A modern diagnostic method with visualization, which can be used to obtain a detailed image and morphological picture of the structures of organs and tissues (including the abdominal cavity), is called magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This study allows us to identify structural changes in organs and tissues that cannot be determined using ultrasound or CT.
Magnetic resonance imaging helps to identify various inflammatory processes, infectious diseases, and oncological formations. Digital images can be saved to a computer for closer examination. Let's look at what organs are checked on an MRI of the abdominal cavity.
What organs are included in an abdominal MRI?
Magnetic resonance scanning of the abdominal organs makes it possible to examine the following organs located in the abdominal cavity:
- liver;
- gallbladder and its ducts;
- pancreas and ducts;
- spleen;
- kidneys;
- adrenal glands;
- lymph nodes;
- soft tissue lining the abdominal cavity.
Image of abdominal organs
Images obtained using a magnetic resonance imaging scanner make it possible to determine the structure, location and pathological changes in these organs. Obtaining a layer-by-layer image makes it possible to examine the entire organ and identify the slightest pathological foci.
What it is?
CT is a modern study based on x-rays , during which the scanned organs are displayed in images. Unlike a typical X-ray machine, a tomograph allows you to obtain more informative images, from which you can not only detect a pathological focus, but also identify its exact location and determine its size.
CT principle
Computed tomography capabilities
During scanning, X-rays pass through tissue and are captured by special sensors and transformed into an image. A computed tomograph is more complex than a conventional x-ray, which greatly expands its diagnostic capabilities.
Advantages of CT:
- Three-position scanning - this allows you to obtain detailed images of the pathological focus without “overlapping” the images on top of each other, as with an x-ray. When viewing in a special program, you can change angles along three axes, which cannot be done with ultrasound.
- Great diagnostic capabilities - CT produces layer-by-layer sections, from which it is easy to determine the size of the pathological focus. When working in the program, you can select the measurement option and obtain data on the width of the cavity or channel down to a hundredth of a millimeter.
- Possibility of studying hollow organs - the use of contrast allows you to obtain a clear image of soft tissues and blood vessels.
Safety of the procedure
CT scanning is often prescribed to diagnose abdominal diseases because this method:
- does not require special preparation;
- carried out quickly;
- painless;
- informative;
- accessible.
Help Unlike X-rays, CT scans expose the body to more radiation.
But single dosages are safe, and clear images are often enough to make a final diagnosis after a single examination. more about the harm caused to the body during a CT scan and the radiation dose received by a person from this article.
Indications for MRI of the abdominal cavity
MRI can be performed both for the primary diagnosis of diseases and to clarify the diagnosis identified using other, less advanced research methods. Magnetic resonance imaging is carried out if it is necessary to clarify or confirm a previously made diagnosis, if it is impossible to anticipate the pathology using ultrasound, as well as if the presence of a tumor is suspected.
Magnetic resonance imaging has also proven itself in diagnostics:
- possible hemorrhages in the abdominal cavity caused by injuries or diseases;
- stones in the gall bladder and ducts;
- accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- damage and diseases of the liver, spleen and pancreas;
- congenital anomalies of organ development.
Magnetic resonance scanning is also used in preparation for surgery in the abdominal area.
How often can an MRI be done?
For patients coming for an MRI for the first time, a key question arises: “Is MRI harmful to the body and how often can it be done?” Science to date does not provide information about the harm to humans from MRI. Many years of medical practice do not confirm the presence of harmful consequences from magnetic resonance exposure. However, undergoing diagnostics more than 2-3 times a day theoretically harms the patient, especially if contrast is used, because this chemical can cause intoxication in the body and cause severe damage to the kidneys. Science does not yet know what effect MRI has on the fetus of the child and his mother. Therefore, in order to be on the safe side, doctors are in no hurry to subject women in early pregnancy to tomography; this will reduce the risk of developing pathologies in the fetus. There are no restrictions on the number of procedures with MRI, unlike CT. MRI is an absolutely painless procedure without radioactive radiation, which means it can be performed as long as necessary without causing harm to the body, even the smallest child. When choosing an MRI of the abdominal cavity, you give preference to the most effective and informative research technique, with which you can monitor various types of internal diseases. And a scrupulous preparatory program for the procedure ensures a reliable diagnosis for the patient! Take care of your health, if discomfort occurs, you should immediately consult a doctor, refuse self-medication!
- MRI of the intestine, pros and cons of the method
- CT diagnostics, or what is computed tomography?
