You are here: Blood test -
Platelets -
Platelet distribution width
- Norms
- Carrying out analysis
- Deviations from the norm
- Possible symptoms
- Who to contact
The width of the platelet distribution is an additional clinical value that indicates the degree of platelet anisocytosis. It should be noted that the relative width of platelet distribution by volume is not considered an independent clinical indicator. The platelet distribution parameter and its norm are further deciphered if such distribution can be considered as one of the symptoms of the pathological process.
Like other laboratory values, the platelet population level may be elevated or decreased. If the norm is not met, this will indicate a certain pathological process. However, only a doctor can interpret the results correctly.
Relative low or high width of platelet distribution by volume does not have specific symptoms. The nature of the clinical picture will completely depend on the underlying factor, therefore, if you feel unwell, you should consult a doctor who will prescribe the necessary diagnostic tests, correctly interpret the results obtained, and on the basis of which he will prescribe treatment.
Norms
The normal PDW (platelet distribution index) for people under 18 years of age is 10–16%, but a slight upward or downward deviation is acceptable - no more than 1%. If the relative width of platelet distribution by volume is increased so much, this will be a sign of some pathological process.
For adults, the norm is 15–17%. A slight deviation is acceptable here - the platelet count may be increased or decreased by 2-3%.
PDW may be increased or decreased erroneously if errors were made during the analysis. Errors can be caused by the following factors:
- weak immunity;
- the patient has chronic diseases about which the doctor has not been notified and there are no entries in the medical history;
- unsatisfactory moral condition of the patient;
- incorrect analysis and/or improper processing of the material.
If the volume indicators are higher or lower than normal, a repeat analysis is prescribed to make sure there is no error.
Platelet distribution index
What to do if the platelet distribution index is elevated?
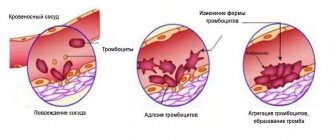
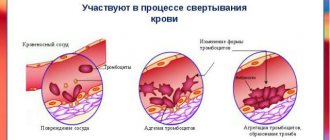
Platelets are the most microscopic blood cells that can stick together to form a blood clot. It is needed in cases where the integrity of a capillary, vein or artery is damaged. Thanks to platelets, damaged vessel walls are sealed from the inside, which prevents the development of full-scale bleeding.
One of the indicators of laboratory tests for platelet count is the PDW index. Thanks to this analysis, the width of platelet distribution is determined - an important indicator by which one can judge the presence of many diseases and pathologies. What standards have been established, and what standards are recognized, as well as the reasons and consequences of increasing the maximum permissible values, we will analyze further.
Norms and deviations from the norm
In a healthy person, the normal width of platelet distribution by volume is 15-17 percent. Deviations of 2-3 percent are acceptable , which are attributed to the following manifestations:
- the blood test was taken incorrectly (on a full stomach, in the presence of drug impurities);
- physical and moral condition of the patient;
- the presence of chronic inflammatory diseases.
For children, the norms are slightly different: under the age of 18, rates from 10 to 16 percent are acceptable, writing off 1% in each direction. Poor immunity and increased vulnerability of the body, as well as the presence of congenital pathologies, make this indicator less reliable when deciphering a blood test.
Based on the fact that the reliability of platelet distribution width indicators is influenced by the general condition of the body , in the presence of chronic diseases, noma indicators may vary.
The increase, dangerous to health, is fixed in the range of 19-20% or more.
In order to determine the width of platelet distribution by volume, it is necessary to take blood from a finger. Blood is added to a test tube with an anticoagulant, after which data for this indicator and many others are obtained using a special apparatus. To get the most reliable result, you need to prepare for the test in advance .
Indications for analysis
There are four cases when a complete blood count and identification of the PDW indicator is mandatory :
- When hospitalized, it is included in the mandatory list of tests required for the initial medical history.
- To monitor treatment, a blood test to determine the width of platelet distribution allows you to see the effect of treatment, or, on the contrary, to find out about its absence and the need to prescribe new drugs.
- An annual medical examination is a mandatory procedure not only for workers in all professions and industries, but also for children of all ages.
- In the presence of diseases of the circulatory system and suspected blood cancer, as well as for diagnosing inflammatory diseases.
Carrying out analysis
The indicator is determined by drawing blood. In order for the indicators to correspond to reality, the following must be taken into account:
- It is not recommended to take the test during the premenstrual period.
- The day before donating blood, you should avoid heavy physical activity and, if possible, avoid taking medications.
