What it is?
Hemostasis includes a complex of functional, morphological and biological systems that maintain the state of blood in liquid form, preventing it from coagulating within a closed circulation. If the integrity of the vessels is compromised, a blood clot forms, which clogs the site of injury, resulting in the bleeding stopping. The basis of the thrombus is fibrin, which is removed later.
Later in the article we will understand why a blood test for hemostasis is needed.
Basic functions of hemostasis
Without hemostasis, it is impossible to maintain the viability of the body; thanks to this system, blood does not leave the circulation. You can figure out what this is after finding out why this system is required in the body.
Experts identify such functions of hemostasis.
- Keeping blood in a liquid state in the bloodstream . It is important to maintain the correct consistency: if the blood is liquid, then the person suffers from increased bleeding, if it is thick, from thrombosis.
- Stop bleeding . With various vascular injuries (for example, cuts), the blood coagulation system is activated.
- Wound healing . This process is called fibrinolysis. The blocking thrombus formed when the integrity of the vessels is disrupted dissolves.
The hemostasis system is quite complex. The body must constantly maintain a balance between the formation of a blood clot and its dissolution. Failures in this process are signs of serious diseases and can lead to dire consequences.
Which enzyme is responsible for clotting?
There are 13 enzymes responsible for blood clotting in our body. Such proteins are called coagulation factors. This process is carried out in several stages and represents the transformation of a proenzyme into an enzyme (or an inactive factor into an active one). This starts a chain reaction. And such a process is usually called a coagulation cascade.
It can be external and internal. For the latter, all the necessary components are already in the blood. And to activate the external pathway, thromboplastin is required, which is a tissue factor. In the normal state it is not present; it is produced only in case of cell damage.
To identify this condition, a blood test for hemostasis is performed.
How to take a hemostasiogram during pregnancy preparation
In order for the results to be as accurate as possible, the patient must know some of the nuances of performing a hemostasiogram. For laboratory testing, blood is drawn from a vein. The test must be taken on an empty stomach, so the best time to donate blood is in the morning.
Also, before diagnosis, you should not drink drinks such as tea, coffee, compotes, juices, etc. Only drinking pure water without additives is allowed. In addition, the day before the test, doctors recommend excluding any physical and emotional stress. And if on the eve of the study you took any medications, then do not forget to warn the medical professional who is conducting the analysis about this, or write down the data about this in a special questionnaire.
Mechanisms
The described process has two main mechanisms:
- Vascular-platelet or primary. It involves blood cells, including red blood cells, platelets, as well as bioactive substances, vessel walls and extravascular tissue. It is caused by the development of a special plug to plug the damage.
- Coagulation or secondary. Plasma and tissue coagulation factors are involved in this process. The mechanism converts fibrinogen into fibrin, which does not dissolve. In this way, it is possible to stop bleeding in those vessels where the primary mechanism was insufficient. This occurs when the platelet clot is unable to cope with the increased pressure in the bloodstream and a larger clot is needed.
The process of hemostasis occurs through the interaction of such structural components as vascular walls, plasma enzymes and blood cells. All its components include elements that prevent it from folding, and those that ensure the formation of a blood clot at the site of damage.
Fibrinolysis is a mechanism that is responsible for the breakdown of fibrin, restoration of vascular patency, and maintenance of normal blood thickness. This system contains plasmin, plasminogen activator, and inhibitors. Fibrinolysis can be enzymatic or non-enzymatic, and sometimes occurs via external or internal activation pathways. This process is based on the ability of leukocytes to destroy and digest pathogenic organisms, eliminate thrombosis and remove its remains.
Comprehensive analysis of the hemostatic system: coagulogram
A coagulogram is a set of laboratory tests that give an idea of the state of the hemostatic, anticoagulation and fibrinolysis system.
Among the tests there are simple (approximate) ones - allowing to identify gross changes, and clarifying ones, which characterize in more detail the mechanism of existing violations.
Complex methods for studying the vascular-platelet hemostasis system include:
- Bleeding time
- Platelet count determination
- Determination of platelet adhesive and aggregation ability
- Blood clot retraction study, etc.
