Reduced level of red blood cells in a child's blood
If your child's blood test shows a decrease in this indicator, this may indicate anemia.
Anemia is a pathological condition that adversely affects the functioning of the body. With such a disease, its supply is first disrupted. A disease such as anemia can occur due to many reasons. This disease can be either a consequence of a primary lesion of the blood system or a symptom of various diseases. In addition, a decrease in the level of red blood cells in the blood can be caused by a physiological reason, namely the presence of an abundant amount of fluid in the body. But this decrease in red blood cells is short-term and soon their number will return to normal.
Sosudinfo.com
Throughout his life, a person turns to doctors for help many times. Of course, there are individuals who have good, good health and strong immunity, but there are only a few of them. Many people become victims of their bad habits: alcohol, cigarettes, drugs have brought millions of lives to the grave. Others inherit poor health, while others become victims of the environment. The most offensive thing is when the disease attacks a little person. He is not guilty of anything, maintains a healthy lifestyle, smiles at the sun, enjoys life. In order to determine the causes of the disease, tests should be taken. This first step will show all changes, problems, threats. What to do if a child has elevated red blood cells, what are the risks and why is this so important?
An increased level of red blood cells in the blood is not always a threat to a little person. It is likely that the baby was overexcited before taking the tests and overheated in the sun. Decreased red cells also do not pose much of a threat. However, if the level of red blood cells in the blood is very different from the norm, this means that the child has health problems. The total number must correspond to certain tabular data on the norms of red blood cells in the blood. The analysis will show the level of cell concentration, but will not tell why there is a decrease or excess of red blood cells in children. Let's try to sort out all the questions.
Red blood cells increased causes
The growth of red blood cells above the optimal value is called erythrocytosis. Most often, this condition occurs in children for physiological reasons.
Firstly, regular physical training and intense sports activities affect the number of blood cells. Constant loads force you to consume additional oxygen, which is supplied to tissues and organs by red blood cells.
Another reason for the natural growth of red blood cells is living in an area located high above sea level. In children living in such areas, elevated levels of red cells are normal and common. This is explained by the increased need for oxygen, since the air in mountainous areas is thinner.
Erythrocytosis appears in those babies whose bodies are overheated in the sun and are dehydrated. Drinking more can save the situation.
A negative factor that provokes cell growth in children is passive smoking. When a child is in a smoky room or near a smoker for a long time, his body begins to suffocate and demand oxygen again and again.
Among the pathological causes, the development of which is accompanied by the growth of red blood cells, the following are distinguished:
- respiratory ailments in the acute phase (rhinitis, bronchitis or allergies);
- congenital and acquired heart disease;
- disruptions in the functioning of the adrenal cortex and bone marrow;
- blood pathologies of a tumor nature, in particular erythremia;
- prolonged vomiting or diarrhea, resulting in dehydration of the child’s body.
Severe obesity (third or fourth degree) is also accompanied by an increased level of red blood cells.
The most dangerous diseases in which red cells jump up are neoplasms in organs such as the kidneys or liver.
There are many reasons for erythrocytosis, but the starting point for this condition is the same: tissues and organs are deficient in oxygen. The body, in defense, is forced to produce red blood cells that save the situation.
The child has elevated red blood cells
Red blood cells
– these are red blood cells, which are the main formed elements of blood and provide transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Red blood cells are found in the blood of children in a certain quantity, which depends on age. Thus, for one-month-old children the standard norm is 3.8 - 5.6x1012/l, for one-year-olds - 3.6-4.9x1012/l, and for children aged 13-15 years - 3.6 - 5.1x1012/l l. If a child has elevated red blood cells, this condition is called erythrocytosis and indicates various pathologies.
Why does a child have elevated red blood cells?
If the analysis shows that the child has elevated red blood cells, then this can indicate both minor disorders in the body and serious functional disorders. This may also be a temporary physiological phenomenon in cases where the child was engaged in vigorous physical activity the day before and became hot or sweaty. At the same time, the excess of the norm of red blood cells in the blood is insignificant.
But, unfortunately, more often the reasons that a child has elevated red blood cells are pathological. Let's consider the main ones:
1. Dehydration is the loss of fluid in a short period of time, which can occur due to:
- intoxication accompanied by frequent vomiting;
- intestinal infections accompanied by diarrhea;
- burn disease;
- disorders of nervous regulation;
- stress, shock, etc.
