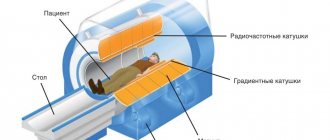
Hemodynamic disorders of the central nervous system pose an enormous danger to life. Despite the long-term absence of obvious symptoms, processes of this kind quickly progress, cause neurological deficits, and become the culprits of strokes of varying severity. This is a direct path to disability.
The only way to avoid such an unenviable fate is to study the state of the body in detail.
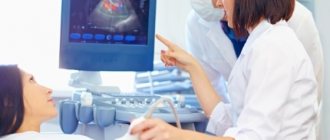
Ultrasound dopplerography of the BCA is an ultrasound Dopplerography (examination) of the brachiocephalic arteries that supply the brain. The technique allows you to quickly detect all possible problems with nerve tissues and the degree of their blood supply.
Compared to duplex scanning (USD), this procedure is somewhat simpler and not as informative. It is used as a survey technique and creates the basis for further examination of patients.
This method is universal in its way and allows you to diagnose atherosclerosis and other disorders. However, we are also talking about a functional method. There is no need to expect detailed visualization of anatomical structures.
As a rule, diagnostics are prescribed in a system with other measures.
The essence of the survey and what it shows
The basis of ultrasound examination of the brachiocephalic arteries (abbreviated as BCA ultrasound) is the ability to create a clear image of the area of interest. However, this is not as informative and accurate a technique as duplex scanning of the vessels of the neck and head, so its scope of application is somewhat narrower. And the doctor will not receive much information.
On the other hand, the equipment is much cheaper, which makes the measures accessible to a wide range of patients. If necessary, more precise methods are prescribed.
During the action, the specialist has the opportunity to evaluate the following important characteristics:
- Local blood flow velocity. The intensity of brain trophism depends on this indicator. Its quality. But not only. Any deviations clearly indicate either functional changes or the presence of atherosclerosis or arterial spasm. The diagnosis needs to be clarified in other ways.
- The nature of local blood flow. Speed is far from the only indicator, although it is important. It must be assessed in a system with the direction of movement of liquid connective tissue and other points. If necessary, the doctor asks the patient to change the position of the head in order to identify deviations in natural motor activity.
- Condition of vascular structures. Wall thickness, its physical properties. Many abnormalities can also be seen using ultrasound of the BCA, although in this case a highly professional doctor is required.
- Doppler ultrasound of the brachiocephalic arteries allows you to detect areas of narrowing of the artery (spasm or stenosis), blocking by foreign objects, be it a blood clot or an atherosclerotic plaque.
On the other hand, this is not enough to obtain comprehensive information, which is the main disadvantage of the study.
How much does the procedure cost?
The price of the study varies between 1200–3200 rubles. The cost depends on the region, clinic, equipment and qualifications of the specialist.
Cost of the study:
| City | Price in rubles |
| Moscow | 1600–3100 |
| Saint Petersburg | 1200–2200 |
| Kazan | 1500–1800 |
| Novosibirsk | 1200–2400 |
If left untreated, vascular diseases lead to irreversible changes in the brain. Timely diagnosis of pathologies is the only way to avoid complications.
If you have had an ultrasound of the BCA, share your impressions in the comments. Be healthy. All the best.
What diseases can be detected
Measures based on the results allow us to identify a group of pathological processes that somehow disrupt the functioning of the brain or are capable of doing so in the short term.
Among them:
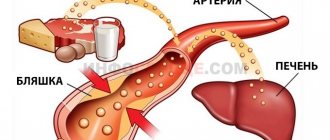
- Cerebral atherosclerosis. A classic disease that is identified by diagnostic results. It is a chronic process in which mechanical narrowing of the lumen of the artery occurs.
Usually the culprit is a cholesterol plaque.
Slightly less frequently, the disorder is accompanied by cerebral vascular spasm. Most often this occurs in hypertensive patients, smokers, alcohol drinkers, and people whose professional activities involve intense physical activity.
To clarify the diagnosis, duplex scanning is prescribed. It is suitable for identifying particularly difficult cases.
