A cough that does not go away for a long time, difficulty swallowing food and saliva, and a constant feeling of a lump in the throat can be a symptom of serious diseases. To diagnose and make an accurate diagnosis for patients with similar complaints, ENT doctors are required to issue a referral for an x-ray of the throat and larynx. What are the features of this procedure and what can be seen in the finished images?
A sore throat
Features of x-ray of the larynx
Radiology is a science that helps doctors make correct diagnoses. With the advent of X-ray machines, the number of diagnostic errors has decreased by an order of magnitude. And modern devices make it possible to obtain the most accurate images and thereby ensure a speedy recovery for the patient.
An X-ray image helps medical personnel in establishing an accurate diagnosis and, accordingly, prescribing the correct treatment. X-ray of the throat allows you to more accurately and more closely assess the condition of the soft tissues of the cervical spine, as well as bones. The X-ray also shows the entire structure of the cartilage. Reflects bone calcifications and tissue changes that occur with age.
X-ray is a procedure for obtaining a diagnosis, which today has no alternative (it is understood that no other procedure can surpass the quality and accuracy).
In medicine, there are ways to conduct x-rays of the larynx - direct or lateral projection (used to obtain information and detect pathologies on both sides).
Doctor's second opinion
The larynx, nasopharynx and esophagus are not organs that can be correctly assessed by any doctor. Thus, a thorough and attentive analysis of CT or MRI images is extremely important because it allows you to answer questions that are important when choosing treatment methods. For example, is the tumor located in the subglottic space or supraglottic?
What is its stage, is there any germination of the surrounding tissue? Is there damage to regional lymph nodes? In order not to make a mistake in diagnosis, you can resort to a Second Opinion and send the research results for consultation with a highly specialized diagnostician. Otherwise, analysis of CT or MRI images may be fraught with errors. Today you can send images for consultation using various medical services, such as the National Teleradiological Network.
Advantages and disadvantages
X-ray of the throat has a significant advantage - the form of diagnosis is accessible to everyone, is quickly performed and has virtually no contraindications. An important point is also that the patient does not need to prepare for a long time for the study. The doctor processes the results quite simply and quickly. The study takes place in any premises (hospital wards, specialized diagnostic centers, operating rooms).
However, there are some disadvantages:
- Radiation exposure is a primary factor, which makes this procedure inaccessible to pregnant patients and nursing mothers.
- Despite the large amount of information that can actually be obtained from an image of this organ, the picture of the disease is not always fully revealed.
- Lack of information about the condition of soft tissues, which becomes a significant obstacle to obtaining a complete diagnosis.
Even if there are shortcomings, doctors recommend x-rays as the most reliable way to obtain information about the problem and make the correct diagnosis. In some cases, in order to avoid an error, an alternative procedure (for example, MRI) is prescribed in addition. But the data obtained from other sources is used as a supplement to the basic information obtained through x-rays.
What does an x-ray show?
The patient, looking at the x-ray, will see the general picture, but the specialist pays attention to many important points. The main thing that an x-ray will show:
See also
What to do if the lymph nodes on the right or left neck are swollen, how to treat?
Read
- The lumen, which looks like a curved strip of clearing and is a continuation of the pharynx, passes into the trachea. Visualized on lateral projection images.
- The cartilages (epiglottis, cricoid, thyroid), laryngeal ventricles, epiglottis and hyoid bone are visible.
- On direct projection x-rays, the thyroid cartilage and subglottic space are clearly visible. In some cases, it is possible to see the upper and middle parts of the larynx.
- In some cases, when performing a study with functional tests, the doctor is given the opportunity to assess the mobility of the vocal cords and the size of the glottis.
X-ray examination makes it possible to study the morphological state of the organ and identify narrowings and deformations along the path of the air column.
In the photographs it is possible to notice such throat diseases as whooping cough, tracheal stenosis, diphtheria and others.
CT with contrast
To identify and diagnose certain diseases, a CT scan of the larynx with contrast is performed. A contrast agent is a substance that enhances the visibility of the organs and tissues being examined. Most often, iodine-based contrast agents are used. The substance is injected into a vein, it spreads through the bloodstream and stains the vessel, after which the drug accumulates in the tissues, thus improving their visibility in the resulting images. Each subsequent image visualizes the branched vascular system more clearly.