2. Prolonged hypoxia, an increased need for oxygen in the child’s body, which may be caused by the following pathologies:
- congenital heart defects;
- hypertension of the pulmonary circulation;
- severe obesity;
- obstructive chronic pulmonary diseases;
- altitude sickness due to oxygen deficiency.
This may also be a consequence of passive smoking, when the child’s body increases the production of red blood cells to neutralize the poisonous gas entering the body.
3. Polycythemia vera is a tumor process in the hematopoietic system that develops as a result of unexplained factors.
4. Kidney diseases, kidney tumors, in which there is an increase in the amount of the substance erythropoietin, which stimulates the production of red blood cells.
Increased red blood cells in the child’s urine
Due to the fact that the renewal of red blood cells occurs constantly, their detection in a urine test is natural, but if their number does not exceed 2-4 units in the field of view. If the norm is significantly exceeded, the color of the urine becomes red or brown. The reasons for this may be diseases of the genitourinary system and pathologies of other organs, leading to general intoxication of the body (respiratory viral infections, osteomyelitis, etc.).
View the discussion thread.
Pathological causes
If the reasons for the increase in the number of red cells are not physiological, then we begin to talk about pathological processes in the child’s body.
Red blood cells in a child’s blood may be elevated for several reasons that require careful examination by a pediatrician:
- Diarrhea or vomiting. With these ongoing processes, severe dehydration occurs, which is not replenished by drinking plenty of fluids. This condition is dangerous, and a persistent level of red blood cells above normal indicates a severe course of the disease. It can be caused by various infections or bacteria and requires urgent treatment, and sometimes hospitalization in an inpatient department.
- Chronic diseases of the respiratory system. The lungs lose their elasticity and are not able to absorb the volume of air necessary for the body. At the same time, the amount of inhaled oxygen decreases, and the body begins to suffer from a lack of oxygen, which leads to erythrocytosis.
- Acute respiratory diseases. Infections, bacteria and inflammation, which are present throughout the acute period of the disease, disrupt gas exchange processes in the body. Oxygen starvation and a subsequent increase in the number of red cells can provoke: cough; runny nose; heat; sore throat.
- Heart failure or its abnormalities. If the heart muscle is not working effectively enough, the blood does not move through the body quickly enough and is poorly renewed, carbon dioxide is retained in the body and there are interruptions in the supply of the required amount of oxygen particles. All this causes erythrocytosis.
- Too much pressure. When the heart works harder and the pressure in it increases, blood moves through the body too quickly. Gas exchange processes do not have time to occur, and a large number of blood cells are produced to compensate for the disturbed oxygen-carbon dioxide balance. Typically, such problems are associated with children growing too quickly, but various heart defects can also occur.
- Hypernephroma disease. This disease is characterized by excess production of the hormone erythropoietin by the kidneys, which causes the production of a large number of red blood cells.
- Abnormal changes in the adrenal glands. In this case, the body produces a lot of corticosteroid hormone. It affects the functioning of the bone marrow, which leads to an uncontrolled increase in the level of red blood cells.
- Allergy. With such symptoms of its manifestation as: runny nose; cough; sneezing; nasal congestion; swelling of the throat, the body does not receive the required amount of oxygen, and the amount of carbon dioxide does not decrease. This leads to increased production of red blood cells.
- Obesity. Excessive body weight leads to: increased blood pressure; compression of the lungs and other organs; violation of water-salt balance; disruption of the heart. All these factors can cause oxygen starvation. The body combats this problem by significantly increasing the amount of blood cells in the blood.
- Bone marrow pathologies. If it does not work properly, the concentration of red blood cells in the blood may increase. To obtain an accurate diagnosis, urgent examination and treatment is required.
What level of red blood cells is considered normal?
The norm of red blood cells in the blood is determined using a clinical blood test, by taking a small part of it from a vein or finger. In addition to examining the content of red blood cells, the analysis detects platelets and leukocytes. Indicators of both the number of blood cells and their qualitative formation are important.
Leukocytes and platelets are also important components of the blood, the condition of which should be monitored.
When receiving the results of laboratory tests of children’s blood, parents should not pay attention to the “norm” column on the form. Because usually test answers are provided on general forms
Therefore, interpretation of tests should be carried out taking into account age, individual health status, as well as other internal and external factors. The norm of red blood cells in a child is calculated in accordance with his age. In children under 1 year of age, the level of red blood cells is often elevated. At 2 years of age, this indicator begins to stabilize and by adulthood it has figures identical to those of an adult.
