Duplex ultrasound scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries, or abbreviated ultrasound BCA, is a modern ultrasound method for diagnosing the vessels of the head and neck, including the carotid and vertebral vessels, which supply blood to the brain, and the subclavian arteries.
First of all, the person who is scheduled for this study may have a question: what are the brachiocephalic arteries and where are they located.
Brachiocephalic vessels are the largest arteries and veins that are responsible for blood flow to the tissues of the head, brain and upper extremities. They are also called main lines.
general information
The brachiocephalic arteries include the carotid, subclavian, vertebral and their junction , which forms the brachiocephalic trunk. The listed vessels and some others near the base of the brain form the Circle of Willis, which is responsible for the distribution of blood flow throughout all parts of the brain.
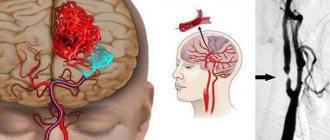
If any pathology has formed in one of the vessels, it can lead to disruption of the others, which ultimately leads to a stroke.
What is duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries, and what is the method based on?
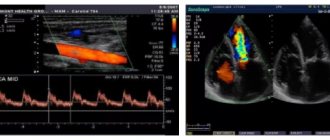
The apparatus for examining the BCA is based on the principles of echolocation . The working surface emits and then picks up ultrasonic pulses. The information is converted into a digital signal. This is how the image appears on the monitor.
The method is based on combining the advantages of B-mode - visual interpretation of the state of blood vessels and adjacent tissues and Doppleroscopy - qualitative and quantitative properties of blood flow. The Doppler spectrum can also be supplemented with color mapping.
Basics of DS BCA
The ultrasound diagnostic method is based on the study of images obtained as a result of the reflection of an ultrasonic wave from internal organs and structures. Ultrasonic waves are vibrations of particles whose frequency is equal to or greater than 20 kHz.
The echographic image is constructed from that part of the reflected ultrasound waves that were received and converted by the ultrasonic sensor. But it is necessary to remember that the most optimal setting of the ultrasound scanner is of great importance in the quality of the resulting images, due to which the individual characteristics of each subject are taken into account.
Methods for studying the vascular system are divided into several groups, the most commonly used and accessible, of which are Doppler (ultrasound and transcranial) and duplex. Nowadays, ultrasound scanners display blood flow in color, called color Doppler mapping, abbreviated as Color Doppler.
Doppler techniques do not allow visualization of the vessel. Using Doppler ultrasound, large superficial vessels can be visualized. Transcranial Doppler sonography allows you to evaluate blood flow in the large arteries of the base of the brain.
The main difference between duplex scanning and Doppler techniques is the combination of visualization of the vessel and surrounding tissues in “black and white” (B-mode) mode with qualitative and quantitative assessment of blood flow. Thanks to this, it becomes possible to visualize most parts of the vascular system.
What does the ultrasound scan of the BCA show?
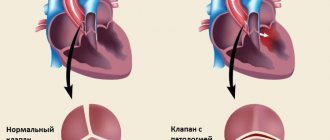
First of all, a duplex examination of the head is prescribed for those patients who have suspicions of atherosclerotic processes, aneurysms and deformations and other pathologies, and is aimed at identifying functional and structural arteriovenous disorders. During the examination, a specialist can recognize the presence of plaques, blood clots, thickening or reduction of vascular walls, a violation of the normal anatomical integrity of the walls, see tortuosity, surrounding tissue, and the speed of blood flow.
Ultrasonic scanning of the BCA shows:
- lumen of blood vessels;
- blood clots, plaques, detachments;
- stenosis, wall expansion;
- ruptures, aneurysms, deformations.
Using ultrasound scanning of the BCA, you can diagnose:
- vascular pathologies;
- vascular hypoplasia;
- violation of wall tone during VSD;
- atherosclerosis;
- arterial aneurysms;
- fistulas between vessels;
- angiopathy;
- thrombosis;
- vascular injuries;
- varicose veins.