- Congenital anatomical defects. For example, hypoplasia (underdevelopment of arteries). Patients do not always have an idea of their presence. Asymptomatic course occurs in more than half of clinical situations.
It makes sense to carry out additional measures to clarify the anatomical component. BCA examination provides information about functional impairment. Precise imaging requires an MRI. Together, these methods provide the best diagnostic results.
- Acquired disorders of arterial structure. They occur after suffering vasculitis or other injuries. A typical option is the formation of adhesions. Gross scar defects of the endothelium (internal lining).
This process is accompanied by obvious symptoms. The same as with atherosclerosis. The brachiocephalic arteries are branches of the aorta that supply the brain. The clinical picture is appropriate and is represented by neurological deficits and pain.
- The influence of other pathological processes on blood vessels. Tumors, changes in the musculoskeletal system and others. As a rule, the result is compression of the arteries and impaired blood flow.
It is necessary to assess the severity of the disorder, the exact localization of the transformation of normal trophism into abnormal. For these purposes, ultrasound examination of the brachiocephalic arteries is used.
- Consequences of injuries. Bruises, fractures of the spine, chest and others.
Decoding
Usually, deciphering the ultrasound examination of the BCA is the prerogative of a neurologist. A big role is always given to the qualifications and experience of a specialist. When diagnosing, the doctor pays attention to: the presence or absence of arterial stenosis (vasospasm), which affects cerebral blood flow, aneurysm, which can rupture and lead to death, blockage of blood vessels with plaque or thrombus with the development of ischemia of cerebral structures, turbulence of blood flow with impaired venous function valves, pathological changes in the structure of the vessel.
This is exactly what the doctor describes in his conclusion. Based on the data obtained, plus the results of additional diagnostics, a correct diagnosis is made, that is, the root cause is found and eliminated, to the extent possible.
Indications and contraindications
The list of reasons for prescribing an ultrasound scan is floating. If necessary and at the discretion of the doctor, it can be expanded.
- Hypertension. Stable increase in blood pressure. Moreover, if a person has a long history of the disorder, he receives treatment and the diagnosis has long been established.
- Cervical osteochondrosis. Degenerative-dystrophic problem. Accompanied by compression of blood vessels by growing osteophytes. Hernias. The effect is also provoked by the instability of the pillar.
- Diabetes. Impaired insulin synthesis or decreased tissue sensitivity to it. Regardless of the type of disease.
- Angina and other heart disorders.
- Increased body weight of the patient.
- Age 45+. Over the years, a person takes more and more risks. The likelihood is determined by other factors, but preventive examinations must necessarily include examination of blood vessels.
- Negative family history. Complicated anamnesis. Such patients are at high risk of developing atherosclerosis, cerebral ischemia and subsequent problems.
- Past inflammatory processes on the part of blood vessels. Vasculitis first of all. They are of autoimmune origin.
The result is scarring of the internal structure, the formation of adhesions in the arteries. These mechanical obstacles do not allow blood to move quickly enough, and also lead to dystrophy and gradual destruction of the blood supply structures themselves.
All these diseases have one thing in common. They are factors in the development of atherosclerosis, which in one form or another is identified by ultrasound examination of the BCA.
Such categories of patients are at increased risk, so diagnostics must be performed at least once every six months. As needed and even more often.
There are other indications for prescribing a study:
- Headache. Of unknown origin. And even more so if the cause has already been discovered earlier. Doppler ultrasound in this case involves clarifying the nature of the disorder.
- Sleep disorders.
- Emotional instability. Irritability, aggressiveness. cerebral ischemia leads to a rapid increase in behavioral changes. Negative aspects are emphasized.
- Focal neurological disorders. From vision problems to the gradual decline of mental abilities. In memory. And other changes.
- Dizziness.
Doppler ultrasound of the brachiocephalic vessels (BCV) also has a number of contraindications. Although small.
- Mental inadequacy. If a person is in an acute condition, is unable to control his behavior and is not aware of the specialist’s instructions. Such a patient is unable to sit or lie. At least until normality is restored. It is necessary to correct the changes, only then prescribe a diagnosis.