Table of values and permissible fluctuations in the norms of red blood cells in the blood depending on childhood age:
It is better if blood tests are deciphered by a qualified doctor. Interpretation of the data by a specialist will allow you to accurately determine the exact diagnosis. If laboratory diagnostics reveal elevated red blood cells in the blood, it becomes necessary to take a repeat test to establish rbc standards to determine the state of hemoglobin.
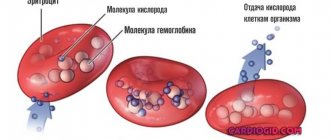
Iron-containing protein is directly responsible for the direct delivery of oxygen to human organs and tissues. Normal hemoglobin in children from 1 month to 14–15 years ranges from 110–140 g/l. A high level of iron is not a virtue, but it indicates the presence of deviations from the required standards and requires the identification and elimination of the causes.
RBC readings in a blood test reveal:
- RDW-SD is the distribution width of red blood cells in the total blood capacity.
- RDW-CV is a proportional expression of the conditional width of the red blood cells.
- P-LCR - expression of large platelets.
- ESR—red blood cell sedimentation rate.
The rbc norm for children from 3 years to 12 years of age is 3.5–5.0 x 10 12 / l, for both boys and girls. Upon reaching the 16th birthday, for girls this value remains the same, and for boys it increases to 4.1–5.5x10 12 / l.
Erythrocytosis is not a death sentence, but a completely controllable condition of the human body. Initially, it is necessary to follow simple rules in nutrition, drinking regime and organization of living conditions. The main thing is to know how you can positively influence the number of red blood cells in a child. And then you can be confident in the excellent health of the younger generation.
- Rita on What vitamins to take for VSD
- Ekaterina L to the post What vitamins to take for VSD
- Natalya on What vitamins to take for VSD
- Alexander on Indian method of treating hypertension with iodine
- Dima on Is it possible to play sports with varicocele and after surgery?
The information posted on the portal is not a guide to self-medication and does NOT replace consultation with a doctor! The Site may contain content that is not intended for persons under 16 years of age.
Reference values for children
The norm of red blood cells in the blood of children of different ages is somewhat different, which is due to the characteristics and stages of their growth and development. Thus, the umbilical cord blood of the described cells contains 3.9-5.5 * 1012 U/l. In a newborn aged 1-3 days, the indicators increase and amount to 4-6.6*1012 U/l.
By the end of the first week of the baby’s life, the coefficients decrease slightly and can vary in the range of 3.9-6.3*1012 U/l. In the second week, the content of red cells drops a little more, and is already within the range of 3.6-6.2 * 1012 U/l. The normal level of red blood cells in the blood of a one-month-old baby is 3-5.4*1012, and in a two-month-old baby – 2.7-4.9*1012.
By six months, the interval of the permissible number of red cells is slightly reduced, that is, the lower limit increases, and the upper limit, on the contrary, decreases, and the reference values for this age are 3.1-4.5 * 1012 U/l. The normal content of these cells in children under 12 years of age varies in the range of 3.5-5*1012.
In adolescents, the indicators begin to differ, which is due to gender characteristics of growth and development of the body. So for young girls 13-19 years old the normal value should be 3.5-5*1012, for teenage boys 13-16 years old - 4.1-5.5*1012 U/l, and for boys 16-19 years old - 3.9-5.6*1012 U/l.
To determine the compliance of this parameter during interpretation, a special table is used, thanks to which even a person who does not have a medical education can see deviations.
Reference values of red blood cells for children of various age categories
Possible pathologies
Red blood cells are quite important bodies in the blood. However, sometimes they may be subject to change. What indicators are taken into account when assessing these bodies?
Pathologies that can be detected in red blood cells:
- Changing shape. The structure of the cells is unusual - they resemble a disk concave on both sides. Changing the shape of cells can lead to their premature death.
- Changes in hemoglobin levels. Hemoglobin is a pigment through which internal organs and cells are saturated with oxygen. Changes in its level are usually associated with the content of red blood cells. However, in some situations the indicators may change independently of each other.
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is a fairly important indicator that is taken into account when taking a clinical blood test. A change in its level may indicate the impact of an infection or an inflammatory process in the body. In children, the norm (up to one year) of ESR is 2-5 mm/h. Subsidence varies depending on the age of the patient. Thus, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate in children after 5 years is 5-11 mm/h.
