How doctors check the stomach
Intestinal problems have become increasingly common lately. Many people try to cope with them on their own, but often a situation arises when they cannot do without the help of a specialist. Having suffered from pain and flatulence, a person wonders which doctor to see. The condition of the intestines is very important for the health of the entire body, because it not only absorbs nutrients, but also produces hormones, enzymes, vitamins, and develops immunity. Therefore, if problems arise, you need to start treatment as soon as possible.
There are several ways to test stomach acidity. The most common is gastroscopic examination. With the X-ray method, it is possible to diagnose such functional disorders and diseases as peptic ulcers, malignant and benign formations, and others.
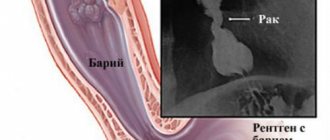
Often, before the procedure, contrasting of the gastric cavity is used, for which the patient takes about 250 ml of a solution of barium salts. With the gastroscopic method, gastric secretion is collected through a gastric tube to determine the acidity of gastric juice.
Computed tomography of the stomach
Before the advent of computed tomography, the main diagnostic tests for identifying various gastric diseases were endoscopy and x-rays. An endoscopic examination allows you to examine the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach, the beginning of the small intestine (examination of the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract), as well as the large intestine (examination of the lower part of the gastrointestinal tract). Examination of the stomach is carried out using gastroduodenoscopy, the following pathological conditions are detected:
- Gastritis.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease.
- Portal hypertension.
- Stomach ulcer.
- Polyps.
- Cancer of the esophagus, stomach.
- Gluten intolerance.
- Anemia.
An endoscopic examination allows for therapeutic measures to be taken - to stop bleeding, remove foreign bodies, and also during the examination a biopsy of stomach tissue is performed.
X-ray of the stomach is a dynamic research method that allows you to take a picture of the stomach and select the desired projection of the organ. An X-ray with barium is also performed; the study allows you to observe the passage of contrast through the gastrointestinal tract using images. X-ray examination allows us to identify the following pathological conditions:
- Varicose veins of the esophagus and stomach walls.
- Polyps.
- Stomach ulcer.
- Malabsorption syndrome.
- Gastrointestinal motility disorder.
- Benign and malignant tumors of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Narrowing of the duodenum.
- Hiatal hernia.
Computed tomography is most often performed to detect stomach tumors. Indications for use include suspected ulcers, Crohn's disease, colitis, cancer and many other diseases. Computed tomography allows you to determine the presence of foreign bodies, injuries, polyps, and make a quick decision on whether to perform surgery or prescribe a specific treatment method. Computed tomography can be used to predict the course of the disease. The gastroenterologist refers the patient to a CT scan if unpleasant symptoms appear:
- Indigestion.
- Heartburn.
- Nausea.
- Blood in urine or stool.
- Pain in the stomach after eating.
- Feeling of heaviness in the stomach after eating or having a small snack.
- Loss of appetite, loss of body weight.
- Digestive disorders.
CT with contrast is used to diagnose stomach diseases. Before a computed tomography scan with contrast, preparation is carried out. The patient undergoes tests for allergies to contrast agents, and kidney function is determined. CT scans are performed on an empty stomach; before the study, the patient abstains from eating for 6-7 hours. In order for the contrast agent to quickly leave the body, it is recommended to drink more fluids the day before the examination. To avoid distortion of CT results, you should come to the examination in clothes without metal buttons or jewelry.
A computed tomography scan of the stomach takes an average of 20 minutes and causes virtually no discomfort to the patient. Computed tomography very well allows you to see the walls of the cavity filled with gas or liquid. The contrast agent is administered intravenously or drunk by the patient. The patient is then placed on a rotating CT scanner table, which moves under the scanner. The scanner takes images in slices, then the patient turns over on his right side, which allows scanning of the outlet of the stomach and the upper intestine. The patient must remain completely still during the scan.
The contrast agent is drunk by the patient in several stages, allowing soft tissues and blood vessels to be more clearly visible. Using contrast, tumors of the stomach and intestines are detected in the early stages of development - contrast highlights the smallest malignant and benign tumors in images of the circulatory system. If a reaction to the contrast agent develops during the study, the doctor stops the diagnosis. A reaction to a contrast agent can manifest itself in the form of tachycardia, severe dizziness, and itching.
Computed tomography helps determine the location of the tumor, size, type, circulatory characteristics and other features of the tumor. CT helps to identify the onset of tumor metastasis, the boundaries of the lesion, and the stage of development of the tumor is very accurately determined. The doctor can see signs of perforation of the stomach walls, obtain accurate data on the condition of other abdominal organs, data on the functionality of the organs, and the peculiarities of the functioning of the organs. Computed tomography is a very accurate study, thanks to which the doctor can prescribe effective treatment and timely diagnose a malignant tumor at an early stage of development.
