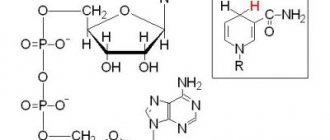
The purpose of the AST test is to determine the level of the enzyme aspartate aminotransferase in the blood. This specific cellular enzyme is involved in amino acid metabolism. It is found predominantly in the liver, myocardium, nervous tissue, and skeletal muscles, which is associated with a high level of metabolic processes in these tissues. It is found in smaller quantities in the kidneys, lungs, and pancreas. The level of AST in the blood should normally be low. If this indicator is elevated, this indicates the destruction of some tissues and the release of the enzyme from damaged cells and their release into the bloodstream. The more active the process of tissue destruction, the more AST enzyme enters the blood. Thus, an increase in the level of this indicator indicates pathological processes occurring in the body.
How is the research conducted?
To determine AST in the blood, a biochemical blood test is performed. The sample is taken from a vein in the morning on an empty stomach. A tourniquet is applied to the arm above the elbow. The needle and injection site are disinfected with alcohol. A needle is inserted into a vein and 15-20 ml of blood is taken, after which the tourniquet is removed, and the injection site is clamped with a cotton swab. The patient should bend his arm at the elbow and wait until the bleeding stops.
Using centrifugation, plasma is separated from formed elements, then the activity of aspartate aminotransferase in the blood is determined using chemical reactions.
Results are usually ready the next day. Decoding is the responsibility of the attending physician, who is familiar with the standards of the laboratory in which the analysis was carried out. It should be said that different laboratories may use different methods and reagents.
How to prepare?
To obtain reliable results, blood donation occurs on an empty stomach, that is, at least 8 hours must pass after eating. In addition, the day before the test you need to give up alcoholic drinks, fatty and fried foods, and avoid physical, mental and emotional stress. In the morning before the analysis, you should not drink tea, coffee, juice, but only clean water. It is recommended to stop taking any medications 1-2 weeks before the study. If this is not possible, you should notify your doctor. As a result, the procedure will be rescheduled for another time, or interpretation will take place taking into account the possible effects of medications on the result. In addition, you must tell your doctor if you are allergic to any medications or if you are pregnant.
You cannot donate blood for several hours after certain procedures, including:
- radiography;
- physiotherapy;
- rectal examinations;
- fluorography;
- Ultrasound.
Why do they do it?
Using this analysis, the following is carried out:
- Checking the liver for damage.
- Detection of diseases such as liver cirrhosis, hepatitis.
- Finding out the causes of jaundice: liver disease or problems in the circulatory system.
- Checking the effectiveness of the treatment.
- Assessing the effect on the liver of medications that can cause liver damage.
- Diagnosis of heart diseases.
Indications for analysis are all liver diseases
AST analysis allows you to determine cytolysis (the process of cell destruction) of the heart muscle and liver. An increase in this parameter is not observed when other organs are damaged. The purpose of the study is to detect damage to specific tissues, as well as differential diagnosis and exclusion of liver and heart diseases.
Indications for analysis
A biochemical blood test, during which the AST level is determined, is prescribed for a number of diseases, including:
We also recommend reading: Treatment of elevated bilirubin in the blood
- All liver pathologies.
- Diseases of the circulatory system.
- Chronic and acute heart diseases.
- Kidney failure.
- Infections.
- Intoxication.
- All types of jaundice and bilirubin metabolism disorders.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Purulent-septic pathologies.
- Encephalopathy of unknown etiology.
- Bile outflow disorders, cholelithiasis.
- Chronic pancreatitis.
- Endocrine diseases.
- Malignant tumors.
- Allergic skin diseases.
- Long-term treatment with antibiotics, chemotherapy and various toxic drugs.
- Injuries to the abdomen and chest.
- Preparation for a complex surgical operation.
- Evaluation of treatment of liver and cardiac pathologies.
Why enzymes may be elevated
The liver is one of the largest glands in the human body. It participates in metabolic processes, cleanses the blood of toxic and poisonous substances, and controls a number of biochemical processes. Most of these changes occur due to enzymes synthesized by the gland itself.
Liver enzymes (enzymes) maintain consistency in the body, acting in a manner invisible to humans. With the development of pathological conditions, the level of liver enzymes changes up or down, which is an important sign and is used in differential diagnosis.
