Norm (reference values) concentration of vitamin B 12
It is determined whether the vitamin B12 norm is increased or decreased based on internationally accepted indicators. The table below shows the norm of vitamin B12 by age.
| from birth to 1 year | from 293 to 1207 ng/l |
| from 2 to 3 years | 264-1215 ng/l |
| from 3 to 6 years | from 245 to 1077 ng/l |
| from 7 to 9 years | from 279 to 1173 ng/l |
| from 10 to 12 years | from 183 to 1080 ng/l |
| from 13 to 18 years old | from 214 to 864 ng/l |
| In women and men over 18 years of age | from 200 to 1000 ng/l |
There are other interpretations, for example, in adults the vitamin level should not exceed 187-883 pg/ml (“Invitro”).
What kind of substance?
Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble substance that is essential for good health. It has a complex structure; scientists have not yet been able to synthesize the molecule artificially. Vitamin B12 is not produced in human organs; its source is foods, mainly meat and dairy products.
Advice! Newborn babies receive vitamin B12 from their mother's milk. Women's breast milk contains the substance in its most easily digestible form.
The intake of vitamin from food is carried out according to the following scheme:
- the vitamin forms a fragile complex with a special protein produced in the human stomach;
- in a complex form, it enters the small intestine, where it breaks down and the released vitamin is recombined with another type of protein that performs transport functions;
- the formed complex spreads throughout the body, entering organs and tissues;
- The metabolism of cyanocobalamin requires a lot of time; reserves in a healthy body, as a rule, last for at least a year.
Normally, vitamin B12 interacts with folic acid. Both of these substances are necessary to ensure the metabolic processes of carbohydrates, fats and proteins. With a lack of cyanocobalamin in tissues, negative consequences are noted in:
- bone marrow;
- Gastrointestinal tract;
- mucous membranes of the mouth, tissues of the tongue.
As a result of a deficiency of the substance, the following is noted:
- impaired hematopoiesis, changes in blood composition, expressed in a decrease in the production of red blood cells;
- the appearance of malabsorption in the gastrointestinal tract;
- metabolic disorder;
- the appearance of ulcers in the mouth due to stomatitis;
- the appearance of neurological symptoms.
Deficiency of nutrients and vitamins during pregnancy is especially dangerous; this condition is equally dangerous for both women and the fetus.
Advice! A lack of vitamin B12 during pregnancy can lead to fetal developmental abnormalities. In women during pregnancy, this condition disrupts the stability of the nervous system.
The daily norm of cyanocobalamin is about 3 mcg, but women during pregnancy require more of the vitamin, for them the norm is 1 mcg more.
Indications for analysis
A blood test for vitamin B12 is performed for medical reasons in the following cases:
age over 60 years;
veganism for several months;
vegetarianism for several years (remember, vegans adhere to a more strict diet, eating only products of plant origin. Vegans do not drink milk, kefir, do not eat cottage cheese, cheese, yoghurts, etc. based on cow’s milk, and do not eat eggs). Therefore, their risk of hypovitaminosis is higher than that of vegetarians.
gastritis (atrophic);
chronic infectious lesions;
alcoholism in chronic form;
irregularities in the results of a general blood test;
neuropsychiatric disorders;
in the differential diagnosis of macrocytic anemia.
Also, a blood test can be carried out when there is a general deterioration in a person’s condition associated with exhaustion and anemia.
B12 sources
The main supplier of B12 is considered to be protein products of animal origin. Most B12 is found in veal liver, kidneys, octopus meat, mackerel, and rabbit meat. It is recommended to consume dairy products. Introduce cheeses into your diet. There is much less of this element in plants. Its maximum content is in algae (kelp or blue-green), brewer's yeast, tofu soy cheese and miso sauce.
There is also synthetic cyanocobalamin, created in laboratory conditions. Available in the form of tablets, capsules, ampoules (intravenous injections). It is used to replenish the body in case of a lack of substance. You should use a synthetic product after consulting your doctor.
How does vitamin deficiency manifest itself?