The cerebral vessels are a complex system that is capable of self-regulation and maintaining cerebral blood flow.
Only comprehensive diagnostics, which includes ultrasound scanning, CT, MRI, allows you to accurately and timely choose treatment, and then evaluate its effectiveness. Ultrasound scanning helps to assess the anatomy of the vessels of the neck and head, determine the characteristics of blood flow, and assess the condition of the walls and lumen . This way, atherosclerotic plaques, blood clots, tortuosity of arteries and their dissection can be diagnosed at an early stage.
What are the differences from ultrasound?
An ultrasound examination primarily measures the patency of blood vessels, responding to the movement of red blood cells in the blood. The image on the screen is one-dimensional; based on the state of patency, one can judge the presence or absence of vasoconstriction, atherosclerosis and other causes of stenosis. The examination is usually cheaper than ultrasound.
Duplex scanning of the vessels of the head and neck, together with conventional Doppler sonography, visualizes the vessels in B-mode, shows the localization of atherosclerotic plaques and thrombotic masses on the inner walls of the veins, their morphological features and the extent of the process. The picture is two-dimensional, in combination with color Doppler mapping (color Doppler mapping) - color.
Such capabilities of ultrasound scanning are its undeniable advantage, because the method not only saves time on diagnosing the disease, but also gives a broader picture of changes in the vessels . However, such research is correspondingly more expensive.
Duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries: why is it needed?
Diagnosis and treatment of vascular pathologies, in particular atherosclerosis, are issues that are relevant at all times. One of the widely used methods for studying the vessels of the neck and the blood flow in them is duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries. What kind of research is this and who is it for?
Ultrasound diagnostics doctor at Clinic Expert Stavropol Lusine Nersesovna Nersesyan talks about the features and capabilities of this diagnostic method.
— Identifying changes in blood vessels is not an easy task. But still, a number of modern research methods make it possible to do this. Lusine Nersesovna, what is duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries?
— Let’s start, perhaps, with what the brachiocephalic arteries include. This is the brachiocephalic trunk, which is divided into the right subclavian and right common carotid arteries, as well as the left subclavian and left common carotid arteries. These vessels perform one of the most important tasks in our body - they supply blood to the brain. Duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries is a type of modern ultrasound examination of these vessels, which, due to its informativeness, safety and accessibility, is widely used today in practice.
Along with this name of the method, you can also find another one - ultrasound scanning of the BCA (ultrasound duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries).
— For what symptoms and diseases is it necessary to do a duplex scan of the brachiocephalic arteries?
“The range of symptoms for which this research may be useful is extremely wide. These include headaches of unknown origin, dizziness, tinnitus, blurred vision, hearing impairment, complaints of memory problems and changes in concentration.
With an increase or decrease in blood pressure, as well as people with a family history of hypertension, smokers with more than 15 years of experience, an ultrasound scan of the BCA is required to assess the condition of these vessels and prevent possible diseases and their complications.
Duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries is recommended for diseases such as hypertension, previous myocardial infarction or stroke. Some endocrinological pathologies (in particular, diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome), injuries to the head and neck area, and toxic damage to the nervous system also require such a procedure. In these cases, the study can be performed repeatedly to assess the effectiveness of treatment, and in chronic processes, to monitor the degree of pathological changes in the arteries.
Experts recommend undergoing this test for preventive purposes after 40 years of age, even in the absence of pathological signs.
You may be interested in our materials on the topic: What to do when the head is cast iron? Spinning until you drop! Where did the glasses go again? We talk about the causes of memory deterioration. Speculation about hypertension. How to prevent myocardial infarction? How to prevent a brain catastrophe?
— What does duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries show?