Bleeding time (BT) is the interval between the time the flesh of the finger is punctured and the bleeding stops.
Normally, bleeding stops within 2-3 minutes from the moment of puncture and gives an idea of the function of platelets.
Prolongation of bleeding time is observed with:
- Hereditary thrombocytopenia
- DIC syndrome
- Vitamin deficiency C
- Long-term use of aspirin and other anticoagulants
Along with platelet counting, platelet adhesion is determined - the property of sticking to the damaged vessel wall.
The normal adhesiveness index is 20-50%.
A decrease in the index indicates a decrease in adhesive ability and is observed when:
- von Willebrand's disease
- Thrombocytopathies (including Glanuman thrombosthenia)
- Acute leukemia
- Kidney failure
Platelet aggregation is the ability of platelets to join together. Spontaneous aggregation is normal - 0-20%.
An increase in aggregation capacity is observed when:
- In the initial period of DIC syndrome
- Atherosclerosis
- Thrombosis
- Myocardial infarction
- Diabetes mellitus
A decrease in aggregation capacity is noted:
- For Glatzmann's thrombosthenia
- For von Willebrand's disease
- For thrombocytopenia
The definition of blood clot retraction is the process of contraction, compaction and release of serum by the blood clot after the formation of fibrin by the action of a protein contained in platelets.
The normal retraction index is 48-64%.
The retraction index is the ratio of the volume of isolated serum to the volume of blood taken. Its decrease occurs with thrombocytopenia.
Methods for studying coagulation hemostasis include:
- Clotting time
- Prothrombin index (PTI)
- Determination of thrombin time
- Determination of fibrinogen amount
- Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT)
- Determination of plasma tolerance, etc.
Clotting time is the interval between drawing blood and the appearance of a fibrin clot in it.
The norm for venous blood is 5-10 minutes.
The norm for capillary blood: start - 30 seconds - 2 minutes, end - 3-5 minutes.
An increase in clotting time occurs during hypocoagulation due to a lack of a number of plasma coagulation factors or the action of anticoagulants. Observed when:
- Hemophilia
- Liver diseases
A decrease in clotting time is noted due to hypercoagulation with:
- Taking oral contraceptives
- After massive bleeding
In DIC syndrome, in the first stage the coagulation time is sharply accelerated, and in the second and third stages it lengthens until complete non-coagulation.
The purpose of a blood test for hemostasis
The described study is carried out to identify disorders in the circulatory system. This is a rather complex analysis aimed at a comprehensive assessment of the entire coagulation process in the human body.
Pathologies can occur on both sides: both in the coagulation and anticoagulation systems. In the latter case, there is a tendency to develop hemorrhagic syndrome, while in the first case, to the formation of blood clots.
A hemostasis test can reveal thrombophilia - a high rate of blood clotting. This is dangerous due to the occurrence of infertility or the inability to bear a child, as well as heart attack, thrombosis of the lower extremities due to varicose veins and stroke.
Low blood clotting is characterized by bleeding. Thus, the damage takes a very long and difficult time to heal. The risk of postoperative complications, hemorrhagic syndrome and internal bleeding increases.
We will consider below how to take a blood test for hemostasis.
Rules for taking the analysis
An in vitro hemostasiogram is performed - the patient’s blood must be taken for analysis. Blood for a hemostasiogram is taken from a vein in the morning on an empty stomach. For women, it is advisable to take this test not during menstruation, since blood loss will lead to a physiological increase in blood clotting.
The results of a hemostasiogram are usually ready 1.5 - 2 hours after the test. If you have been prescribed a hemostasiogram, deciphering the analysis by parameters may be difficult for a non-specialist.
USEFUL INFORMATION: Abdomen after laparoscopy
You can roughly determine your performance. Find the form with the heading coagulogram or hemostasiogram. The norm or reference values are usually indicated in brackets or in a separate column. Compare your performance with the norm. However, only a doctor can make the final interpretation of the analysis.
When is such research necessary?
The need for hemostasis analysis is due to the following situations:
- Diagnosis of the causes of bleeding, hemorrhagic rashes and hemorrhages.