Enzyme groups
Important! Digestive problems, fatigue, papillomas and warts can be a consequence of infection of the body with parasites. They live for years in our body, sucking all the juices out of us, suppressing the immune system and destroying internal organs.
- Indicative. These enzymes indicate the presence of organ pathology in the form of destruction of its cells. These include AST (aspartate aminotransferase), ALT (alanine aminotransferase), GGT (gamma-glutamyltransferase), GDH (glumate dehydrogenase), LDH (lactate dehydrogenase). The first two enzymes are most often used for diagnostic processes.
- Secretory (cholinesterase, prothrombinase). Participate in supporting the functioning of the blood coagulation system.
- Excretory (representative - alkaline phosphatase). Found in bile components. During research, this enzyme shows the functioning of the biliary system.
Alt and ast
These are microsomal liver enzymes, the level of which is monitored by a biochemical blood test. AST is an endogenous enzyme produced inside hepatocytes. It is also synthesized by cells of other organs, but in smaller quantities (heart, brain, kidneys, intestinal tract). A change in the level of an enzyme in the blood indicates the development of the disease, even if there are no visible symptoms yet.
ALT is produced by cells of the liver, heart muscle, and kidneys (insignificant amounts). It is determined by a blood test in parallel with the first enzyme. An important diagnostic point is to clarify the ratio of Alt and ast.
Reasons for the increase
The increase in liver enzymes can be minor, occurring due to taking a number of medications or the accumulation of toxic substances in the body, or pronounced, appearing during the development of diseases.
Enzymes can increase with long-term treatment with painkillers, statins (drugs that are used to remove “bad” cholesterol from the body), sulfonamides, and Paracetamol.
Provoking factors may be drinking alcohol and consuming fatty foods.
If the blood test for liver enzymes shows elevated levels, this indicates the following pathological conditions:
- viral inflammation of the liver (hepatitis);
- cirrhosis;
- fatty liver hepatosis;
- primary malignant tumor of the liver;
- secondary tumor processes with the formation of metastases in the gland;
- inflammation of the pancreas;
- myocardial infarction;
- myocarditis of an infectious nature;
- heart failure.
Such manifestations may not have visual symptoms or be accompanied by a number of complaints from the patient:
- decreased performance, constant fatigue;
- abdominal pain syndrome;
- loss of appetite;
- itching of the skin;
- yellowness of the sclera and skin;
- frequent bruises, nosebleeds.
A blood test for enzymes involves not only assessing the level of well-known Alt and Ast, but also other enzymes. Alkaline phosphatase and GGT have important diagnostic value. The level of these enzymes goes beyond normal limits in pathologies of the biliary system, for example, in cholelithiasis, tumor processes.
Together with these enzymes, bilirubin, which is a bile pigment, is assessed. Clarifying its numbers is important for cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, cirrhosis, lamblia, vitamin B12 deficiency, and poisoning with alcoholic beverages and toxic substances.
During the period of bearing a child, a number of changes occur in a woman’s body. Her organs and systems begin to work for two, which is reflected not only in her general condition, but also in laboratory indicators.
Alt and ast levels during pregnancy are up to 31 U/l. If toxicosis develops at 28-32 weeks of gestation, the numbers increase. The first two trimesters may be accompanied by a slight deviation from acceptable limits, which is not considered a problem, since the load on the liver becomes maximum during this period.
The norm of alkaline phosphatase is up to 150 U/l. Active growth of the fetus from the 20th week until the moment of birth causes an increase in enzyme numbers. The level of alkaline phosphatase changes when taking large doses of ascorbic acid, antibacterial drugs, and calcium and phosphorus deficiency.
Acceptable indicators of the main important enzymes are indicated in the table.
When determining elevated liver enzymes, the doctor prescribes a number of additional examinations to clarify the patient’s condition. The specialist immediately recommends that the patient begin treatment by adjusting the diet. The goal is to reduce the load on the liver, reduce the level of fatty deposits in it, and remove toxins and waste.
It is important to increase the amount of vegetables you eat. Spinach, kale, greens, lettuce, and dandelion greens are considered especially healthy. You also need to increase the amount of foods you consume that contain antioxidants (avocados, nuts).
