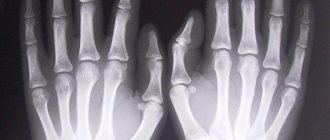
Anatomical features of the hand
The hand is the most unique part of the human body, having a complex structure and many unique functions. It is she who is the most working organ and elevates man above the entire animal world. The unique structure also provides its unique capabilities, for which this organ is rightly called “God’s gift.”
It consists of 27 bones connected by joints, there are 21 in total, and 34 muscles that provide varied and precise movements. In addition, there are a large number of ligaments, tendons, arteries, veins and nerves.
Anatomically, the hand is divided into 3 main sections:
- the wrist, consisting of 8 bones (scaphoid, pisiform, trapezoid, trapezium, lunate, triquetrum, capitate, hamate);
- metacarpal section, consisting of 5 metacarpal bones connecting to the fingers;
- fingers - there are only 5 of them, 4 of them consist of 3 bones (phalanxes) and 3 joints, and 1 (thumb) consists of 2 phalanges and 2 joints.
The wrist is connected to the forearm through the wrist joint, which is formed by the radius and ulna on one side, and the first row of carpal bones - the scaphoid, lunate and triquetrum bones.
Where to conduct the examination
Specialists who work with blood vessels are phlebologists and angiosurgeons. Based on this, the examination should be carried out where consultation with an appropriate specialist is possible. The best option would be if an angiosurgeon or phlebologist personally conducts the study. After all, during an ultrasound, not only a correct examination is necessary, but also correctly performed functional tests during the analysis process.
The best place to conduct the examination is specialized phlebological centers, but ultrasound of veins in a clinic is also possible, because the equipment is widely available and there is no shortage of phlebologists. If the patient does not have the opportunity to get to the appropriate medical institution, then an ultrasound can be performed at home . The diagnostic value is somewhat reduced, but sometimes it is enough to make a final diagnosis.
In modern medicine, when varicose veins, atherosclerosis and other vascular diseases are widespread, it is impossible to do without ultrasound examination of the veins and arteries of the legs and arms. The most commonly affected parts of the body are the limbs, especially the legs, because they are more prone to blood stagnation than others. This is due to the characteristics of venous blood flow and the presence of collectors in which blood accumulates in pathologies. Therefore, if there are signs of the disease or if the patient is at risk, he needs to perform an ultrasound and consult a specialist.
Causes of the disease
Various reasons can lead to hand pathology. Most often these are various injuries - bruises, fractures, ruptures of ligaments and tendons, open and penetrating wounds.
The other most common cause is systemic diseases - rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus (Jaccoud's arthropathy of the hands), scleroderma with the development of contractures and muscle atrophy, metabolic-dystrophic polyarthritis.
The condition of the hand is affected by endocrine diseases - diabetes mellitus, dysfunction of the thyroid gland, as well as age-related changes in the bones - osteoporosis, cartilage degeneration, and the development of arthrosis.
There are also hereditary diseases of the hand, for example, Dupuytren's contracture (formation of a fibrous cord that bends the fingers). Finally, the hand can also be affected by tumors of soft tissue, cartilage, and bone. All this pathology is detected by ultrasound scanning.
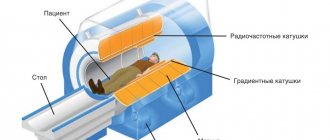
Which is better - CT or MRI?
There is no big difference between MRI and CT (computed tomography). Both diagnostic methods are completely safe, painless and maximally informative. Computed tomography of the hand is prescribed for injuries, fractures or serious dislocations. With the help of CT, doctors obtain accurate data about bones and joints; it works using x-rays. However, in case of blood flow disorders and soft tissue pathologies, CT scan of the hand is not informative.
What is best for diagnosis is decided by the attending physician, based on the patient’s complaints or diagnosis.
