Diseases of the urinary system in newborns and young children are a serious problem in pediatrics. Often, a process that began in the neonatal or early childhood period does not manifest itself in a clear clinical picture and remains unnoticed for many years until more severe consequences and impairment of renal function occur.
It has been established that urinary system infections in newborns in 80% of cases, and in children of the first year of life in 40%, are detected by chance during hospitalization for other reasons. Important diagnostic signs of urinary tract diseases are laboratory methods for determining leukocytes, bacteria and protein (proteinuria) in the urine.
Let's take a closer look at why a child has increased protein in his urine, the norms and deviations of this indicator, and what measures parents should take.
Every day, many liters of blood pass through the kidneys, which are filtered through special filters. Water and small and medium molecules pass through physiological barriers, but albumin and other large molecules do not. However, normal amounts of protein may be excreted in the urine. This is physiological proteinuria.
When conducting a general analysis, protein in the urine (the norm in a child) should not be detected or present in an amount of less than 0.03 g/l. Indicators above this value are considered pathological and require identification of the cause. Protein molecules damage the kidney and these processes must be normalized.
It is also important to determine whether the protein in the child’s urine is elevated - is this a temporary phenomenon or permanent.
What does protein in a child’s urine mean and why is it dangerous?
If an increase in protein is detected in your baby, there is no need to panic, because... this may indicate the physiological state of the body, for which protein in the urine in children is normal. For example, in infants in the first weeks of life, proteinuria is a variant of the norm . The level of protein in a child's urine can reach 0.3 before the age of 1 month of life as a result of breastfeeding or high mobility.
It is necessary to regularly determine the level of protein in a child’s urine using laboratory tests. An increase in protein in the test results can be normal or pathological. What does an elevated protein level indicate and how to correctly interpret the results?
The protein level in a child’s urine may be 0.1, since the urinary system at an early age does not yet have sufficient blood filtration. A 14-year-old teenager may experience an increase in protein levels due to intense physical activity and regular consumption of protein foods. This can also happen due to hormonal changes in the body. If urine is collected incorrectly before the test (this is especially true for boys who neglected to clean their genitals before taking the test), test results may show unreliable data.
Temporary or physiological increase in protein
Sometimes the appearance of proteinuria in children does not indicate the presence of pathology and is possible under normal physiological conditions. Thus, the protein in the urine of a breast-fed baby can increase if the mother is not eating properly, if she violates her diet, if the baby is highly mobile, as well as with overfeeding. In an infant in the first month of life, the genitourinary system is simply not yet sufficiently formed. However, if after a month from birth the indicators do not change, it is necessary to carefully examine the baby for the presence of renal pathology.
Protein in the urine of a 14-year-old teenager may increase during physical activity if the child consumes a lot of protein in food. Teenage proteinuria occurs as a result of hormonal changes in the body.
Increased protein in the urine of a child appears after hypothermia, a stressful situation, allergies, burns, insolation, dehydration, or long-term drug therapy. If urine is not collected properly for testing, protein may also be contaminated.
Orthostatic proteinuria is a renal functional proteinuria that is observed in children 7–18 years old, mainly boys. The reason is the increased excretion of albumin in an upright position. To rule out orthostatic proteinuria, a sample is collected in a horizontal position or a 24-hour test is ordered to detect protein in the child’s urine. Proteinuria often appears after an infectious disease.
These situations do not require special treatment; after neutralization of the primary factors, temporary proteinuria goes away on its own. But you still need to be careful and attentive to the detected protein in the urine. In any case, you should consult your doctor.
Reasons for appearance
Every day, the kidneys filter about 30-50 liters of urine. This is primary urine; most of it is not excreted from the human body. It is blood plasma in which there are no protein compounds.
Such urine, passing through the kidneys, releases substances beneficial to the body, which are absorbed back into the blood cells. Secondary urine, in turn, removes harmful compounds, for example, creatinine, ammonium in the form of salts, urea and others.