The daily menu should contain at least 50 g of dietary fiber, in particular fiber. Such substances cleanse the body of “bad” cholesterol and help normalize the functioning of the biliary system. Fiber-rich foods:
- fruits;
- nuts;
- cereals;
- berries;
- legumes;
- leafy green vegetables.
Treatment includes the supply of a sufficient amount of protein, because protein substances are considered the necessary basis for the restoration of damaged hepatocytes. However, the doctor will tell you exactly how much of it should be present in the daily diet. It is important not to consume too much, so as not to overload the liver’s mechanism for processing proteins.
It is necessary to drink enough clean water. Every day you need to drink up to 2 liters of liquid: on an empty stomach, before each meal, before and after physical activity, before evening rest.
Herbal medicine has a beneficial effect on the condition of the liver and reduces pathological enzyme levels. Treatment consists of drinking teas based on herbal ingredients. It is important to consult with your doctor about the possibility of such activities.
You need to add turmeric to your food, which reduces the manifestations of inflammatory processes, and garlic, which has an antitumor effect. Antioxidant-rich dietary supplements can be used with your doctor's approval.
Treatment of diseases
If during diagnostics a pathological process is discovered, which was the cause of the increase in liver enzymes, it must be treated. A qualified specialist will select a treatment regimen for the patient according to a specific clinical case.
Liver enzymes play a significant role in a number of processes occurring in the human body. Their diagnostic value is the ability to detect diseases and pathological conditions in the early stages.
Liver enzymes, mainly alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), provide a detailed assessment of normal and pathological organ functioning.
Enzymes (liver enzymes) are produced in large quantities and enter the blood. When the functions of this organ are impaired, certain enzymes increase or decrease in the blood and this indicates a disease.
Enzymes - what are they?
Metabolic processes are carried out thanks to enzymes contained in the hepatobiliary system. Microsomal liver enzymes in dynamic constancy determine the normal functioning of this organ.
Thus, mitochondria contain enzymes for liver energy metabolism. Most enzymes are amenable to proteolysis (cleavage), some enzymes are excreted in bile.
Using laboratory diagnostics, one or another liver enzyme can be determined. A liver enzyme test can be done at any time; there are rapid tests to determine the necessary indicators. Today, analysis and objective evaluation of enzyme tests are important for clinical practice.
Enzyme inducers of cytolysis and inducers of cellular damage, cholestasis, and disruption of the synthetic function of the organ are discussed.
Liver enzymes are divided into several groups:
- Secretory (prothrombinase, cholinesterase). They affect the blood coagulation process; if the functions of the hepatobiliary system are disrupted, these enzymes are reduced;
- Indicator (AST, ALT, LDH). They are found inside cells, when an organ is affected, they are washed out of the cells and their level rises in the blood;
- Excretory (alkaline phosphatase). They are synthesized and excreted in bile. When the flow of bile is disrupted, this liver enzyme increases.
Most often, to diagnose diseases of the hepatobiliary system, they use the determination of AST, ALT, gamma-lutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP).
Liver enzymes GGT and LDH can be measured during pregnancy. The liver enzyme alkaline phosphatase is necessary for accurate differentiation of diseases of the hepatobiliary system.
Having done the analysis, the patient will be able to go with the data to the doctor, who will evaluate the functions of the affected organ. During pregnancy, it is especially important to do a biochemical analysis to monitor the woman and fetus in order to identify pathology in the early stages.
When does AST increase?
The reasons for the increase in the enzyme in most cases are associated with diseases. Among them:
- acute myocardial infarction is the most common cause of high AST levels, and the more extensive the tissue damage, the higher the concentration of the enzyme in the blood;
- infectious or autoimmune myocarditis;
- rheumatic heart disease;
- heart injury (open);
- liver cancer;
- liver metastases;
- viral hepatitis;
- alcoholic hepatosis;
- fatty hepatosis;
- toxic liver damage;
- damage to the liver and heart in malignant myeloid leukemia;
- heart failure;
- angina pectoris;
- massive muscle destruction: generalized myositis, crash syndrome, myodystrophy;
- acute pancreatitis.
In addition, the enzyme can be increased during alcohol intoxication, heat stroke, skeletal muscle injuries, burns, emboli in blood vessels, and poisoning with poisonous mushrooms. A slight increase is observed when taking certain medications (antibiotics, sedatives, etc.) and during significant physical exertion.