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the cervical spine
- CT and MRI - what's the difference?
- Magnetic resonance imaging or MRI
What is revealed during an abdominal MRI examination?
Thanks to its unique accuracy, magnetic resonance imaging allows you to see a whole range of diseases and identify abnormalities in the functioning of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space.
Installed in a modern Philips Intera 1.5 Tesla tomograph, it is capable of diagnosing the following pathologies:
- Benign and malignant tumors of the abdominal organs.
Tomography can accurately determine the nature of the tumor. The contrast agents used for research stain benign and malignant tumors with different intensities. The malignant tumor grows into surrounding tissue and has jagged edges - these features appear on MRI scans.
- Metastases and enlarged lymph nodes.
With widespread cancer, metastases can occur in the abdominal cavity. It is quite difficult to identify them, since they can be located not only on the surface of the internal organs, but also grow into them or be localized in the soft tissue of the peritoneum (omentum and mesentery). It is extremely difficult to detect enlarged lymph nodes in this area. Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to see even the slightest malignant foci located in hard-to-reach places that cannot be visualized using other diagnostic methods.
- Liver lesions.
Diseases such as fatty hepatosis, cirrhosis, and hepatitis are primarily diagnosed using ultrasound. Using a magnetic resonance imaging scanner, you can get a more detailed picture of the damaged organ.
- Pathologies of the gallbladder and ducts.
The presence of stones is usually clearly visible using ultrasound. MRI, as a more advanced type of diagnostic study, is used when it is important to examine the lumen of the ducts, determine the size and location of the gallbladder, assess the condition of the mucous membrane lining the ducts and gallbladder, and the possible presence of cysts and polyps. For the most detailed examination of the ducts, MR cholangiography can be used.
- Condition of large vessels of the abdominal cavity.
MR images show the condition of the abdominal aorta, hepatic vein and other large vessels. The images may help identify an aneurysm or ischemia. For targeted examination of blood vessels, MR angiography using a contrast agent is usually prescribed.
- Enlarged spleen.
An increase in the size of the spleen can occur in a number of diseases. For a detailed diagnosis of the organ, magnetic resonance imaging may be prescribed.
- Kidney pathologies.
MRI displays the structure of the kidneys, changes in their structure caused by diseases such as polycystic disease and pyelonephritis.
Contraindications for MRI
According to doctors, MRI of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space is a relatively safe diagnostic method, which is prohibited in certain cases. The study is contraindicated if the patient has metal prostheses or a pacemaker. The procedure is not carried out if the patient’s weight is higher than indicated in the device’s operational passport.
Pregnant patients may not be allowed to undergo MRI. At least this applies to women up to 13 weeks of pregnancy.
The doctor decides to conduct a study if the patient is diagnosed with chronic kidney disease, multiple myeloma (plasma cell tumors). The procedure is questionable if the subject is allergic to the contrast solution. MRI is also not recommended during lactation. If there is an urgent need, the test is carried out on a nursing mother, after which she is prohibited from breastfeeding a newborn for 2 days. Otherwise, the likelihood of an allergy in the baby to the components of the contrast agent increases.
Advantages of MRI in the study of abdominal organs
To examine internal organs, along with MRI, CT (computed tomography) and ultrasound (ultrasound) are also used.
Each of these methods has its own indications and contraindications:
CT allows you to obtain a detailed picture of the structure and location of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity only with the use of a contrast agent, which significantly increases the cost of the study. MR diagnostics of the abdominal organs is quite informative even without the use of contrast. Contrast agents used for MRI are much easier to tolerate by the patient's body than similar drugs for CT.
Magnetic tomograph Philips
CT is more appropriate to use for studying hollow organs: the stomach, intestines, veins and arteries of the abdominal cavity, as well as in cases where there are objective contraindications to magnetic resonance imaging.
MRI is a safer technique than CT. It does not use X-rays, and magnetic waves are absolutely harmless to humans.
Ultrasound is usually prescribed as the first choice test for pain and discomfort in the abdominal area. MRI is preferable to ultrasound when blood, urine and physical examination of the patient raises suspicion of the presence of neoplasms or when abnormalities in the structure and location of organs need to be examined in detail
How much does the procedure cost?
The research is expensive. On average, the price of a survey tomography of the abdominal cavity ranges from 5-9 thousand rubles. If a contrast study is necessary, the cost of diagnosis doubles and in some private medical centers reaches 15 thousand rubles.