As a rule, CT with contrast is used to study areas of inflammation and cancerous tumors, since these lesions have their own blood supply system, which differs from normal. CT images show this difference perfectly, and the attending physician can immediately diagnose an adenoma, cyst or malignant tumor.
Sometimes the neck area can be examined with oral contrast, for example, a CT scan of the esophagus if stenosis, cancer, or a mucosal polyp is suspected. Contrast drugs are completely eliminated from the body within two days.
Indications for use
The patient can have an x-ray of the larynx without a doctor’s prescription, at his own request. If the doctor has prescribed a procedure, then there is a suspicion of the following pathological conditions:
- Traumatic injury to the neck organs.
- The presence of a foreign body in the lumen of the larynx or trachea.
- Chemical or thermal burns of the larynx, pharynx, upper esophagus and trachea.
- Chronic laryngitis.
- Paresis and paralysis of the larynx.
An X-ray diagnosis of the larynx is prescribed by a doctor if the patient suspects various injuries - external or internal. For burns, x-rays are sometimes prescribed. The most valuable method for diagnosing paresis and paralysis.
As an auxiliary study, x-rays of the larynx are used to diagnose chronic pathologies of the larynx with inflammatory processes, as well as tracheal stenosis, malignant tumors, whooping cough, and diphtheria.
X-rays also play a key role in diagnosing laryngeal cancer. The study is used in tandem with other types of diagnostics to obtain an accurate result.
Classification of tongue cancer
Tongue cancer can be localized on any part of the surface of this organ. In this regard, the classification of the disease may be as follows:
- cancer on the side of the tongue;
- tongue root cancer;
- cancer of the lower surface of the tongue.
The lateral part of the tongue is most often affected by tumors. Cancer can occur on the lower surface in no more than 10% of cases.
There are other classifications of the disease. For example, cancer is distinguished by microscopic characteristics. The most common cases of squamous cell tumors occur; histological cancer can be found extremely rarely.
Macroscopic characteristics can also be a criterion for the classification of this malignant tumor. Experts usually make a distinction between endophytic and exophytic forms. In the first of them, tongue cancer manifests itself in an infiltrative form, in the second form - in an ulcerative form.
Preparation for the procedure
No preparatory steps are required from the patient for radiography. The main condition is to remove your jewelry before the examination. The conditions for the procedure are described below.
In some cases, to improve image clarity, the organ being x-rayed is “shaded” or “illuminated” with medications. This option requires more thorough preparation (for example, refusing to eat a few hours before the procedure).
How to conduct an examination
To take a correct picture of the larynx, the patient must take a position lying on his stomach. When placed sideways, the image shows the lumen of the larynx. In some difficult cases, radiopaque agents are used, which are sprayed on.
The procedure proceeds as follows:
- The patient is placed on his side.
- A specialized film is applied to the back of the neck opposite the recording device.
- A focal distance of about 60 centimeters is maintained.
- The patient holds his breath while the image is taken. This is necessary to obtain the clearest image.
See also
Treatment of inflammation of the lymph nodes with chickenpox in children and adults
Read
In rare cases, a second x-ray is taken. To do this, the patient is numbed with drugs to the area being filmed, and the film is placed in the area of the larynx. The X-ray beam is directed clearly at the area of the disease focus, which makes it possible to accurately reflect the nature of the disease.
What diseases does CT detect?
Computed tomography of the nose and paranasal sinuses reveals diseases of any nature. Using X-rays, the device takes a series of layer-by-layer images, and a computer program converts them into a 3D volumetric image. After scanning, a tomogram of the sinuses shows:
- polyps and cysts;
- sinusitis;
- ethmoiditis;
- frontal sinusitis;
- sphenoiditis;
- displacement of bones after trauma to the skull and nose;
- foreign bodies;
- neoplasms (tumors);
- osteomyelitis of the skull bones.
CT scanning of the paranasal sinuses records slices 1–2 mm thick, so the method detects the lesion at a very early stage of development. In addition, the doctor has the ability to rotate the sinus CT image on the computer to view it from any angle. In this format, for example, pathological ingrowth of the last molar into the jaw joint area is detected, which is often accompanied by severe pain.
CT scans are also done before dental implantation and bone tissue augmentation to restore teeth.