High blood cell counts can cause your baby's blood to thicken. That is why some measures should be taken to liquefy it. The child should be given oatmeal, beets, apples, and cocoa. Some types of berries should also be given. The child also needs to drink more fluids.
However, there is no need to be alarmed, since blood clots occur quite rarely in children. If blood density is greatly increased, the pediatrician may prescribe certain medications that are aimed at thinning the blood.
To monitor your child’s condition, you must undergo a full medical examination at least once a year. It is then that the mother will be confident in the health of her baby. In the early stages of a child’s life, the mother will have to visit the pediatrician frequently. Erythrocytosis is not an independent disease; it only indicates the presence of disturbances in the functioning of the body.
So, red blood cells are red blood cells, thanks to which the blood gets its color. Elevated levels in children can occur for many reasons. The most common is hypoxia, which occurs in the child while still in the womb. Hypoxia – suffocation. By increasing the level of red blood cells, the child received more oxygen. In addition, after birth, the baby needs time to get used to the new environmental conditions. In addition to increasing, red blood cells may also decrease. One of the most common causes is anemia. Symptoms of anemia are similar to common illness: loss of appetite, rapid fatigue, inactivity. To monitor the level of red blood cells, it is necessary to take a general blood test.
Why is erythropenia dangerous for a child?
Erythropenia leads to decreased immunity
Of course, the question: why is this situation dangerous for the baby worries many parents who are faced with such a diagnosis. It is important to understand here that a decrease in the level of red blood cells leads, first of all, to an insufficient supply of oxygen to the body tissues. And he is the basis of life. In addition, at the same time, the removal of carbon dioxide from cells deteriorates. Against this background, the functioning of the body begins to deteriorate, and disruptions occur in the functioning of internal organs. In childhood, this is especially dangerous and leads to developmental delays.
And against this background, the child’s body’s defenses begin to deteriorate and immunity drops. There are also problems with blood clotting.
When worries are unfounded
However, if the norm of red blood cells in children is too high, this is not always bad. In a child who plays sports, their level can increase noticeably. The reasons for this process lie in the increased needs of the body. It requires a lot of oxygen and other nutrients to function properly. This anomaly is also observed in children who live in mountainous areas. Their red blood cell count is also elevated, but this is not considered an unnatural process.
In contrast to the stated facts, we need to put passive smoking. If one of the parents in the house takes up a bad habit - smoking, then high levels of red cells in the child’s blood are virtually inevitable. The bone marrow begins to produce them in large quantities. This is how the body compensates for the lack of oxygen. If this is the case, the doctor will not even have to look for the reasons for the abnormality, why the baby has an increased rate of red cells.
Low or high levels are determined after drawing blood from a finger. The concentration of elements in one ml3 is taken as a basis. Depending on the gender and age of the patient, the doctor will tell you what tests he has, that is, whether his red cells are elevated or low. For women and men, the norm ranges from:
- 3.7-4.7 per cubic liter;
- 4-5 per cubic liter respectively.
Red blood cells in a child’s blood depend, first of all, on age, lifestyle and living conditions. As mentioned, athletic children have a higher rate of red cells. Other reasons for its increase are also indicated above. It is worse if erythrocytosis is a sign of other, more dangerous ailments. Pathologies associated with this phenomenon require close supervision by a physician.
Why is the increase happening?
Since red blood cells are responsible for enriching cells with oxygen, an increase in their number indicates a change in blood characteristics: density and fluidity. This also indicates an increase in pressure in the circulatory system. Red blood cells in a child's blood may be increased due to various factors.
Depending on the cause of the deviation from the norm, erythrocytosis is divided into types:
- Conditional, or physiological . With this deviation, the actual number of red cells does not exceed the norm for their content. This condition occurs when the density and viscosity of the blood increases or when there is slight dehydration due to diarrhea, vomiting or profuse sweating. This type of erythrocytosis is not dangerous to health, but requires medical supervision.
- True, or pathological . With such a deviation from the norm, the number of blood cells is actually increased. This indicates the constant production of red cells by the bone marrow.
Red blood cells in the blood are elevated in a child due to the presence of:
- inflammation;
- diseases;
- improper functioning of the bone marrow.
Such conditions require additional tests and examination by a pediatrician.
Causes of erythrocytosis in children
Increased red blood cells in a child’s blood (erythrocytosis) can be detected for various reasons. In accordance with the etiology, erythrocytosis can be physiological or pathological.
