The state of the hormonal system affects the functioning of all organs and systems; this is especially noticeable in the female body in connection with reproductive function. The most serious consequences can lead to cancer, so it is extremely important to carry out all examinations, including mammography, in a timely manner.
Indications
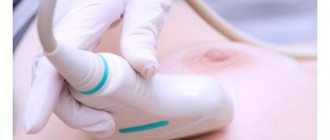
Mammography is primarily needed to prevent cancer. Breast cancer is the most common type of cancer in women. He occupies a leading position in mortality among women, despite the fact that his prognosis for recovery is high. This is due to the fact that the disease can be asymptomatic for a long time. Often symptoms appear at stages 3-4 of the disease. That is why all women are recommended to regularly visit a mammologist and undergo breast screening examination, which includes mammography. The painless and routine procedure, which takes 5-10 minutes, has saved the lives of many women.
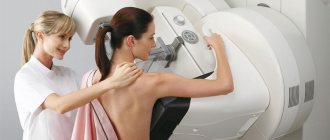
The photo shows a standard mammography procedure
Mammography is an x-ray examination. It is not painful and safe to do. It is indicated for women over 40 years of age to detect breast tumors in the early stages of their development.
Mammography is informative for oncological diseases, but with the help of ultrasound it is easier to detect benign neoplasms.
All women of the recommended age must undergo the study, even if there is no indication.
It is also prescribed in the presence of the following indications:
- detection of compactions during self-examination;
- detection of pain in the breast area;
- breast cancer in close relatives;
- chest injuries;
- mastopathy;
- breast examination after completion of breastfeeding;
- prevention of neoplasms when using oral contraceptives and hormonal drugs;
- control the course of the disease.
The examination is prescribed by a mammologist, gynecologist, family doctor or therapist.
Subject of study
Mammographic examination is aimed at identifying malignant and benign neoplasms, pathological changes in tissues, the size of tumors and lumps, their structure and localization.
A mammogram can reveal:
- A cyst is a fairly common disease of the gland, a hollow neoplasm with fluid inside. This is not a cancerous disease, and since a mammograph cannot distinguish a cyst from cancer, the doctor will definitely order additional examination.
- Fibroadenoma is a benign tumor that can grow. The disease is often found in young women.
- Calcifications are numerous small deposits of calcium salts located in layers of tissue. Calcifications are often the first symptoms of the early stage of cancer. Large collections are not usually associated with malignancy. However, we should not forget that the appearance of calcifications can be triggered by the development of an oncological process.
Detection of lumps on one side is a reason to examine both breasts.
This is necessary in order to compare both images and identify pathological processes in the other breast.
When going to the radiologist, you need to take with you previous images, if any.
This procedure is an X-ray examination with a small dose of radiation.
As a result, it is not recommended for women to undergo this diagnosis during pregnancy and lactation.
How often should you do it?
The procedure is informative for women over 40 years of age, because the risk of breast cancer at this age
increases. This is also due to the peculiarity of the structure of the female breast. At a young age, glandular tissue predominates in the breast, which is best examined using ultrasound.
After 40 years, involution of glandular tissue occurs, which is replaced by adipose tissue. It is not visible on x-rays, so pathological formations are visualized and the doctor is able to determine their location.
According to the recommendations of doctors, the examination should be carried out:
- to all women once at the age of 35-40 years, even with no symptoms;
- once every two years for women over 40 years of age;
- after completion of breastfeeding once;
- in the presence of other indications: trauma, breast disease, use of hormonal drugs;
- burdened heredity.
A doctor may prescribe a study for women with obesity, endocrine pathologies, autoimmune diseases, or if there are signs of breast cancer.
Interpretation of breast mammography
Using an X-ray of the mammary glands, the doctor examines the condition of the lymph nodes, ducts, vessels, and tissue texture. If there are no compactions, the tissue structure in the breast is uniform, then we can judge the absence of pathological changes.
Ducts and capillaries should be clearly visible on the images. If there are disturbances in the structure of the breast tissue or enlarged lymph nodes, the presence of pathology is diagnosed.
With the help of deciphering mammography of the mammary glands, it is not difficult for a specialist to determine the foci of development of a neoplasm, its quality, shape, and size.
Types of mammography
There are two types of mammography - classical and digital. Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages.
Classic or film
Mammography is accessible and cost-effective, but its capabilities are limited. The doctor cannot edit the image by enlarging it or changing the projection. Small tumors may go unnoticed. In this type of study, the body is exposed to a higher dose of radiation. A significant disadvantage is that if the image is damaged or lost, the data cannot be restored.
Digital mammography
more informative and safer. The results of the inspection can be recorded on various electronic media. They can be edited, enlarged, and you can study in more detail what the image shows. It's easier to save. If the file is lost, you can restore the data by contacting the medical institution where the study was conducted. The radiation dose is minimal. The downside is the cost of equipment and its maintenance.
The effect of the procedure on the patient's body
Any examinations related to tissue irradiation are perceived by most patients as causing significant harm to the body. This opinion is not true. Speaking about mammography, it is worth noting the small volume of tissue that is affected by X-rays. Therefore, there is practically no harm caused to the body. The radiation dose for mammography n2 is 0.03-0.1 mSv, which is comparable to the results of conventional fluorography. In addition, modern high-tech examination devices provide minimal radiation exposure without compromising the quality and accuracy of the examination. This allows specialists to prescribe as many procedures as necessary to obtain comprehensive answers to any questions or doubts about the patient’s health condition.
If mammography is performed at high frequency, treating physicians usually avoid prescribing additional studies that increase the total radiation dose. A variety of examination options makes it possible to obtain an accurate clinical picture using other methods that exclude even minor adverse effects on the patient’s body.
