What do the stages of pneumonia look like on an x-ray?
Pneumonia on X-ray can be differentiated by a large number of signs and parameters.
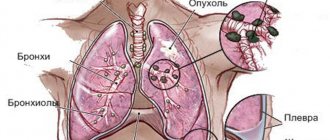
The volume of the inflammatory process plays an important role in how pneumonia looks on an x-ray. The pathology can affect a specific area (focal pneumonia), a zone of the lung, half (subtotal) or the entire lung (total). Based on these data, the choice of drugs and their dosage is made, since, for example, total pneumonia is an extremely severe pathology in adults and children, which often leads to death. Unfortunately, the answer to the question of whether pneumonia is always visible on X-rays will not please patients. The correct diagnosis sometimes cannot be made in the first stage (hot flash), which lasts for the first 12 hours. This is due to the uneven rate of vascular reactions.
Moreover, sometimes the unfavorable location of the lesion also occurs. The problem is that the projection of a rib or other bone on an x-ray hides the pathology. In such cases, a repeat image after some time or even a CT scan is required.
Tide stage
The hot flash stage is characterized by the initiation of the pathological process. Its duration usually ranges from 12 hours to 3 days. At this moment, the antigenic agent is actively introduced into the lung tissue, which causes a number of vascular reactions. Blood and its components actively pass through the vascular wall and permeate the lung tissue.
On the radiograph at this stage, primary changes are noticeable, which are random in nature. An initial darkening of the pulmonary pattern is often visible, but it is impossible to assess the exact size of the pathological focus.
Red liver stage
At the stage of red hepatization, the lung tissue becomes significantly denser, which occurs due to its active impregnation with red blood cells. As pathomorphologists note, at this stage the lung is a compaction, very similar to the liver and has a rich red color, which was the reason for such a non-standard name.
X-ray in direct projection of the lungs at this stage is the most informative, since the darkening of the pulmonary pattern is already visible. The pathological focus has clear boundaries, the size of the affected lung segments is determined. The duration of this stage of the disease ranges from 24 to 72 hours with adequate treatment.
Gray hepatization stage
The stage of gray hepatization is characterized by the beginning of the breakdown of blood components that previously permeated the lung. Red blood cells are actively lysed (destroyed), and leukocytes and blood plasma appear in the alveoli. The presence of infiltrate is an important sign. This stage lasts for a maximum of six days. The X-ray picture does not undergo major changes, since the density of the lung tissue remains unchanged.
Resolution stage
The stage of resolution of pneumonia on the radiograph corresponds to the normal structure of the lung tissue. During this period, the histological integrity of barriers and tissues is restored, so the x-ray picture returns to normal. Local anomalies still occur, but over time everything returns to normal.
What is pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory disease that involves the lung tissue. The provocateur of the pathological process is bacteria, fungi or viruses.
If the pathology is not treated, inflammatory processes can lead to serious consequences, including death. The disease poses a greater danger to older people and young children. Treatment for pneumonia begins after diagnosis. One of the effective diagnostic methods is fluorographic examination.
X-rays for pneumonia
Pneumonia is a disease characterized by damage to the lower respiratory tract. X-ray is prescribed when a clinical picture of pneumonia is detected. Unlike other methods, x-ray examination is considered the most accessible.
Often patients who are referred for examination wonder whether the x-ray will show pneumonia. Yes. Using this procedure, you can see the inflamed areas in the image, assess the condition of the pulmonary pattern and the roots of the lungs.
Indications and contraindications for radiography
The patient is referred for examination if the following symptoms are present:
- cough with sputum. Possible pain in the chest area;
- high temperature, chills;
- wheezing;
- increased level of leukocytes in a blood test.
X-ray diagnosis of viral pneumonia plays an important role, since signs of the disease are not always obvious. There are atypical manifestations of pneumonia, including: normal body temperature, the patient initially does not suffer from suffocating attacks of coughing, wheezing, chest pain and looks completely healthy and mobile. It's especially easy to make mistakes when it comes to children. Therefore, the patient’s further treatment depends on how the x-ray picture looks like during pneumonia.
There are no contraindications to X-rays. The only limitation may be pregnancy. However, if a woman is suspected of having pneumonia, an examination should be carried out, because making the correct diagnosis is important for choosing the course of treatment. At the same time, measures are taken to minimize the harmful effects of rays - the patient’s body is covered with a lead apron.