Sometimes high red cell levels are temporary. So, with passive smoking, that is, in the case when someone close to the child smokes in the family, the number of red blood cells in his blood may increase.
If we talk about newborns, then most often an excess of red cells is observed in children whose mothers’ blood is diagnosed with a low oxygen concentration.
Children living in mountainous areas may suffer from compensatory erythrocytosis. In addition, a false increase in red blood cells occurs against the background of constant mental and physical stress, stress and emotional experiences.
Video:
Physiological erythrocytosis often occurs against the background of dehydration. Since in the laboratory the concentration of red blood cells is calculated relative to one liter of blood, a lack of water causes an increase in red cells.
Physiological erythrocytosis due to dehydration is often observed in the summer against the backdrop of hot weather and during excessive physical exertion in athletes.
In addition, the pathological condition occurs with vomiting, diarrhea, and fever. In any case, to normalize the level of red blood cells, it is enough to increase the amount of fluid you drink (preferably plain drinking water).
Within a few days, the concentration of red blood cells stabilizes and reaches normal values.
Pathologies of the respiratory system and, accordingly, lack of oxygen in the body lead to an increase in the level of red bodies in the blood. Oxygen deficiency often occurs with congenital heart disease and lung diseases.
The fact is that it is these organs that are involved in the removal of old red blood cells and their pathologies can lead to an increase in the number of red cells.
Exceeding normal values is observed with chronic renal failure and malignant neoplasms in the kidneys. With these pathologies, increased red blood cells in the urine are often diagnosed.
Erythremia is considered a fairly rare and not fully understood disease, which is characterized by an active increase in the number of red blood cells.
Erythremia is characterized by an excess number of red blood cells with a simultaneous increase in the concentration of platelets and neutrophils.
Blood viscosity increases, blood flow in the vessels slows down, and hypoxia occurs. The condition most often occurs in older people, but can also occur in children.
Physiological reasons
Causes of conditional erythrocytosis:
- Birth . During pregnancy, the baby breathes through the mother's blood, and he needs a large number of red blood cells. After birth, the child takes his first breath, and the body starts the process of reducing the number of blood cells to the required level. So, with age, children adapt to various environmental factors.
- Location . Children who live in mountainous areas are susceptible to mountain sickness - hypoxia due to lack of oxygen at altitude. This may cause: dizziness; headache; hallucinations; vomiting From birth, the child’s body adapts to the conditions of insufficient oxygen and produces more red blood cells to avoid altitude sickness.
- Infections in the intestines . Pathogenic organisms during the acute phase of illness can cause vomiting or diarrhea. Which leads to dehydration of the body, and consequently, to an increase in blood viscosity. In this case, the level of red blood cells will be higher than normal.
- High temperature in various diseases . This factor provokes profuse sweating, which removes water from the body. At the same time, the blood thickens and the number of red cells increases.
- Constant physical activity . Sports or simply excessive activity promote the release of sweat, which slightly reduces blood flow and increases the content of blood cells. Also, under excessive stress, the child begins to breathe frequently and deeply due to insufficient oxygen supply. At the same time, the absorption capacity of the lungs increases and the number of red blood cells increases for better gas exchange between cells.
- Hot weather and dry air . Under these conditions, children experience very rapid dehydration, which entails an increase in blood viscosity and an increase in the level of red blood cells.
- Passive smoking or smoke inhalation during fires or grass burning. When you inhale smoke of any origin, a huge amount of carbon dioxide enters the body, and the number of oxygen particles drops. To eliminate the acute lack of oxygen and remove excess carbon dioxide, the body begins to increase the production of red cells.
Red blood cells in the child's blood are elevated - the cause may be passive smoking.
- Children drinking carbonated or untreated water . When using such liquids, carbon dioxide enters the body, which the body gets rid of by increasing the content of blood cells.
All of the above conditions do not pose a danger to the health and life of children. But the validity of their influence on changes in blood composition should only be confirmed by a pediatrician. It is necessary to monitor erythrocytosis for some time.
Pathologies and their detection
Pathologies in which the circulatory system contains red blood cells in excess of normal are known in medicine under the general name of erythrocytosis. The causes and manifestations of these diseases are varied. In some cases, the increase in the content of blood cells is relative, and is caused by a decrease in the amount of plasma, while the content of blood cells is generally normal. It is worse when absolute erythrocytosis is detected, in which the number of formed cells of the blood circulating through the blood vessels is actually increased. True, sometimes it happens that the observed high level of red blood cells in children and infants occurs without obvious visible reasons, and is not a pathology, but an individual developmental norm.