How to check your stomach
How doctors check the stomach
If a patient has complaints about gastrointestinal disturbances, then he needs to undergo a full medical examination. There are several methods of medical diagnosis:
- Physical method. Based on a visual examination of the patient and collection of anamnesis.
- Laboratory research . Includes taking tests prescribed to confirm a preliminary diagnosis.
- Hardware methods . They provide the opportunity to examine the gastrointestinal tract and identify the presence of pathologies.
Only a doctor can select the optimal diagnostic option or prescribe a comprehensive examination. The choice will depend on the nature of the patient’s complaints, the collected medical history and preliminary diagnosis. We will talk about hardware research options.
Instrumental diagnosis of gastritis
A number of instrumental methods are used to diagnose chronic gastritis. To determine pathology, the following is prescribed:
- FGDS;
- biopsy;
- radiography;
- Ultrasound;
- pH-metry.
In case of acute development of the disease, an examination is carried out without gastroscopy, since in case of acute inflammation, the mechanical effect of the probe on the mucous membrane will only aggravate the situation.
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy
The main method for diagnosing chronic gastritis is FGDS. This is an endoscopic research method that allows you to evaluate changes in the mucous membrane of the stomach, as well as the esophagus and duodenum. Rules for conducting FGDS:
- the procedure is carried out strictly on an empty stomach;
- a separate office must be equipped to conduct it;
- the patient is placed on his side, and a special plastic insert is inserted into the mouth;
- To reduce discomfort, local anesthesia is used (lidocaine spray is sprayed);
- A thin flexible hose with a built-in camera is inserted through the mouth and the inner surface of the upper gastrointestinal tract is examined. The image is displayed on the monitor;
- The duration of the procedure is 5 minutes.
With gastritis, the doctor will note changes in the mucous membrane:
- hyperemia with superficial inflammation;
- thinning of the mucous layer in the atrophic form;
- the appearance of folds or polyps in the hyperplastic form;
- formation of erosions in the erosive form.
Biopsy
During gastroendoscopy, tissue particles can be collected. This procedure is carried out using special tools.
Advice! There are no nerve endings in the mucous layer, so a mucosal biopsy is a painless procedure.
The tissue particles obtained as a result of the procedure are sent for research, and the following is carried out:
- cytology;
- microbiological studies;
- histology;
- urease test.
The studies carried out make it possible to detect the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection, as well as determine the level of acidity.
PH-metry
To determine the acidity of the gastric environment, special tests are performed. There are several types of research:
- endoscopic (sampling is taken during FGDS);
- express method (duration – 15-20 minutes)
- short-term method (2-3 hours);
- daily allowance
Advice! In order for the measurements obtained with pH measurements to be objective, the patient must take antacids and proton pump blockers 72 hours before the test.
When conducting a short-term test, the patient, after inserting the probe, remains in the treatment room for 3 hours under the supervision of physicians. A special electrode is installed at the end of the probe to measure the acidity level. During the examination, the probe is placed against different parts of the stomach to obtain an objective picture.
To conduct a daily study, a thin probe is used, which is inserted through the nose. A special recorder is attached to the wrist to record the examination results. This probe is worn for 24 hours; it practically does not interfere with leading a normal life.
Advice! There is also a more modern research method: the patient swallows a special capsule, which transmits the research results to the registrar.
Radiography
X-ray is a research method that allows you to identify various pathologies of the stomach. It is used to evaluate:
- shape and size of the organ and its parts;
- position;
- the state of the sphincters at the exit from the esophagus and at the entrance to the duodenum.
To obtain a high-quality image, a contrast agent is used that does not transmit x-rays, usually barium salts. Sometimes, after taking a contrast agent, the stomach is additionally filled with air so that the barium salt solution fills all the folds.
Advice! Radiography is usually used to diagnose gastritis if it is not possible to perform an FGDS.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is not very informative for diagnosing gastritis, but this method is used to identify concomitant diseases. Using ultrasound, you can detect the presence of pathology of the liver and gallbladder, as well as the pancreas.
The procedure is absolutely painless for the patient and is performed strictly on an empty stomach.
How to check your stomach by swallowing a probe
Any medical examination begins with collecting anamnesis during a personal conversation with the patient. The doctor then begins a visual examination of the patient. By palpating, the specialist finds out the localization of pain, the tension of the walls of the organ and the presence of dense structures. The next stage of the examination will be to study the stomach using a hardware method.