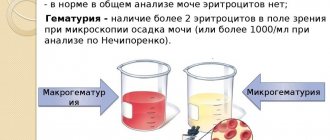
However, urine should not contain protein substances. The volume of secondary urine excreted in the body per day is called daily diuresis. Protein levels are normal at: 0.003 reactive protein per liter. If tests reveal an increase in protein and red blood cells in a child’s urine, the doctor should prescribe additional examination and appropriate treatment. A pathological increase in red blood cells in urine is called hematuria .
There are a number of reasons for the appearance of protein in a child’s urine above normal:
- An allergic reaction in an aggravated form.
- Intoxication of the body.
- Tuberculosis.
- Disruption of the process of formation of blood cells.
- The disease is in its early stages.
- Diseases of the urinary tract or kidneys.
- Hypothermia of the body.
- Presence of infections.
- Severe stress.
- Physical exercise.
- Intoxication of the body due to taking medications.
- Starvation.
- Increased content of vitamin D in the body.
- Anemia.
- Epilepsy.
The causes of proteinuria can only be identified through laboratory tests. To do this, you should visit a pediatrician who will give you a referral to a urologist, nephrologist or hematologist.
What are the causes of proteinuria?
A healthy person does not have protein in urine, since during the processes of urine formation it is absorbed into the blood and lymph. If the filtration function of the kidneys is impaired, proteinuria is detected - an increased content of protein elements in a urine test. Protein tests are prescribed to diagnose diseases associated with kidney damage, as well as to monitor the treatment process.
Why might there be increased protein in the urine? This is influenced by a variety of pathological factors. Proteinuria in children, regardless of age, can appear with a viral infection, including common ARVI, as well as with many other diseases, such as:
- kidney diseases and injuries,
- multiple myeloma, hemoblastosis,
- hemolytic disease in a newborn,
- diabetes,
- brain injuries,
- epilepsy,
- cystitis,
- bacterial infections such as tonsillitis, etc.
With inflammation, in addition to albuminuria, increased levels of mucus, bacteria, red blood cells, and white blood cells are often observed in the urine.
Based on the localization of the pathological process, several types of increased protein in the urine are distinguished:
- Postrenal proteinuria - manifests itself in diseases of the urinary tract and genital organs.
- Renal – inflammation is localized in the kidneys.
- Prerenal – characteristic of various oncological conditions or intoxications of the body.
Symptoms that should alert parents
First of all, you should pay attention to the baby’s well-being. There is no need to worry if the tests reveal proteinuria, but the child has no complaints. However, if the protein level is elevated and there are clear signs of a disorder in the body, you should be wary.
With a pathological increase in protein, the following may occur: swelling of the arms, legs, face, vomiting, deterioration in the general condition of the body, as well as an increase in body temperature. Protein significantly affects the clarity of urine, as a result of which it becomes cloudy and turns brown or red.
Parents should be vigilant in case of development of drowsiness, rapid fatigue in children , as well as poor appetite.
In case of vomiting, to avoid dehydration, give the child Regidron. The severity of symptoms depends on the location of inflammation in the body. For example, if you have cystitis, you may experience repeated urination accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen.
Signs of an elevated level
Minor proteinuria, as a rule, does not affect the baby’s condition. External symptoms can be seen with a significant increase in protein in the urine. Signs of increased reactive protein in urine include:
- pain in the bones;
- dark shade of urine;
- frequent urination;
- strong thirst;
- swelling of the lower extremities;
- swelling of the eyelids after waking up;
- intoxication of the body, manifested in the form of nausea, lack of appetite;
- deterioration of the general condition of the body.
Kidney diseases can be painless for a long time. The appearance of pain in a baby may occur in a different location than in adults. Children most often complain of pain in the abdominal area. We advise you to familiarize yourself with the causes of pain in the navel area in children and the probable symptoms of diseases that cause pain.
In infants, proteinuria may be normal
It is much more difficult to find the source of proteinuria in infants , the signs of which may be the following:
- swelling of the eyelids;
- pale skin;
- increased body temperature, with no symptoms characteristic of a cold;
- disturbing sleep, the child does not sleep during the day (in the case of a newborn or infant).