Indications for examination
The reasons for undergoing an ultrasound scan of the wrist and other parts of the hand are the following cases:
- damage to the hand - any of its structures;
- pain and limitation of function;
- external changes – swelling, redness, deformation;
- crunching when moving the joints;
- the presence of systemic diseases (polyarthritis, lupus, scleroderma, psoriasis);
- endocrine, oncological pathology with symptoms of hand damage.
Under the control of an ultrasound machine, diagnostic punctures are also performed in the area of various structures of the hand - joints, hematomas, and biopsies are taken.
Indications and preparation
Have you been trying to heal your JOINTS for many years?
Head of the Institute for the Treatment of Joints: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure your joints by taking the product every day for 147 rubles ...
Read more "
The full list of indications for ultrasound examination of joints is very large. But if we talk about the main indications , they are presented like this:
- trauma to the joint capsule and surrounding soft tissues;
- systemic pathologies;
- autoimmune diseases;
- inflammatory diseases (both acute and chronic);
- obesity with the need for an ultrasound of the knee joint;
- enlargement (swelling) of the joint capsule and surrounding soft tissues;
- routine diagnostics of hip joints in newborns;
- if there is a suspicion of dislocation or subluxation;
- for dynamic monitoring of the condition of articular joints in the treatment of their dysplasia;
- for unexplained muscle pain and soft tissue pain;
- palpable subcutaneous formations in the soft tissue area;
- for dynamic monitoring of the course of therapy for arthritis, tendonitis and tenosynovitis;
- if you suspect the presence or rupture of a Becker cyst, as well as other diseases of the same name;
- during dynamic monitoring of the course of therapy for bursitis;
- for endocrine pathologies;
- osteochondropathy and other pathologies of the same name;
- for pain of unknown etiology (causes);
- immobility or stiffness in the limbs.
This procedure does not require any specific preparation. But it is important to know that 6 hours before the ultrasound examination you cannot make injections into the joint joint being diagnosed.
Preparing for ultrasound of the hand
The hand is not an internal organ; its condition does not depend on diet, medication or other reasons. Therefore, there is no need to prepare for an ultrasound scan of the hand. The only thing that is required from the patient is that the skin is clean, without any cosmetics or creams. It is also necessary to remove rings, bracelets, chains, and watches so that they do not interfere with the examination.
Does ultrasound have contraindications?
This method is not only the safest of all existing today, it also has no contraindications.
Read also: is ultrasound examination harmful?
In this video you will find an example of how a wrist examination is performed:
However, it is worth noting that in some cases diagnosis can be difficult. For example, if there is an open wound on the area being examined. In this case, it is advisable to abandon ultrasound diagnostics and find an alternative. Since the specialist will not be able to obtain comprehensive information about the state of the area under study.
How is an ultrasound of the hand performed?
The patient frees one or both arms up to the elbow from clothing, sits in a comfortable position, places his hands loosely on his knees, relaxing. The doctor applies a special contact gel to the skin and applies the sensor, moving it from one area to another, directing it to individual structures of the hand. At the same time, he may ask the patient to rotate, bend or straighten the arm.
The sensor directs ultrasound beams to an object and picks up reflected beams from various structures of the hand - bones, joints, tendons. Each type of tissue has its own echogenicity - the ability to reflect waves depending on the density of the structure. All this data is included in the scanner program. The capturing sensor transmits the reflected waves to the scanner analyzer, and after they are digitally processed, an image appears on the screen.
The duration of the procedure usually does not exceed 20 minutes. It is possible to conduct an ultrasound of an individual finger of the hand, if only there is pathology in it, and the rest of the hand is healthy. This study will take much less time. The patient does not experience any discomfort during the procedure.
The essence and procedure of the examination
Ultrasound of soft tissues does not require any special preparation, as when examining the abdominal cavity or pelvic organs. To carry out the procedure, it is enough to expose the area that will be studied. During all manipulations, the patient is in a sitting or lying position, taking different positions at the request of the specialist.