“It allows us to evaluate the structure of blood vessels, their patency, as well as functional hemodynamic parameters, in particular, blood flow speed. During the examination, you can see the course of the arteries, their deformations (for example, in the form of a loop, a wave). We also see abnormalities in the development of blood vessels in the form of aplasia (absence), hypoplasia (reduced diameter) or duplication of arteries. In addition, this diagnosis makes it possible to detect disturbances in the location of the brachiocephalic arteries, as well as signs of compression of the vessel from the outside by a tumor or hematoma.
An important nuance is that ultrasound scanning makes it possible to detect narrowing of the lumen or blockage of the brachiocephalic arteries due to atherosclerosis, thrombosis or embolism, or inflammation of the vascular wall.
More materials on the topic: Atherosclerosis: what does modern medicine know about it? Find and neutralize. How to protect against blood clots?
— Which specialists prescribe this study?
- Almost any. First of all, these are, of course, neurologists and cardiologists. In addition, general practitioners, endocrinologists, ophthalmologists, and audiologists can refer ultrasound scans of the brachiocephalic arteries. Since these arteries supply the brain, any changes associated with the possible involvement of the central nervous system in the pathological process may be a reason to conduct this study.
— Lusine Nersesovna, does ultrasound scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries require special preparation?
— No, no preparation is provided for this procedure.
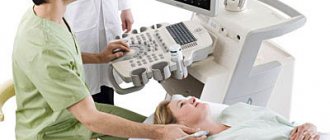
— How is duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries done?
— This procedure is performed in an ultrasound diagnostic room. The patient lies down on the couch in a supine position, turning his head slightly to the side. Using ultrasonic sensors of different frequencies, the specialist passes over the surface of the neck and receives an image of the arteries on the monitor. He can measure their diameter, assess the condition of their walls and all the necessary indicators of blood flow in them.
The study is usually carried out first on the right, then on the left side of the neck. Some functional tests may require a change in head position. The procedure lasts on average from 20 to 40 minutes.
Subsequently, the doctor analyzes all the data received, writes a conclusion and recommendations on the necessary consultations with specialists, as well as on the timing of re-diagnosis.
— Are there any contraindications to this study?
- No. You can undergo this diagnosis at any time for any condition of the patient. The main thing is that it is transportable. There are also no age restrictions. Safety, painlessness, high information content and accessibility - these characteristics contribute to the popularization of duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries among specialists and patients.
Interviewed by Sevilya Ibraimova
You can sign up for duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries (USD BCA) here ATTENTION: the service is not available in all cities
The editors recommend:
Doppler, duplex, triplex... What types of vascular ultrasound are there? Transcranial duplex scanning of cerebral vessels: when is this study needed? Are your legs bothering you? Check your blood vessels! Who can benefit from ultrasound scanning of lower extremity vessels?
For reference:
Nersesyan Lusine Nersesovna
In 1994 she graduated from the Pediatric Faculty of Yerevan State Medical Institute. In 1996, she completed her internship in Pediatrics. In 2005, she underwent professional retraining in ultrasound diagnostics, and in 2008, advanced training in complex ultrasound diagnostics of peripheral and great vessels. Currently works as an ultrasound doctor at the Expert Clinic, Stavropol. Receives at the address: Dovatortsev St., 39A.
Features of diagnosing atherosclerosis
The initial sign of atherosclerosis, which an ultrasound examination can show, is not even a plaque, but a thickening of the wall of the carotid artery by just a fraction of a millimeter . With duplex scanning, this indicator is well determined. The thickness of the intima-media complex (the so-called IMM) is also called. IMT is taken into account to assess the effectiveness of treatment.
An increase in IMT of more than 1 mm is most often associated with risk factors such as smoking, arterial hypertension, diabetes, increased cholesterol, etc.
As the disease progresses, plaques begin to form. Usually they are localized in the so-called. Carotid bifurcation is the site of division of the common carotid artery into internal and external. The presence of a plaque in this segment is a serious risk factor for stroke and myocardial infarction. Therefore, it is very important to promptly identify atherosclerotic changes in the early stages .
