Childbirth is a natural process, but still stressful for a woman’s body. Weakness and some deterioration in well-being even after a normal birth are common occurrences. Young mothers rarely pay attention to their health at this time - they are absorbed in communicating with the baby. However, if the analysis shows that leukocytes in the blood are elevated after childbirth, you will still have to pay attention to this. This may be both a normal phenomenon and a signal of the beginning of the development of pathology.
Leukocytes - why is it so important to know about them?
Leukocytes are white blood cells that are the first to respond to microbes and infections entering the body. Their main function is protection. When foreign agents are detected, the body increases its production to detect and destroy them. If the level of white cells increases, this is a signal that there is an inflammatory process in the body.
A healthy adult has 1000 times fewer leukocytes than red blood cells. But their number is not constant - it varies slightly for various reasons. For example, their levels increase slightly in the evening or after eating.
A persistent or significant increase in cells signals a focus of inflammation, possible blood problems, or complications after childbirth or surgery.
Neutrophils are a type of leukocyte that is responsible specifically for neutralizing pathogenic pathogens. They absorb harmful cells and die in the process (actually, pus is destroyed neutrophils). Therefore, when assessing a blood test, you need to pay attention to this indicator.
Leukocytes: types and functions
Leukocytes or white blood cells are colorless cells that move through the circulatory system and cleanse the body of infections and harmful substances. During illness, the number of foreign agents increases many times, which does not allow leukocytes to fully absorb them. This leads to the formation of swelling, increased body temperature and redness of the affected areas.
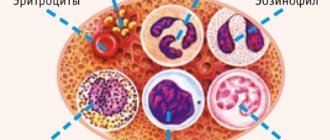
Leukocytes differ in structure and size and are divided into 2 large groups: granulocytes and agranulocytes. Granulocytes are characterized by a granular structure and the presence of a segmented nucleus. Cells of this group make up about 80% of all leukocytes.
In turn, these cellular formations are divided into the following types:
- neutrophils - destroy bacteria and fungi, stimulate cell division;
- eosinophils – absorb foreign protein formations and the body’s own dead cells;
- basophils - increase vascular permeability and regulate blood clotting, trigger allergic reactions.
Agranulocytes have larger oval-shaped nuclei. These cells are able to penetrate from the bloodstream into the connective tissue to carry out phagocytosis. The functions of agranulocytes depend directly on the cell type:
- monocytes - absorb large foreign particles, over time they turn into macrophages, which participate in cellular and humoral immunity;
- B lymphocytes - produce antibodies against foreign proteins;
- T-lymphocytes – destroy foreign microorganisms, enhance the immune response;
- NK lymphocytes - recognize their own altered and foreign cells, destroy cancerous formations.
Normal level in pregnant women
During the period of bearing a child, the following are considered normal BC indicators:
- 1-3 months: 4 – 7x109/l,
- 4-6: 7.6 – 10x109/l,
- 7-9: 10.4 - 12 x109/l.
It is customary to talk about physiological leukocytosis - a temporary increase in white blood cells, which is considered a medical norm, and pathological - constant and dynamic, which is a sign of inflammation.
Physiological leukocytosis
Nature has provided many mechanisms to protect the fetus. One of them is leukocytosis. By the second half of pregnancy, the mother’s body is already weakened. The consumption of vitamins and nutrients actually costs two. And the body adapts - it produces a large number of leukocytes that react to the slightest deviations and suppress the infection before it has time to develop. Thus, the norm of leukocytes in the body of a pregnant woman is higher than that of an ordinary adult.
Leukocytosis persists for another 1-2 weeks after birth. After this period of time, your white blood cell count should return to normal.
The following reasons can cause an increase in neutrophil levels:
- Physical activity or stressful situations.
- Breastfeeding also often keeps white blood cell levels above normal.
- The beginning of the menstrual cycle is 1-2 days before menstruation.
- Visiting a bathhouse or sauna the day before the test.
- Donate blood on a full stomach.
If the test shows elevated white blood cells, it is recommended to take it again after a few days. If the level has decreased or at least not increased, we are most likely talking about physiological leukocytosis.
Why are leukocytes in the blood elevated after childbirth? List of physiological reasons
Elevated leukocytes in the blood after childbirth do not always indicate the presence of some kind of pathology. The reasons may be completely natural, physiological in nature.
In order to bear and give birth to a child, a woman’s body adapts: changes in hormonal levels are observed, an increase in blood volume, etc. Immediately before childbirth, leukocytes begin to accumulate in the area of the uterus, stimulating the contraction of its muscles and preventing the penetration of infection. This is why the number of white blood cells increases by about 20-30%.
Childbirth is associated with tissue damage to one degree or another. That is why elevated leukocytes in the blood after childbirth (especially if the child was born via cesarean section) are considered quite normal. This helps speed up the tissue healing process, prevent infection and the development of further complications. In most cases, the number of white blood cells in the mother's body returns to normal 3-6 days after the birth of the baby.
Pathological leukocytosis
If leukocytes after childbirth are higher than normal, or their level continues to increase, it is customary to speak of pathological leukocytosis.
In women in the postpartum period, pathological leukocytosis occurs as a reaction to the following conditions:
- Inflammation of the genitourinary organs.
- Large blood loss.
- Mastitis.
- Endometritis.
- Pyelonephritis.
With pathological leukocytosis, there are accompanying symptoms characteristic of inflammatory processes: chills, fever, and often pain and weakness. Bloody or purulent discharge may occur. If you have these signs, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Associated symptoms
An increase in the number of white blood cells after childbirth is indicated by symptoms such as dizziness, fatigue, decreased appetite and general weakness. In severe cases, vision problems and nosebleeds may occur. These symptoms are characteristic of all forms of leukocytosis, regardless of its cause.