Modern medicine can offer several diagnostic options that can, to one degree or another, replace FGS:
- capsule gastroscopy;
- desmoid test according to Saly;
- radiography;
- ultrasonography;
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging).
Advice. Before you go for a stomach check, you need to consult a specialist. For example, if a patient’s initial examination reveals possible gastritis, ultrasound will be useless in this case. Below we will examine each diagnostic method in more detail.
How to check your stomach without swallowing: capsule gastroscopy
Modern achievements of science and technology have indeed made it possible to achieve serious progress in terms of the development of endoscopic equipment. Currently, gastroscopy of the stomach can already be performed without swallowing the probe. We are talking about research using a special capsule. This technique appeared not so long ago. In the Russian Federation it began to be practiced already in the 21st century. Currently, it is still significantly inferior in frequency to conventional gastroscopy, but this figure is gradually increasing.
Today, to solve this problem, a special camera is used, which is made in the form of a capsule. It is relatively small in size. Most often we are talking about a capsule with dimensions of 10*30*10 mm. This video capsule is capable of taking photographs at a fairly high frequency. Even before the introduction of such a microendoscope, a special sensor is glued to the patient’s skin, to which all the information received is transmitted.
How to check the stomach without swallowing a probe: desmoid test
Gastroenterologists often use a desmoid test to determine the degree of gastric juice activity. During the test, the patient swallows a bag filled with methylene blue powder and tied with catgut thread.
Gastroenterologists often use a desmoid test to determine the degree of gastric juice activity.
After the thread dissolves, the dye is gradually absorbed into the blood and no later than 18–20 hours later it is eliminated from the body. The study is based on assessing the intensity of urine staining. If the first portion of urine acquires a bright blue-green color, it means that the acidity of the stomach is increased.
Capsule gastroscopy
This research method is based on replacing the probe with a special capsule equipped with a video camera. The device allows for a thorough examination of the gastric mucosa and detects the disease in the early stages of development.
Capsule gastroscopy does not cause discomfort or unpleasant sensations
To make a diagnosis, the patient must swallow the capsule. For the inspection to be successful, you should prepare for it:
- The patient must adhere to a diet for 2 days before the procedure. It is recommended to exclude fatty, heavy foods, alcohol and dishes that cause flatulence from the diet. Food should be well chopped and steamed or boiled.
- The study is carried out in the morning, on an empty stomach. The capsule can be taken with ½ glass of plain liquid.
The process does not take much time and does not cause any discomfort to the person. During the examination, the patient can return to normal life, limiting physical activity. After 7–8 hours, the patient visits the doctor’s office again, where the doctor transfers the indicators recorded by the capsule into the computer and makes a diagnosis.
After a certain time, the device leaves the body naturally. The advantages of this procedure are obvious, but the method has not found wide application due to the rather high price of the device. In addition, such an examination does not allow you to perform a biopsy, remove polyps, or stop bleeding.
You can see how the stomach is examined using the capsule method in the video:
Desmoid test
Gastroenterologists often use a desmoid test to determine the degree of gastric juice activity. During the test, the patient swallows a bag filled with methylene blue powder and tied with catgut thread.
Using methylene blue to check the acidity of gastric juice
After the thread dissolves, the dye is gradually absorbed into the blood and no later than 18–20 hours later it is eliminated from the body. The study is based on assessing the intensity of urine staining. If the first portion of urine acquires a bright blue-green color, it means that the acidity of the stomach is increased.
Radiation research methods
You can check the gastrointestinal tract in an adult using both invasive manipulation and radiation diagnostics. Such examination methods make it possible to obtain information about the configuration of the stomach and the presence of neoplasms, but do not make it possible to assess the condition of the mucous membrane.
Of the radiation methods, X-ray is the most widely used. Equipment for examination is available in almost every medical institution, so the examination is available to all segments of the population.
MRI and ultrasound are more modern research methods and pose less of a threat to the health of patients.
You can learn about the differences between these procedures from the video:
X-ray
Using radiography, a stomach ulcer is detected, its configuration is checked, and its size is assessed. R-graphy is carried out using a contrast agent - barium suspension. It is prescribed when the patient complains of rapid weight loss, the appearance of blood in the stool, frequent and debilitating diarrhea, and constant pain in the gastrointestinal tract.
X-ray of the gastrointestinal tract is informative and does not take much time, but has contraindications
The procedure is completely painless and not very complicated, but requires compliance with some rules:
- For 2–3 days before the examination, you should exclude alcohol, thick, fatty and solid foods from your diet.
- On the eve of the test, it is necessary to cleanse the intestines using an enema or special means with a laxative effect.
