0
Author of the article: Marina Dmitrievna
2017.08.02
607
Platelets
Platelets are small, flattened, disc-shaped blood cells without a nucleus. Their deficiency or excess in the body negatively affects the patient’s health, which is especially noticeable at a younger age. Thrombocytopenia is a disease that causes a lack of platelets in the blood of children. Read more about what this is and what parents should do in such a situation later in the article.
Platelets
What platelet level is considered low?
The optimal level of these blood cells is 150-400 *109/l. If this indicator drops below 150*109/l, the patient is diagnosed with thrombocytopenia, due to which the blood stops clotting.
Thrombocytopenia can be a separate disease or a sign of various diseases. To accurately establish the cause of its development and select appropriate therapy, the patient is sent for additional examination.
Norms
Causes of thrombocytosis in children
In medicine, it is generally accepted that the causes of thrombocytosis can be:
- erythremia – increased formation of blood platelets by red bone marrow;
- too slow “utilization” of platelets – this usually occurs when the spleen is removed;
- impaired distribution of platelets in the bloodstream - most often observed against the background of mental or physical fatigue.
If a high level of platelets is detected in blood tests, the doctor will have to determine the true cause of the development of such a pathological condition, for which additional examinations of the patient will be prescribed. In children, thrombocytosis can develop at any age, but parents should be aware that such a diagnosis is made by doctors even with a minimal increase in the number of platelets in the blood.
Thrombocytosis in medicine is divided into three main types:
- Clonal thrombocythemia. In this case, there is a defect in stem cells in the bone marrow, which may also be due to their damage by the tumor process. Stem cells do not respond to ongoing endocrine processes, and therefore the formation of the blood component in question becomes uncontrollable.
- Primary thrombocythemia. This condition is always associated with the proliferation of several areas of red bone marrow, and the result is an incredible amount of newly formed platelets. Some hereditary/congenital diseases, as well as erythremia or myeloid leukemia, can lead to such a pathology. Primary thrombocythemia is characterized not only by an increase in the number of platelets, but these blood components are enormous in size and have an altered shape.
- Secondary thrombocytosis. The mechanism of its development is quite variable:
- against the background of removal of the spleen, when old platelets have not yet been destroyed, and new ones are already actively being formed;
- during the inflammatory process, the body intensively produces a hormone that promotes the maturation of blood platelets;
- in case of malignant neoplasms, they produce biologically active substances that have a stimulating effect on bone marrow megakaryocytes, which increases the number of newly formed platelets.
Secondary thrombocythemia can develop in the presence of a number of pathologies in a person:
- any malignant neoplasms;
- tuberculosis;
- amyloidosis;
- anemia of iron deficiency or hemolytic type;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- rheumatism occurring in the active stage;
- fractures of tubular bones;
- ulcerative colitis;
- acute blood loss;
- osteomyelitis;
- splenectomy;
- acute and/or chronic infectious diseases;
- any major surgical interventions.
With secondary thrombocytosis, a less pronounced increase in the number of platelets in the blood will be characteristic, while their morphology and functions are absolutely not impaired.
If the pathology in question was diagnosed for the first time, the doctor will definitely refer the patient to undergo the following tests:
- determination of C-reactive protein;
- determination of serum ferritin and iron;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal and pelvic organs;
- blood coagulation analysis;
- bone marrow examination.
Causes of thrombocytopenia
Short-term thrombocytopenia may occur due to:
- monthly bleeding;
- pregnancy;
- vitamin deficiency;
- taking antidepressants, hormones and antibiotics);
- alcohol and chemical poisoning;
- surgical intervention;
- severe injuries;
- abuse of garlic, onions, cherries, lemon and ginger;
- vitamin B12 deficiency.
B12 deficiency
Severe platelet deviation occurs when:
- tuberculosis;
- leukemia;
- hepatitis;
- HIV;
- aplastic anemia;
- liver cirrhosis;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- herpes;
- heart failure;
- mononucleosis;
- measles;
- allergies;
- ARVI and acute respiratory infections;
- DIC syndrome.
Herpes
Platelets are below normal: what is the danger?
If, after the next blood test, it turns out that the child has fewer platelets than he should have at his age, this is a reason to sound the alarm.
Platelets are responsible for blood clotting. The list of their functions includes:
- release of special substances that accelerate the healing of damaged tissues;
- blockage of damaged vessel sites to stop bleeding;
- delivery of nutrients to the vascular endothelium.
When there are few such cells, the blood becomes more fluid and wound healing slows down.
Poor healing
Functions of platelet cells
- Normally, when the walls of the vascular bed are damaged, substances that activate platelets are released into the blood.
- Activated platelets change their shape, becoming flatter, migrate to the area of vascular damage and begin to actively form a platelet thrombus.
- The formation of a blood clot is carried out due to the pronounced ability of platelets to stick together and attach to the damaged area of the vascular bed.
- After the completion of the formation of the primary platelet thrombus, platelets secrete substances that promote compaction and stabilization of the platelet clot.
- Also, the surface of platelet cells contains immune complexes that actively maintain vascular spasm in the area of vascular damage.