Impaired renal function in infants can occur as a result of tissue swelling. This can be detected by residual traces from the elastic bands of diapers or onesies.
Pathological protein fractions
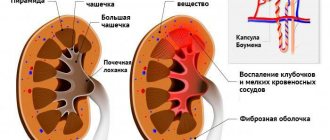
Albumin appears in urine when the reabsorption of this protein by the kidneys is impaired (nephrotic syndrome, renal failure, glomerulonephritis).
Physiologically, the blood albumin level is 30 mg per day. Pathology is observed when the distal tubules of the kidneys are damaged.
They process a third of albumin. The Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein is secreted in this region.
Urine contains some of the proteins of the renal wall, prostatic and vaginal discharge.
Classification of proteinuria by qualitative composition:
- Non-selective.
- Selective.
The non-selective species is characterized by the appearance of high and medium mass proteins (gamma globulins, beta lipoproteins, alpha2-macroglobulins). A wide range of protein components of urine is observed in serious kidney diseases (nephrotic syndrome, renal failure).
Selective proteinuria is accompanied by the presence of low mass protein. It is considered favorable prognostically, as it is based on albumin.
Gradation of proteinuria by size:
- High (nephrotic).
- Moderate.
- Low (microalbuminuria).
Microalbuminuria is the excretion of protein in urine in a concentration of up to 500 mg/day. The symptom is the first sign of nephropathy in hypertension and diabetes. If these diseases are suspected, proteinuria should be determined.
With a moderate degree of pathology, 1-3 grams of protein per day are determined in the urine.
The symptom can be observed in the following diseases:
- Tuberculosis.
- Kidney tumor.
- Nephrolithiasis.
- Pyelonephritis.
- Glomerulonephritis.
The magnitude of proteinuria depends on the severity of inflammation that occurs in the genitourinary tract.
High concentration of protein in urine - over 3.5 grams per day. The symptom indicates nephrotic syndrome.
Types of proteinuria
An increase in protein levels in urine indicates that renal functional activity is reduced. The kidneys help cleanse the blood of various toxins and wastes, products of the metabolic process of proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
After this, the paired organ removes them from the body by emptying the bladder. Proteins are absorbed back into the blood. As a result of some pathologies, filtration is impaired, thereby allowing proteins to enter the urine.
Types of proteinuria:
- Postrenal. Develops with the development of inflammation in the genitourinary organs.
- Renal. Occurs due to decreased performance of nephrons. As a result, they cannot absorb large molecular proteins.
- Perenal. Appears when there is an excess of proteins in the circulatory system.
There is also an orthostatic increase in protein, which manifests itself in adolescence due to unstable hormonal levels. As a rule, such a pathology is considered temporary and does not require drug treatment.
Causes
In a healthy child, a temporary increase in protein levels may be associated with functional disorders. These include:
- depression;
- physical exercise;
- allergy;
- burns;
- poisoning;
- infection;
- taking certain medications;
- overeating foods containing protein;
- elevated temperature;
- heavy sweating.
Fever
When these factors are eliminated, the protein will return to normal. Natural causes include adolescence and the first days of a child’s life. But in some cases, the causes of proteinuria can be serious disorders in the body: kidney pathology, urolithiasis, diabetes mellitus, epilepsy, concussion, tumor, polycystic disease.
Diagnostics
Without following strict rules for collecting urine, the results of the analysis may be blurred.
To detect protein in the urine of children, the following studies are used:
- general urinalysis (UCA);
- daily examination of urine for protein;
- analysis according to Zimnitsky;
- rapid test using special diagnostic strips;
- Nechiporenko's method.
Based on a general urine analysis, laboratory assistants calculate the protein level in the morning. How to test daily proteinuria? To establish daily proteinuria, it is necessary to collect urine for 24 hours in one sterile container intended for this procedure. You need to send a complete urine sample or a portion of it to the laboratory. Before this, the daily diuresis in ml should be determined.