- General difficult situation of the patient. In some cases it makes research impossible.
- Pronounced hyperkinesis. Especially the head and neck areas. Spontaneous movements create problems with the application of the sensor and interfere with the doctor’s work.
The list is small, such contraindications are rare, and after eliminating the problems, an ultrasound scan can be prescribed.
Indications
Angiography of the brain
Indications for performing BCA ultrasound are the following symptoms and diagnosed diseases:
- constant or recurrent headache;
- loss of consciousness;
- instability of blood pressure (hypertension or hypotension);
- dizziness;
- temporary or permanent visual impairment;
- endocrine diseases leading to disruption of metabolic processes in tissues (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism);
- hyperlipidemia (increased blood cholesterol levels);
- obesity.
Preparing for the examination
No special events required. If we talk about recommendations:
- About 12 hours in advance, you need to give up drinks and food that change vascular tone. This includes tea, coffee, sweets, pickles, rich foods, some vegetables and acidic fruits.
- For 6 hours, drugs that can artificially affect the condition of the arteries are excluded. Antihypertensive, others. This measure is not always mandatory. It is better to clarify whether or not you can take medications from your specialist. Refusal can be dangerous. Especially if you plan to take the drug at night or in the evening.
- During the same period, 12 hours before, you cannot smoke, drink alcohol, or take a steam bath. In order not to provoke narrowing or artificial expansion of the arteries.
Preparation rules
A few days before the study, you need to start preparing for an ultrasound scan. It is necessary to avoid foods that affect vascular tone.
These include:
- coffee;
- alcohol;
- tea and foods rich in caffeine and tannin;
- energy;
- salt;
- pepper.
2–3 days before BCA ultrasound, it is worth limiting smoking. Any medications taken by a person are studied by a doctor. If possible, medications that affect blood vessels are discontinued before the procedure. These measures are necessary for reliable research and accurate verification of the diagnosis.
Progress of the procedure
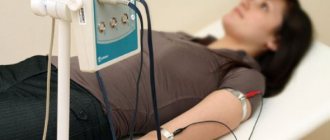
The examination is carried out on an outpatient basis. The patient sits or lies down, depending on the intended diagnostic methods. The doctor places the sensor on it and begins the examination.
During the procedure, you must follow the specialist's instructions. It is possible to change body position, take a deep breath, etc.
Also, the diagnostician often conducts functional tests in parallel. You need to bend your neck and perform certain actions. This is a more informative modification of the study. But it doesn’t always make sense.
Ultrasound of the brachiocephalic vessels of the head and neck lasts about 10-15 minutes. Plus or minus. It happens that it is much less if there are no deviations from the arteries.
Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor prepares a conclusion. A person receives both the eyeliner itself from a specialist and a full protocol of the study with a thorough description of the characteristics found, changes and normal phenomena. It is possible to provide images, usually in digitized form.
With the results of the diagnosis, you should consult a doctor. Which sent for research or another.
Are there any contraindications?
Ultrasound of the brachiocephalic arteries is a modern diagnostic method that does not have any harmful effects on the body. Therefore, there are no contraindications to its administration to patients. The procedure is performed on absolutely all people, regardless of the presence of diseases, age, individual characteristics of the body and other factors.
Ultrasound scanning is performed even on women carrying a child. This helps to detect possible deviations in the baby’s development. Diagnosis is carried out for children of any age. Moreover, the procedure does not cause any discomfort.
Decoding the results
Neurologists do the interpretation. You won’t be able to decipher it yourself, since you need to have a certain set of knowledge and specific skills. Experience also plays a big role.
Based on the diagnostic results, the specialist can note the following deviations:
- Stenosis. Narrowing of the lumen of the artery to a certain percentage of the norm, leading to cerebrovascular accident. In this case, there is no blockage of blood vessels.
Read more about the causes of cerebral vasoconstriction and treatment methods in this article.
- Aneurysm. A wall protrusion in the form of a pouch protruding in one or both directions relative to the vertical axis. An extremely dangerous abnormal condition, fraught with violation of the anatomical integrity of the artery. Massive bleeding and death.