What other liver tests are there?
In addition to the main AST and ALT, the levels of GGT, ALP, and LDH are determined.
The GGT norm is up to 40 U/l. In addition to the main organ, GGT is found in large quantities in the kidneys, pancreas, and walls of the bile ducts. The determination of GGT is a particularly sensitive test during pregnancy and in children. Increased GGT activity is observed in hepatitis, cirrhosis, tumors, cholestasis, alcohol intoxication, obstructive jaundice, cholangitis.
Dynamics of ALT, AST, GGT, alkaline phosphatase depending on age
Decreased GGT activity – in decompensated cirrhosis. GGT is a highly sensitive indicator, especially in the presence of toxic effects. If the analysis is done and aminotransferase levels are normal, then GGT levels will be increased.
Alkaline phosphatase
The norm of alkaline phosphatase is up to 270 U/l.
It is also found in bone tissue, the walls of the bile ducts, and kidneys. An analysis is done if the functions of the hepatobiliary system are impaired.
An increase in the indicator occurs with cholestasis, obstructive jaundice, biliary cirrhosis, and hepatitis. Increased during pregnancy (in the third trimester), with the use of hepatotoxic drugs. If you do a test and the alkaline phosphatase level is low, this indicates the use of glucocorticosteroids.
The norm of lactate dehydrogenase is up to 250 U/l. There are several LDHs, so LDH 1-2 is found in the myocardium and erythrocytes, LDH 5 is in the liver, LDH 4-5 is in skeletal muscles. In case of dysfunction of the hepatobiliary system, an analysis is performed for LDH 5. Increased activity is observed in acute hepatitis, obstructive jaundice, and tumors. There is also an increase in activity during pregnancy and massive physical exercise.
AST growth levels
There are three levels of increase in AST in plasma:
- minor – with fatty deposits in the liver, taking certain medications (antibiotics, statins, aspirin, antitumor drugs, barbiturates, etc.);
- medium – for heart attack, heart failure, liver cirrhosis, some types of cancer, alcoholism, autoimmune diseases with muscle damage, taking high doses of vitamin A, lung and kidney damage, muscular dystrophy, mononucleosis;
- high – with multiple liver damage due to viral hepatitis, reactions to drugs and medications, with necrosis of a large tumor.
AST in the blood has diagnostic value in myocardial infarction
The highest level of AST is observed at the onset of the disease with significant tissue destruction. A decrease in the enzyme in the blood means the beginning of liver restoration and recovery. A slight increase in AST is not yet a sign of tissue destruction. An AST level that is more than twice the normal level has diagnostic value.
AST and ALT ratio
The aminotransferase ratio is pathognomonic for hepatobiliary system disease. The liver enzyme AST itself is also found in the myocardium, skeletal muscles, and kidneys. The liver enzyme ALT is found only in this organ.
The ALT norm is 10-40 U/l, the AST norm is 10-30 U/l.
ALT:AST ratio = 1 (alanine aminotransferase level greater than or equal to aspartate aminotransferase) indicates acute hepatitis. If ALT:AST is higher than 2:1, then this ratio indicates alcoholic illness. An AST:ALT ratio greater than 1 (AST exceeds ALT) indicates cirrhosis.
Increased activity of AST and ALT occurs with necrosis of hepatocytes of any etiology, obstructive jaundice, and fatty degeneration. A decrease in activity is characteristic of extensive necrosis and cirrhosis.
ATTENTION!
Many of our readers actively use a well-known technique based on natural ingredients, discovered by Elena Malysheva, to treat and cleanse the liver. We recommend that you check it out.
In addition, these liver enzymes play an important role in determining the hepatotoxicity of drugs. Thus, AST and ALT increase during long-term use of anticoagulants, barbiturates, hormonal contraceptives, antiepileptic drugs, ascorbic acid, codeine, morphine, erythromycin, gentamicin, lincomycin. A decrease in activity is observed during pregnancy.
How to downgrade?
An increase in AST in the blood is always caused by the development of some pathology associated with the destruction of cells of the heart muscle, liver and some other tissues. It is important to understand that it is impossible to reduce the concentration of the enzyme without treating the primary disease. Therefore, the main task of the doctor when detecting increased AST activity in the blood plasma is to diagnose and prescribe treatment. A decrease in AST will occur only after the disease is eliminated. With proper and timely treatment, normalization is possible within a month to a month and a half.