- Prevention of hemorrhagic syndrome after surgery.
- Detection, prevention and treatment of heart attacks, strokes and thrombosis.
- Gynecological diseases, pregnancy planning, gestation period.
A certain system for deciphering hemostasis in a blood test is used.
Where can I rent it and what is the price?
You can get tested for hemostasis in Invitro laboratories. The company's offices are located in all major cities. Only high-level specialists work in the laboratories, and consultant doctors will be able to help with deciphering the results. Prices for studying the hemostasis system can be found on the Invitro website. All of them are true.
Thus, when prescribing a coagulogram, both regular and extended, it is worth contacting the Invitro laboratory network. This is where the most accurate results are provided at low prices.
Nowadays, it is worth paying close attention to your health. Therefore, preventive examinations should be carried out at least once a year. And in old age it’s better to do it twice. This will help prevent most diseases. You shouldn’t brush aside your own health, because then it may be too late.
Indications for and types of tests
Most often, a blood test for hemostasis is carried out when large blood losses are expected, as well as in a comprehensive examination to identify certain diseases. A coagulogram is included in the list of examinations in the following cases:
- during the period of bearing a child;
- in the pre- and postoperative period;
- for thrombosis and venous dilatation of veins;
- for autoimmune diseases - rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, etc.;
- for liver pathologies;
- after heart attacks and strokes;
- during therapy with antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants;
- with hemorrhagic diathesis;
- during the planning period for an upcoming pregnancy.
The latter especially concerns women with a history of gynecological diseases, including infertility and miscarriage.
Cost of analysis
This type of analysis is quite complex. If a hemostasiogram is recommended for you, the price, depending on the number of parameters, can reach several thousand rubles. In some cases, the doctor may order an incomplete test. In this case, the direction will indicate the type of analysis and separately the parameters that should be determined. For example, like this: hemostasiogram (RFMC, INR, APTT, fibrinogen).
Our health is priceless. The results of a hemostasiogram are of great importance for the successful treatment of a number of pathologies. Correction of coagulation system disorders without analysis is impossible.
During pregnancy, the female body, more than ever, must work harmoniously, but not all expectant mothers experience this time well. Even minor violations have a negative impact not only on the health of the woman, but also the child.
Therefore, it is necessary to pay special attention to the work of your own body in order to identify and eliminate various diseases in time; many deviations in its work can show
Tests
Analysis for hemostasis consists of conducting several tests, namely:
- INR—determines the time it takes for blood to clot.
- APTT is the time required for a clot to form after combining plasma with reagents.
- Thrombin time is the period during which fibrinogen is converted to fibrin under the influence of thrombin.
- Fibrinogen.
The result of the study is a coagulogram, which requires interpretation by a specialist. The main indicators are APTT and INR, since they demonstrate activation along the external and internal pathways of blood coagulation. When they are normal, this indicates the absence of serious problems with hemostasis. What abnormalities does a blood test for hemostasis reveal?
Fibrinogen and APTT
Fibrinogen is a protein synthesized in the liver and converted into fibrin under the influence of factor XIII. The normal level of fibrinogen in the blood is 2-4 g/l.
An increase in fibrinogen indicates increased coagulation and the risk of blood clots and is noted:
- At the end of pregnancy
- After childbirth
- After surgery
- For pneumonia
- For lung cancer
- In phase I of acute DIC syndrome
A decrease in fibrinogen is noted:
- In phases II-III of acute DIC syndrome
- For severe forms of hepatitis
Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) is used to investigate plasma defects in thromboplastin formation.
Normal APTT is 28-38 seconds.
An increase in APTT is noted:
- With hypocoagulation (factor deficiency - II, V, VIII, IX, XI, XII)
- In phases II and III of DIC syndrome
- When using heparin
A shortening of time indicates activation of the blood coagulation process (increased activity of plasma factors).
Violations
If there are deviations from the norm in the study parameters, the patient may experience the following pathologies:
- Cogualopathy. Impaired functioning of blood coagulation and anticoagulation systems.