- Before the procedure, the patient is prohibited from eating or drinking colored drinks.
An X-ray of the stomach lasts 30–40 minutes. All this time, the doctor asks the patient to take certain positions and takes six pictures of the gastrointestinal tract in different projections.
The procedure has its advantages and disadvantages. The advantages include the possibility of obtaining information that is not available when using a fiber gastroscope. For example, using FGS it is impossible to detect narrowing of the intestinal lumen or stenosis of the pylorus of the stomach.
Attention. Contraindications to x-rays are the first trimester of pregnancy and internal bleeding. In addition, x-rays are undesirable if you are allergic to iodine preparations.
Ultrasonography
Today, ultrasound is performed if bleeding or the presence of cancer in the organ cavity is suspected. This is a fairly popular, but not very informative diagnostic method.
Ultrasound is an uninformative method of checking the stomach
The procedure helps to identify only the main disorders in the gastrointestinal tract. For a more accurate diagnosis, the patient will have to use other diagnostic methods. Therefore, ultrasound is most often prescribed not to identify the disease, but to confirm an existing diagnosis.
Advice. Ultrasound examination is completely safe and can therefore be recommended for women at any stage of pregnancy.
Radiation research methods
You can check the gastrointestinal tract in an adult using both invasive manipulation and radiation diagnostics.
Such examination methods make it possible to obtain information about the configuration of the stomach and the presence of neoplasms, but do not make it possible to assess the condition of the mucous membrane. Of the radiation methods, X-ray is the most widely used. Equipment for examination is available in almost every medical institution, so the examination is available to all segments of the population. MRI and ultrasound are more modern research methods and pose less of a threat to the health of patients.
Ultrasound or MRI? Which method is best to use when examining the stomach?
To examine the stomach, both methods are used - ultrasound and MRI - sometimes one is preferred, sometimes both methods are used. It all depends on the specific circumstances and objectives of the survey. The choice is usually made by the attending physician, taking into account the advantages, disadvantages, indications and contraindications for use.
| The advantages of ultrasound include the possibility of use in children |
The benefits of ultrasound
relate:
- The safety of the method, which is based on the ability of ultrasonic waves to penetrate inside the body and be reflected differently from tissues with different structures and densities (echo effect), while ionizing radiation and other negative factors are completely eliminated. Therefore, the method is widely used in gynecology, obstetrics, neonatology and pediatrics.
- Painless (non-invasive method).
- Comfortable conditions for performing the procedure.
- The ability to study an organ in real time.
- Scanning speed – the process takes from 10 to 15 minutes.
- There are no contraindications, restrictions on use are associated with skin damage in the study area and an excess layer of subcutaneous fat.
- Possibility of receiving results immediately after the study.
The disadvantages of ultrasound
relate:
- It is impossible to examine the entire stomach; there are sections that are inaccessible for scanning.
- The information obtained about the condition of the stomach concerns mainly superficial structures and anatomical features.
- Identified deviations from normal ultrasound parameters require clarification using additional diagnostic methods.
- The method is not highly accurate.
- Ultrasound cannot perform a diagnostic biopsy and determine the nature of the pathology.
- Subjectivity of conclusions based on the research results, because decoding depends on the experience and qualifications of the doctor.
| MRI of the abdominal cavity in adults |
The MRI method is based on the phenomenon of magnetic resonance. The main physical factor underlying MRI is electromagnetic waves, which are emitted with varying intensities by hydrogen atoms in the constant magnetic field of the tomograph under the influence of an alternating magnetic field. The MRI method is a more modern diagnostic method compared to ultrasound.
Benefits of MRI
when examining the stomach:
- The opportunity to obtain information not only about the anatomical features of the organ or the condition of the outer shell, but to penetrate inside the organ and study in detail the structure and structure of the tissue.
- As a result of MRI, a series of numerous thin sections are obtained, made in three projections, which practically eliminates the presence of a “blind spot”.
Series of sections of the stomach with MRI - Diagnostic accuracy reaches 98%.
- The method allows you to immediately obtain information about all parts of the stomach.
- Using MRI, it is possible to determine the pathological process at an early stage of development, when the size of the lesion does not exceed 1-2 mm and there are no clinical manifestations.
- The objectivity of conclusions based on MRI results, because decryption occurs automatically, the subjective factor is minimal.
Disadvantages of the method
:
- The method is not absolutely safe, because... there are restrictions on use in pregnant women in the first trimester and in children.
- The procedure takes 30-40 minutes.
- The method has many contraindications (the presence of electronic or metal objects in the patient’s body, severe claustrophobia, excess weight or too large parameters of the patient).