Advantages of X-ray examination
We have already said that fluorography (both classical and digital) is primarily a preventive measure. A patient with symptoms of pneumonia consults a physician. Is X-ray or fluorography prescribed in this case? The most suitable study for detecting an infiltration focus in the lungs is an x-ray taken in two projections.
Even a classic radiograph, unlike fluorography, shows a clear clinical picture. For example, it allows you to visualize shadows up to 5 mm in diameter. Namely, they distinguish the development of such dangerous pathologies as pneumonia, sarcoma, tuberculosis.
Why are X-rays taken of the chest organs in two projections? This allows you to most fully study the structure of the damaged tissue, which is decisive in making the correct diagnosis. For example, a direct projection cannot demonstrate calcification of the ribs, but a lateral projection visualizes them very well.
So does fluorography show pneumonia? Yes, but the “picture” is not so clear, it does not allow one to judge the nature of the lesion (shadows, darkening) as well as with an x-ray examination. A fluorogram is sufficient to notice destructive changes in the lungs, but is not sufficient to make an accurate diagnosis, on which the success of treatment will depend.
Modern fluorography methods
At the beginning of the 20th century, the main method of examining internal organs was x-rays. It was used for mass monitoring of human health. Fluorography was considered less accurate, although less safe, and was used extremely rarely. Gradually its role in medicine became more significant. Doctors recognized its many advantages and the possibility of participating in mass examinations. It began to be used for preventive examinations. The purpose of fluorography is to detect pathological processes.
In modern medicine, there are two types of fluorography: traditional and digital. With traditional X-rays, X-rays passed through the human body are reflected and converted into a pattern on an X-ray image. Advantages of the traditional method:
- low financial costs;
- small (compared to x-ray) dose of radiation received;
- possibility of mass application;
- the ability to examine a huge number of patients;
- the chance of creating an archive of X-ray images due to their small size.
With the advent of digital technology in various industries, it became possible to create a digital fluorography method. There is no need to take pictures. After passing through the internal organs, the rays are projected into an image on the monitor screen. This happens with the help of special sensors that record radiation and its intensity and transmit it to the screen. Next, the photo is processed using the latest computer technologies. The image quality with the digital method has improved significantly and become clearer. The radiation dose received by humans has decreased significantly. Safety and accuracy give this fluorography method significant advantages over the traditional method. But its high cost practically negates its use in medicine.
FLG - as a method for diagnosing pneumonia
Fluorography, at its core, involves passing X-rays through a person’s chest and transferring the result obtained to a screen and then to film.
The method is primarily needed to detect TB, oncology, and study other organs. FLG can reveal:
- inflammatory changes in the bronchi and lung tissue that accompany pneumonia;
- exudation in the lungs;
- proliferation of connective tissue in some pulmonary diseases.
Repeated X-ray examinations for pneumonia
Medical indications for X-rays of the lungs in two projections (anterior, lateral) include suspicion of pneumonia if the patient has the following symptoms:
- Fever above 38°C with acute onset of the disease.
- Cough with sputum of any nature (from mucous to purulent with streaks of blood).
- Presence of auscultatory and percussion symptoms of pneumonia: moist rales, crepitus, shortening of tone.
- Changes in the general blood test according to the type of leukocytosis with numbers above 10*10 9 /l or the presence of a band shift above 10%.
If pathological changes characteristic of pneumonia are detected on an x-ray, the patient is prescribed appropriate therapy.
X-ray schedules
However, once the diagnosis is made, it remains unclear for the patient how often he needs additional X-ray examinations.
Uncomplicated pneumonia, mild and moderate severity of the disease, as a rule, require a double x-ray after 3-4 days and 6-10 days from the start of antibacterial therapy. If, during the second control study, positive dynamics are noted in the form of resolution of infiltration of the lung tissue, its significant reduction, the patient is considered to be recovering.
The recovery criteria for pneumonia are listed below:
- Normalization of the patient's condition (subjective assessment).
- Disappearance of physical, radiological and laboratory symptoms of pneumonia.
After treatment, the patient is transferred to the clinic for clinical observation, which usually lasts 6 months. Examinations by a therapist, OAC, OAM, biochemical blood tests and lung radiography are performed on a schedule of 1-3-6 months after clinical recovery.
The total radiological load for the entire period with uncomplicated pneumonia ranges from 0.2 to 0.5 mSv (digital radiography method).