- Tests must be taken on an empty stomach; in the morning you can only drink a glass of water.
The determination of indicators is carried out using the Fonio method. The material for the study is blood obtained from a finger, mixed with a sterile solution of magnesium sulfate.
From the resulting material, a smear is made on glass, which is placed in special equipment. The automatic counter counts the number of different forms of platelets per 1000 red blood cells. Using a special formula, the percentage of the width of the distribution of blood platelets is calculated.
Reasons for the decline
A decrease in the number of platelets in a blood test indicates a high risk of bleeding due to low blood clotting. This must be taken into account in surgical operations.
A reduced PDW in a blood test occurs with myelodysplastic syndrome. This disease affects the bone marrow, where platelets are formed. Hepatitis provokes a decrease in PDW. In this case, the analysis will show increased bilirubin. Possible cancer.
An increased distribution of platelets in a child may be due to an inflammatory process. Also, the number of leukocytes in this case will be high.
Why deviation is dangerous and what to do
If the test result shows that the PDW does not meet the norm, the therapist will order you to take it again in different laboratories. If this is confirmed, then a comprehensive examination is prescribed. If the patient has additional symptoms, it is easier to make a diagnosis.
A reliable result is not only due to the patient’s good preparation, but also to the laboratory in which the blood is drawn. Poor quality reagents incorrectly determine blood composition. It is advisable to take tests in laboratories that have quality certificates and modern equipment.
Only a specialist should explain the result: there are many nuances in deciphering the PDW indicator. In some cases, the indicator is looked at in relation to other points of laboratory research.
Important information: How much ESR for oncology in an adult (table)
Possible reasons for deviation from the norm
Elevated parameters may indicate the following pathological processes:
- inflammation in the body;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- liver diseases;
- oncological processes, metastasis to the bone marrow;
- anemic syndrome;
- heavy metal poisoning;
- Alzheimer's disease.
The index will be increased due to the following factors:
- consequences of corticosteroid therapy;
- massive blood loss;
- postoperative period after removal of the spleen;
- excessive physical activity;
- recovery after surgery.
Reduced index values will indicate the following pathological processes:
- DIC syndrome;
- anemia;
- myelodysplastic syndrome;
- viral diseases;
- septic processes;
- radiation sickness;
- severe liver diseases.
PDW can be lowered temporarily as a result of taking certain medications, including cytostatics.
Increased rate
Too high a level of platelets in the blood leads to the risk of blood clots and blockage of veins. With a significant increase in the indicator (thrombocytosis), there is a direct threat to the patient’s life. In such cases, immediate hospitalization and the use of medication to thin the blood are required. After the platelets return to normal, the patient remains under observation for some time. Thrombocytosis is considered to be an increase in the indicator to a level (above 450 × 109/l), which can be caused by some serious diseases.
- Inflammatory processes in the body
- Infectious diseases
- Active growth of malignant tumors
- Serious physical trauma and damage lead to active production of lamellar blood cells
- Consequences of surgical operations
- Splenectomy
- Actions of some medications
With a slight increase in the number of lamellar cells in the blood, to normalize the indicator, it is enough to change the diet and prescribe a therapeutic diet under the supervision of a doctor. It is possible to use folk remedies. If the indicator increases significantly, the patient is prescribed drug treatment.
Possible symptoms
There will be no specific clinical picture. Symptoms will depend on the underlying factor; the collective symptom complex may include the following:
- weakness, increasing malaise;
- sleep cycle disturbance - drowsiness or, on the contrary, insomnia;
- dizziness, frequent headaches;
- nosebleeds may be present;
- decreased ability to work, apathy and irritability;
- unstable blood pressure;
- pale skin;
- hemorrhagic rashes;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases - will be accompanied by additional symptoms;
- nausea and vomiting;
- disruption of the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- symptoms of general intoxication.
This clinical picture can be present in almost any disease, so there is no need to self-medicate - you should consult a doctor for advice. The doctor will determine exactly what the relative width of the platelet distribution across the volume is.
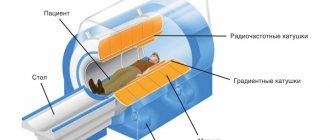
Blood test for PDW (platelet distribution by volume)
One of the most accessible and effective types of examination in medicine is a general blood test. It is the most common and is prescribed in almost all cases of visiting a general practitioner.
Changes in the composition of the blood make it possible to suspect the development of many diseases at the initial stage, as well as to establish the causes of certain symptoms. During a clinical analysis, the parameters of all blood cells are assessed.