- The need to remain motionless for a long time and in a confined space of a tomograph often leads to the use of anesthesia.
- Drawing up a conclusion based on the results of the examination takes a lot of time (1-2 hours, sometimes more than a day).
All these points should be taken into account by the doctor when choosing a method.
.
- If a preventive examination
of the stomach is necessary, ultrasound is prescribed: monitoring the formation of the stomach in the fetus; - detection of congenital anomalies of the stomach in children during the first year of life;
- medical examination of children aged 7 and 14 years;
- periodic examinations of the working population and medical examination of adults;
- dynamic monitoring of the effectiveness of treatment and the course of the postoperative period.
| Stomach cancer on MRI |
| Acute appendicitis (perforation stage) with MRI |
When comparing the availability and cost of diagnostic methods, ultrasound gives an advantage. All medical institutions are equipped with sonographs; not all clinics have tomographs, only large ones. Ultrasound and MRI can be performed free of charge, under the compulsory medical insurance policy, but the waiting period for an MRI will be much longer. The average cost of an ultrasound scan of the stomach is 700-1500 rubles, MRI – 3000-4000 rubles.
In some cases, only an ultrasound scan is sufficient to identify the causes of stomach pathology. In other cases, it is better to immediately use the more informative MRI method. And sometimes the need for more accurate diagnosis requires the use of two methods at once. The doctor decides which method to choose. The main thing is to obtain reliable information about the nature of the pathological process in order to determine the correct diagnosis and promptly prescribe effective treatment.
How to check the stomach without gastroscopy: x-ray
Using radiography, a stomach ulcer is detected, its configuration is checked, and its size is assessed. R-graphy is carried out using a contrast agent - barium suspension. It is prescribed when the patient complains of rapid weight loss, the appearance of blood in the stool, frequent and debilitating diarrhea, and constant pain in the gastrointestinal tract.
The procedure is completely painless and not very complicated, but it requires compliance with some rules: For 2-3 days before the examination, you should exclude alcohol, thick, fatty and hard foods from your diet. On the eve of the test, it is necessary to cleanse the intestines using an enema or special means with a laxative effect. Before the procedure, the patient is prohibited from eating or drinking colored drinks.
- An X-ray of the stomach lasts 30–40 minutes.
- All this time, the doctor asks the patient to take certain positions and takes six pictures of the gastrointestinal tract in different projections.
- The procedure has its advantages and disadvantages. The advantages include the possibility of obtaining information that is not available when using a fiber gastroscope.
For example, using FGS it is impossible to detect narrowing of the intestinal lumen or stenosis of the pylorus of the stomach. Attention. Contraindications to x-rays are the first trimester of pregnancy and internal bleeding. In addition, x-rays are undesirable if you are allergic to iodine preparations.
Modern methods of examining the stomach
Based on the results of the analysis, it is possible to assess the general condition of the body, morphological tissue damage, determine the functional characteristics of the organ, determine the stage of the inflammatory process and the effectiveness of therapy.
Today, special gastroenterological panels have been developed, including a set of tests with blood taken from a vein. The panel may include, for example, tests for the level and proportions of pepsinogens I and II, stimulated or basal gastrin-17, for the presence of antigens (IgG) to the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which can lead to H. pylori-associated chronic gastritis. In addition, indications for such a study are usually the risk of peptic ulcer disease and various dyspeptic disorders.
It is known that during inflammation of the pancreas, the enzyme lipase (triacylglycerol acylhydrolase) enters the blood, so if lipase can be detected in the blood in a volume of more than 78 U/l, we can talk about acute or chronic pancreatitis or a perforated gastric ulcer.
To confirm or refute autoimmune pathologies of the stomach (chronic atrophic gastritis, pernicious anemia, etc.), blood serum is taken for antibodies (IgG, IgA, IgM) to the parietal cells of the stomach, as well as for antibodies (IgG) to the internal Castle factor and antibodies ( IgG) to Saccharomyces - baker's yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae (ASCA).
Although perfect specific tumor markers for gastric cancer have not yet been discovered, it is known that the level of some antigens correlates with the stage of cancer. Such antigens especially include oncofetal carbohydrate antigens CA 72-4 and Ca 19-9. The latter is used to monitor pancreatic carcinoma together with carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA).
How can you check your stomach without gastroscopy?
Today, ultrasound is performed if bleeding or the presence of cancer in the organ cavity is suspected. This is a fairly popular, but not very informative diagnostic method.