ALT and ASAT in a biochemical blood test: what is it, the norm, explanation
GGT, ALT, bilirubin, AST, albumin in hepatic cirrhosis can say a lot about the course of the disease; they are some indicators. Cirrhosis is a rather dangerous disease, which today most often occurs in people in the age group from 30 to 70 years.
In the CIS countries, such a terrible disease is detected in every hundredth person. Most of the patients are men. The disease and the complications it can cause are the cause of numerous deaths.
The duration and quality of life of the patient largely depends on the stage at which the disease was detected. To identify this pathology, various diagnostic methods are used - tissue biopsy, ultrasound, blood tests. Based on the information received, the doctor selects supportive treatment that allows the patient to live with the disease for a long time.
In most cases, in the first stages, the symptoms of the disease do not manifest themselves in any way. To avoid detection at later stages, preventive examinations should be carried out every 6 months.
This is a disease that provokes structural changes in the liver, resulting in liver failure and high pressure in the portal zone and its tributaries. The nature of the disease in question is chronic, the disease gradually progresses. The causes of liver cirrhosis can be different. Among them:
- presence of hepatitis virus in the body;
- consumption of large quantities of alcoholic beverages, chronic alcoholism;
- the presence of an autoimmune process in the body;
- poisoning with toxic substances;
- heart failure;
- long-term influence of helminths, as well as their metabolic products.
Usually this disease manifests itself with secondary symptoms, to which the patient does not always respond. Symptoms:
- increased body temperature;
- high fatigue, general weakness;
- itching of the skin;
- irritability, sleep disturbance, mild excitability;
- disruption of digestive processes;
- change in color of stool, urine;
- sudden weight loss.
After some time, the patient’s whites of the eyes and skin begin to turn yellow, pain appears in the right side, nausea and vomiting occur, and the vascular wall expands.
The protracted course of the disease passes with the development of complications. If cirrhosis is not treated, this can cause the development of portal hypertension, abdominal dropsy, and atrophy of the body’s functioning - complete or partial.
If there is a disease, the doctor determines what tests need to be done to make an accurate diagnosis. It is impossible to get rid of this disease. Maintenance treatment is prescribed, the main task of which is to eliminate the symptoms that appear and thereby alleviate the condition of the sick person. The prognosis for the patient is usually unfavorable.
Determining liver cirrhosis involves prescribing various tests. Laboratory indicators make it possible to obtain the most complete picture of the disease based on the results. The indicators of the main enzymes are taken as a basis. They show the condition of the liver.
To date, a generalized liver test has not been developed, so experts take the tests together and decipher them.
Diagnosis is carried out taking into account the following blood parameters:
- quantitative alanine aminotransferase assay;
- quantitative assay for gammaglutamyl transpeptidase
- quantitative aspartate aminotransferase assay;
- quantitative study of albumin;
- assessment of prothrombin time;
- quantitative study of bilirubin, as well as qualitative;
- review of total blood protein;
- analysis by quantitative ALP testing;
The assessment of synthetic processes in the liver and the percentage of its saturation with toxins is based on the interpretation of test data. Thanks to the blood test, accurate indicators can be seen very quickly, which makes it possible to quickly begin treatment of the disease.
Alanine aminotransferase is synthesized in liver cells. Often only a small amount of the enzyme enters the blood. When the cells of a diseased organ are destroyed, ALT is released and enters the blood vessels through the blood. This condition can provoke:
- presence of hepatitis;
- disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas;
- the patient has renal or heart failure;
- poisoning;
- presence of liver cirrhosis.
Based on the deviation of ALT from the norm, which ranges from 6 to 37 IU per liter, conclusions can be drawn about how damaged the organ was. Often, with a complex course of the disease, the ALT level increases 10 times or more.
Sometimes this indicator can increase in pregnant women. This happens due to a deficiency of B vitamins and the presence of toxicosis in the woman’s body.
This condition can occur in the first three months of bearing a baby; in subsequent months the condition returns to normal.
For a detailed study, the indicators of two enzymes are taken into account simultaneously - AST and ALT, the level of which increases significantly during the analysis.
