session, radioactive sugar is injected into the patient through a vein. The process lasts about an hour and a half, the drug itself spreads throughout the body within an hour.
Hydrogen test
The patient should breathe into a special tube for two to three hours. Using a hydrogen test, the doctor determines disturbances in the microflora of the small intestine, as well as intolerance to a number of substances (fructose, lactulose, etc.).
Photo gallery
Indications
Most often, this method is used when pathology of the small intestine . Experts recommend conducting the study only if other methods have not given the desired result: this is due to the high cost of capsule endoscopy.
Indications for the procedure are as follows:
- intestinal bleeding of unknown etiology ;
- abdominal pain, the cause of which cannot be determined by other methods;
- suspicion of an oncological process in the small intestine ;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis ( Crohn's disease );
- blood in the stool of unknown etiology;
- diagnosis of polyposis nodes in the intestines - especially with a family history;
- suspicion of celiac disease.