When the substance is deficient, a person develops characteristic symptoms, which is a signal for a blood test. The following symptoms suggest you suspect B12 deficiency:
excessive fatigue;
frequent headaches;
frequent dizziness;
sleep disorders - some experience excessive sleepiness, while others experience insomnia;
absent-mindedness, which is often noticed by the patient himself;
cardiopalmus;
shortness of breath, even with slight exertion;
specific neurological disorders: gait disorders, especially in the dark, when you cannot see your legs. This is called sensory ataxia. The reason is damage to the posterior columns of the spinal cord, which carry joint and muscle sensitivity. The performance of purposeful movements worsens, and pain may appear.
For more information about vitamin deficiency in the body, read the article Vitamin B12 deficiency: symptoms in adults.
The analysis reveals how low the vitamin level is and suggests the main cause of the pathology. Next, additional examination is carried out to make a final diagnosis and treatment.
Why do a blood test for cyanocobalamin levels?
In its action, cobalamin is in close relationship with folic acid and is involved in metabolic processes, the breakdown of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Lack of the element for a long time leads to changes in proliferating cells (tongue, oral cavity, brain cells, gastrointestinal tract). As a result, hematopoietic processes are disrupted, and stomatitis, glossitis and intestinal malabsorption may develop. Also, in case of B12 deficiency, the following consequences are possible :
- Megaloblastic anemia.
- DNA synthesis failures.
- Violation of the division and maturation of red blood cells, as well as a decrease in their volume.
- Development of panitopenia.
- A decrease in methionine levels, which often leads to mental disorders and dysfunction of the spinal cord.
Blood levels of B12 decline with age , often leading to neurological disorders. As mentioned, due to a deficiency of cyanocobalamin, homocysteine accumulates in the body, which leads to the development of another disease - atherosclerosis.
Cyanocobalamin itself is involved in the production of methionine and choline, has a beneficial effect on liver function, and acts as a prophylactic agent in the development of fatty hepatosis.
A vitamin B12 blood test is also important for infants. Megaloblastic anemia develops when there is a genetic disorder in the enzymes used to convert cyanocobalamin into the coenzyme, or when the volume of the carrier protein is low. It manifests itself after a few weeks or months of childbirth with slightly reduced cobalamin levels. If the cause of anemia is a violation of the processes of absorption of nutrients in the gastrointestinal tract, then the volume of cyanocobalamin decreases sharply.
A decrease in vitamin levels is also dangerous for the nervous system. In this case, the problem manifests itself as tingling in the limbs and loss of sensitivity. With a deficiency of cyanocobalamin, the immune system may be weakened, as well as a decrease in bactericidal function.
A cobalamin test is a chance to promptly diagnose malnutrition, impaired absorption of nutrients in the gastrointestinal tract, or macrocytic anemia. If the test is done in old age, then the results obtained are an opportunity to determine changes in mental state, namely the risk of developing paranoia, irritability and depression.
Donating blood for vitamin B12 is recommended for anyone prone to deficiency of this element. Thanks to the test, it is possible to control the concentration of the substance and determine treatment in a timely manner. People who have congenital problems with the absorption of cyanocobalamin also face this need.
If the absorption of vitamin B12 is impaired, the norm in the blood decreases. In this case, the factors on which the absorption of the vitamin depends should be taken into account:
- Condition of the mucous membrane of the ileum.
- Production of intrinsic factor Castle in the stomach.
- The state of microflora in the intestines.
- The presence of transcobalamin in the blood in a volume sufficient to transport B12 to the cells.
In practice, it is the insufficient absorption of cyanocobalamin that leads to vitamin deficiency. Also, the reason may be old age, lack of vitamin during pregnancy and refusal of food of animal origin.
Causes of elevated vitamin levels
An increase in vitamin B12 in the blood occurs for several reasons and is most often asymptomatic. Pathology is usually detected during a general examination of the patient regarding the underlying disease. An increase in vitamin levels is usually caused by:
liver diseases;
heart failure;
oncology of the hematopoietic system;
renal failure;
Excessive production of transport protein by the small intestine.
