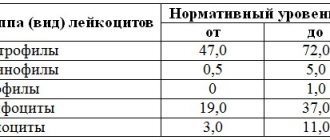
Pulmonary pattern - what is it?
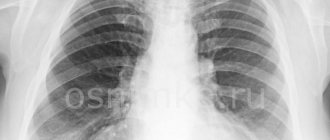
If a person’s lungs are completely healthy, then the normal pulmonary pattern is a picture of blood circulating through the veins and arteries . Lymph nodes or bronchi do not participate in shadow formation. The pattern is clearly visible in the root zone, where the maximum diameter of the vessels is, with a gradual weakening towards the periphery, becoming barely visible.
The complex pulmonary pattern is represented by a large number of intertwined blood vessels. Vascular shadows can be layered on top of each other, which forms dense foci in the image. They differ from real foci, which can arise during various inflammations, by other vessels extending from them in different directions. Such lesions can disappear even with the slightest change in the patient’s body position and are no longer recorded on repeated photographs. Bronchial branches also take a small part in the formation of the pulmonary pattern, which look like a lighter background for homogeneous vascular lines.
Associated symptoms and additional examination
With diffuse lung damage, which is observed on a fluorographic image, there are usually concomitant signs of the disease in the form of any of these symptoms:
- temperature increased to subfebrile levels;
- discharge of purulent or bloody sputum;
- severe shortness of breath;
- attacks of suffocation;
- pain in the heart area;
- high blood pressure;
- infrequent or worsening cough.
If fluorography shows an intensification of the pattern over large areas of the vascular network, the patient is sent for examination. Usually he is prescribed sputum, blood and urine tests, an ECG and a repeat X-ray examination.
When no other complaints and symptoms, except for increased vascular network in the image, are observed, the doctor evaluates the advisability of further examination. For small local deviations in the form of dilation of blood vessels in the root zone or deformations of the contours of the vascular network in smokers, the pulmonologist may prescribe a repeat X-ray examination or consider this to be normal temporary or age-related changes in the structure of the lungs.
An increased pulmonary pattern on a fluorographic image does not always indicate the presence of any health problem. Sometimes the vessels are dilated due to an inflammatory process. If extensive deformations are observed in the image, the patient is sent for additional examination to determine the cause of this deviation .
One of the symptoms identified by chest x-ray is an increase in pulmonary pattern. What does this sign mean? What diseases manifest themselves in this way? Does the enhancement appear only in lung diseases, or could it be a symptom of some other pathology?
What is meant by this symptom?
The pulmonary pattern is the network of vessels passing through the lung tissue. Normally, it is clearer at the roots of the lung and blurs as it moves away from them. This is due to a decrease in the diameter of the vascular lumen as they move away from the root of the lung. Normally, this pattern is more clearly visible in the lower lobes of the lungs, since the largest vessels are located there. X-rays do not show bronchi and lymphatic vessels.
Strengthening the pulmonary pattern - this is said when an X-ray image reveals increased clarity of the images of the vessels and roots of the lungs. In this case, the pattern becomes equally clear both in the upper and lower lobes, in the center and on the periphery of the lung.
The pulmonary pattern is formed by blood and lymphatic vessels and the bronchial tree of the lungs
In what cases can you see an increase in the pulmonary pattern?
This symptom is detected by X-ray examination of the chest organs, including fluorography. What diseases are manifested by increased lung pattern:
- bronchitis - acute or chronic, obstructive and non-obstructive;
- focal or lobar pneumonia;
- tuberculosis process in the lung;
- malignant lung tumors;
- occupational diseases - pneumoconiosis, silicosis;
- pulmonary edema;
- heart diseases - congenital or acquired defects, cardiomyopathy.
Sometimes the pulmonary pattern intensifies outside of the disease - this condition may be a manifestation of age-related changes.
Increased pulmonary pattern can be local or diffuse. It depends on the nature of the pathological process. If the process is limited (focal pneumonia or a small tumor), the symptom will also be limited, localized in a small area of the lung. If the pathology is widespread (lobar pneumonia, bronchitis, miliary tuberculosis), enhancement will be observed in all fields of the lung.