Approach for complicated course
A complicated course of the disease or lack of effect from antibacterial therapy requires a different approach to X-ray diagnostics.
If there is no effect from the antibiotic (AB), the first x-ray examination is performed 3-4 days from the start of treatment. Based on its results (and clinical picture), the need for a change in etiotropic therapy is assessed. Then repeated radiography is performed in two projections for a period of 7-10 days after replacement of the AB. The following are possible patient management options:
- If there is no infiltration of the lung tissue on the third control X-ray (14-20 days after changing antibacterial therapy) and clinical recovery, the patient is transferred for clinical observation to the clinic, the duration of which is extended to a year. During this period, examinations, laboratory and X-ray examinations are carried out according to a schedule of 1-3-6-12 months.
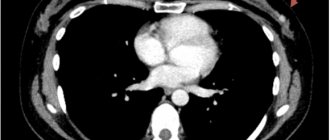
- In the absence of positive X-ray dynamics, as a rule, a consultation with a phthisiatrician, bronchoscopy, and computed tomography of the lungs are necessary. Further based on the results of an additional examination.
In case of complicated pneumonia, there is no schedule for conducting x-ray examinations, since sometimes it is impossible to predict the course of subsequent development of the disease.
Complications of pneumonia requiring frequent R-graphy:
- Pleural empyema, pyothorax.
- Abscessation of the lung.
- Formation of encysted pleurisy.
- Pneumothorax.
- Pulmonary edema.
- Hydrothorax, effusion pleurisy.
- Sepsis.
The total radiological load in pneumonia with a complicated course can increase to 2 mSv when using the digital method.
In the end, it should be noted that the decision to conduct an additional R-examination for this disease is made by the attending physician based on a clinical examination, therefore the above deadlines can in no way be used to assess the competence of medical personnel.
results
When deciphering the results of an X-ray examination from an image, the specialist pays attention to any pathological changes. The localization of the source of inflammation, its size, shape, and limitation are analyzed. Moreover, if we compare X-rays and fluorography, the first diagnostic method is more informative simply because the dimensions of the projection image are much larger.
Another undeniable advantage of radiography is the fact that the picture is taken in two projections. This makes it possible to detect pathological changes that may not be visible only in direct projection.
When “reading” an X-ray image, the doctor takes into account changes in appearance (depending on size), degree of darkening intensity and area of the lesion.
The division of outbreaks by type is as follows:
- small – no more than 2 mm in size,
- average - 3-7 millimeters,
- large – within 8-11 millimeters,
- focal - their size starts from 12 mm, but they can cover the entire organ.
There are 3 variations in the gradation of lesions according to the degree of intensity:
- the initial degree of inflammation - the color of the lesion is darker than the bone, but lighter than healthy areas of the lung tissue,
- medium degree of inflammation - the color of the lesion approximately matches the appearance of the bones on an x-ray,
- severe degree - bright light spots or areas in the pulmonary projection.
Regarding the affected areas, unilateral and bilateral pneumonia are distinguished in accordance with the lobe of the paired organ in which the inflammatory process has formed. In the description of the radiograph, the radiologist records all the indicators, after which the main diagnosis is made (if additional diagnostics are not required).
How to identify focal pneumonia on an x-ray
To identify focal pneumonia in an image, we offer readers its signs:
- The presence of an intense infiltrate of a non-homogeneous structure;
- A “bad” shadow has an unclear outline;
- With inflammation of the pleura, linear heaviness or fluid level is observed in the costophrenic sinus on the affected side;
- As the process resolves, the infiltration area becomes highly heterogeneous due to areas of decay and healing of the lungs.
X-ray signs of pneumonia at the resolution stage:
- Disappearance of infiltration;
- Linear heaviness due to connective tissue;
- Commissure of the costophrenic sinus (veiling).
After the disappearance of infiltrates over several months, the area of the lung lesion is characterized in the image by a deformation of the pattern. Residual changes after pneumonic shadows require dynamic monitoring of patients. For these purposes, radiography is prescribed every month.
How does lobar pneumonia differ on x-ray?
Lobar pneumonia on X-ray is characterized by compaction of the pleural wall and stagnation of fluid in the pleural cavity. To assess the affected areas, a radiograph is taken in frontal and lateral projections.
Features of x-ray images in the stage of tide with lobar inflammation
The image shows a uniformly darkened segment with uneven borders, or a lobe of the lung.