A doctor's supervision is needed in this condition, but, compared to a deficiency of the substance, the condition is not considered severe. Exceeding the norm is a symptom of concomitant diseases that require treatment, and an artificial decrease in the B12 indicator is not required.
Causes of deficiency and symptoms
Most often, the cause of a deficiency of this vitamin is a deficiency of another equally important component of the same group - vitamin B6. The second allows B12 to be absorbed faster, since this process is quite complex.
Vegetarians are most susceptible to lack of this vitamin. These people eat foods of plant origin, which contain fairly small amounts of cobalamin. Most of it is found in red meat, various types of fish, as well as animal liver and kidneys.
Deficiency can occur when the gastrointestinal tract does not function properly. For proper absorption, it is necessary that the mucous membrane lining the inner surface of the stomach is not damaged. By connecting with it, cobalamin begins to be absorbed. It is deposited in the liver, and after some time the excess is released into the intestines, from where it again moves into the blood.
It would seem, where could a deficiency of a vitamin of this group arise if it replenishes itself? But cobalamin deficiency is nevertheless common. The cause may be taking medications that disrupt the intestinal microflora. Most often, people with a disease such as diabetes suffer from this point. In older people, absorption is even worse, and therefore problems with cobalamin deficiency are common among them.
Oxygen is delivered to many human tissues and organs through red blood cells, in the creation and division of which cobalamin ideally participates, but in case of its deficiency this cannot happen. A person begins to feel constant fatigue, despite the fact that he has done practically nothing. Even a good sleep cannot save the situation. However, this is not the only cause of fatigue.
In addition to fatigue, a person begins to feel weakness in all parts of the body, movements become sluggish and lazy. At the same time, you shouldn’t immediately blame vitamin deficiency, since this can be a normal person’s condition after a hard day at work. A lack of vitamin can manifest itself through numbness and tingling of the extremities. In some cases, situations occur when patients report that they feel as if they are being pierced by an electric discharge.
Memory lapses appear and concentration is lost. Sometimes dizziness occurs (especially in old age). Due to a deficiency of red blood cells, fewer are produced or the pigment in them is destroyed. The main role in this case is played by bilirubin, which has a yellow tint, which makes the skin appear much paler than it should be.
Unpleasant sensations arise on the tongue: it begins to ache and itch on the sides. Food loses its taste, and therefore a person wants to eat less, which is why weight begins to drop significantly. Frequent mood swings may also indicate a cobalamin deficiency. Vision deteriorates, a feeling of double vision appears, and shadows appear.
How to prepare for analysis
To obtain reliable results from a B12 blood test, you need to properly prepare for collecting the material. The picture of the normal level of a substance in the blood is influenced by many factors.
You must donate blood in the morning, observing the following requirements:
abstinence from alcohol 3 days before the test;
quit smoking 12 hours before the test;
refusal of physical activity the day before the analysis;
refusal to take medications with the doctor’s permission 2 days before blood sampling - when this is not possible, you should inform the laboratory in advance where the material will be tested;
refusal to eat 12 hours before the test.
Before submitting the material, you can drink only clean, still water. Any drinks are prohibited, as they significantly change the blood picture.
The material for research is taken from a vein. If no additional analysis is performed, then 5 ml of blood is enough.
Preparation
In order for the vitamin B12 test to go smoothly, you need to prepare properly. Many factors can affect the overall picture; you need to take maximum care.
To ensure clean and informative results, the patient must:
- do not drink alcoholic beverages (even at low levels) for 3 days before the procedure;
- do not smoke for 12 hours;
- do not play sports or expose yourself to any physical activity;
- do not take medications for 2 days, and if you have chronic diseases and have to take medications constantly, be sure to inform the laboratory about this;
- do not eat for 12 hours and come to the clinic on an empty stomach;
- do not drink chemical drinks, only clean water without gas with a volume of no more than 100 ml is allowed.