Diffuse Gain
Root strengthening
What are the mechanisms
This symptom is observed due to three pathological changes in the lung tissue:
- increased blood filling of blood vessels, which often occurs with heart defects;
- inflammation of the vascular wall itself during pneumonia or tuberculosis;
- the appearance of connective tissue in the pulmonary parenchyma during prolonged pneumonia and chronic bronchitis, as well as during occupational lung diseases.
The earliest enhancement appears directly at the roots of the lungs. As the pathological process spreads, the pulmonary pattern becomes clear on the rest of the surface. The pulmonary pattern in various pathologies can be formed not only by blood vessels, but also by inflamed small bronchi, lymphatic vessels and connective tissue layers.
Most often, there is an increase in the hilar pulmonary pattern
How the symptom manifests itself
The vascular network on x-ray looks like a cluster of cells. When deformation of the vascular pattern appears, it appears as a clearer definition of the contours of each cell. This is combined with a decrease in the transparency of the lung fields. At the same time, other symptoms may be detected that indicate a particular disease:
- decrease in respiratory excursion - mobility of the pulmonary edge and diaphragm during breathing movements. This is detected during the inflammatory process or proliferation of connective tissue;
- the appearance of a shadow in the lung - this indicates the presence of an abscess or tumor, a tuberculosis focus.
Corresponding clinical symptoms are also characteristic, which help to establish the causative disease - cough, sputum of various types, shortness of breath, chest pain, limited mobility of one of the halves of the chest during breathing movements.
For a more accurate diagnosis of a disease manifested by such a symptom, it is necessary to conduct an x-ray examination in two projections. Fluorography cannot always reveal an increase in the pulmonary pattern, since this method has less resolution than x-ray examination. However, fluorography is carried out much more often than a full X-ray examination, so its assistance in diagnosing diseases is quite high. X-ray examination to detect this symptom should be carried out using rays of increased rigidity.
If a symptom such as increased pulmonary pattern is detected, it is necessary to prescribe a further more targeted examination. This symptom can indicate not only relatively harmless conditions, but also such serious lung diseases as cancer and tuberculosis.
Changes in pulmonary pattern in diseases
The normal pulmonary pattern may change if there are pathologies of the mediastinal organs and lung diseases. This is due to the fact that inflammation occurs around the blood vessels, causing thickening of their walls, which is necessarily reflected in the x-ray . The walls of the bronchi also begin to take part in shadow formation - they thicken, and layers appear between the connective tissue, which should normally be absent.
Due to the fact that the appearance of lymphatic and blood vessels is highly convoluted, they become clearly visible. Such an enhanced vascular pattern is usually observed in various diseases that are accompanied by severe hemodynamic disturbances:
- pneumosclerosis;
- combined mitral valve stenosis;
- sarcoidosis stages 2 – 3.
An image with high reliability can only be studied using a high-resolution tomogram or radiograph. It is considered optimal to prescribe a study that is carried out with high-hardness rays, since in such images all parts of the lungs are clearly observed. To clarify the diagnosis, it is important to evaluate radiographs taken at different times and follow-up. There are two types of changes in the pulmonary pattern - rarefaction and intensification .
The primary tuberculous focus is the focus of the primary
1. Pneumonic – expansion of the root with deformation of the pattern, loss of structure; 2. Resorption; 3. Compaction – after 2 years;4. Ossification and calcification of primary lesions (after 5 years).
Strengthening of the hilar pulmonary pattern during the infiltrative tuberculosis process is accompanied by the artery extending beyond the boundaries of the mantle-like zone. Normally, the small pulmonary vessels end no less than 1 cm before the outer border of the shadow of the pulmonary fields on the radiograph.
In what cases is there an increase in the pulmonary pattern?
Local enhancement, which is accompanied by deformation, is very easily diagnosed by comparing the patterns of the opposite lungs. Changes often indicate inflammatory diseases . This could be, for example, tuberculosis, pneumosclerosis caused by limited suppuration in the lungs, the initial stage of pneumonia or its chronic form. At the same time, the clinical picture is not always well expressed - intoxication is usually mild, there is a cough with purulent or mucous sputum.
Although on radiography the bronchi are deformed and brought closer together, they are passable, and on bronchography a specialist can detect bronchiectasis. After acute pneumonia, residual effects can manifest themselves for a long time in the form of increased pulmonary pattern and this condition persists for up to six months.