It is possible to carry out free diagnostics on a planned or emergency basis if you have a policy and direct indications and a doctor’s referral. Referrals for diagnostics are issued by oncologists, cardiologists, nephrologists, urologists, surgeons and other specialists.
The MRI procedure of the abdominal cavity is a modern, highly informative diagnostic method. It helps to identify many pathologies of the abdominal organs, as well as the retroperitoneal space.
If necessary, it is possible to build a 3D model, which helps determine the tactics of surgical intervention. A dynamic study can determine the course of the disease (progression or regression) and the effectiveness of therapy. The main disadvantage is the cost of the procedure.
Preparing for an MRI of the abdominal organs
The procedure is carried out on an empty stomach. Fasting is required for at least 6 hours before the test. The day before, you should try to exclude foods that contribute to the formation of gases in the intestines, as well as foods high in fiber.
It is also highly advisable to refrain from drinking liquids, chewing gum and smoking. All this will help relax the gallbladder, which will improve the visualization of its structure and possible pathologies.
Is contrast needed when performing an MRI of the abdominal organs?
An MRI examination gives a clear picture of the location and structure of the abdominal organs. Contrast is used when an even more detailed examination is necessary. In the presence of tumors, metastases and suspicion of them, intravenous administration of a contrast agent is used.
Dynamic contrast enhancement is often used to diagnose abdominal organs. The scan begins without contrast and then, at a certain point in the procedure, dyes are injected.
This technique allows you to evaluate how quickly and evenly the tissues are stained, which is important when assessing the malignancy of a neoplasm.
Research standards and interpretation of results
To find out exactly what results were obtained as a result of the MRI, you will need to decipher the examinations obtained. Even for an experienced specialist this will take at least a couple of days. It happens that after a tomography, a specialist can only report preliminary results and only after the required period has passed, a final diagnosis will be made. Sometimes the image shows abnormalities even in organs that at first glance appear healthy and normal in size. There are a number of indicators that are taken as a basis when conducting research. These include:
- there are no signs of infection or inflammation;
- the internal organs of the abdominal cavity must be within existing standards and correctly located;
- blood vessels function correctly and do not have any developmental disorders;
- the patient does not have malignant or benign formations;
- the patient does not suffer from blockage of the ureters;
- the ducts of the liver and gallbladder are not blocked;
- no abnormal bleeding or fluid accumulation;
- There are no obstructions to blood flow, and the patient does not have a vascular aneurysm.
If everything is normal in the patient, then we can say that there are no pathologies during MPR.
Contraindications for MRI of the abdominal cavity
Despite the modernity and safety of the MR scanning technique, the procedure is not without contraindications.
Research is strictly prohibited for people:
- having a pacemaker;
- insulin pump;
- metal structures in the body;
- weight more than 130 kg;
- in the first trimester of pregnancy.
You should approach this with caution in the following cases:
- late stages of pregnancy.
The procedure is possible, but you should first consult with your doctor;
- claustrophobia.
The patient may take sedatives shortly before the examination to avoid fear of the confined space of the tomograph;
- the presence of implants in the body.
Most modern medical structures are made of metals that are insensitive to magnetic radiation. Their presence in the body does not interfere with the procedure.
Before conducting the study, the radiologist will definitely ask you about possible contraindications.
Is contrast harmful in abdominal tomography?
Do not be afraid of undergoing an MRI with contrast - undiagnosed diseases in time can lead to death or significantly worsen the quality of life
For the vast majority of people, the contrast used during MRI, if the dose is calculated correctly and in the absence of contraindications, does not cause harm and is completely eliminated from the body. There are conditions when the introduction of a paramagnetic drug is unacceptable, these include:
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- decompensated form of renal and cardiovascular failure;
- generalized allergic reactions to one of the components of the contrast agent.
Lactation is not an obstacle to MRI with contrast, but the woman is advised to store milk for three subsequent feedings.
In Russia, paramagnetic agents based on gadolinium are used, which have passed all clinical trials and are approved for use. An unpleasant taste in the mouth, headache, and a slight decrease in blood pressure are quite acceptable - the above are classified as vegetative reactions that are not dangerous and go away on their own after a few minutes. Some subjects develop hyperemia and itching at the site of contrast injection. The manifestations do not require special measures and are not considered a significant hypersensitivity reaction. It is necessary to inform the doctor about your health via speakerphone if:
- a feeling of increasing swelling, squeezing the throat, difficulty breathing;
- the appearance of blisters on the skin, generalized itching;
- profuse sweat;
- pre-fainting state.