This enzyme is a component of the tissue of organs such as the heart, liver, kidneys, and is also a component of the nervous system. An increase in ALT levels in the analysis can be detected in the presence of:
- malignant neoplasms;
- myocardial infarction;
- liver cirrhosis;
- severe burns;
- traumatic influence.
An increased indicator indicates that poisoning has occurred with toxic substances, as well as the presence of developed fibrosis. A strong increase in the analysis (in women the normal value is up to 35 IU per l, in men - a maximum of 41 IU per l, in children - a maximum of 50 IU per l) develops with parallel destruction of liver cells.
AST and ALT in hepatic cirrhosis should be assessed together. The ratio of these enzymes is called the de Ritis coefficient.
When the indicators go off scale during analysis, this indicates that the organ tissue has died, that is, necrosis of the organ has occurred.
A mandatory test in the presence of hepatic cirrhosis is the HGG study. This component is synthesized in the cells of the liver and pancreas. It is involved in amino acid metabolism.
If a person’s health is in order, then this indicator has the following standards:
- for women - from 6 units. per l to a maximum of 42;
- for men - from 10 units. per l to a maximum of 71.
An increase in the amount of this component in the bloodstream occurs under the influence of:
- overdose of medications;
- drug use;
- alcohol abuse;
- poisons;
- toxins.
In hepatic cirrhosis, the level of HGG also increases. If the concentration of GGG remains high for a long time, this indicates a serious condition of the organ.
The analysis also takes into account the ALP indicator. Stands for alkaline phosphatase. For women in a healthy state, this figure should not exceed 250 units per liter, for men - 270 units per liter.
The component in question takes part in the production of bone tissue; it is for this reason that children during the period of active growth have a slightly higher quantity of this component. In addition, ALP take part in the formation of bile ducts, mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, in the fetal placenta, and mammary glands during the lactation period.
An increased amount of this indicator indicates the destruction of liver cells, as well as obstructed bile outflow.
The indicator can increase significantly in case of mechanical damage, hepatitis, autoimmune diseases of the organ, and necrosis.
This element is a component of bile. It is the main indicator of blood bioanalysis for cirrhosis. Bilirubin synthesis occurs in liver cells and spleen tissues. There are such states of components: direct, another name for which is free, and indirect, another name for which is bound.
In cirrhosis, tests can show an increase in the normal value (maximum 4.3 mmol per l) of the associated type. This is caused by liver damage as a result of the influence of the pathological process. Cells in the liver are actively destroyed.
In addition, the enzyme molecules will not fully bind, and this process will be disrupted. Its increased amount in the bloodstream will cause a change in the color of the sclera and skin - they will turn yellow. The patient will also have a change in the color of urine and feces, and itchy skin will appear. Tests for bilirubin are required.
A high value (over 17 mmol per l) of indirect bilirubin occurs if there is obstruction of the bile ducts. This condition can be caused by biliary cirrhosis. In case of hepatic cirrhosis, the indicators of the component in question should not be higher than 20.5 mmol per liter.
In case of hepatic cirrhosis, the specialist determines what tests the patient should undergo. A prothrombin index test is usually prescribed. This is the percentage ratio of the clotting time of blood plasma to the clotting time of the test material. Normal values are in the range of 94-100%.
An increase in the index indicates that congenital bleeding defects are present. This may also be a clear sign of a deficiency of certain vitamins or the presence of cancer. An increase may also be caused by the use of oral contraceptives. An increased index is also seen in patients with hepatic cirrhosis.
Albumen
This component is also being studied. If the indicator is low (its norm is 35-50 g per l), then complex lesions of liver cells are detected.
conclusions
- Liver tests are an integral part of the diagnosis of hepatic cirrhosis, a dangerous disease that cannot be cured and is chronic.
- Thanks to modern diagnostics, this disease can be cured in the early stages.
- To establish a diagnosis, the results of various biochemical tests are used.
- Based on the results, the doctor can choose the right therapy for the patient, thus prolonging his life.
When a person is sick, it is almost impossible to make a correct diagnosis and prescribe competent treatment without tests. Often it is not necessary to undergo all existing laboratory tests.
Today, it is enough for a doctor to study the transcript of a biochemical blood test and the normal values of ALT and AST in an adult or child in order to understand the full nature of the disease. One of the most important indicators in this analysis is the level of liver enzymes - ALT and AST.