- Hypocoagulation-hemorrhagic syndrome. It is characterized by a reduced level of platelet accumulation, which leads to a decrease in the activity of plasma and tissue clotting factors. The result is bleeding and hemorrhagic syndrome.
- Hypercoagulation-thrombotic syndrome. High levels of platelet accumulation and activity of plasma and tissue clotting factors, which leads to the formation of blood clots.
- Thrombo-hemorrhagic syndrome or DIC syndrome. This is disseminated blood coagulation within blood vessels with the formation of an abnormal number of blood clots and blood cell aggregates. As a result, a malfunction occurs in the circulatory system, which becomes the cause of dystrophic pathologies.
general information
It is important to understand that hemostasis is a complex of various processes and functional and morphological mechanisms that ensure blood fluidity and prevent its clotting. If a crack forms on the walls of blood vessels, it is thanks to hemostasis that it is sealed by the formation of a blood clot, which is removed after restoration of the soft tissue.
Gene mutation test
Deciphering a blood test for hemostasis does not always allow one to predict possible risks associated with the occurrence of pathologies in the area of coagulation in a particular patient. Therefore, additional research is being carried out on the genes responsible for the activation of the entire system, for example, in the presence of inflammatory processes and during pregnancy. Indications for sending blood for the study of gene mutations are:
- Selection of oral contraceptives.
- Infertility and inability to bear fruit.
- Hormone replacement treatment.
- Smoking by patients under 50 years of age.
- Thrombosis in patients under 50 years of age.
- Before gynecological surgery, endoprosthetics and transplantation.
- Previous strokes, thrombosis, heart attacks under the age of 50 years, pulmonary embolism. Moreover, this concerns not only the patients themselves, but also their closest relatives. The same rule applies to relatives of those who died before reaching 50 years of age.
- Hearing impairment of unknown etiology.
- After chemotherapy.
In all of the above cases, there is a need to examine the blood for gene mutations in the coagulation system, as well as folic acid metabolism.
Polymorphism of hemostasis genes
These are mutational changes in genes responsible for hemostasis, which lead to various pathologies. Polymorphism happens:
- Congenital and representing hereditary transmission in a descending line, disorders of the properties of blood and the structure of blood vessels. The child runs the risk of inheriting such problems from one or both parents. The abnormality may affect one or more genes. Symptoms of carriage appear:
- in childhood;
- during pregnancy;
- during therapy with hormone replacement drugs, the use of oral contraceptives;
- never. Blood clotting disorders in close relatives are a reason to consult a doctor to check the functionality of your own hemostatic system.
- Acquired, which is the result of exposure to various factors. For example, antiphospholipid syndrome - an autoimmune pathology - leads to the fact that the body begins to synthesize antibodies to “native” phospholipids, which leads to blood clotting disorders. This is rare, but mutations in hemostasis genes also occur for reasons such as:
- prolonged exposure to chronic infections, stress;
- oncological or endocrine pathologies;
- injuries;
- taking certain medications.
Doctors are increasingly adding tobacco smoking to the list of factors, since nicotine affects blood clotting, which means it may be one of the acquired causes of mutation of hemostasis genes.
The consequences of congenital defects of hemostasis genes are such conditions as:
- thrombophilia is a pathology caused by increased blood clotting, resulting in an increased risk of thrombosis (the development of vascular blood clots);
- fetoplacental insufficiency during pregnancy;
- miscarriage;
- the birth of underdeveloped or dead children.
The polymorphism factor of hemostasis genes can be identified by undergoing a special hemotest.
Blood test for hemostasis during pregnancy
Women during pregnancy occupy a special place in the study of the functioning of hemostasis. During this period, the risk of increased blood clotting is especially high, which can lead to blockage of disseminated vessels. The result of this process can be thickening of the blood and, as a result, a disruption of the blood supply to the placenta.
Along with the blood, the fetus ceases to receive sufficient oxygen, as well as useful nutrients. An anomaly in the development of the child occurs, which ends in the fading of the pregnancy or the death of the fetus. Timely diagnosis of such disorders will enable a woman to bear and give birth to a healthy baby.