The procedure is monitored from the adjacent room, and for unforeseen situations there is a specially equipped first aid kit. Allergy to gadolinium-containing drugs occurs in 2% of people.
How long does an abdominal MRI take?
The procedure for MRI diagnostics of the abdominal cavity will last about 40 minutes.
Radiologist at work
If the study is carried out using contrast, the duration of the procedure will be about 1 hour.
After completion of the procedure, the patient is given a disk with recorded images and a written conclusion from the doctor.
How research is done
The opportunity to undergo an MRI examination is available in any modern clinic in the metropolis. This is an accessible but relatively expensive procedure. The device itself is an almost completely closed cylindrical chamber, which consists of a movable table of the diagnostic capsule itself. People with various forms of claustrophobia may be examined in an open MRI capsule; in some clinics it is allowed to invite a loved one with them.
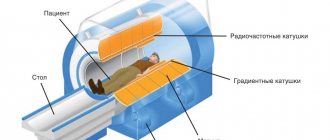
At the beginning of the examination, you need to lie down on the table, after which the specialist will fix your arms and head so that involuntary actions do not occur. This is necessary because after starting the device you need to lie still. During operation, the device takes a large number of pictures, which are then combined into one whole 3D image using a special program.
From time to time you may have to hold your breath for a short time. How long does an MRI take? It depends on the goal set for the medical staff. If one organ is checked, it takes 5-10 minutes; if the abdominal cavity is examined completely, you need to prepare for a procedure lasting 30 minutes or more.
After the examination, with or without a contrast agent, the result takes approximately two to three hours to prepare. With a more serious and extensive examination, if an MRI of the abdominal cavity is performed with contrast, the conclusion will be ready only the next day. The results obtained will need to be shown to the attending physician, who will prescribe subsequent treatment with medications.
MRI of the abdomen with contrast agent
If the doctor has prescribed an MRI of the abdominal cavity with contrast, before the examination begins, a special medication will be injected into the vein, acting as a dye. It accumulates in the cavity of the organ being examined and provides detailed information about the disease.
Interpretation of MRI results of the abdominal organs
The radiologist begins receiving images on the computer even before the end of the study, while the patient is undergoing the procedure. At the DiMagnit center, the doctor begins to interpret the results without waiting for the end of the procedure. The images received on the computer are immediately examined for the presence of pathologies. This allows you to significantly reduce the waiting time for a conclusion after the study. . This helps you save a lot. To draw up a final conclusion about the area being examined, the doctor will need about 30-40 more minutes after completing the study.
MRI of the abdominal organs is a safe procedure that allows you to accurately identify abnormalities in the functioning of internal organs. There is no need to be afraid of the procedure - it is absolutely painless. The results of the study can be obtained and transferred to the attending physician on the same day.
| MRI of the rectum in Rostov-on-Don |
| MRI of the pancreas in Rostov-on-Don |
| MRI of the liver in Rostov-on-Don |
| MRI of the abdomen with contrast |
| MRI of ureters |
| What does an MRI show? |
Preparation for the procedure
For emergency indications, no preparation is required, however, during routine diagnostics, to improve quality and efficiency, it is necessary to prepare for MRI.
The main preparation is diet:
- exclude for 2-3 days foods that contribute to increased gas formation (legumes, cabbage, alcohol);
- when examining the pancreas, it is not recommended to eat carbohydrate foods for 2-3 days;
- perform a cleansing enema the day before if necessary;
- test for allergies to a contrast agent;
- 4 hours before the diagnosis, do not drink any liquid;
- 30-40 minutes before the patient is recommended to take an antispasmodic drug (“Spazmalgon”, “No-Shpa”, “Drotaverine”);
- remove metal objects: jewelry, piercings, belts, metal dentures.
Features of this diagnostic: advantages and risks
The main advantages of MRI of the retroperitoneal space are its versatility and diagnostic accuracy. This procedure is completely safe, but only if you follow the rules and pay attention to established contraindications. When following the doctor's recommendations, any risks are completely excluded, regardless of how long the MRI lasts.
How often can an MRI be done? The frequency is dictated by the detected pathologies and the time frame of the prescribed therapy. In other words, magnetic resonance imaging of the abdominal cavity can be performed as many times as required, without the harmful radiation of x-rays.