Decoding the results
The clarity of the image in the image, as well as the correct decoding of the available data, largely depends on the type of equipment on which the study is carried out. Modern digital devices transmit information more accurately than their analog predecessors.
All interpretation of the results should be carried out by the attending physician. This is necessary so that the patient does not prematurely and independently make an erroneous diagnosis, which will lead to negative consequences.
An erroneous diagnosis of a patient leads to typical self-medication, which ends in unforeseen complications. It is critically important at any stage of the disease or diagnosis to focus on the recommendations of a specialist and act in accordance with the instructions.
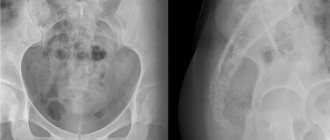
Pathologies that are visible on radiographs
One of the symptoms that can be seen on a plain x-ray is a displacement of the trachea to the side. This condition should be studied in detail, and, if necessary, an additional research method, including targeted radiography, should be prescribed.
If there is an increase in pressure in one half of the chest, the trachea moves to the opposite side. And vice versa, if the pressure level drops on one side, then the lungs collapse and pull it along with it in the direction of the lesion. Also in the picture, the narrowing of its lumen, which is normally equal to two centimeters, is clearly visible.
Sight radiography of the trachea with stenosis
Stenosis is possible with the following pathologies:
- sarcoidosis;
- amyloidosis;
- relapsing polychondritis;
- benign tumors of the mediastinum;
- tracheal papillomatosis;
- primary malignant tumors;
- metastasis into the airways;
- connective tissue diseases (tracheopathy, osteoplastic dystrophy of the trachea);
- Wegener's granulomatous vasculitis.
An X-ray shows a similar picture - the trachea is narrowed, the presence of medium and low density formations in the mediastinum, which compress it from the outside, or grow inside it.
There is a group of diseases that are classified as congenital anomalies of the trachea. X-ray is a key method in their diagnosis. These include:
- Agenesis, or blind ending trachea.
- Congenital tracheostenosis.
- Cartilage hypoplasia. It manifests itself as an underdeveloped wall, which is difficult to see on the image, and a narrowing of its lumen.
- Tracheal fistulas. Visible on x-rays with contrast, when wall defects and contrast fluid in the mediastinum become visible.
Contraindications
Before going to a radiologist for a picture of the larynx, you need to consult an otolaryngologist. Only the attending physician prescribes the procedure based on the indications and can take into account possible negative consequences. The only contraindications are pregnancy and breastfeeding, as mentioned above.
When conducting contrast diagnostics, there are a number of additional contraindications:
- patient intolerance to drugs containing iodine;
- problems with the thyroid gland;
- patients suffering from active tuberculosis;
- liver and urinary tract problems;
- decompressed diabetes mellitus.
X-ray is a procedure that involves exposure to radiation. Therefore, people who do not suffer from acute diseases of internal organs should resort to it. If the patient has, for example, a cold or open bleeding at the time of the procedure, it is better to reschedule the x-ray.
Possible risks
Various types of diagnostics based on X-rays have a negative effect on the human body. During a computed tomography scan, X-rays affect only the area of the body being examined, so the person receives minimal radiation, the dose is several times less than that of X-rays.
It is necessary to maintain the recommended time interval between such studies, since excessive exposure to radiation can provoke the development of formations and the occurrence of other pathologies.
Similar diagnostic methods
Since x-rays of the larynx classify the functionality of the organ, there are a number of methods aimed at the same:
- Valsalva maneuver. The procedure is performed when the patient exhales with the glottis closed and the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall tense after a deep inhalation.
- Carrying out the study while taking a long breath or pronouncing the vowel sounds “i”, “o”, “u”, “e”.
- CT scan.
- MRI.
Despite the number of alternative diagnostics, x-rays of the larynx remain an effective and affordable diagnostic method. Even when several diagnostic methods are used, X-ray readings remain decisive in making a diagnosis.
Similar techniques
These include computed tomography, which is an improved version of radiation examination. It makes it possible to obtain a series of layer-by-layer sections of all parts of the body, which can later be viewed one by one. It is used to examine the structure of some pathological formations and organs, to identify the exact localization of processes.
Magnetic resonance imaging is based on the phenomenon of nuclear resonance of atoms. It is used primarily for imaging soft tissues of the body.