These requirements apply to any blood test. It is not difficult to comply with them, but you can be sure that third-party factors will not affect the result.
Deficiency Symptoms
Manifestations of vitamin B12 deficiency are not immediately noticeable, since liver depots can replenish physiological losses over several years. Symptoms are often disguised as exacerbations of existing diseases or are attributed to age (memory impairment or shortness of breath).
Manifestations
- increased fatigue
- headache and dizziness
- drowsiness or insomnia
- absent-mindedness
- shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat
- severe pain in arms and legs
A laboratory sign of vitamin B12 deficiency is megaloblastic or macrocytic (pernicious) anemia with typical changes in a general blood test:
- decreased red blood cell count
- decreased hemoglobin levels
- increase in the average size of a erythrocyte - MCV index, the average concentration of hemoglobin in an erythrocyte - MCHC, the average amount of hemoglobin in one erythrocyte MCH
- shift of the leukocyte formula to the right - the appearance of a larger number of old leukocytes
Neurological disorders
They occur only with a deficiency of vitamin B12; with a lack of folic acid, they do not exist. Funicular myelosis
- a degenerative disease of the posterior and lateral cords of the spinal cord, which gradually “rises” to the cerebral cortex, part of the neuroanemic syndrome.
Methylmalonic acid (MMA) accumulates and destroys myelin, the insulating sheath of nerve fibers.
Symptoms of funicular myelosis
- constant painful feeling of tingling and “crawling” in the arms and legs (rises from the feet to the knees and thighs, from the palms to the shoulders)
- deep sensory disorder
- gait disturbances
- muscle spasticity
- irritability, psychosis, dementia
- decreased visual acuity
Stages of vitamin B12 deficiency
- I - the level of cobalamin in cells is reduced
- II - decreased level of vitamin in the blood, early consequences of a negative balance - increased homocysteine, reduced rate of DNA synthesis
- III - visible metamorphoses in the blood, at the same time reversible changes in the nervous tissue
- IV - irreparable changes in the structure of nerve fibers
Why does a woman’s body need vitamin B12?
There is no vitamin in nature that, when introduced into the body, does not have an effect on humans. Every woman needs B12. The body can independently synthesize this component, but only in small quantities. For proper functioning of all organs, supplementation in the form of food or medicine is required.
Important! A woman's daily requirement of B12 increases during pregnancy.
This is explained by the fact that this component is required for the correct occurrence of various chemical reactions. The benefits of vitamin B12 for women are as follows:
- Creation of DNA links. If the concentration of this compound is insufficient, the process of information transfer between chromosomes suffers.
- The component is involved in brain development. Without B12, cells will not be able to divide, which will cause disruption of all body systems.
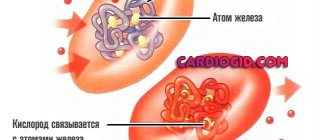
- To stimulate the synthesis of red blood cells, which are involved in the process of oxygen transport. When blood circulation is impaired, tissues do not receive enough energy.
- B12 protects liver cells from the effects of toxic substances. This includes drug components, alcoholic beverages, drugs and viruses. Also reduces the risk of gallstone formation.
- To protect the walls of vascular tissues, reducing the likelihood of blockage.
- B12 helps normalize the rhythm of the heart and also strengthens muscle tissue.
- The component stimulates the regeneration of bone marrow cells. The compound helps form osteoblasts. For women during menopause, B12 reduces the risk of fractures. This is explained by the fact that an insufficient number of osteoblasts provokes the formation of cavities in the bones.
- For women, the vitamin helps fight diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
- To eliminate allergy symptoms.
- The component enhances the protection of mucous membranes.
- Helps fight wrinkles, paleness and dry skin. Prevents the appearance of age spots.