Read more about carotid artery aneurysm here.
- Occlusion. It's a blockage of a vessel. Typically a cholesterol plaque. Much less often - a blood clot. Atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries is described in detail in this article.
- Turbulence of blood flow. With turbulence of liquid connective tissue. Occurs as a result of aneurysms and other processes. A reverse movement is possible - this is a consequence of a malfunction of the venous valves.
- Changes in the condition of the vascular wall.
All findings and diagnoses are, one way or another, described by these deviations. Next, you need to determine what disease occurs in this case.
What is ultrasound examination of BCS
Brachiocephalic vessels participate in the blood supply to the head, neck, shoulder girdle, and upper extremities. These include the brachiocephalic trunk, common carotid, subclavian, and vertebral arteries.
Extracranial vessels of the head and neck are subject to examination. Using ultra-high-frequency waves, the condition of the vascular wall and blood flow in the arteries are studied. In the presence of vascular atherosclerosis, the size of the plaques and their composition are determined.
In addition, ultrasound examination of the BCA allows us to identify:
- vasculitis (inflammatory vascular diseases) of various etiologies;
- stenosis, its severity;
- pathological formations that interfere with normal blood supply (benign and malignant tumors).
Dynamic assessment of blood flow is necessary to calculate the risk of ischemic strokes and other vascular accidents. In the presence of significant obstruction, hemodynamics are disrupted, which contributes to the appearance of the “steal” symptom (decreased blood supply to the brain). This provokes neurological pathologies.
Pros and cons of the study
Among the advantages of the technique:
- Lack of invasiveness. Doppler ultrasound is a completely painless method. It does not create burden or discomfort.
- No lengthy preparation required. It's simple. The event can be carried out without any special action on the part of the patient.
- Minimum contraindications. Since the diagnosis is safe, does not create a harmful load on the body, and does not require invasive measures.
- Availability. The cost, even with a paid passage, is insignificant. It is possible to receive services under a compulsory medical insurance policy.
- Survey speed. Everything takes a few minutes.
- Information content.
Among the disadvantages are the following:
- High requirements for diagnostician qualifications. It takes sufficient experience and a trained eye to assess the condition of the arteries and not lose sight of anything important.
- Relatively narrow scope of application of the survey. Comparatively less than more advanced methods.
Ultrasound diagnostics
The study of the main arteries using ultrasound is by far the most informative diagnostic method, allowing to identify not only physiological changes (wall deformations, width of the vascular bed, bends, the presence of atherosclerotic plaques), but also qualitative and quantitative indicators of blood flow.
Ultrasound scanning used to diagnose pathologies of the brachiocephalic arteries can be divided into 2 types:
- Doppler ultrasound (USDG);
- duplex scanning.
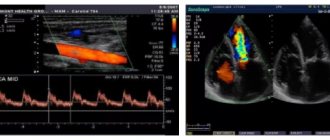
Both methods are based on the Doppler effect, the essence of which is to capture the reflected ultrasonic wave from moving objects. In the case of blood flow studies, red blood cells act as moving objects that reflect ultrasound. The change in the frequency emitted by the sensor (Doppler shift) occurs in direct proportion to the speed of red blood cells moving along the bloodstream, and if the red blood cells move towards the sensor, the frequency increases and the sensor records a positive shift, and if away from the sensor, the frequency decreases and a negative shift is recorded.
On the ultrasound monitor this is reflected in the form of a color image of multidirectional blood flows - red (positive shift) and blue (negative shift). The BCA ultrasound method has both positive and negative sides. A positive feature is the possibility of examining the transcarnial parts of the brain, that is, the arteries located inside the cranium, while for classical ultrasound examination (β-mode) this area is inaccessible.
The negative side is the inability to accurately determine the position of the vessel, and therefore diagnostics are carried out based on its probable location and changes in scanning depth. In rare cases, with an anatomically uncharacteristic location of the arteries, USDG cannot reflect blood flow, but this is not an unambiguous sign of its actual absence.
Duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries is performed using the latest generation ultrasound scanners, combining classical β-mode ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound. The condition of the arteries and the quality of blood flow are assessed based on a two-dimensional (duplex scanning) or three-dimensional (triplex scanning) image. In this case, the vessel can be displayed in the transverse plane and in length.
The use of extracranial ultrasound (examination of vessels located outside the cranium) in duplex mode allows one to obtain the following detailed information:
- condition of the vessel wall;
- thickness, structure and number of atherosclerotic plaques;
- size of the vascular lumen;
- blood flow speed.
Important! Color Doppler mode reflects information about the quality of blood flow, and spectral mode is used to obtain quantitative information.
Analogues of the method
This can be called duplex scanning as a more sensitive ultrasound examination, and as a complement to MRI diagnostics.
The latter does not convey functional components, but concentrates on a static picture of what is happening and anatomical deviations, which duplex scanning cannot.
Ultrasound dopplerography of the BCS is Doppler ultrasound of the brachiocephalic vessels. A necessary examination for a comprehensive assessment of the condition of the brain and its trophism (nutrition). Prescribed according to indications.
Due to its complete safety and sufficient information content, it is often used.
results
The first sign of atherosclerosis detected by ultrasound of the brachiocephalic vessels is not a cholesterol plaque, but an increase in the thickness and density of the intima-media complex (IMC). The wall of any vessel consists of 3 layers. Intima is the inner membrane covered with endothelium, which is in direct contact with the bloodstream. The intima consists of collagen fibers, an elastic membrane and has a thickness equal to 1/10 of the thickness of the media.
The media is the middle and thickest membrane, consisting of many layers of elastic membranes and smooth muscle cells. All arteries located outside the skull have an elastic membrane on the outside. Adventitia is the outer shell of the vessel, the structure of which contains chaotically located collagen and elastic fibers, as well as tiny blood vessels that provide nutrition to the artery wall.
With duplex scanning of the BCA, the inner and middle membranes are quite clearly visible, while the outer one merges with the surrounding tissues. During the IMT study, an analysis of echogenicity and distinct differentiation into layers is performed, that is, a visual separation of the intima and media. As a rule, in the presence of atherosclerosis, the following changes occurring in the IMT are noted:
- the appearance of areas with an uncharacteristic echostructure (usually increased echogenicity);
- lack of obvious differentiation into layers or the appearance of new layers with different echogenicity;
- the appearance of zones of wall thickening.
Important! The maximum acceptable thickness of the intima-media complex of the carotid artery is 1.1 mm. When the IMT increases by more than 1.3–1.5 mm or by 50% of the thickness of the adjacent area, the presence of a cholesterol plaque and, accordingly, atherosclerosis can be diagnosed.
The structure of the arterial wall allows us to understand the subtleties of pathological processes
When plaques are detected, their morphological structure is analyzed. In practice, the following types of atherosclerotic plaques are usually distinguished:
- smooth and having a complex surface;
- hypoechoic or hyperesogenic;
- homogeneous (one-component) or heterogeneous (having a complex composition).
Interpretation of the results of ultrasound scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries includes data on the state of hemodynamics, that is, blood flow velocity, in various parts of the cerebral arteries. A characteristic phenomenon for atherosclerotic changes in the internal carotid artery, which allows one to accurately diagnose the degree of its damage, can be considered an increase in blood flow velocity at the time of systole (cardiac output).
Table. Changes in systolic blood flow velocity depending on the degree of atherosclerotic lesion of the internal carotid artery.
| Artery stenosis percentage % | Highest systolic speed, m/s |
| — | less than 0.6 |
| 10 | equals 0.6 |
| 20 | 0,6–0,8 |
| 30 | 0,8–1,0 |
| 40 | 1,0–1,4 |
| 50 | 1,4–1,6 |
| 60 | 1,6–2,0 |
| 70 | 2,0–2,4 |
| 80 | 2,4–2,8 |
| 90 | more than 2.8 |
An obligatory step when performing an ultrasound examination of the BCA is the determination of the following quantitative indicators characterizing hemodynamic parameters:
- Vрs – the highest blood flow velocity observed at the moment of cardiac output, measured in m/s or cm/s;
- Vеd – maximum blood flow velocity recorded at the moment of rest of the heart muscle;
- RI is an indicator that reflects the degree of resistance of the vessel to the volume of incoming blood.