Pneumonia enters the gray hepatic stage 4-6 days after the onset of the disease. At this time, the affected lobe of the lungs is dense with fibrous deposits on the pleura. Signs of pneumonia on x-rays: changes in the pulmonary contour, lack of a clear root structure, and fibrous bands are visible.
Nuances and stages of resolution of pneumonia on x-ray/fluorography
Resolution of pneumonia is accompanied by characteristic signs. Among them:
- reducing the intensity and size of the darkening;
- detail on the radiograph of the patient’s pulmonary pattern with characteristic root expansion.
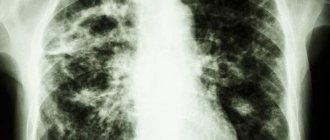
Also during this period, the presence of adhesions or fibrous layers is characteristic, which complicates the respiratory process. A characteristic picture is presented in the X-ray image below.
Complications of pneumonia in photographs
Complications of pneumonia can often be observed on photographs in the form of an abscess, pleurisy or periscissuritis - inflammation of the interlobar pleura.
Complications are possible if the disease is not treated in a timely manner or if it is severe. May be accompanied by a rise in high temperature, signs of intoxication of the body are possible. Respiratory failure may also occur, which is manifested by a decrease in the level of oxygen in the blood and shortness of breath.
Interstitial x-rays in pneumonia are atypical and may be characterized by decreased lung volume.
How to recognize an abscess in photographs
An abscess can be recognized by the following signs:
- the presence of some cavity with a vague rounded contour and perifocal one or more foci of inflammation;
- the presence of an infiltrate that gives a darkening in the projection of decay with a change in the picture after drainage.
Symptoms of pleurisy on an x-ray
Pleurisy is often a secondary process that develops after pneumonia, tuberculosis, and neoplasms. X-ray allows you to determine how much exudate (liquid) has accumulated in the pleural area, as well as the degree of darkening of the lungs.
The X-ray picture of perisissuritis is described by the following signs:
- dilated root of the lung on the affected side of the lung;
- violation of the contour of the gap and changes in the lumens of the segmental and subsegmental bronchi, which indicates infiltration.
Thus, a shadow with blurred edges on one side is characteristic. This clinical picture can only be seen on an x-ray.
The main radiological signs of pneumonia
In conclusion, we will tell you what main signs on an x-ray image can be used to judge inflammation of the lung tissue. This:
- Medium intensity foci-infiltrates.
- Fuzzy contours of infiltrative spots.
- Strengthening the pattern of the lungs (may reach the boundaries of the pulmonary field).
- Condensed, expanded root of organs.
So, fluorography helps to detect pneumonia, tuberculosis and lung cancer in the early stages. Therefore, it is common during preventive medical examinations. The exact diagnosis is made on the basis of an x-ray. However, sometimes this is not enough, so laboratory diagnostics are required to determine some forms of the disease.
Can fluorography show pneumonia?
Patients are often interested in the question of whether fluorography will show pneumonia. This research method is based on the fact that X-rays pass through the body, and given the fact that tissues absorb them differently, the pattern in the image appears heterogeneous. Light spots are the heart, bronchi and bronchioles. The lung tissue should be uniform, and if there is inflammation, darkening will be visible in the image.
Such research can be carried out by those who have already reached 18 years of age. However, it is not recommended to do fluorography more than once a year. But this only applies to examinations of healthy lungs, when additional images are not required.
Fluorography or X-ray?
Not everyone distinguishes between these methods for detecting lung lesions. Sometimes patients confuse them and, due to an incomplete understanding of the features of fluorography and x-rays, voluntarily expose themselves to an extra dose of radiation.
It is important to understand that fluorography is a preventive method, and x-rays are diagnostic. Fluorography is designed to detect cancer, pneumonia or tuberculosis in the early stages
Therefore, this method is widely used.
If we compare images taken by both methods, we can see with the naked eye that shadows or pathologies are better visible on an x-ray, while fuzzy threads are visible on fluorography. If the doctor who will review the images has doubts, the patient may be asked to take an x-ray.
The question arises, why not immediately take an x-ray, which is more informative? The fact is that mass fluorography costs the state much less, and consumables are also used more economically
It is also important that fluorography covers the area of the lungs and heart, while x-rays are not limited to the chest. Conclusion - the patient receives a lower radiation dose
How to recognize pneumonia on a fluorogram
A fluorography photo may show the following changes:
- A site of inflammation of lung tissue.