The procedure helps to identify only the main disorders in the gastrointestinal tract. For a more accurate diagnosis, the patient will have to use other diagnostic methods. Therefore, ultrasound is most often prescribed not to identify the disease, but to confirm an existing diagnosis. Advice. Ultrasound examination is completely safe and can therefore be recommended for women at any stage of pregnancy.
Examination of the gastrointestinal tract
Various gastrointestinal diseases now occur in almost every second adult.
In this case, periodic nausea, intestinal upset, heaviness in the stomach or indigestion are disturbing. But not every person consults a doctor about this. This attitude can lead to serious consequences, because any disease is easier to cure at an early stage. Therefore, if abdominal discomfort periodically appears, it is necessary to check the stomach and intestines.
The examination will help to detect pathologies in time and prevent complications.
When to see a doctor
Only a doctor can determine whether the digestive system is functioning properly. Therefore, if the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted, it is necessary to contact a gastroenterologist. It is especially important to examine children in a timely manner, since their pathologies can progress quickly, which seriously affects the condition of the body.
It is recommended to consult a doctor for examination if the following symptoms appear:
- increased gas formation, bloating;
- nausea, periodic vomiting;
- constipation or diarrhea;
- the appearance of pain in the abdomen or side;
- feeling of heaviness after eating;
- frequent belching or heartburn;
- the presence of mucus, blood or undigested food in the stool;
- decreased appetite.
It is also recommended to periodically examine the gastrointestinal tract for people with chronic pathologies of the digestive system. This may be gastritis, peptic ulcer, pancreatitis, reflux, colitis, duodenitis, biliary dyskinesia. Older people need regular checks of their intestines to detect the presence of a tumor in time.
Diagnostic procedures
Even an experienced doctor cannot always determine the cause of the illness based on external symptoms. Moreover, not every person can describe what he feels.
Therefore, the diagnosis of gastrointestinal diseases has its own sequence and cannot be done without instrumental and laboratory examinations. Some pathologies do not manifest specific symptoms at the initial stage, but gradually progress.
Therefore, examination of the gastrointestinal tract is very important for the timely detection of diseases and prescribing the correct treatment. It is recommended that even healthy people undergo it periodically.
Before making a preliminary diagnosis and choosing examination methods, the doctor conducts a conversation with the patient. It is necessary to tell in detail about your feelings, what provokes them, when they arise.
At the same time, the doctor is interested not only in the patient’s complaints. The specialist will definitely ask about habits, diet, and the presence of chronic diseases. It is also very important what illnesses parents and close relatives have.
After this, the patient is examined. The doctor does this using physical methods.
These include palpation, percussion and auscultation. At first glance, it may seem that such an external examination is useless in determining the condition of the internal organs. But for an experienced specialist, even such an examination is informative. First, an examination of the oral cavity is performed, where the digestion process begins. The condition of the mucous membrane, teeth, and color of the tongue are important.
The examination begins with a conversation and general examination of the patient.
Then the doctor feels the patient’s stomach, determining whether the organs of the digestive system are enlarged, whether there are hardenings, scars, or enlarged veins.
Palpation also allows you to determine the shape of organs, their pain and location. Auscultation or auscultation allows you to hear what sounds the intestines make as they work.
Percussion is tapping, which allows you to clarify the shape, location and condition of internal organs.
After this, the doctor determines what other methods of examining the gastrointestinal tract the patient needs. There are quite a few of them, but usually 2-3 methods are chosen. It can be:
What does gastroscopy of the stomach show?
- pH-metry;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- probing;
- X-ray examination;
- colonoscopy;
- Ultrasound;
- scintigraphy;
- CT or MRI;
- blood, urine and stool tests.
Instrumental examination methods make it possible to assess the condition of the mucous membrane of the digestive tract, the secretion of gastric juice, the level of acidity, and motor function. With their help, you can detect the presence of tumors, cysts, erosions or ulcers.
Usually, to diagnose gastrointestinal diseases, the doctor prescribes FGDS and blood tests. Sometimes it is also necessary to check the condition of the liver, bile ducts and pancreas.
Such a complete examination of the digestive system is necessary when it is difficult to make a diagnosis.
If a person doubts whether his digestive organs are functioning normally and whether he should go to the doctor, you can check the stomach and intestines yourself.
To do this, you need to squeeze half a glass of juice from raw beets and leave it for a couple of hours. Then drink and observe bowel movements.
If it happens quickly and the stool is beet-colored, it means the stomach and intestines are working normally. If your urine is colored and you don’t have bowel movements for a long time, you should consult a doctor.
Gastroscopy
To examine the condition of the gastric and duodenal mucosa, endoscopic examination or fibrogastroduodenoscopy is most often used. This is the most accurate method for identifying gastrointestinal diseases at the initial stage. Gastroscopy is a sounding.