If the disorder is caused by inflammation, the patient also notes:
- pain in the lower abdomen and lower back;
- low-grade fever accompanied by chills;
- redness and pain in the chest;
- compactions when palpating the mammary glands;
- frequent and painful urination;
- darkening and cloudiness of urine, the appearance of pus and blood clots;
- yellow, green and brown vaginal discharge with a strong odor.
A significant increase in leukocytes in women is a characteristic sign of a number of genitourinary diseases, during which the following clinical manifestations of pathological changes in the body may occur:
- high blood pressure;
- nausea and vomiting;
- nagging pain in the lumbar region;
- pain in the lower abdomen, in the pubic area;
- increased body temperature;
- blood in the urine;
- disruption of the normal process of urination (frequent, delayed, accompanied by severe pain and pain, a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder).
In addition, during general clinical blood tests, leukocytosis, a high level of ESR, and an increased concentration of proteins (CRP) are detected, which in itself confirms the presence of inflammation. The appearance of the urine itself indicates illness: the color is changed (brown, greenish, the color of meat slop, milky white), there is a lot of turbidity and suspension in the urine.
If the test results fit within the specified range (from 5 to 10), then the woman is healthy. But sometimes the indicators exceed the norm. By the number of leukocyte cells in the urine, one can judge the intensity of inflammation in the genitourinary system.
• Cystitis. This disease can have a hidden course or manifest itself with frequent urge to urinate and cutting pain. Women during pregnancy are prone to cystitis as the ureters dilate and relax.
• Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory disease that affects the pyelocaliceal system and renal parenchyma. This disease in pregnant women occurs due to compression of the ureters and stagnation of urine, in which pathogenic microorganisms actively multiply.
• Inflammation of the urethra. The disease can be triggered by an infection or a growing fetus. Urethritis is manifested by burning and itching during emptying of the bladder.
• Urolithiasis (stones in the kidneys or urinary tract). A characteristic symptom is paroxysmal or aching pain of different localization.
• Glomerular nephritis is an inflammatory lesion of the glomeruli (glomeruli of the kidneys). This disease often occurs with late toxicosis. Manifested by swelling, change in urine color.
Leukocyturia manifests itself in pregnant women with characteristic symptoms. First of all, the color of the urine changes, it becomes cloudy, darkens, sediment and an unpleasant pungent odor appear. Patients complain of sharp or aching pain in the lower abdomen or lower back. The disease is characterized by frequent urge to urinate, burning, itching during urination and increased temperature. In addition, blood pressure increases and blood appears in the urine.
All of the above symptoms are typical for pregnant women with leukocyte counts of 30–50. Therefore, if you notice changes in your urine, do not delay your visit to the doctor.
Many mothers face the problem of elevated leukocytes in the blood after childbirth. Reviews from doctors indicate that in most cases, such changes in the blood count are associated with stagnation of milk or infection of the ruptures.
In itself, an increase in the number of white cells in the blood only indicates inflammation. But the accompanying symptoms can clarify the picture:
- The inflammatory process is inevitably accompanied by an increase in body temperature, sometimes up to 40 degrees or more.
- Bloody and sometimes purulent discharge from the vagina may appear. Sometimes they turn into full-blown bleeding.
- The presence of pain and burning during urination, as well as nagging pain in the lower back. All this is typical for various diseases of the excretory system (in particular, the bladder and kidneys).
- Headaches, severe weakness, chills, body aches, nausea, and vomiting may occur.
If you notice such symptoms, you need to contact your gynecologist as soon as possible.
Risk factors
In the case of a difficult birth, rupture, heavy bleeding or cesarean section, the young mother should be especially careful about her health. If a blood test reveals an increase in neutrophils, this may indicate:
- inflammatory process,
- remnants of the placenta in the uterus and the beginning of the inflammatory process,
- exacerbation of chronic diseases in the postpartum period,
- postpartum inflammation of the genitourinary system,
- disorders of hematopoietic function or blood clotting function,
- penetration of infection through cracks in the nipples.
During pregnancy, a woman’s body consumes a significant amount of vitamins and beneficial microelements. Elevated leukocytes can also indicate their critically low level.
Drug treatment
In the treatment of diseases of the genitourinary system, uroseptics are used. They help develop immunity against germs and cleanse the body of existing ones.
Depending on the severity of the disease and the general condition of the patient, he is prescribed:
- fluoroquinolones - broad-spectrum drugs in tablet form: Levofloxacin, Ofloxacin;
- Penicillins are drugs produced in tablets and injections. The most common is Amoxicillin.
- cephalosporins, such as Cefuroxime. The drug has a wide spectrum of action and is available in the form of injections.
- oxolinic acid;
- Nitroxoline;
- Nifuratel is effective against fungal and infectious nature of the disease.
How to normalize indicators
With elevated BC, the expectant mother may be prescribed:
- antibiotics, if a violation of the norm is a consequence of an infectious disease,
- a special diet if white blood cells are impaired due to liver problems.
Patients with low BC need:
- eat buckwheat, raw vegetables, red fruits, oats,
- Avoid products with animal fat, meat and liver.
Preparing for urine collection
To obtain reliable results from a urine test, it is necessary to collect it correctly. Doctors recommend avoiding eating spicy, fried and salty foods and foods that can change the color of urine the day before.
You should also refrain from taking any medications. For urine, you need to prepare clean containers, for example, a sterile container from a pharmacy. The analysis requires the first portion of urine after waking up.
Procedure:
- Careful hygiene using soap.
- Be sure to dry yourself.
- Due to the close location of the vagina, it is better to cover it with a cotton swab.
- Direct the first few drops of urine into the toilet, and the rest into a container for analysis.
The study requires 0.1-0.15 liters of urine.