The normal lifespan of platelet cells is about ten days.
In this regard, to maintain normal platelet levels, their stable and constant renewal is necessary.
An imbalance between the production of platelets by bone marrow tissue and their destruction can lead to the development of thrombocytosis (an increase in the number of platelet cells) or thrombocytopenia (low platelets in a child or adult).
Symptoms of thrombocytopenia can have varying degrees of severity (from prolongation of bleeding time from wounds to massive nasal, gastrointestinal, etc. bleeding)
Severity, symptoms
There are several forms of thrombocytopenia:
- mild - if the readings are within 75-99 × 10⁹/l;
- moderate – 50-74 × 10⁹/l;
- average 20-49 × 10⁹/l;
- heavy – 20 × 10⁹/l.
Low platelets in a child at the first or second stage can only be detected through blood donation. Often this condition does not produce any symptoms. This is especially true for babies who cannot tell about their well-being.
Among the external signs one can note:
- frequent nosebleeds;
- bleeding gums;
- rashes all over the body;
- urine mixed with blood;
- causeless bruising;
- vomiting blood.
Hemorrhagic syndrome
A decrease in platelet count leads to undesirable consequences:
- prolonged wound healing;
- bruises even from light touches;
- relatively large loss of blood from scratches;
- hemorrhages from the gastrointestinal tract;
- in girls during puberty - uterine bleeding.
As you can see, these are quite dangerous complications. Failure to see a doctor in a timely manner can have a negative impact on the child’s well-being.
If at least one of the above symptoms develops, parents urgently need to show their child to a doctor.
Important! Before visiting a doctor, remember all the factors that could provoke the manifestation of the symptom.
The slightest detail is enough to suggest the correct reason the first time. Knowing it, it will be easier for the doctor to create a treatment plan.
What to do
If low platelets are detected in a child, with a slight deviation from the norm, it is necessary to make changes to the diet, supplementing the diet with iron-containing foods, vitamins C and A. Increase the diet with foods such as buckwheat, meat, fish, herbs, and vegetables. You should avoid fruit juices, and you should also remove seaweed and cranberries from your diet.
It is necessary to control the daily routine, the child must sleep a sufficient amount of time and maintain moderate physical activity, be in the fresh air more often, and relax with his parents in nature.
If a child has low platelets, it is allowed to use traditional medicine in the form of herbal infusions, but only after mandatory consultation with a pediatrician. In the moderate and severe stages of falling particles, in addition to proper nutrition, drug treatment is necessary, which will consist of eliminating the main cause of the pathology that has arisen. Medicines and other methods of therapy should be selected by a pediatrician.
Important information: What is toxogenic granularity of neutrophils in a child’s blood test?
The following drugs are used:
- A group of corticosteroids - are involved in the process of regulating the formation of cells in the bone marrow in sufficient quantities. It is important to use this group of medications correctly to avoid side effects. In case of severe pathology of the liver and kidneys, use is contraindicated.
- Immunoglobulins - used in injections if the reason for the reduced level of particles is an inflammatory process. With this therapy, not only does the number of blood cells increase, but their life period also extends, and local and general immunity is strengthened.
- Preparations in the form of serums that slow down the process of platelet destruction. If the amount drops to a critical level, and drug therapy is not effective, a transfusion is performed using donor blood.
- In case of pathology in newborns up to three months of age, special milk and dairy-free formulas are selected, and, if necessary, drug treatment or blood transfusions are also prescribed.
Why are platelets low in a child?
Most often, a strong decrease in the number of blood platelets is caused by thrombocytopenic purpura - an independent disease that manifests itself more often in the period from 2 to 6 years. Other causes of thrombocytopenia in childhood:
- infectious diseases (measles, rubella);
- autoimmune reactions of the body;
- heavy metal vapor poisoning;
- oncohematological diseases.
Purpura can be diagnosed even in a newborn. To minimize the consequences, you should immediately consult a doctor. He will compare platelet standards for children and the data obtained and, if the platelet count has really dropped, prescribe tests and treatment.
The norm depends on age:
- in a newborn – 100-420 × 10⁹/l;
- in infants (up to one year) – 150-350 × 10⁹/l;
- after a year – 180-320 × 10⁹/l.
Obviously, a reading of 70 × 10⁹/L means a low platelet count in a child and requires close monitoring of health.
One of the reasons
Complications
The most dangerous manifestation of thrombocytopenia in a newborn is blood loss due to bleeding and hemorrhage. The level of risk of consequences depends on their frequency and location:
- Posthemorrhagic anemia, which is characterized by frequent intrauterine bleeding of the gastrointestinal tract. They can be identified when blood clots appear in the stool. If the blood loss is large, the baby may die.
- Brain hemorrhage. It is extremely rare in newborns. Moreover, a quarter of such situations result in death. Bleeding of the nose and gums are harbingers of this condition. Retinal hemorrhage can be identified by the presence of red threads in the retina and on the eyeball. This condition is fraught with problems with visual acuity; in the most severe cases, complete loss of vision can occur.