Today there are more than 20 important indicators, among which is PDW. This is one of the platelet blood indices. The meaning of the abbreviation is the width of the distribution of platelets by their volume.
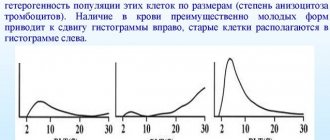
This indicator reflects the heterogeneity of the population of blood platelets in size and reflects the degree of anazocytosis - changes in cell size. That is, the platelets in the blood differ in size from each other, and the PDW analysis shows what percentage of the total number are micro- and macroplatelets.
Norm
The platelet volume distribution should normally range from 15 to 17%. Minor deviations are acceptable - 1-2%, which may be due to the individual characteristics of the organism.
How is the analysis carried out?
The PDW value is determined during a general blood test along with many other indicators. Blood is taken from the (ring) finger on an empty stomach in the morning. Whole blood with an anticoagulant is used for the study.
The result may be unreliable if the patient ate food before the analysis, is being treated with medications during this period of time, or underwent an X-ray examination or physical procedures the day before. In addition, the indicator may be higher or lower than normal during pregnancy, before menstruation, or after heavy mental or physical stress. In such cases, a repeat study is prescribed. To avoid distortion of the results, you should properly prepare for the analysis.
Nowadays, modern hematological analyzers are used for blood testing, which obtain up to 24 indicators. Determining platelet volume alone is not sufficient for effective diagnosis.
Normal hemostasis depends not only on the quantitative content of nuclear-free plates, but also on their functional indicators. Therefore, it is so important to study their quality characteristics, which is only possible on new equipment.
Hardware methods for studying blood elements have many advantages over manual ones:
- a large number of cells are examined - from 10,000;
- provide accurate results - without errors;
- all stages of the study are standardized.
With the help of modern blood analyzers, histograms are obtained - a graphical representation of the results in the form of thrombocytometric curves.
The importance of this study is due to the fact that the size of platelets determines their functionality, the change in their volume before gluing the plates in the process of clot formation, as well as the tendency to adhesion and the content of bioactive substances in anucleate cells.
Hardware blood testing methods allow you to get accurate results in a shorter time
If there are predominantly young platelets in the blood, the histogram is shifted to the right, old platelets are located on the left of the graph. Thus, platelet volume decreases as platelet aging occurs.
Analysis transcript
Interpretation of the results is the responsibility of the attending physician. Deviation of PDW from the norm indicates a violation of the size of the population of anucleate cells.
An increase in this indicator may be associated with the presence of microerythrocytes, erythrocyte fragments, and platelet aggregates. Changes in PDW can be observed in myeloproliferative diseases.
This group includes the following pathologies:
The PDW platelet distribution index helps identify the following pathologies:
- inflammatory diseases,
- anemia,
- parasitic infections (helminthic infestations),
- malignant diseases,
- condition of the walls of blood vessels.
The value of the platelet index is not considered separately, but only in conjunction with other indicators.
Conclusion
A general blood test makes it possible to evaluate both the quantitative content of its components and the quality of the formed elements. The study of the platelet fraction of blood is an important component of the analysis of the coagulation system. This requires a whole range of specific tests.
Additional indicators make it possible to evaluate the morphological characteristics of nuclear-free plates and their functional activity. One of the important parameters in diagnosis is the platelet index PDW, or relative volume distribution width.
If this indicator is higher or lower than the normal value, it is possible that an inflammatory process or other diseases are developing in the body.
Source: https://icvtormet.ru/krov/analiz-krovi-pdw-raspredelenie-trombocitov-obemu
Increased platelet distribution index - what does this mean and what to do?
Hospitalization of the baby is necessary only in the most extreme cases. If the cause is not oncology, treatment is carried out using conservative methods:
- nutrition correction;
- taking medications;
- compliance with the daily routine.
The medicinal part of treatment may include drugs with the following spectrum of action:
- for blood thinning;
- to reduce platelet production;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- vitamin and mineral complexes.
Be sure to exclude from your diet foods that produce this blood component. You should add foods that are rich in vitamin B6 and magnesium to your menu. It is necessary to monitor the drinking regime - the child should be given clean water, herbal decoctions, juices and compotes.
Decoding
Many people ask what PDW is in a blood test and who interprets the test. The doctor must decipher the PDW blood test. PDW may be normal, elevated, or decreased.
A normal index occurs when the number of old and young cells is the same. This index occurs in healthy people. If the indicator is elevated, then their number has sharply increased, and a large number of young and old cells are contained.