What does the strengthening of the pattern in a fluorographic image indicate?
Strengthening the pulmonary pattern is a clear image of the vessels along the entire surface of the lungs and their roots. The image clearly shows the pattern of the upper and lower lobes of the lung. This may indicate the course of such pathological processes:
- tuberculosis;
- oncological neoplasms;
- pneumonia;
- heart defect (congenital or acquired);
- acute, obstructive and chronic bronchitis;
- pulmonary edema;
- some occupational diseases – silicosis, pneumoconiosis.
Depending on the type and extent of the pathological process, the enhancement can be local or diffuse. Ailments such as focal pneumonia and malignant neoplasms are displayed on the image as one or several foci of inflammation. With such processes, the pattern is enhanced precisely in those areas where pathology develops. This is called local enhancement of the pulmonary pattern.
If an extensive pathological process occurs in the lungs, then the pattern is enhanced over the entire surface of the bronchopulmonary tree, from the roots to the outer borders and at the periphery. Diffuse enhancement of the pulmonary pattern in the image may indicate the presence of diseases such as miliary tuberculosis, lobar pneumonia, chronic and obstructive bronchitis.
In what cases should you sound the alarm?
Any person who sees an unclear word in a diagnosis begins to worry. In fact, you shouldn't get upset ahead of time. Quite often, the conclusion “increased pulmonary pattern” is a consequence of overdiagnosis , which is what radiologists usually “sin”. When diagnosing chronic bronchitis, quite often doctors do not check additional analyzes of x-rays that were taken some time ago.
This is explained by the fact that doctors in municipal clinics usually do not have enough time for such proceedings. In addition, x-rays are considered a subjective research method, when a person makes a decision relying only on his own experience, so errors are possible. The wording “increased pulmonary pattern” is not a fatal diagnosis and sometimes has no practical significance. But in cases where the conclusion indicates a specific pathology - pneumonia, tumors or tuberculosis, treatment cannot be postponed.
Increased pulmonary pattern in a child
Sometimes an X-ray examination is prescribed for children under 15 years of age, because this procedure is considered the only method that confirms the condition of the child’s body. X-rays are performed quickly, allowing even the smallest children to be examined. The child enters the X-ray cabin with one of the parents, who will hold him motionless. To get a high-quality photo, the child should not move for one second .
If the report says “increased pulmonary pattern,” this may indicate bronchitis or pneumonia. But often such a drawing is obtained due to a violation of the examination rules, for example, when the child cried or did not hold his breath during the examination.
Is X-ray diagnostics safe?
Digital radiography of the lungs
In some cases, the doctor will prefer a different research method. All received radiation is necessarily taken into account and summed up - thus eliminating the possibility of “overdose” and causing harm to a person. However, each person must take care of himself independently - if he undergoes such examinations on his own initiative, it is mandatory to report them to the attending physician.
Benefits of radiography
This procedure is carried out quite quickly, and the result appears on the computer monitor in a few seconds. In addition, the advantages of x-ray examination are as follows:
- safety for the patient;
- thanks to preliminary contrast, an accurate diagnosis can be made in doubtful cases;
- a small number of contraindications;
- You can obtain additional information during the research process using software.
Thus, if, during an X-ray examination, a specialist concluded “increased pulmonary pattern,” then you should not panic ahead of time, since this does not always indicate a serious illness. It is likely that some error occurred during the research.
What should a normal photo look like?
In a healthy person, an image obtained by fluorographic examination looks like this:
- Drawings of the right and left lungs should be of equal clarity.
- The vessels in the image have straight branches.
- In its general appearance, the outline of the lungs resembles a butterfly; the vascular branches are smooth and fan-shaped.
- From the roots of the lung to its periphery, the intensity of the display of the vascular network decreases. The shadows end approximately one-third from the outer border of the chest.
- The visibility of the vascular network should be lower than the visibility of the costal shadows.
- The thickness of the vessels in the image should decrease evenly from the root to the periphery of the lungs.
The pulmonary pattern is formed by a network of arteries emerging from the pulmonary root. In a healthy bronchopulmonary system, the vascular network narrows evenly from the root zone to the outer contours of the lungs.