- PI – pulsation index, an indicator with the greatest sensitivity, characterizing minimal changes in the lumen of the vessel.
How are the results assessed?
The interpretation of the results of ultrasound examination of the veins is given in the table below:
| Parameter | Explanation |
| Arterial wall thickness | The standard value is 0.9 mm. Deviation within 0.2 mm is permissible in the direction of increase and decrease |
| Diameter of the spinal arteries | Normally exceeds 2 cm (over the entire length) |
| Speed of blood flow through the veins of the spine | Standard indicator – 0.3 m/s |
| Vein lumen | A healthy person has free |
| Pathological venous branches | Normally absent |
| Turbulence | Present only in the area where veins branch |
| Signs of vascular compression (compression effect) | In the absence of pathologies there are no |
The basic method of recording the results of Doppler studies of blood vessels is a Dopplerogram. It is a picture of frequency shifts, which consists of an envelope curve and a spectrogram. These components are assessed comprehensively or separately.
How does the procedure work?
Here is a traditional algorithm for performing ultrasound Dopplerography of veins:
- The patient is placed on the couch.
- The desired area of the body is freed from clothing.
- A gel is applied to the sensor, the device is applied to the patient’s skin - a study is carried out by moving the sensor.
- During the procedure, the necessary indicators are recorded.
During the examination, the patient does not experience pain or discomfort. The doctor may ask you to hold your breath, turn your head, raise your limbs, and tense your neck muscles. Typically, a specialist needs from 20 to 60 minutes.
Before the examination, the patient should not smoke, drink alcohol, strong tea, coffee, or energy drinks. In addition, at this time you should stop taking antispasmodic drugs (No-shpa, Papaverine).
Atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries (BCA) is their main pathology
Atherosclerosis is considered one of the most common pathological processes occurring in the arteries supplying blood to the brain and limbs. Vasoconstriction inevitably affects the functioning of the brain, which experiences a lack of arterial blood supply and hypoxia.
Atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries develops for the same reasons as similar damage to the aorta, arteries of the heart, kidneys, and limbs. Mature and old age, excess weight, lack of physical activity, poor nutrition, bad habits, and fat metabolism disorders predispose people to it.
The prerequisites for the appearance of a plaque are damage to the inner layer of the arterial walls, which occurs as a result of active blood flow, high intravascular pressure, and turbulent blood flow in places where vessels branch. A growing plaque can go unnoticed for a long time, because the lumen of the arteries is quite wide, but the progression of atherosclerosis sooner or later leads to disruption of blood supply to the brain.
Atherosclerosis of the BCA can be:
- Stenotic;
- Non-stenotic.
Non-stenotic atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries is said to occur when the plaque grows predominantly along the length of the artery, without causing significant narrowing. It is clear that blood flow will still be disrupted, but complete blockage usually does not occur. As such a flat plaque grows, the circulatory system of the brain is rebuilt to accommodate new conditions - collaterals are turned on, blood is redirected along the components of the circle of Willis, and the brain receives the amount of nutrition it needs.
Atherosclerosis is also considered non-stenotic when the plaque does not cover half the lumen of the artery. As the disease progresses, a non-stenotic lesion can become stenotic - the growing plaque will cover half or even more of the diameter of the vessel.
The situation of stenosing atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries seems much more serious. In this case, the atherosclerotic plaque protrudes into the lumen of the vessel and leads to severe stenosis, and its rupture or damage to the outer cover threatens local thrombus formation and complete obstruction of the artery.
stages of development of complete artery stenosis
Against the background of stenosing atherosclerosis of the BCA, blood flow is also restructured, and its functionality depends on the structure of the circle of Willis. Considering that the classic branching of the arteries of the base of the brain is much less common than various types of variations, most patients with atherosclerosis experience a lack of collateral circulation, and therefore the risk of adverse consequences (stroke, for example) increases significantly.