The sonologist will lubricate the area of the body being examined with a special gel for greater contact with the sensor, and then install the latter over the site of possible pathology. The patient does not experience any discomfort or pain during these actions. All manipulations performed are recorded, and the picture is displayed on a nearby monitor in real time. The image formation during the examination occurs due to reflected ultrasonic waves.
Interpreting the data obtained, the specialist must clearly record the parameters and location of the pathology, assess the condition of the tissues and blood flow, detect existing cavities and characterize their contents. It should be understood that if the patient is overweight or if the source of the problem is too deep, an MRI will be required, since the information obtained will not be fully informative.
If the procedure is carried out for the purpose of examining muscles, the affected component will be noted in the ultrasound protocol.
Important: Ultrasound of soft tissues is an absolutely safe manipulation that can be performed with any necessary frequency. Examination in this way is used when working not only with adult patients, but also with children and pregnant women.
Decoding the results
Upon completion of the ultrasound examination of the hand, its bones, joints, tendons, and muscles, the doctor makes a written conclusion describing the data obtained for each of these structures. If no pathology is detected, it is concluded that the structures of the hand and wrist joint are within normal limits.
When a pathology is identified, the specialist describes it. For example, this is what an ultrasound of the joints of the hand shows with arthrosis: the cartilage of the joint is thinned, its contours are uneven, eroded, the joint space is narrowed, with osteoporosis: the echogenicity of the bone tissue is reduced, and so on. The description ends with a conclusion in which a presumptive diagnosis is written, and the patient is given recommendations for further examination, if necessary.
What tissues can be examined by ultrasound?
Patients involuntarily begin to doubt the effectiveness of the procedure, comparing it with x-rays. After all, it seems that only x-rays can show significant deviations. But this is a common misconception, since ultrasound allows you to examine soft and bone tissue.
During an ultrasound of the elbow joint or hand, the doctor has the opportunity to evaluate the structure of not only the ligaments, but also the muscles. Moreover, the device allows you to carefully examine articular cartilage and tendons. In addition, the specialist responsible for the procedure has the opportunity to assess the condition of the nerve endings in the hand. This is very important for diagnosing many diseases.
What can ultrasound diagnostics determine?
Based on the results of an ultrasound scan, it is possible to identify with a high degree of probability various types of pathology:
- bone fractures – fresh and old;
- damage to soft tissues - ligaments, muscles, tendons;
- muscle atrophy;
- the presence of a purulent focus of inflammation in the bone (osteomyelitis), in soft tissues - abscess, phlegmon;
- inflammatory diseases – tendinitis, tendovaginitis, synovitis, ligamentitis;
- hygroma (cyst) of the tendon;
- dystrophic and systemic diseases of the joints - arthrosis, various arthropathy;
- bone osteoporosis;
- tumors (osteomas, chondromas, cysts, malignant formations).
In addition, modern ultrasound technologies combined with Dopplerography, the so-called color duplex mapping (CDC) of the hand.
This technique allows you to examine blood vessels and determine the state of blood circulation. It is also very informative in detecting malignant tumors, which are characterized by increased blood supply.
What can be revealed
Using ultrasound of the vessels of the upper extremities, it is possible to identify many different diseases at an early stage. Among them are not only arthritis and arthrosis. But also such difficult-to-diagnose pathologies as tenosynovitis, bursitis, tendinitis. In addition, it is with the help of this type of diagnosis that tumors can be detected in time.
The device can examine tumors not only in bone, but also in soft tissues. This plays an important role in the timely diagnosis of both malignant and benign tumors.
Where to get the test and its cost
The ultrasound procedure is performed in any hospital or clinic where this type of diagnosis is available. It is included in the list of medical services under compulsory health insurance, so it can be completed free of charge in any public hospital. You need to have a compulsory medical insurance policy, a doctor’s referral, sign up for a waiting list and show up on the appointed day and time.
Much faster and easier, at a time convenient for the patient, the test can be done in any private clinic, its cost is low. For example, the price of an ultrasound scan in private hospitals in Moscow varies from 800 to 1500 rubles, its size depends on the rating and distance of the clinic from the center of the capital.