The patient swallows a special flexible tube with a camera at the end. With its help, the doctor can examine in detail the condition of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum.
Probing allows you to timely diagnose peptic ulcers, inflammation of the mucous membrane, and take gastric juice for analysis to determine its acidity.
Important: such an examination is recommended to be done periodically in case of chronic pathologies of the stomach to monitor the correctness of treatment and prevent complications.
Endoscopic examination can cause discomfort to the patient, although modern devices for this make the procedure as comfortable as possible. But many patients refuse it due to fear of pain or vomiting.
In this case, as well as to examine the small intestine, capsule intubation may be prescribed. This is a modern minimally invasive diagnostic method. The patient is asked to swallow a special capsule with a video camera.
As it moves through the digestive tract, it will transmit an image to the monitor. Then the capsule comes out naturally.
Gastroscopy is the most informative method of examining the upper digestive tract
X-ray
X-ray diagnostics is the most accessible and cheapest examination method. It allows you to evaluate the thickness of the walls of organs, their shape and size, and see the presence of ulcers, erosions and neoplasms.
One of the types of x-ray examination of the gastrointestinal tract is irrigoscopy. This is the name of an examination using contrast agents. When examining the stomach, the patient is given a capsule of barium to drink, and to take pictures of the intestines, this substance is injected through the anus. Barium is opaque to X-rays, allowing for a more accurate image.
Ultrasound
Modern ultrasound diagnostic devices allow you to clearly see the size, location and shape of internal organs, the presence of foreign bodies and tumors.
Usually, it is ultrasound that begins the diagnosis when a patient consults a doctor with complaints of abdominal discomfort.
This method can be used for preventive purposes, for the timely detection of tumors, decreased intestinal motility, narrowing of the intestinal lumen, and disruption of the sphincters.
Ultrasound examination of the gastrointestinal tract is also used to confirm the diagnosis and to monitor the correctness of treatment.
This is necessary for gastritis, gastroduodenitis, colitis, irritable bowel syndrome, the presence of polyps or cysts, cholelithiasis, pancreatitis. Ultrasound is informative for examining the intestines.
Some preparation is required before the procedure. And before the scan itself, liquid is injected into the intestines. This way you can detect the presence of polyps, tumors, and narrowing of the intestinal lumen.
Tomography
If difficulties arise in diagnosis, a computed tomography may be prescribed. It allows you to obtain information about the shape and size of the digestive organs, the condition of bones and muscles, the thickness of the abdominal wall, and the presence of foreign bodies. CT is more informative than x-rays, but the radiation exposure from such an examination is less.
More accurate information about the state of the gastrointestinal tract can be obtained using MRI. This way you can examine the stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, gall bladder and ducts. An MRI image allows you to evaluate the condition of blood vessels and lymph nodes, the presence of stones, cysts, polyps or tumors, and the structure of organ tissue.
Bowel examination
Due to the structural features and location of this organ, it is difficult to examine it. The condition of the duodenum can be determined by endoscopy through the esophagus. But the probe does not penetrate further. The rectum is viewed during colonoscopy. But the small intestine is more difficult to examine. To identify its pathology, a comprehensive examination using several methods is necessary.
The most commonly used is colonoscopy - examination of the rectum using a probe. It is inserted through the anus. Using a special camera at its end, you can examine the condition of the intestinal walls, the presence of tumors or stagnation of feces.
During the procedure, you can take a sample of the mucous membrane for analysis or even remove small polyps. And retromanoscopy also allows you to assess the condition of the large intestine. In this case, a special probe moves to a distance of more than 30 cm.
This examination is recommended for every person over 50 years of age. This makes it possible to detect cancer at an early stage.
Analyzes
At the stage of making a preliminary diagnosis, laboratory diagnostic methods must be used. These include analysis of biological fluids of the body: blood, urine, and feces.
They allow you to determine the activity of enzymes, the presence of inflammation, infections, parasites, and the state of the intestinal microflora.
These tests do not make a diagnosis on their own, but are necessarily included in a comprehensive examination of the gastrointestinal tract:
- Diagnosis always begins with blood tests. It is taken on an empty stomach, it is advisable to stop taking alcohol and medications the day before. The blood is checked for ESR to detect the presence of an inflammatory process, pancreatic enzymes, antibodies to Helicobacter pylori or helminths.
- A general urine test is necessary for severe diarrhea and vomiting, as well as for suspected cancer. The density of urine, its color, and composition are assessed.