We recommend reading: The best vitamins for women over 40: reviews, names, which ones to choose
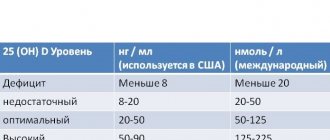
Norm
| Children | ng/l | pmol/l |
| 0-1 | 293-1207 | 216-891 |
| 2-3 | 264-1215 | 195-897 |
| 4-6 | 245-1077 | 181-795 |
| 7-9 | 271-1173 | 200-863 |
| 10-12 | 183-1080 | 135-803 |
| 13-18 | 214-864 | 158-638 |
| adults (men and women) | 200-1000 | 148-738 |
ng/L x 0.738 = pmol/L
Remember that each laboratory, or rather laboratory equipment and reagents, has its own standards. In the laboratory test form they appear in the column - reference values or norm.
B12 in the blood: norm by age (table), reasons for increase and decrease
From the article you will learn the norms of vitamin B12 in the blood, the daily requirement, the causes of deficiency and excess of the substance, methods of correction and prevention of deviations.
The importance of cyanocobalamin for the body
Vitamin B12 is the only vitamin that contains the trace element (cobalt). Essentially, B12 is a combination of two cobalamin molecules: cyanocobalamin and hydroxocobalamin.
The main task that cobalamin performs in the body is to participate in the synthesis of red blood cells and their further development.
Red blood cells are responsible for the process of hematopoiesis and cell division, which ensures the formation of DNA and the formation of immunity.
Without B12, the nervous system cannot function normally; it controls stress, depression, psycho-emotional stress, and has a mild sedative effect.
Cobalamin stimulates the regeneration of skin cells and mucous membranes, which is very important for violations of the integrity of tissues of any origin. In children, B12 normalizes appetite, improves concentration and memory.
Cobalamin has other beneficial qualities:
- participates in the formation of nerve fibers;
- controls fat and carbohydrate metabolism;
- plays a role in energy supply to the body;
- prevents anemia;
- improves cerebral blood flow;
- prevents fatty liver hepatosis by stimulating choline synthesis;
- activates muscle growth;
- controls the functions of the spinal cord.
B12 can be used to treat polyneuritis, psoriasis, diseases of the digestive system, joints, radiation sickness, and anemia of various origins.
Daily value of vitamin B12 for adults and children
The intake level of vitamin B12 is determined in each country separately by national nutrition committees and ranges from 1 to 3 micrograms per day.
In the Russian Federation, the level of vitamin B12 in the blood is correlated with age.
AgeNormal in ng/l
| Up to a year | 290-1200 |
| Up to three years | 260-1215 |
| Until 6 | 245-1075 |
| Up to 9 | 280-1170 |
| Up to 12 | 180-1080 |
| Before 18 | 215-865 |
| In adult women and men | 200-1000 |
Causes of deficiency and excess of vitamin B12
The level of vitamin B12 in the blood can fluctuate up or down for a variety of reasons.
The concentration of cyanocobalamin increases as a result of drug overdose, liver pathologies, leukemia, and high levels of transport protein - transcobalamin.
Low concentration of the vitamin is due to: vegetarianism, helminthic infestation, inflammation of the intestines, pancreas, low stomach acidity, taking antibiotics and sugar-lowering drugs (impaired vitamin synthesis), AIDS, genetically determined Imerslund-Gresbeck syndrome.
Indications for analysis for cyanocobalamin
Taking into account the reasons that cause fluctuations in vitamin B12 in the blood, tests are prescribed to determine its level for patients over the age of 60, with chronic atrophic gastritis, vegetarians, alcoholics who have had infectious, neuropsychiatric diseases, with suspected macrocytic anemia, and athletes.
If general biochemistry gives questionable results, a full clinical and laboratory examination is prescribed to identify the root cause of the pathological abnormality.
Preparing and taking the test
Pre-preparation for blood testing for B12 level is standard: blood is donated on an empty stomach, the last meal is 12 hours before the test, drinking water up to 100 ml is allowed, alcohol and physical activity are excluded three days before the test, smoking is prohibited 12 hours before the test, all medications, which the patient takes are agreed upon with the doctor.
Blood is usually taken from a vein, rarely from a finger. The results are assessed by comparison with standards. In this case, special indicators are used. The results are deciphered within 5 days.