Duplex scanning reveals the location of the plaque, as well as its shape, size, structure and degree of stenosis (narrowing of the lumen). When the lumen is already completely closed - this is occlusion .
During the examination of the BCA, tortuosity of the arteries is often revealed due to their elongation. Arteries lengthen due to atherosclerosis and high blood pressure. Tortuosity of the vertebral arteries usually occurs due to defects in the cervical spine. If tortuosity leads to compression of the lumen, this can cause disruption of cerebral blood flow.
Ultrasound scanning is also used to examine patients with traumatic vascular lesions: wall dissection or similar. The main symptom of this disease is a severe headache that cannot be relieved with conventional painkillers.
Advantages of this method:
- non-invasiveness
- safety
- dynamic control
- assessment of atherosclerotic plaque by shape, extent, structure
- visualization of the anatomical course of blood vessels
- assessment of quantitative and qualitative characteristics of blood flow
- research in various positions and planes.
- Duplex scanning combined with a color indicator is called triplex scanning.
To better understand the purpose of the study, it is necessary to know the functions and location of the brachiocephalic vessels of the head and neck.
The largest vessel in the human body is the aorta. From its arch depart: the brachiocephalic trunk (brachycephalic artery), the left common carotid and left subclavian arteries. Subsequently, the left common carotid artery is divided into internal and external, the latter giving off many important branches.
Advantages of the method
The advantages of BCA ultrasound are:
- high information content;
- efficiency of research;
- safety and possibility of repeated implementation;
- painlessness of the procedure.
Ultrasound scanning of the BCA is more informative than conventional ultrasound scanning of the brachiocephalic vessels.
During the examination, an image is formed on the monitor, similar to a conventional ultrasound, but against its background the vessel in which the blood flow is formed is clearly visible. Due to the advantages of ultrasound scanning, BCA is considered the gold standard for diagnosing pathologies. A timely vascular ultrasound can save lives and prevent possible disability.
Learn more about the study and how duplex scanning of the vessels of the head is done from the video:
Benefits of the study
In addition to rich research capabilities, color duplex ultrasound scanning has a number of other advantages:
- The procedure is painless, which means the examination is comfortable for the patient.
- The method is completely safe, duplex scanning has no contraindications or adverse reactions and can be used even where some methods are undesirable.
- It makes it possible to identify even those signs of vascular diseases that have not yet manifested themselves clinically.
Indications for use
The vessels of the brachiocephalic region include intracranial (intracranial, directly supplying the brain and surrounding tissues) and extracranial (extracranial, which capture the tissues of the neck, face, back of the head, etc. in the blood supply network). With duplex scanning, both the first and second groups are assessed.
Indications for prescribing duplex scanning of the BCA are:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- violation of movement coordination;
- blood pressure problems;
- fainting;
- elevated cholesterol levels;
- impaired sensitivity (numbness) of the limbs;
- blurred vision;
- flickering spots in the eyes;
- memory impairment and decreased concentration;
- preoperative examination.
Direct indications for the study are the following pathologies:
- atherosclerosis;
- VSD;
- hypertension;
- heart pathologies;
- neck injuries;
- compression of arteries and veins and other vascular injuries;
- vasculitis;
- blood diseases;
- suffered a stroke or heart attack.
Duplex scanning is also an important study for patients over the age of 40 years, with a history of stroke - acute cerebrovascular accident - and TIA - transient ischemic attack, with arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, elevated blood lipid levels, high body weight and planned myocardial surgery .
Indications and contraindications for sonography
In newborns, duplex ultrasound (synonymous with sonography) of the brachiocephalic vessels is performed if defects of the BCA and brain, or birth trauma are suspected. Regardless of age, ultrasonography is prescribed for all pathological conditions with a likelihood of deterioration of the blood supply to intracranial tissues. In surgery it is also used in the preparatory period for surgery and during rehabilitation.