What is a blood test for mutations in hemostasis genes? This is a common question among pregnant women. The fact is that hemostasis can change during gestation. Causes may include excess weight, injury, stress, chronic infections and cancer. But before pregnancy, a woman may not be aware of existing clotting problems. From the moment of conception, her body undergoes significant changes associated with a weakening of protective characteristics, which can lead to pathology of hemostasis and manifest itself as thrombosis or bleeding.
Such disorders can cause gestosis, anemia, placental abruption and fetal death. Therefore, it is very important for a woman to get tested before pregnancy or during pregnancy. The ideal option is to check before conceiving a child, during pregnancy planning. If pathologies are identified, then pre-administered therapy will allow you to safely carry and give birth to a healthy baby.
In order not to distort the results of the study, you should not take blood thinning medications or drink alcohol a week before the test.
How to prepare for donating blood for a hemostasiogram
Blood is donated on an empty stomach, from a vein. 12 hours before hemostasis, you must adhere to a diet excluding fatty and protein foods. The last meal (light snack) is possible 4 hours before blood sampling. It is prohibited to drink alcohol the day before the test. It is recommended to replace any drinks with water. This is done so that sugar does not affect the overall picture.
If you are taking medications that may affect the results of the data, this must be indicated when taking the test. This will be taken into account when deciphering the testimony.
It is not recommended for women to undergo the procedure during menstruation.
It is also better to refrain from playing sports in the previous day, to avoid stress and overexertion. Smokers are advised to give up cigarettes during this time.
The process of drawing blood also affects the accuracy of the result. When collecting from a vein, it is better to use a vacuum system. If this is not possible, then a syringe is used and the blood is allowed to flow on its own.
Indicators
It is extremely problematic to independently understand the results obtained without special education. Based on the results of the hemostasiogram, you must make an appointment with a hemostasiologist or hematologist.
The form indicates the results obtained and the norms given in two columns. These are indicators of prothrombin, aPTT, prothrombin time, prothrombin index, fibrinogen, platelet function, thrombin time, RKMF, INR.
In a detailed analysis, an additional test for D-dimer, lupus anticoagulant, and antithrombin III is often prescribed.
Tests during pregnancy
Hemostasiogram
Pregnancy management
Hemostasiologist during pregnancy
Normal indicators
According to APTT data, the rate at which blood clots is assessed. Ideally, it should be from twenty-four to thirty-six seconds, laboratory referents differ - ADD. With a lack of vitamin K, this time will be longer. In this case, you should be wary of severe blood loss from cuts and deeper wounds. If the time, on the contrary, is less, this means that there is a risk of a blood clot. In this case, during pregnancy the baby will not receive enough nutrients.
The line with data on prothrombin contains the same results, but in percentage equivalent. So prothrombin should be from 78 to 95 to 105 percent.
Fibrinogen should normally be from two to four grams per liter; during pregnancy it can increase.
With normal levels, antithrombin III ranges from 71 to 115 percent,
Exact standards in laboratory abstracts. If deviations are greater or lesser, blood clots or bleeding may appear.
Thrombin time should be from eleven to eighteen seconds, and prothrombin time should be from fifteen to seventeen.
Platelet function is from 30 to 50%, a decrease in function indicates the risk of bleeding or the effectiveness of antiplatelet therapy, an increase indicates an increase in the aggregation function of the blood.
Hemostasiogram in pregnant women
Pregnant women need to especially carefully monitor blood clotting. This will avoid complications during the birth process, as well as throughout pregnancy.
During pregnancy, a hemostasiogram is taken once per trimester or more often if indicated.
The attending physician may prescribe additional tests if there is a threat of miscarriage, also to assess the effectiveness of anticoagulant therapy. It is also recommended to do a hemostasiogram in case of high blood pressure, edema, the presence of protein in a urine test, before surgery, or when prescribing OCs and HRT.
If test results are poor, consultation with a hemostasiologist is necessary.
Do not be alarmed if you suddenly discover that the coagulation rate is slightly higher than required. In pregnant women, this may also be a normal option. This may happen due to changing hormonal levels. For women in an interesting position, it is unstable and can change more than once. The result may be affected by the appearance of an additional circulation that connects the uterus and placenta and an increase in blood volume.