- Fibrosis.
- Changes in the pulmonary pattern and its roots.
- Enlarged lymph nodes on the roots of the lungs.
- Calcifications and petrifications.
At the same time, doctors say that suspicion of pneumonia can be caused by dense foci among the infiltration and foci behind the shadow of the heart. If one of these factors is present in the image, then further examination is necessary.
However, the thin linear shadows that are present in pneumonia are poorly visible on the fluorogram. For example, the walls of thin cavities are not clearly visible, so the likelihood that a doctor will detect a small cyst is reduced.
Some types of pneumonia are not clearly shown by fluorography. Sometimes pneumonia can develop in children in the first year of life who have immunodeficiency. In this case, chest fluorography shows an enhanced pattern of the lungs. After the onset of the disease, foci of darkening are visible only after 7-9 weeks, but the contours still remain unclear.
The clarity of the fluorography image depends on the type of infection that affects the lungs. Mycoplasma infection can provoke an increase in the pattern of the lungs, which is most often diagnosed in people who are often in crowded places. The risk category includes patients aged 5 to 25 years who attend kindergartens or educational institutions. Unlike mycoplasma, chlamydial infection affects older people.
The fluorogram must be done by a specialist. The patient’s health depends on how he reads it.
If the doctor detects changes in time, he will prescribe additional tests, for example, an x-ray, which will show a more complete and clear picture of the disease.
Otherwise, without proper treatment, pneumonia can develop into a severe form.
What can’t a radiograph “see” in the lungs?
Will fluorography and x-rays show pneumonia in the pictures? As we have already noted, fluorography can “miss” small infiltrative spots in the lung tissues, whose size is less than 5 mm. They are also poorly visible on x-rays. Only when these foci merge with each other, forming larger units, can one judge from the image the specific signs of pneumonia (focal or segmental).
Thus, neither x-ray nor fluorography will be the only accurate diagnostic methods. The minimum that modern equipment can detect is focal pneumonia.
X-ray examination today cannot yet detect the following types of pneumonia:
- Small focal pneumonia.
- Small infiltrates that are located deep in the lung tissue.
- Strong airiness of organ tissue.
Difference from X-ray
The image obtained as a result of fluorography is small. In other words, the image projected from the fluorescent screen is significantly reduced, which does not have the best effect on the diagnosis of pneumonia.
To “read” the image, radiologists use special magnifying equipment. If we compare fluorography with x-rays of the lungs, we can highlight several more quite significant differences:
- Carrying out FLG takes much less time.
- Low cost due to reduced image size (less raw materials required).
- Among all types of diagnostics that use X-rays, FLG has the lowest radiation intensity.
- FLG, unlike x-rays, is done only in the anterior projection.
Important! Fluorography is not the most informative diagnostic method due to the size of the image. For this reason, the main purpose of FLG is mass screening of the population for the development of pulmonary forms of diseases
The speed and low cost of the procedure only emphasize this fact.
Digital X-ray diagnostic methods
We figured out whether fluorography can show pneumonia. It is also important to distinguish its digital technique from digital x-ray diagnostics. Both of these methods are modern, but there are key differences between them.
Digital X-ray examination differs from classical X-ray examination in that the image is not recorded on film, but is recorded on a special transducer-sensor. The resulting frames are easily read by electronic devices and a wide range of software applications.
Today, the following types of modern (digital) X-ray diagnostics are distinguished:
- Fluorescent radiography.
- Selenium.
- Radiography through an electron-optical converter.
The advantages of the new technique are not only in simplifying the recording of images on a storage medium. The main advantage is a reduction in the radiation dose to the person being examined. Hence the second name of the modern digital technique - low-dose X-ray diagnostics of the lungs.
What is fluorography and why is it needed?
So, before answering the question of whether fluorography shows pneumonia, it is worth understanding its principle of action. It is quite simple to understand and you do not need any special education for this. It all lies in the fact that X-rays irradiate the area of the lungs and as a result, a picture of the lungs appears on the computer, which, as a rule, is heterogeneous. That is, it depicts the heart, bronchi and bronchioles with light spots. The lung tissue itself has a smooth and uniform shape. When a person has pneumonia, the picture will show some darkening, which will initially mean that the person has pneumonia.