- To assess the state of the gastrointestinal tract, stool analysis or coprogram is very informative. It allows you to identify the presence of bleeding in the digestive tract, the presence of parasites, and infections. Undigested food remains indicate indigestion. You can also assess the state of the intestinal microflora.
Blood tests can reveal an inflammatory process, impaired enzyme activity, and the presence of parasites
Preparation
Any research methods require certain preparation, without which the result may be distorted. It is usually recommended to prepare for diagnosis 3-5 days before the procedure. There are specific recommendations for each method; the doctor should warn the patient about them. But there are also general recommendations that are related to the specific location and functioning of the digestive organs.
- Be sure to follow a diet a few days before the examination. To prevent gas formation, it is recommended to avoid legumes, brown bread, large amounts of fiber, and heavy foods. Approximately 10-12 hours before the procedure, you are not allowed to eat at all; sometimes you are not even allowed to drink water.
- It is advisable to avoid drinking alcohol and not smoking, especially 12 hours before the examination.
- Sometimes it is recommended to take certain medications that will help cleanse the gastrointestinal tract and improve digestion. These are enterosorbents, enzymes, drugs against nausea and flatulence.
- When examining the intestines, you need to take laxatives or do an enema for several days to cleanse it.
- Before probing, you can take an anesthetic or antispasmodic. Some people are also advised to take a sedative.
Contraindications
To check your gastrointestinal tract, you must first visit your doctor. It will help you decide which methods are best to use. After all, not all of them are equally informative; in addition, some have contraindications.
An instrumental examination is not performed if the patient has an infection, fever, or acute inflammation. It is also contraindicated in the presence of heart or lung disease, bleeding disorders, or allergies to certain drugs.
Regular examination of the gastrointestinal tract will help identify various pathologies at the initial stage. This will make it easier to treat them without complications.
Source: https://vrbiz.ru/diagnostika/obsledovanie-zheludochno-kishechnogo-trakta
How to check the stomach without FGS
Checking the stomach with MRI is completely safe and does not require swallowing a tube or injecting a barium solution. At the same time, the procedure is quite informative and allows you to evaluate the structure of the organ, the thickness and condition of its walls, and the presence of neoplasms. MRI is a modern method for diagnosing stomach diseases. During the examination, a three-dimensional image of the stomach is displayed on the monitor, allowing you to see polyps and other lumps. To get a better picture, you need to properly prepare for the procedure:
- For several days before the MRI, it is recommended to follow a diet, taking only boiled, liquid and crushed food that does not cause flatulence. Before the event, it is necessary to cleanse the intestines using an Esmarch mug or laxatives.
- The last meal should take place no later than 19–20 hours on the eve of the examination. Computed tomography is most often prescribed to patients who already have a diagnosis and have undergone specific treatment, as well as people who have crossed the 50-year mark.
- To effectively visualize cavities, a contrast agent or air is used.
- At the request of the patient, the procedure can be performed under slight anesthesia.
- Attention. MRI scanning is contraindicated in pregnant women and patients with perforation of the intestinal wall. If an MRI is not possible, the doctor may prescribe another, more gentle diagnostic method.
Capsule fibrogastroscopy
In recent years, medicine has made a big step forward, thanks to which many new examination methods have appeared that do not cause discomfort to the patient.
Today, it is possible to study the patient’s stomach and esophagus without gastroscopy - using capsule fibrogastroscopy.
The procedure involves swallowing a special capsule, which helps the doctor examine the condition of the gastrointestinal tract from the inside.
Before the examination, the patient should remove cabbage, legumes and other foods that can cause bloating from the diet. The examination helps to study not only the condition of the walls of the stomach, but also the entire intestine.
When the patient swallows the capsule, it moves along the digestive tract and remembers all the images. To facilitate the movement of the capsule, it should be washed down with plenty of water.
The patient goes about his usual business, and after the capsule comes out naturally, the patient gives it to the doctor.
The images obtained from the capsule allow the doctor to see the condition of the stomach and intestines and assess the extent of damage to the organ.
The main features of the method are its undoubted convenience, effectiveness, and the absence of the need for gastroscopy. However, the method also has some disadvantages.
READ What does stabbing pain in the stomach indicate?
First of all, this is the cost of the procedure, which is significantly higher than conventional gastroscopy.
In addition, unlike classical gastroscopy, when swallowing a capsule, the doctor cannot perform any manipulations, for example, remove a growth on the stomach wall or cauterize a bleeding vessel.
Therefore, the procedure has a purely diagnostic purpose.
In some cases, the device can not only take images of the organ, but also measure additional indicators:
- acidity level;
- mucus level;
- intestinal temperature;
- condition of feces;
- the presence of stones in the intestines.