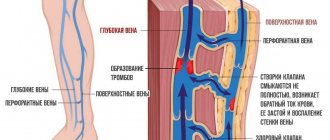
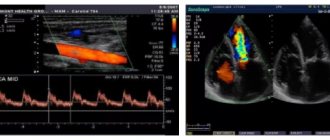
A person in the modern world has to deal with a huge number of stressful situations, severe nervous, mental and physical stress, and unfavorable environmental conditions. All these and many other factors negatively affect the circulatory system, resulting in various types of vascular problems.
It is very important to promptly identify the changes that have begun in order to avoid the development of serious vascular pathologies. In the twenty-first century, there are many methods for diagnosing diseases of the veins and arteries of the human body. One of them is rheovasography.
- 2 Advantages and disadvantages of diagnostics
- 3 Indications and contraindications
- 4 Preparation for the examination
- 5 Carrying out diagnostics
5.1 Possible consequences
The essence of the rheovasography method
Rheovasography began to be used in cardiology in the last century (1932). This technique was based on the resistance of electrical alternating current. In rheovasography, resistance occurs in muscle tissue and blood vessels.
Current passes through the body with a frequency from 400.0 hertz to 600.0 hertz. Getting deep into the human body, this beam of current receives different resistance from muscle tissue and vessels of different types, which creates individual fluctuations in electrical voltage.
The rheovasograph creates these resistances into visible graphs (rheogram).
The biological fluid blood is a good conductor of electrical impulses, and muscle tissue resists the passage of the electrical wave. The best indicator of resistance is the bone tissue of the human body.
The walls of blood vessels are deformed due to pathologies of the blood flow system, and this is reflected by the rheovasograph. With the pathology of atherosclerosis, the walls of the arteries become denser and plaques form on them, and with inflammatory edema they stretch, and this is reflected by the instrumental equipment.
There are certain standard indicators and deviations from the standards can be obtained in the interpretation of the rheovasography method.
The following indicators are determined:
- Image of the condition of the vein or artery being studied;
- The shape of the blood vessel and its direction are revealed;
- The internal and external diameters are calculated, and its degree of expansion under the influence of pathology, as well as narrowing;
- Vascular tone is revealed;
- The ability of blood vessels to contract;
- Phases from filling with biological fluid;
- Outflow of biological fluid from the lower extremities;
- Symmetrical blood flow to all extremities;
- Connecting shunts with other vessels, as well as arterial anastomoses, are detected.
It is on these indicators that the rheovasography method for peripheral vessels and hemodynamics in them is based. The rheovasogram looks like a curved line, which reflects all the indicators necessary for decoding.
The current frequency is 10 mA, which makes it safe for the body and allows you to conduct research using this method several times without fear of its negative impact on the body.
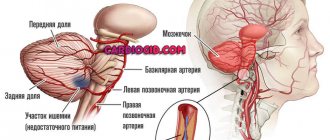
Features of blood circulation in the body
A person has 2 circles of blood circulation: large and small. The first carries arterial blood and collects venous blood throughout the body, while the second serves only the lungs. When breathing, blood is saturated with oxygen and flows to the heart, which, during contractions, distributes it throughout the body thanks to an extensive network of arteries. Oxygen and nutrients remain in the tissues, and metabolic products and carbon dioxide are taken away by the venous system. The latter carries blood through the veins to the lungs, where exchange occurs again.
Disruption of the circulatory system (arteries, veins, small capillaries, venules) affects organs and tissues, leading to functional or organic changes. Even minor vascular stenoses and capillary spasms can be expressed in pain, numbness, decreased temperature of the extremities, and other symptoms. That is why it is so important to determine the level and nature of the lesion in time in order to prescribe appropriate treatment as early as possible.
When is rheovasography performed?
Rheovasography is used for the following pathologies in the body:
- Numbness of the lower and upper extremities;
- Pain in the legs when moving, as well as pain at rest;
- Swelling in the lower extremities;
- Condition of leg cramps;
- Blueness appears on the fingers of the limbs;
- Lameness;
- The appearance of non-healing wounds and ulcers on the lower extremities.
If your hands go numb when working at a computer, then you simply need to undergo a study of the condition of the upper extremities using the rheovasography method.
This technique is also used for the effectiveness of drug therapy for pathologies such as:
- Atherosclerosis of the arteries of the lower extremities;
- Varicose veins on the limbs;
- Thrombosis, or thrombophlebitis;
- Pathology of Raynaud's syndrome.
Examination of the condition of the walls of peripheral vessels is indicated for people with diabetes mellitus. This pathology concerns not only the metabolic process in the body, but also affects the blood flow system, especially its peripheral parts.
It is also recommended to undergo a rheovasography study in case of traumatic fractures of the arms, as well as lower extremities and in case of trauma to the pelvic bones. For elderly people, the use of rheography results will allow us to identify and prevent the further development of many pathologies.
There are no contraindications for conducting a study using the rheovasography technique; the study can be carried out even during pregnancy.