It is worth noting that fluorography is performed only on people over 15 years of age. It is also dangerous for health to take a photo more than once a year, since, first of all, this is radiation, which is harmful to the body.
For people who have little knowledge of medicine, it is important not to confuse x-rays and fluorography. To clearly distinguish between these two procedures, you need to understand that x-rays diagnose the disease, and fluorography, in turn, is a preventive measure
Most people undergo this procedure (fluorography) during a medical examination so that a disease, for example, tuberculosis, cancer, pneumonia, can be detected at the earliest stages. By comparing two different images, you can make sure that all darkening and deformations are much better visible on an x-ray, while with fluorography, only fuzzy threads will be visible, from which you can still suspect something. Accordingly, if the doctor, after reviewing the patient’s tests, has any questions, he can immediately refer him for an x-ray in order to more accurately confirm his suspicions.
Why doesn’t the patient get an X-ray immediately, because anyway, if something is discovered, another additional X-ray will need to be taken, and this, of course, is an additional dose of radiation? The whole point is that fluorography is financially much cheaper for the state than x-rays. Another factor, as mentioned above, is that with fluorography, only the area of the lungs and heart muscle is irradiated, while with x-rays, the irradiation area is much larger.
Features of the event
Since in both cases X-ray radiation is used, the techniques differ little in the methods of implementation. The main differences lie in the degree of exposure and the results.
Fluorography
It is carried out in a fluorography room. The person being tested removes clothing from the chest part of the body and presses against the X-ray machine. In order for the specialist to see a clearer picture, it is necessary to hold your breath. A deep breath is taken, and after 5-10 seconds the doctor allows you to breathe fully again. You can see the doctor’s explanation on the same day, since writing out a conclusion takes no more than 20 minutes.
X-ray
The initial stage of radiography in adults does not differ from the first steps in fluorogram. The patient needs to stand in front of the radiation tube, exposing the chest. At the command of a specialist, you must hold your breath.
X-rays usually require taking pictures in different projections. If there is no need to change the position of the body during fluorography, then here you will have to rotate the body several times.
- Survey. Allows you to find out the details of pneumonia in the initial stages. The radiation is given to the right or left side of the body to obtain a lateral projection, and is also directed directly through the chest. Therefore, you must first stand against the device with your chest, and then press your shoulder against it.
- Sighting. Often prescribed for congestive pneumonia. It is done at different angles, which is why the procedure can take several minutes. Thanks to targeted research, doctors understand the characteristics of atypical forms of pneumonia.
Indications and contraindications for undergoing FLG
Indications for conducting fluorographic examinations once a year are the following reasons:
- the need for a preventive examination to detect lung diseases in all persons starting from the age of 16;
- examination to obtain results on the condition of the lungs when applying for a position related to working with children or in large groups of people;
- living together with pregnant women or infants in order to prevent their possible infection with tuberculosis or other diseases of the pulmonary system;
- military conscription for military service or work in the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation under a contract;
- routine screening of patients diagnosed with AIDS.
Carrying out such a procedure has a minimum of contraindications. They are associated with the possible consequences of exposure to ionizing radiation. It is not performed on the following categories of patients:
- children under 16 years of age;
- pregnant women. X-rays can cause irreparable harm to the fetus, including interruption of pregnancy;
- nursing mothers (relative contraindication). After undergoing fluorography, it is recommended to stop feeding for 1-2 days;
- patients in serious condition;
- people who are unable to maintain a state of rest or hold their breath for a few seconds (the information content of the study is reduced).
If the doctor sees pathological changes in the image, the person is prescribed additional examinations that can provide more detailed information: X-rays or CT scans.
Routine examination
Fluorography was initially intended for mass screening of the population for pulmonary diseases, which include pneumonia. According to the recommendations, FLG must be performed every 2 years. Routine examinations begin at school. During epidemics of pneumococcal infection, this is especially important.
The need for scheduled inspections is not an empty phrase or an exaggeration. According to statistics, in the Russian Federation alone, mortality from pneumonia annually reaches approximately 9%.
These statistics do not include cases of lung cancer, bronchitis and tuberculosis, which can also be detected by fluorography. Thus, by regularly undergoing diagnostics, you can protect yourself and your loved ones .
Will fluorography show pneumonia?
In some cases, FLH may not show pneumonia during the initial examination if, for example, dense foci of inflammation are located behind the heart, being in its shadow. If there is a suspicion of a serious disease, a re-examination will be required, usually in an alternative projection using an X-ray machine, during which the nature of the pathology can be determined with greater accuracy.