To obtain reliable information about protein levels in urine, you must follow the recommendations for urine collection:
- The sample must be collected at the appropriate time of day, which is predetermined by the research method.
- Before urinating, you should wash your baby.
- The jar for collecting urine must be sterile.
- To collect daily urine from children under one year old, urinals should be used, which are sold in any pharmacy.
Additional information on the rules for collecting morning urine to determine protein in the urine, as well as the reasons for its presence in the tests, is provided by a nephrologist in the video:
Decoding the analysis according to the table:
| Protein level in urine | Characteristic |
| Up to 0.033 g/l | Protein is normal |
| Up to 0.099 g/l | Stressed renal function may occur due to stress or hypothermia |
| From 0.099 to 0.3 g/l | ARVI, cold |
| From 0.3 to 1 g/l | Moderate proteinuria. If additional signs appear, then inflammation in the kidneys may develop. |
| From 1 to 3 g/l | Significant increase in protein in urine. In this case, it is necessary to examine the baby in detail to identify the causes. |
If laboratory test results reveal an increase in protein and white blood cells in a child's urine, this may be a sign of serious diseases in the body. An increase in white blood cells is called leukocyturia .
Home testing
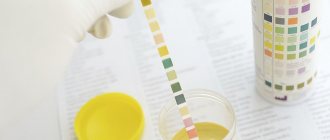
Test strips for determining the level of protein in urine can be purchased at pharmacies.
You can determine the level of proteinuria yourself using strips that are impregnated with a special reagent.
To do this, you should collect urine, taking into account all the recommendations, then lower the strip into it for a couple of minutes.
Express test results:
- “-”: protein is normal or completely absent (less than 10 mg per 100 ml);
- “color change”: traces of protein are detectable (10-20 mg per 100 ml);
- “1+”: moderate increase in protein (no more than 50-60 mg per 100 ml);
- “2+”: increased content (up to 100 mg per 100 ml);
- “3+” and “4+”: noticeable renal impairment.
Despite the existence of home testing, a more accurate result can be found using laboratory tests.
Table with the norms of protein in the urine of a child, depending on age:
| Age | Indicators considered normal (mg/l) |
| Up to 30 days (term birth) | 94-456 |
| Up to 30 days (premature birth) | 90-840 |
| Up to 12 months | 71-310 |
| 2-4 years | 37-223 |
| 4-10 years | 32-235 |
| From 10 years | 22-181 |
Treatment of proteinuria
Before treating proteinuria, you should find out the exact cause of its occurrence. To do this, you need to undergo some tests, after which the doctor will be able to prescribe medications:
- Antibiotics.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Diuretics.
- Steroid medications.
- Means for lowering sugar. Products that lower its level are discussed here.
- Medications for hypertension.
In addition to medications, it is necessary to normalize nutrition and water regime. If there is increased protein in a child’s urine, pediatricians prescribe diet No. 7, which contains a low protein content, and the level of fats and carbohydrates remains normal.
All medications presented above are strictly prohibited to be used without a medical prescription. Self-medication can worsen the condition of the child’s body and lead to the development of complications.
ethnoscience
Traditional medicines are quite effective in treating high protein levels. However, they should be taken only after a visit to the pediatrician.
Traditional medicine helps get rid of swelling, support the immune system and normalize blood sugar.
Below are the remedies that are effective in the treatment of proteinuria. Take if you are not allergic to the components included in the composition. Drink 100-150 ml three times a day.
- cranberry and lingonberry fruit drinks;
- pumpkin juice with pulp;
- decoction of parsley root, rose hips or birch buds;
- infusion of parsley seeds or fir bark.
If an allergic reaction occurs (see the article about the types of rashes on the face in children) or your health deteriorates, you must stop using the listed drinks.
Why does prerenal proteinuria occur?
Myeloma under a microscope
Prerenal proteinuria is caused by secondary pathological diseases:
- Waldenström's macroglobulinemia.
- Rhabdomyolysis.
- Baines-Jones proteinuria.