Preparation for the procedure
No special preparation is required for mammography. But in order for the photo to be reliable and the result to be correct, it is important to adhere to the following rules:
- Before the study, do not use creams, deodorants and antiperspirants, talc, etc. They contain components that are visible in the image and distort it;
- it is necessary to inform the doctor about all operations, injuries and diseases in the breast area;
- If lumps are detected during self-examination, inform the doctor about them and indicate their location;
- During the examination, the patient should not be wearing chains or other jewelry, and her hair should also be collected.
The patient should inform the doctor about the medications she is taking, especially hormonal medications. It is also important at what age a woman began menstruation and the characteristics of her cycle. If possible, the results of previous studies should be shown for comparison with the current state of the breast.
How to do a mammogram
The day on which a mammogram is done does not affect the results. But, on days 7-14 of the cycle, the breasts are less sensitive, so a woman will be more comfortable having a mammogram during this period.
The examination consists of two stages. The first is performing a mammogram and obtaining an image. This stage will take the woman no more than 10 minutes. X-rays are taken in two projections to obtain an informative image.
The second stage is the doctor’s description of the result obtained.
Many refuse the study due to fear of receiving a large dose of radiation. In fact, modern devices are safe and the radiation dose is minimal and cannot harm health. Digital mammographs are the safest, so it is better to give preference to them.
The procedure for obtaining an image is as follows:
- a woman needs to remove clothes from her upper body;
- after that the doctor will ask you to go into the cabin of the device, explaining how to stand correctly;
- Using a fixing plate, the chest is slightly pressed against the device;
- During the photo, you need to hold your breath for a few seconds at the entrance, not move for a few seconds, then you can get dressed and wait for the results of the study.
During the examination, the doctor instructs the woman in detail and tells her what to do so that the mammography is performed correctly.
Do not be afraid of unpleasant and painful sensations - mammography does not hurt.
Decoding the result
The most important stage of the study is the description of the image and interpretation of the results. The doctor studies it in detail and gives the result with his conclusion and recommendations. It is necessary to indicate which tissue predominates in the mammary gland - fibrous or glandular. The condition of the milk ducts is assessed. If any pathology is detected, the doctor describes it in detail, indicating the size of the tumor, location, structure, etc.
If signs of any disease are detected, the doctor will definitely recommend contacting a specialized specialist for a more thorough examination.
False positive and false negative results
If after the examination the doctor diagnoses the possibility of oncological pathology, then additional studies are prescribed. However, mammography readings may not always be correct and unambiguous. Let's consider these cases.
False positive result
When a specialist has the slightest suspicion of cancer, the patient is prescribed additional examinations. If the mammologist’s diagnosis is not confirmed, then this is a false positive result. The woman is considered healthy.
Note that such indications have consequences for the patient’s physical and psychological health. As a rule, upon learning about the possibility of a tumor, a woman immediately begins to feel worse, both psychologically and physically. In addition, this result implies additional financial costs for further consultation research.
False negative result
But it happens that the results of mammography of the mammary glands are received, the interpretation of which shows the norm. And after a certain period of time, the woman is diagnosed with advanced breast cancer. These are the results that are called false negatives.
According to statistics, mammologists do not detect cancer in 20% of patients. Usually this embarrassment happens to young people. Their breasts have a denser structure than those of older women.
We list a number of factors that influence obtaining a false negative result:
- small size of tumors;
- incompetence or inexperience of the doctor conducting the examination;
- high levels of sex hormones;
- dynamic growth of malignant neoplasm.
The danger of this result is that a woman may postpone a visit to a specialist even with obvious signs of oncology, since she will consider herself completely healthy. This approach to one’s own health often leads to death. Remember that a mammogram result is not an absolute verdict on your health. If you notice any unwanted symptoms, consult a doctor immediately.
Which is better: ultrasound or mammography
Another effective way to examine the breast is ultrasound (ultrasound). Both methods are effective and informative. Often ultrasound and mammography complement each other, allowing you to get a detailed picture of the disease.
The differences between mammography and ultrasound are as follows:
- with the help of ultrasound, glandular tissue, which predominates in young breasts, is better visualized;
- Ultrasound is more informative for identifying benign formations, when mammography is more sensitive to malignant ones. This is due to the peculiarity of the structure of the malignant tumor, which is clearly visible on x-ray;
- Ultrasound is recommended for girls with small breasts, since ultrasound waves do not penetrate deep tissues. Mammography is informative for women with large breasts.
Ultrasound has no contraindications, is safe for health, and can be performed frequently.
Taking into account the features of each method, the doctor determines which method is suitable for the patient: mammography or ultrasound.
Contraindications and restrictions
The only contraindications to mammography are pregnancy and lactation.
The conditional limitation - age up to 35 years - is explained by the specific structure of the mammary gland, because Due to the high density of tissues, radiography may not be sufficiently informative. Women under 35 years of age undergo an ultrasound scan.
The presence of implants is not a contraindication and, if necessary, is performed with great care, although ultrasound is preferred. Before the study, the patient must first inform about the presence of endoprostheses.
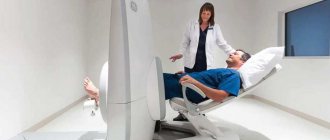
Which is better: MRI or mammography?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a method of examining the breast to identify pathologies in the early stages of occurrence. Its advantages are as follows:
- safety - during MRI there is no irradiation of the body;
- detects neoplasms of minimal size, accurately determining the size, structure, and location of the tumor;
- the ability to identify both benign and malignant neoplasms;
- no age restrictions;
- The result is not affected by the patient’s weight, breast size, etc.
The downside is the high cost of the procedure. Therefore, MRI is often used as an additional or primary research method after ultrasound or mammography if pathology is suspected.