Fluorography in the early stages will show only emerging changes in lung tissue that are located in places directly projected onto the film or screen. FLG is still used, rather, as a preventive technique for examining healthy lungs. If there are changes in them, the examination continues using diagnostic X-ray equipment.
Some types of pneumonia are not visualized clearly enough by fluorography. For example, in children in the first year of life with existing immunodeficiency, only an enhanced pattern of the lungs is recorded. Foci of darkening appear 7-9 days after the onset of the development of the inflammatory process, but the contours still remain unclear.
Advantages of digital fluorography of the lungs
Using digital devices, the doctor will be able to see pneumonia or other inflammation in detail, since this image format allows you to enlarge any area of the image in order to carefully examine even small changes in the lungs. In addition, the use of this more modern technology reduces procedure time, provides the ability to store records electronically, and is considered safer due to reduced radiation exposure to the patient.
What does pneumonia look like in a photo, what can be seen on a digital fluorogram
Fluorography will show pneumonia in the form of darkening on the film. If the pictures of a patient with pneumonia are unclear, then a second examination is possible, but this time using X-ray equipment or a computed tomograph. A CT or X-ray gives a clearer and more visual picture of the condition of the respiratory organs. It immediately shows the focus of inflammation, while on a fluorogram you can only see shadows or a blurred outline of the lungs.
If the quality of the image is satisfactory, the radiologist will be able to examine the number and size of foci of inflammation, their location, as well as the nature of the contours (clear or blurry).
What the photo won't show
If pneumonia is not detected during fluorography, and the doctor suspects the presence of an inflammatory process, then he can send you for a secondary examination using more advanced techniques. Often, linear shadows that appear during pneumonia are poorly displayed in photographs. FLG does not allow one to clearly see the walls of thin cavities, so in this way, for example, it is not always possible to immediately notice a small cyst.
Fluorography is also powerless for:
- small focal pneumonia;
- pleurisy with limited fluid;
- atypical pneumonia with delayed radiological symptoms.
How many times can FLG be done for pneumonia?
If pneumonia is suspected, the doctor may prescribe a re-examination, this depends on the patient’s age and general condition. If the lesion can be seen immediately, one photo is enough. In cases of unsatisfactory visualization, the patient is referred for additional examination. As a rule, at the end of the course of treatment, the supervising doctor prescribes a control X-ray. However, it is impractical to do both repeated diagnostic and final studies using fluorography due to the limited capabilities of the method. As a rule, fluoroscopy copes better with this task, allowing you to vary the angle and direction of projections to obtain a large-format image.
There are only 2 types of fluorographic examination:
• Film is a traditional research method for Soviet times, but today it is already outdated and is used only in clinics and small provincial towns or villages. With film fluorography, the image is captured on a small film.
• Digital is a more modern and highly technological method that requires expensive equipment. With this method, the image is transmitted to a computer screen, where changes in the lungs can be studied in more detail than in the image. The radiation dose is several times less.
Types of fluorography
Film FLG is the cheapest diagnostic method, but in 15% of cases there is no accurate result, defects occur, which is why the study has to be repeated. And this is the second dose of radiation. In addition, the picture is obtained only in 1 copy.
Digital FLG does not have these disadvantages and the radiation dose is lower. With modern software, the doctor can examine the image even after the examination is completed.
The data is saved, and if necessary, after digital fluorography of the lungs, the patient can ask to print the number of images he needs. This may be necessary in complex diagnostic cases, when it is necessary to contact several doctors.
Fluorography remains today a preventive diagnostic method. Every year, the population of the Russian Federation who has reached 18 years of age undergoes fluorography.
Contraindications
X-ray is an informative study that has almost no contraindications or age restrictions. But pictures cannot be taken if the patient is in serious condition. Sometimes minimal exposure causes severe consequences.
X-ray examination is prohibited during pregnancy. Radiation disrupts the development of the fetus and causes its death. For infants after 2-3 months of life, x-rays are not contraindicated and help prevent serious illness and its consequences. X-rays are considered cutting-edge technology in medicine.
With a low dose of radiation, it provides a clear image of organs and pathological changes in them. But only a doctor knows what bronchitis looks like in a picture, so you should not try to diagnose the disease yourself.
Author: Glushko Raisa Therapist, pulmonologist, immunologist