In general, the prognosis for thrombocytopenia in infants in the first months of life is unfavorable. Only immediate and adequate medical intervention will keep the platelet level at a sufficient level and gradually increase it.
Diagnosis and treatment
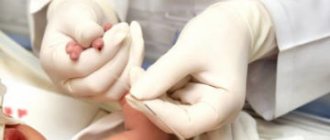
To identify pathology, you need to donate blood. It is possible to take it from a finger or vein, and in the case of infants, from the heel. To rule out that the platelets in the child’s blood have decreased temporarily (a reaction to stress or illness), blood samples are taken several times with an interval of 3-5 days.
Taking blood from your finger is a quick way to find out your platelet count
Important! In teenage girls, a decrease in the number of blood platelets is allowed. This is due to the formation of the menstrual cycle.
Since other diseases can lower platelet levels, they are treated first, and only then do they look at the situation. If complications still exist and thrombocytopenia has not disappeared, a number of medications are prescribed. The list of activities may include:
- immunoglobulin injections;
- taking hormonal drugs and cytostatics;
- introduction of special hemostatic drugs;
- platelet transfusion.
Let us consider in more detail the various methods of treating thrombocytopenia.
Medication
It involves the use of drugs that block antibodies that destroy platelets and inhibit their synthesis. Such medications include:
- Prednisolone. A tableted medication that stops the formation of antibodies in the spleen, protects platelets from destruction and strengthens capillary walls. Minimum price – 120 rubles.
- Intraglobin. The medication has a positive effect on the immune system, destroys antibodies and prevents them from contacting platelets, and kills viral cells. The cost of the medicine is 135-170 rubles.
- Vincristine. Injection powder prevents the formation of pathogenic cells and blocks the synthesis of antibodies in the spleen. You will have to pay 155-210 rubles for the medicine.
To improve the therapeutic effect of medications, you need to follow a certain diet.
Vincristine
Diet
The basics of therapeutic nutrition for thrombocytopenia are equally suitable for adult and young patients.
The patient's diet should be based on:
- buckwheat;
- nuts;
- corn;
- beef liver;
- barley groats;
- oatmeal;
- sprouted wheat;
- spinach;
- parsley;
- dill;
- asparagus;
- green onions;
- freshly prepared vegetable and fruit juices.
Recommended product
It is useful for a child to eat:
- melon;
- apricots;
- legumes;
- pumpkin;
- avocado.
A small patient's diet should not include fast food, spicy, fried, smoked or salty foods.
Traditional methods
Thrombocytopenia is well eliminated:
- Infusion of medicinal verbena. The drink saturates the body with iron and improves blood circulation.
- Sesame oil. The substance stabilizes platelet levels and improves blood clotting.
- Infusion of stinging nettle. Stops bleeding and stimulates wound healing.
Sesame seed oil
Treatment of newborns
Therapy for newborn babies involves the use of:
- donor milk for 14-21 days, then, under constant monitoring of platelet levels, mother’s milk can be given;
- immunoglobulin intravenously or as infusions;
- prednisolone at a dose of 2 mg per 1 kilogram for 14 days;
- ascorbic acid and rutin;
- platelet transfusions.
Important! In severe forms, you need to be prepared for the fact that the spleen will need to be removed.
Such surgical intervention is completely justified if the low level of platelets in the child’s blood is not regulated to the required extent with the help of medications.
In severe stages, bed rest is prescribed. It is recommended to eat more nuts, bananas and pomegranates - in a healthy body they naturally provoke an increased production of blood platelets.
If a child’s platelets are severely or moderately low, it makes sense to give him only warm food - this will have a positive effect on the gastrointestinal mucosa and reduce the risk of bleeding.
Functions and role of platelets
Platelets are small plates that are part of the blood. They prevent the formation of blood clots and protect blood vessels. If the walls of a capillary or vessel are damaged, platelets accumulate around the diseased area and form a clot.
The life cycle of platelets begins from the moment they are separated from the red bone marrow and lasts about 8-10 days. At this time, the blood platelets retain their spherical shape and move freely through the vessels. The destruction of dead cells occurs in the liver and spleen.
Blood clotting depends on the number of platelets in its composition. To eliminate damage to the endothelium, they are deformed, acquiring a star shape. Layering one on top of the other, platelets form a blood clot. The rapid formation of a blood clot is facilitated by coagulation proteins released into the blood.
Platelets perform four main functions in the human body:
- The angiotrophic function ensures tissue integrity. When blood platelets are destroyed or interact, biological substances are produced that serve as food for the walls of blood vessels.
- The hemostatic function is to constrict blood vessels when damage occurs. Platelets accumulate in the resulting holes, thereby forming platelet plugs. This makes it possible to narrow the channel passage to avoid the leakage of biological fluid.
- The phagocytic function allows platelets to fight the development of pathogenic microorganisms. They attach to the walls of bacteria and inhibit their vital activity. Thus, the negative impact of external factors on the body is minimized, and the functioning of the immune system is stabilized.
- The regenerative function promotes the restoration of vascular walls due to growth factors. When the level of platelets decreases, the risk of blood loss increases due to the appearance of internal bleeding, since the strengthening of blood vessels will be insufficient.