The favorite zones for the formation of atherosclerotic plaques are considered to be those areas of vessels where they divide or change the direction of their course, which leads to turbulence in the blood flow and damage to the intima, and the most common localization of atherosclerosis of the BCA is the zone of division of the common carotid artery into external and internal branches.
Due to damage to the brachiocephalic arteries, blood flow in the brain suffers, the latter experiences ischemia (dyscirculatory encephalopathy) or necrosis occurs (stroke). The mechanism of development of these complications is associated with hemodynamic reasons, when partial or complete occlusion of the artery occurs, as well as with emboli, when particles of carotid artery plaque and microthrombi from areas of atherosclerotic lesions become emboli.
Hemodynamic preconditions and, in fact, atherosclerosis are much more common in the extracranial parts of the BCA, while blockage of intracranial arterial segments is usually caused by thromboembolism from larger underlying trunks.
The risk of stroke against the background of atherosclerosis of the BCA increases significantly with thrombus formation, the presence of a loose plaque with hemorrhage into its thickness or ulceration of the surface, as well as with severe arterial stenosis (70-80% or more).
In addition to atherosclerosis, other pathological processes are possible in the system of brachiocephalic arteries, leading to their narrowing and disruption of blood flow. Thus, frequent changes in blood vessels include kinks and looping, which are usually eliminated surgically. Aneurysms of these arteries also occur, but are relatively rare.
Video: about carotid artery stenosis - “Live Healthy” program
Indications for ultrasound examination
This diagnostic method allows you to identify a wide range of different vascular lesions.
Doppler ultrasound is an effective diagnostic tool that is used during routine preventive examinations. The study is recommended for people of all age groups, in particular those over 40 years of age. Doppler ultrasound can also reveal the effect of other diseases on the circulatory system. This applies to patients with osteochondrosis, vegetative-vascular dystonia, as well as patients who have suffered a stroke or traumatic brain injury.
General indications for ultrasound scanning are:
- frequent migraine attacks;
- severe headaches;
- sleep disorders;
- fast fatiguability;
- episodes of loss of consciousness;
- dizziness;
- noise in the ears and head;
- increased weather dependence;
- asymmetry or absence of pulse and pressure in the hands.
The study is also prescribed by neurologists to prepare the patient before surgical intervention in the cardiovascular system.
Doppler scanning is often prescribed by phlebologists to assess the condition of the veins and blood flow of the lower extremities. Indications for the procedure include:
- legs swelling in the evening;
- change in the appearance of veins;
- change in the color of the skin of the legs;
- pain when walking;
- muscle numbness;
- pain in the calves;
- the appearance of spider veins;
- chilly feet.
The manipulation brings clarity to the nature of the patient’s condition and allows the doctor to prescribe effective corrective therapy in a timely manner.
The absolute harmlessness of the method allows it to be used when examining children under two years of age. Often, pediatricians and pediatric neurologists order a test for the baby a few days after birth. In children of different ages, indications for the procedure are:
- restless sleep;
- prematurity;
- unusual skull shape;
- facial asymmetry;
- suspected congenital defects of the cardiovascular system;
- the baby's weight is too small or large;
- manifestation of asthenic conditions;
- speech and memory disorders.
Interpretation of ultrasound examination of BCA
At the end of the BCA ultrasound procedure, the diagnostician produces a result about what it is and what pathologies were found in the patient. A transcript may be issued immediately after the examination. It compares the results obtained with normal values. The difference in indicators determines the presence or absence of pathology of blood vessels and arteries.
In conclusion, the diagnostician states:
- Character of blood flow.
- Condition of the vascular walls.
- Pathological changes, if any.
Normal results of color circulation of arteries and BCS are visualization of their straight course, uniform surface and parallelism of their walls. if atherosclerotic inclusions are detected, then the conclusion indicates their composition, size and location. The degree of influence on blood flow and vasoconstriction in the area where the plaque has formed is noted.
The results obtained are compared with the indicators of the standard table. This is how the diagnostician determines the pulsation index and the resistance index, which indicate the degree of vascular resistance and their patency.
Anatomy of the vessels of the neck and head
The ASG, left CCA and RCA emerge from the aortic arch.