Next steps for the patient
With a deciphered rheovasogram of the vessels of the lower extremities, the patient is sent to the doctor who prescribed the examination. Based on the results obtained, a diagnosis is made and treatment tactics are selected. In non-dangerous stages of vascular damage, the doctor prescribes special medications that strengthen the vascular walls, dietary nutrition, rational physical activity, and compression garments. In some cases, it is recommended to change your field of activity if work aggravates the disease.
Serious changes in the blood flow system are an indication for additional research. A more detailed analysis of the hemodynamic process includes the following methods:
- RK angiography (x-ray contrast). Diagnosis of vascular diseases using x-rays with a contrast agent;
- MR angiography. Magnetic resonance imaging examination;
- Ultrasound Doppler. Ultrasound examination using Dopplerography.
Depending on the final results, the patient is prescribed conservative therapy or surgery. If you experience systematic discomfort in the lower or upper extremities, you should consult a phlebologist or vascular surgeon. The sooner the pathology is identified, the less radical the method of eliminating it will be.
Preparation for rheovasography
The process of preparing for the study of peripheral hemodynamics and the process of rheovasography itself:
- Rest in a relaxed state for 15 minutes;
- Do not smoke more than 2 hours before rheovasography;
- One day before the scheduled time of the study, stop taking medications;
- During the period of research checking the condition of the lower extremities, they should be naked.
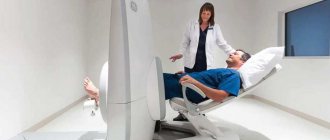
When examining using rheovasography, the patient is in a horizontal position. The skin is degreased using medical alcohol. Information reading sensors are placed in certain areas.
Electrodes for rheovasography are attached to the lower extremities and connected to sensors and the device via wires.
Sensors for receiving information transmit it to the central screen of the device, and the rheovasograph records the study indicators on the rheogram.
The RVG method of the lower extremities is carried out using a multi-channel rheograph device, and rheography can be carried out sequentially in accordance with the areas of examination, starting from the far points of the periphery and gradually approaching the center.
If the upper extremities are being examined, then the process of recording the readings on the rheovasograph begins from the wrist, then in the ulnar notch. If it is necessary to examine the shin of the lower extremities, then information sensors are placed under the knee fossa and on the ankle joints.
Studying the readings on the fingers and toes - the electrodes are placed strictly symmetrically at a distance of no more than 4 centimeters from each other.
This instrumental examination procedure lasts no more than 25 minutes. The average is 20 minutes.
The results of the performed technique allow us to draw conclusions about the development and degree of pathology of the peripheral hemodynamic system.
This technique allows you to determine the nature of the blood flow disturbance:
- Functional type of impairment;
- Organic character.
Interpretation of rheovasography indicators
Table of indices for the norm and for deviations based on the results of the rheovasography technique:
| Name of the index under study | Norm in indicators | Deviations from the norm | Decoding |
| rheographic index | higher than 0.050 | less than 0.040 | ischemic pathology of the studied area due to disturbances in the filling of arteries with biological fluid |
| vascular elasticity index | higher than 0.40 | from 0.20 to 0.40 | decrease in elasticity is moderate; |
| less than 0.20 | a sharp decrease in vascular elasticity | ||
| peripheral resistance index | from 0.20 to 0.450 | more than 0.550 | resistance is sharply increased; |
| less than 0.15 | resistance is significantly reduced | ||
| indicator of venous blood flow | from 0.20 to 0.50 | Less than 0.20 | easy outflow of venous blood; |
| more than 1.50 | obstructed venous outflow |
By deciphering the indicators of rheovasography results, one can judge various pathologies of the body:
- The rheographic index has a standard value of no higher than 0.050. The rheographic index is sharply reduced to 0.040, indicating stage 1 insufficiency of the blood flow system. This is expressed in poor sensitivity to temperature changes, as well as in low temperature of the lower and upper extremities. If the index is lowered by more than 0.40, then this condition is critical for the blood flow system;
- Based on the elasticity coefficient, we can talk about a disorder in the vascular system, as well as in the cardiac organ;
- The index of venous blood outflow from the lower extremities indicates the possible development of thrombophlebitis and blockage of the veins when the index is higher than 0.50. With this indicator, obstructed outflow of venous blood from the lower extremities occurs;
- The resistance coefficient indicator is a standard from 0.20 to 0.450. Anything below or above this standard indicates that there are disturbances in the blood flow system. The higher the percentage of deviation, the more serious the pathology develops in the vascular and heart systems.
Many pathologies can be diagnosed using rheovasography, which is not only available in every ultrasound room, but is fast and does not require a long period of preparation of the body.
How it goes
The room where the procedure itself takes place must be quite warm, since the patient is forced to take off his clothes, freeing his limbs for examination.
In order for the fixed electrodes to show accurate data, the person must lie in a motionless position. For convenience, a soft couch is available.
Before fixing the sensors, the surface fatty layer is removed from the skin. They are installed clearly according to the principle of longitudinal or transverse placement. This depends on the limbs being examined.
If the mechanical activity of the vessels of the arms is examined, then the sensors are placed in four places throughout the limb. On the legs these are the feet, legs and thighs.
Is it possible to use the rheovasography method to study the brain?