Direct indications of duplex sonography of the BCA:
- hyperlipidemia, increased cholesterol;
- blood diseases;
- atherosclerosis;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD);
- arterial or intracranial hypertension;
- heart disease, aorta;
- head and neck injuries;
- pathologies with the likelihood of compression/damage to the brachiocephalic vessels;
- inflammation of the walls of the BCA (vasculitis, arteritis, other types);
- neoplasms in the area of the BCA;
- history of stroke, cardiac ischemia, heart attack.
Examination of the great arteries of the head (MAG) and neck is also indicated for people at risk. These are people suffering from diabetes, osteochondrosis, autoimmune vascular pathologies, metabolic disorders, cardiomyopathies, and obesity.
Ultrasound scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries is indicated when:
- frequent attacks of cephalalgia (headache);
- migraines;
- fainting;
- dizziness;
- darkening of the eyes, lethargy, persistent desire to sleep;
- deterioration of vision, hearing, mental activity;
- violations of motor abilities, coordination;
- areas of the body with numbness, loss of sensitivity;
- persistent deviation of blood pressure (BP) from the norm;
- unequal blood pressure readings on the right and left arms.
Duplex BCA is also indicated for elderly smokers with nicotine addiction for more than 10 years. It is advisable to undergo ultrasound scanning for people whose relatives have had cases of cerebral circulatory disorders (stroke, ischemia, etc.).
There are no contraindications to brachiocephalic vessel duplex. A temporary limitation of sonography in the area of BCA scanning is acute inflammation or deep damage to the skin due to injury or disease.
Pay attention to the video review from a specialist about diagnosing BCA:
Contraindications
The use of the device is absolutely harmless and does not have any effect on the human body. There are no restrictions on the use of this modern technique , and for any age group of patients.
In some cases, calcified atherosclerotic plaques can obstruct the ultrasound beam and interfere with diagnosis.
Do not forget that the doctor’s professionalism and good equipment play one of the key roles in deciphering the results of duplex scanning, so if a medical organization does not have professionals in this field or suitable equipment, it is better to use other diagnostic methods.
Methods for conducting duplex of large arteries
The ultrasound scanning procedure is a complex of capabilities of B-mode ultrasound (visual examination of the vessel and nearby tissues) and Doppleroscopy (study of blood flow functions).
Color mapping (or color duplex scanning - CDS BCA) can complement duplex research for a more visual perception of the speed of blood movement through the vessels.
The advantages of the duplex method in studying the functioning of blood vessels are obvious - the procedure makes it possible to:
- Identify any anomaly of the arterial bed (including narrowing, pathological tortuosity, occlusion).
- Establish the speed of blood flow, track its changes and find the cause of the pathology, for example, atherosclerotic plaques, emboli or blood clots.
- Assess the shape of the vessels and their thickness. As well as the uniformity and mobility of the wall.
Preparation for the procedure
Preparation before the study consists of excluding from the menu foods and dishes that can affect the tone and filling of blood vessels, which will distort the results of the study.
On the day of the study, you should not drink tea, coffee, energy drinks, Coca-Cola, alcohol, and do not indulge in overly spicy and salty foods . Directly before ultrasound examination of the BCA, you should not be in stuffy or smoky rooms, as this can also change the blood flow to the vessels.
It is better to refrain from taking vitamins and nootropics the day before the study. Be sure to consult a specialist if you are taking medications that affect the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
Preparation
No special preparation methods are required for ultrasound scanning. But there are some restrictions.
First of all, on the eve of the procedure, the patient is not recommended to take drinks that increase vascular tone.
These include:
- coffee;
- tea;
- energetic drinks.
It is not advisable to smoke a lot before the examination.
After consulting with your doctor, you may temporarily stop taking certain medications that may interfere with your results. Such drugs include Betaserc, Cinnarizine and others.
Immediately before starting the procedure, you will have to remove metal jewelry and objects.
How is it carried out?
The patient lies on his back on a couch near the device, and the doctor places a cushion under his neck. The head should be turned in the direction opposite to the device. The doctor lubricates the surface of the skin with a gel that facilitates the passage of the ultrasound signal.