At the level of the right sternoclavicular joint, the ASG is divided into the right CCA and RCA. The RCA lies in an arc on the dome of the pleura, passes between the anterior and middle scalene muscles, and dives from under the collarbone into the armpit.
PKA branches:
- I segment to the scalene muscle - vertebral, thyroid-cervical, internal thoracic artery;
- II segment in the interscalene canal - costocervical trunk;
- The third segment at the exit from the interscalene canal is the transverse artery of the neck.
Click on pictures to enlarge.
The OCA passes behind the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The CCA has no branches; at the upper edge of the thyroid cartilage it is divided into the ECA and the ICA.
The expansion of the bifurcation (bulb) contains chemo- and baroreceptors that regulate the functioning of breathing, heart and blood vessels.
The ECA begins medially, then runs outward from the ICA; has a short trunk; near the angle of the lower jaw it divides into eight branches.
Branches of the ECA: superior thyroid, lingual, facial, ascending pharyngeal, occipital, posterior auricular, maxillary, superficial temporal.
The BSA is wider than the NSA; on the neck it rises between the pharynx and the IJV, does not give branches; passes into the cranial cavity through the canal of the pyramid of the temporal bone.
In the skull, the branches of the ICA are the ophthalmic, anterior cerebral, middle cerebral, and posterior connective; maxillary artery - middle meningeal.
The VA departs from the first segment of the RCA, ascends through the openings of the transverse processes C6-C1, and enters the skull through the foramen magnum.
The PAs of both sides merge into the main artery at the posterior edge of the bridge; The basilar artery divides into the posterior cerebral artery at the anterior edge of the pons.
I segment from the mouth to C6; II segment in the canal of the transverse processes C6-C2; III segment from C2 to the entrance to the skull; IV segment before merging into the basilar artery.
The ICA and VA form an arterial circle at the base of the brain with the help of the anterior and posterior communicating arteries; more often one of the branches is missing.
The essence of the method
During the procedure, mainly the common, internal and external carotid arteries (CCA, ICA, ECA), as well as the vertebral artery (VA), are examined on both sides. The peculiarity of the CDK of the BCS is that to obtain longitudinal and transverse sections of the vessels, a typical two-dimensional mode (B-mode) is used for ultrasound, and another method is used to assess hemodynamic parameters - Doppler sonography. It is based on the Doppler Effect (named after the Austrian physicist and mathematician Christian Doppler), with the help of which, after appropriate signal processing, blood flow in the brachiocephalic arteries is visualized, its speed and strength are measured.
Most often, ultrasound is performed with color Doppler mapping in conjunction with spectral Doppler. The first allows you to determine the direction of movement and speed of red blood cells through Doppler frequency measurements. Blood flows are color coded in 2D images. The blood flow directed to the ultrasound sensor is mapped in red, and from it in blue. The CDB of the BCS makes it possible to clearly visualize areas of complex vascular geometry and turbulent blood flow.
Typically, the sensor head is turned towards the patient's head, so arteries are highlighted in red and veins in blue. Since color Doppler is used simultaneously with B-mode, it is called duplex sonography. The speed of blood flow is determined by the brightness of the color at individual points. Light indicates high speed and dark indicates slow.
The procedure for conducting the examination and the principle of operation of the device
It is advisable to arrive for the procedure 30 minutes before the scheduled time to rest and calm down. Walking and physical activity affect vascular tone and distort the examination results.
The procedure itself is carried out in a specially designated room. The doctor invites the patient to undress to the waist and lie down on the couch. A special gel is applied to the skin of the neck to facilitate the sliding of the device. The doctor moves the sensor of the device over the neck area in different places. Be prepared to be asked to repeatedly roll over onto your stomach or side. This is necessary for a comprehensive assessment of the condition of the cervical arteries.
The average duration of the procedure is 3-5 minutes. During this time, the doctor will have time to collect all the necessary data to assess the state of blood supply in the neck and make a diagnosis.
The device is absolutely safe; it emits only ultrasonic waves, which are reflected from the internal media of the body and provide data about them on a special monitor. The operating principle of the equipment was described in more detail above.