The technique for studying the cerebral vascular system is called rheoencephalography. It has similarities in principle with the rheovasography method, but encephalography is performed only in the head and neck area.
This technique is used in conjunction with the graph of the limbs, since the rheoencephalogram complements the results of the rheovasography study.
Rheoencephalography reveals abnormalities in the brain, in its circulatory system, as well as in the condition of the cerebral vessels.
Using this research method, the following deviations can be identified:
- Cerebral ischemia;
- Complications after a traumatic situation on the skull;
- The initial stage of atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels;
- Detection of osteochondrosis of the cervical and thoracic spine.
The preparatory process is the same as for rheovasography. The duration of the brain examination procedure is no more than 10–15 minutes.
The method is performed in a sitting position.
A headband with attached electrodes and sensors is placed on the fronto-occipital part. It is necessary to apply a specialized gel to the sensors for improved contact between the information sensors and the skin.
What is a Rheovasogram?
Rheovasogram, or brain gram - the encephalogram has the type of teeth, like a cardiogram. The main teeth of the rheovasogram go down, and there are also additional teeth.
The size of these teeth and their type differ depending on the area of study of the organism. The height of the teeth with healthy legs reaches 1.2 centimeters. Width is measured in seconds - and ranges from 0.2 seconds to 0.25 seconds for legs.
If the vessels are in a healthy state, then there are equal fluctuations up and down. The ascending part of the rheovasogram indicates the ability of the vascular walls to contract. A descending curve indicates the ability of the walls to stretch under the pressure of incoming blood.
The rheovasography curve is inextricably linked with the systole of the cardiac organ, so the sensors are also connected to the ECG machine.
The curve varies depending on the type of pathology in the body.
With atherosclerosis of the lower extremities, the height up and down decreases, but the time between the teeth expands. This indicates damage to the blood vessels and their low elasticity.
With sclerosis of the lower extremities, there is no expansion in the teeth, but their height decreases.
With obliterating endarteritis, the complex of teeth expands.
Rheovasographic study of the blood flow system also involves conducting tests to identify the root cause of circulatory pathology, factors of hidden deviations and disorders.
Tests based on the rheovasography method
Before diagnosis, control rheovasography is done using the test method.
There are 2 types of functional tests when studying rheovasography:
- Nitroglycerin test type - after taking a dose of Nitroglycerin, any deviation at the time of vasospasm is measured after a time interval of 5 minutes. If there is an increase in blood flow in the system, then the elasticity coefficients and rheography index increase. This test is positive and functional. If there is no dynamics in spasms, then organic damage to the arterial walls appears;
- A compression test is a fairly important diagnosis for thrombosis of the leg veins, which lie deep inside the limbs. This procedure is quite often prescribed to women during the period of intrauterine pregnancy, and in order to avoid thrombosis of arteries and veins. A cuff from a device that measures the blood pressure index is placed on the thigh of the diseased limb, or two, and by forcing an air flow into it, the veins in the limbs are compressed. The compression test is based on determining the time of outflow of venous blood from the lower extremities.
Example of rheogram results
Main indications
The disease can be identified and a procedure prescribed based on a person’s complaints.
The patient must list the symptoms manifested over a certain period of time. Complaints:
- Swelling of the extremities;
- leg cramps;
- visible venous network;
- sharp pain in the limbs when walking, which disappears as spontaneously as it appears;
- numbness of the feet or hands;
- pale skin color on the extremities.
How much does it cost to do a study using rheovasography?
The cost of examining the extremities using the rheovasogram technique depends on the location of the examination. If you conduct examinations at a local clinic, it will cost less than at a well-known diagnostic center.
On average, the price for rheovasography in Russia ranges from 600.00 rubles to 2500.00 rubles. The cost of the procedure is also affected by the power of the rheovasograph and its technical data.
Cost in Ukraine:
- Rheovasography of the upper extremities - 250.00 hryvnia;
- Examination of the lower extremities - 250.00 hryvnia;
- Studying the upper and lower together - 400.00 hryvnia.
Advantages and disadvantages of diagnostics
The main advantages of this technique include:
- Availability. Almost any medical institution is equipped with equipment that allows diagnosing vascular pathologies in representatives of any group of the population (from children to the elderly).
- Safety. Rheovasography is a non-invasive way to study the state of hemodynamics, allowing it not to penetrate the human body, due to which it is considered absolutely safe.
- Speed and accuracy of diagnosis.
- With the help of rheovasography, even slight narrowing of blood vessels can be determined.
- The result can be obtained within a few minutes after the examination.
The main advantages of diagnostics are the absence of contraindications and safety
Despite all the positive aspects of such diagnostics, it also has disadvantages:
- Sometimes the technique gives false results (often this depends on non-compliance with the rules of preparation for the procedure or conditions such as swelling of the lower extremities, muscle spasms and others).
- Lack of opportunity to study the properties of blood vessels (for example, the diameter and condition of the vascular membranes, etc.).
- There are situations when several doctors evaluate the same rheogram differently (the interpretation of the results obtained directly depends on the qualifications and experience of the specialist).