Another group of reasons for high levels of red blood cells are disorders of the hematopoietic organs. For example, erythremia (polycythemia vera) is often observed. This is a benign tumor process of the blood system. It increases the production of blood cells, not only red blood cells, but also platelets and neutrophil leukocytes. This is fraught with the development of thrombosis of arterial and venous vessels of the brain, heart attacks, and cirrhosis of the liver.
Erythrocytosis itself is not considered a separate disease; it is only a consequence of disease processes present in the body, such as:
- heart defects;
- kidney and liver diseases;
- lung diseases;
- malignant and benign tumors;
- Vaquez disease;
- Aerz's disease;
- Pickwick's syndrome.
The fact that the erythrocyte content is increased (or decreased) is detected by taking a general blood test, during which the number of red blood cells per unit volume of blood is counted and the result is compared with normal values. Also, during a general blood test, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is determined. A decrease in sedimentation rate can be evidence of a wide range of diseases, including erythrocytosis.
Testing is only valuable when its results are compared with characteristic clinical symptoms. A general practitioner or hematologist can professionally assess the manifestations of the disease and prescribe a treatment program appropriate to the disease. Additional medical tests and studies will help identify the causes of the disease. Correctly prescribed therapy will help normalize blood composition.
Sometimes there is a misconception that an increased content of red blood cells can provoke their detection in the feces of children, including infants. In fact, the detection of traces of blood in the stool can only indicate the presence of internal bleeding of one or another level of danger in the child’s gastrointestinal tract, but will not help in any way with the question of the qualitative composition of the blood. Urine tests will also not be able to tell you about a low or high level of red blood cells.
Role and functions of red blood cells
Red blood cells are the most numerous particles of blood. Their total number reaches 25 trillion. They are also called red blood cells. They are produced in the bone marrow and have a disc-shaped concave shape on the upper and lower planes. Due to their large quantity, the blood is red. Their main function is to saturate cells with oxygen and utilize carbon dioxide in the lungs. They also transport nutrients. If red blood cells are low, this may mean anemia, a disease in which the body lacks iron.
The reasons why the number of red blood cells in children’s bodies increases noticeably is the development of other pathologies. Unfortunately, there are not so few of them and they are all dangerous to health. Finding out what the child’s blood level is at the moment is very simple. You need to take a general finger test and go to the pediatrician with the results. He will decipher the contents of the laboratory test table and give a comprehensive answer.
The norm of red blood cells in the internal environment in children is indicated in the table below. By turning to it, you can compare the given data and the number of red cells indicated in the blood test. That is, an increased or decreased level of red blood cells in a child.
| Normal red cells in children | |
| Immediately after birth | Up to 8×109/l (min. quantity - 4.3×109/l) |
| In the first month after birth | 3.5 - 6×109/l |
| From a month to six months | 3.5 – 5×109 /l |
| From one to two years | 4.5×109/l |
| From 2 to 12 years | 3.5 - 5.4×109/l |
| From 13 years of age | The norm is close to adult indicators |
Some parents know that red blood cells carry hemoglobin - one of the foundations for the normal functioning of the body, and when the norm in the blood of their child is exceeded, they are often surprised that this is very bad. If the content of oxygen “transporters” is higher than the accepted values, the doctor has the right to make a diagnosis of erythrocytosis.
What to do?
If the average number of red cells is increased, it is first determined what this means and whether pathology occurs. This will require a number of additional studies. And then they determine treatment tactics, if necessary.
General recommendations if the baby’s red cells are too high:
- offer more mineral water without gas and chlorine;
- include blood thinning foods in your diet;
- regularly ventilate the room;
- control the temperature.
In case of pathology of the heart, blood vessels, or bone marrow, a more thorough examination is carried out, after which appropriate drug therapy is prescribed.
Increased level of red blood cells in a child's blood
The condition when red blood cells are higher than normal in a child is usually called erythrocytosis or erythremia. However, in children this phenomenon is quite rare, and is usually due to physiological reasons.
In very small babies, who often suffered from hypoxia inside the mother’s womb, the high concentration of red blood cells is explained by the desire of the small body to urgently compensate for the lack of oxygen by producing more red blood cells. In addition, newborn babies have to adapt to new living conditions and increased costs from the first days.