This happens with bone marrow pathologies or other diseases.
An increased value of the indicator is determined in cancer, iron deficiency, and inflammatory processes. This result occurs with infectious diseases or when the patient uses hormonal drugs. A decreased PDW indicates that there are more old particles, which may indicate bone marrow disease, viral diseases, or certain medications.
When doctors decipher the result, sometimes the study shows that a person has too large platelets, which indicates the presence of disturbances in the functioning of the immune system or Bernard-Soulier disease.
Increased level
An increase in the indicator indicates heterogeneity in platelet volume. This can cause the development of pathologies in the body. In patients, blood vessels gradually become clogged, blood circulation is disrupted, and metabolism slows down. Heart disease gradually develops.
An increase in PDW occurs:
- For anemia. The process causes oxygen starvation, which contributes to a change in cell volume.
- For bleeding after surgery.
- With the development of neoplasms and inflammatory processes.
- If, in addition to an increase in PDW, an increased number of leukocytes is noted, then the doctor diagnoses inflammation.
Distribution width is higher than normal
The indicator is highly lable, so the slightest pathology of the body changes the percentage of PDW.
The main reasons for increased platelet indices are:
- Any type of inflammation. This cause can be suspected if, in addition to increased heterogeneity, there is a high ESR and leukocytosis (signs of inflammation).
- Anemia. An increase in the indicator should be associated with a decrease in hemoglobin and the number of red blood cells.
- Malignant formations. It is assumed that the index increases when the metastasis process is activated. Platelets help with this through thromboembolism. They spread cancer cells.
- Blood loss (operative, traumatic, menstrual). The bone marrow actively produces cells and many young forms appear.
- Thrombocytopathies, thrombocytopenia associated with impaired immunity.
- Other causes include heavy exercise, sports, overeating, pregnancy and medications. Therefore, if the doctor sees a deviation from the PDW norm, but other indicators are normal, then there is no need to sound the alarm. It can be changed for a trivial reason. Over time, the numbers return to normal.
What to do if the platelet distribution index is elevated
Platelets are the most microscopic blood cells that can stick together to form a blood clot. It is needed in cases where the integrity of a capillary, vein or artery is damaged. Thanks to platelets, damaged vessel walls are sealed from the inside, which prevents the development of full-scale bleeding.
One of the indicators of laboratory tests for platelet count is the PDW index. Thanks to this analysis, the width of platelet distribution is determined - an important indicator by which one can judge the presence of many diseases and pathologies. What standards have been established, and what standards are recognized, as well as the reasons and consequences of increasing the maximum permissible values, we will analyze further.
In a healthy person, the normal width of platelet distribution by volume is 15-17 percent. Deviations of 2-3 percent are acceptable, which are attributed to the following manifestations:
- the blood test was taken incorrectly (on a full stomach, in the presence of drug impurities);
- physical and moral condition of the patient;
- the presence of chronic inflammatory diseases.
For children, the norms are slightly different: under the age of 18, rates from 10 to 16 percent are acceptable, writing off 1% in each direction. Poor immunity and increased vulnerability of the body, as well as the presence of congenital pathologies, make this indicator less reliable when deciphering a blood test.
Based on the fact that the reliability of platelet distribution width indicators is influenced by the general condition of the body, in the presence of chronic diseases, noma indicators may vary.
It is necessary to prepare for the test in advance
When thrombocrit is low
A decrease in PCT occurs when the production of platelets or platelet precursors, which are megakaryocytes, is blocked. With a decreased PCT, there is a tendency to bleed.
This indicator is reduced during pregnancy. The drop in thrombocrit in women can be 2 times lower than normal, but during pregnancy this reduces the risk of thrombosis, and means that blood circulation and fetal nutrition will not be affected.
PCT decreases in conditions caused by:
- anemia - folate deficiency, aplastic, megaloblastic;
- autoimmune diseases – systemic lupus erythematosus, collagenosis;
- chronic diseases of the liver, kidneys;
- poisoning by poisons, drugs - diuretics, cytostatics, antibiotics, corticosteroids;
- chemotherapy;
- oncological diseases - hemoblastosis, leukemia.
When the thrombocrit is lowered and is less than 0.11%, then in adults this indicates a disorder of hematopoiesis in the bone marrow or an acceleration of the breakdown of platelets in the spleen.
A low PCT thrombocrit in a child’s blood test may be explained by:
- in infants - prematurity, low birth weight, hypoxia;
- in a child of an older age group – parasitic infection.