When is this analysis indicated?
There are many situations when testing for hemostasis mutations is indicated:
- Miscarriage or miscarriage more than once. This may also occur due to poor blood clotting.
- Toxicosis, which affects pregnancy. Characterized by increased blood pressure, edema and the presence of protein in the urine.
- Hypertonicity of the uterus. May cause miscarriage.
- Placental abruption. Most often this occurs due to disturbances in hemostasis. Therefore, a mandatory consultation with a hemostasiologist is required.
- Relatives have problems such as stroke, heart attack, thrombosis and varicose veins.
- Infertility.
If disturbances in the functioning of hemostasis are detected during pregnancy, therapy is prescribed, selected on an individual basis. It consists of correcting the damaged mechanism. In the first trimesters of pregnancy, the most gentle option for drug treatment is selected.
As you can see, a blood test for hemostasis mutations is informative and very necessary for pregnant women.
Types of hemostasis
Hemostasis differs in its mechanism of action:
- vascular platelet;
- coagulation
Vascular-platelet hemostasis
The primary function of the hemostatic system is to ensure normal blood clotting. This process is carried out by platelets. When tissues and blood vessels are damaged, platelets come into contact with an adhesion inhibitor - collagen, as a result of which they expand, swell, form processes, and attach to the walls.
This process takes 1-3 seconds. It requires calcium ions and von Willebrand factor (a protein produced in the endothelium) to begin. Next, platelet aggregation occurs to the damaged area, which takes about 10 seconds. This provokes an increase in the growth of the blood clot. Aggregation is primarily stimulated by collagen. The process is also influenced by serotonin, catecholamines, and ADP. Next, substances are released from platelets that have undergone adhesion and aggregation that stimulate the secondary process of platelet production. This involves: adrenaline, serotonin, norepinephrine, antiheparin factor. A little later, granules are synthesized, which contain lysosomal enzymes.
Coagulation hemostasis
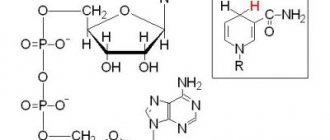
Coagulation or plasma hemostasis is the final phase of blood coagulation. There are 15 plasma blood clotting factors in total. They are designated by Roman numerals in the order in which they were opened.
I - fibrinogen-euglobin. It is synthesized in all tissues and organs that have a system of phagocytic mononuclear cells. Most common in lymph, plasma, exudate, transudate, BM. It is an inactive form of fibrin and is converted into it under the influence of thrombin.
II - prothrombin-euglobin. Produced in the system of phagocytic mononuclear cells. Most of them are located in the liver; in other organs and tissues there are much fewer of them. When interacting with vitamin K, they are processed into the active form - thrombin.
III - tissue thromboplastin.
IV - calcium ions.
V - proaccelerin, plasma AC globulin.
VI - accelerin, serum AC globulin.
VII - proconvertin, this factor is stable and is produced in the liver with the participation of vitamin K.
VIII - antihemophilic globulin A.
IX is a component of the plasma form of thromboplastin, Christmas factor, produced with the participation of vitamin K.
X - antihemophilic globulin C, prothrombinase, Stewart-Prower factor.
XI is a plasma precursor of thromboplastin.
XII - Hageman factor, or contact. After its activation occurs, it remains on the surface of the damaged vessel, preventing the blood clotting process from spreading throughout the body.
XIII is a fibrin-stabilizing factor produced in the liver.
XIV - kallikrein.
XV - kininogen.
To indicate whether a factor is activated, add the letter “a” or “f”. The second symbol means that only one of the fragments of the factor becomes active.
In modern medicine, it is believed that before the activation of prothrombin, a complex multi-stage process occurs, consisting of sequential activation and interaction of various factors.
There are two mechanisms for triggering coagulation - external and internal. With an external mechanism, tissue thrombin is stimulated to enter the blood plasma. Internal blood coagulation occurs without the participation of thrombin. In this case, the triggering moment is the Hageman factor. To produce it, there must be contact with a foreign traumatic object.