- Multiple myeloma.
- Intravascular hemolysis.
For all of the above diseases, the level of urine protein is in the range of 0.1-20 grams. Proteinuria over 3 grams per day is a sign of nephrotic syndrome, myeloma nephropathy, hypoalbuminemia, myeloma.
Causes
Renal proteinuria occurs when tubular and glomerular filtration is impaired. In the renal form of the disease, a decrease in the permeability of the glomerular filter is formed.
The renal form of the disease appears in the following diseases:
- hypertonic disease;
- nephrosclerosis;
- amyloidosis;
- nephrosis;
- nephropathy;
- pyelonephritis.
This form of pathology includes physiological proteinuria (stress, hypothermia, tension, newborns).
With glomerulosclerosis, congestive changes and glomerulonephritis, a violation of glomerular filtration can be observed.
Tubular proteinuria is observed in tubulopathy, nephritis, and Fanconi syndrome.
In both forms of pathology, the following types of urine proteins can be observed:
- Beta2-macroglobulin;
- Albumen;
- Alpha1-macroglobulin.
Let's consider the morphological causes of renal proteinuria:
- Increased concentration of pathological and normal proteins (Baines-Jones, hyperproteins).
- Enhancement of tubular secretion with determination of Tamm-Horswell protein.
- Decreased tubular reabsorption.
- Increase in filtered proteins due to increased permeability of the glomeruli of the kidneys.
Causes of postrenal proteinuria
The postrenal (extrarenal) form of pathology occurs with bacterial damage to the lower parts of the genitourinary tract.
There are 2 forms of the disease:
- True.
- False.
The true form can be seen in the following diseases:
- vulvovaginitis;
- urethritis;
- prostatitis;
- pyelitis;
- cystitis;
- kidney tumors;
- renal tuberculosis;
- urolithiasis disease.
The false form is characterized by an increase in red blood cells, white blood cells, and traces of protein in the urine. The breakdown of these elements can be observed in the alkaline reaction of urine, which increases renal filtration. When the cause of the pathology is eliminated, urine tests return to normal.
Prevention
For prevention purposes, the following recommendations should be followed:
- Monitor your baby's water intake and avoid drinking all carbonated drinks and packaged juices.
- Maintain strict control over the children's diet, minimize the intake of fatty and salty foods.
- Harden, do massage, especially when coughing (see more details here), ventilate the living space.
- Get tested at least twice a year.
- Monitor your baby's regular urination.
- Avoid hypothermia of the child's body.
- Treatment of any disease is carried out to the end.
By following these simple preventive measures, it is possible to prevent the development of diseases of the kidneys and urinary system. If proteinuria occurs, you should not delay visiting a specialist.
Treatment
Because proteinuria is a symptom and not a disease itself, medical care is aimed at treating the underlying condition.
The main goals of treatment are often:
- normalization of blood pressure in people with hypertension;
- controlling blood sugar levels in people with diabetes.
For example, when diabetes or hypertension is present, treatment includes:
- blood pressure control;
- use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACE-I);
- Ace inhibitors prevent the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a substance that normally causes veins to constrict.
The result is a decrease in blood pressure. ACE inhibitors are drugs used primarily to treat hypertension. However, they are also very effective in reducing proteinuria, regardless of whether the patient has hypertension.
People with nephrotic syndrome and fluid overload should moderate salt intake in their diet. The nephrologist may also recommend moderate protein restriction.
Reviews from parents
Anastasia 20 years old, Voronezh, daughter 3 months old
We took tests, one of them was for elevated protein levels. A positive result came. After additional examination, it was discovered that this was due to overfeeding the daughter with milk. Now I began to carefully monitor the amount of food she consumed.
Inna 24 years old, Tomsk, nephew 14 years old
Once again, my sister’s son underwent a medical examination. The results of the TAM indicated proteinuria. The doctor ordered an additional examination so that we could understand the reason. The increase in protein compounds in urine turned out to be due to hormonal changes in the body. The topic worries me because... I'll be a mother soon