An increase in red blood cells in a child’s blood from birth is observed when living in mountainous areas, since at high altitudes the air contains much less O2 molecules, its density is reduced and it can be difficult for an unaccustomed person to breathe. But with constant exposure to such conditions, the body knows how to adapt, producing more red blood cells. In such a situation, a constant value of 5.5 red blood cells in a child is considered normal.
Also, it should be noted that parents who abuse smoking in the presence of children expose their body to the activation of natural self-defense by creating an increased content of red blood cells due to a lack of oxygen in the lungs.
But, in addition to physiological factors, an increased number of red blood cells in a child’s blood can be associated with various pathologies and diseases, and this is a more alarming situation that requires an additional examination as soon as possible, identifying the causes and eliminating them.
Probable pathological causes of erythrocytosis:
- congenital heart disease or heart failure;
- dehydration due to prolonged diarrhea or vomiting;
- erythremia or other diseases of the hematopoietic system;
- disruption of red blood cell production in the bone marrow;
- disruption of the normal functioning of the adrenal glands;
- disorders of the respiratory system, respiratory diseases (rhinitis, bronchitis, asthma, lung diseases);
- obesity degree III or IV;
- pulmonary hypertension (persistent increase in pressure in the pulmonary vessels);
- lack of vitamins or enzymes.
The most serious and terrible diagnosis in which red blood cells in a child’s blood can be elevated is cancer of the kidneys or liver.
In any case, you should not sound the alarm as soon as elevated red blood cells are detected in a child; this is by no means a diagnosis, and any conclusions should be made by a doctor only after a thorough examination and monitoring of the state of hematopoiesis.
And in this case, parents are recommended to let their child drink as much liquid as possible (up to 1.5 liters per day), the main thing is that the water is of high quality and without harmful impurities, you should also monitor the children's diet so that it is rich in various types of fruits and vegetables In addition, children should not be exposed to stressful situations and should not be allowed to spend a long time at the computer and experience prolonged mental and physical stress.
Health to your children!
Signs and symptoms
Erythrocytosis most often occurs asymptomatically due to physiological reasons for its occurrence.
In the presence of various serious diseases, an increase in the concentration of red cells has obvious symptoms:
- Prolonged vomiting or diarrhea.
- Change in skin color. It can be painted in: red; Blue colour; crimson color. Skin staining can be localized or localized. The mucous membranes with erythrocytosis also have an abnormal color.
- Constant headaches due to poor blood circulation. When the blood cell count is high, the viscosity of the blood increases.
- Pain in the limbs. In children, this symptom often manifests itself as pain in the fingers and toes due to a lack of oxygen in the tissues.
- Pain in the spleen due to its enlargement. This organ is responsible for processing blood cells. With a high concentration of red blood cells, it is subject to heavy loads, which leads to a change in its size.
- Constant high blood pressure. This symptom is characteristic of renal abnormalities.
- Deterioration of vision as a result of high blood pressure.
- Frequent and sudden dizziness.
- The child constantly feels tired and sleepy.
Any of the listed symptoms does not indicate a specific disease, so a thorough examination of the entire clinical picture by a pediatrician and collection of additional information is required.
The role of red blood cells in health and development
If we notice the consequences of the complete absence of lymphocytes and platelets in the blood only after some time, then without red blood cells our body will die in a few seconds.
Men's blood contains slightly more red blood cells than women's. And for the body of infants, whose characteristic feature is rapid somatic growth, their normal content is significantly, sometimes two to three times higher than that of adult organisms. In middle-aged children, the content is normally at the level of adult organisms.
Quite often, a decrease in the content of red blood cells occurs for natural and everyday reasons. For example, very often a high level is observed during natural dehydration of the body. It is observed with the onset of hot weather, during long-term physical training in children who engage in high-speed sports - that is, when large volumes of liquid begin to evaporate through the skin. For the tests to return to normal, it is enough to provide children (including infants) with plenty of fluids for several days. There is no need to fear that the indicators will become too low as a result; this is not observed in practice.
The situation with elevated red blood cells is observed due to active or passive smoking, since the smoke generated during the combustion of tobacco contains a significant amount of carbon dioxide, which acts as the antipode of oxygen. As a result, the body has no choice but to increase the hemoglobin content in the blood to ensure a normal level of oxygen supply to the tissues. That is, the cause of the problem in the baby may be a smoking mother.