Using the sensor, the doctor will examine segment by segment in the neck area, observing the change in signal on the monitor. He may press the sensor lightly on the vessels or ask you to stop breathing for a short time.
If pathological changes are detected, a more thorough examination of all vessels extending from these branches is carried out.
Functional tests can be carried out to assess changes in indicators in horizontal and vertical positions of the body: lying down, sitting, and standing.
no uncomfortable sensations during the examination : the procedure feels no different from the usual ultrasound scan familiar to everyone. The study lasts 20-30 minutes.
Useful video about how transcranial duplex scanning of cerebral vessels is performed (through the cranial bone):
Features of transcranial duplex scanning of the BCS
The bones of the skull are designed in such a way that the ultrasound with which we conduct research can penetrate inside the skull only in certain places - this is the area of the temporal bone and the foramen magnum. This is where the doctor will place the ultrasound sensor.
Unfortunately, in part of the adult population (about 10%), the structural features of the skull are such that it is very difficult or completely impossible to examine the vessels inside the skull.
In such cases, you may see the phrase “inadequate echo window” or “no echo window” in the study protocol narrative.
Decoding the research results
The scanner will record the necessary indicators, and the doctor will enter them into the scanning protocol. Decoding the Doppler spectrum and blood flow charts will take no more than 10 minutes , after which you will receive the results.
The result of the scan is a printed sheet with a list of the examined vessels and a description of their sizes and condition. The decoding makes it possible to determine whether the vessels correspond to the anatomical norm , whether there is pathology, etc. Based on the decoding, your attending physician, if necessary, prescribes treatment.
Decoding is carried out by comparing indicators:
- nature of blood flow;
- its speeds: systolic (max) and diastolic (min);
- wall thickness;
- pulsator index (so-called PI) is the ratio of the difference between max and min speeds to the average (the sum of max speed and two min, divided by 3);
- resistive index (so-called RI) is the ratio of the difference between max and min speeds to min;
- systolic-diastolic ratio: max speed divided by min.
Based on the last 3 indices, the patency of the vessel is judged.
Blood flow is assessed in the external and internal carotid arteries, common (ECA and ICA, CCA), supratrochlear (SBA), main (OA), vertebral (VA) and in its segments, each of which has its own designations, for example, Vo, V1, V3 etc. Also in the anterior, posterior, middle cerebral arteries (ACA, PCA, SMA), subclavian (RCA), anterior and posterior communicating (ACA, PCA) arteries.
Normal indicators
Different vessels of the brachiocephalic zone have their own individual standards based on the results of duplex scanning. For the common carotid artery, a diameter of 4-7 mm, a systolic blood flow velocity of 50-105 cm/sec, a diastolic velocity of 9-36 cm/sec, and a vessel resistance index of 0.6-0.9 are considered normal.
The following values are acceptable for the branches of the common carotid artery:
- diameter of the internal branch – 3-6.5 mm; outer branch – 3-6 mm;
- systolic blood flow velocity of the internal branch – 33-100 cm/sec; outer branch – 35-105 cm/sec;
- diastolic blood flow velocity of the internal branch – 9-35 cm/sec; external branch – 6-25 cm/sec;
- resistance index of the internal and external branches is 0.5-0.9.
Normal parameters of the vertebral arteries:
- diameter – 2-4.5 mm;
- systolic blood flow velocity – 20-60 cm/sec;
- diastolic blood flow velocity – 5-25 cm/sec;
- resistance index – 0.5-0.8.
Decoding
Duplex scanning of the BCA is the key to diagnosing many abnormalities, diseases or congenital pathologies that have shown little or no evidence at all. Nevertheless, any anomalies or prerequisites for the disease have their consequences and explain the general condition of the patient. For example, diagnosing thickening of the vessel walls raises suspicion of Takayasu syndrome. In its manifestations and clinical picture, it is very similar to atherosclerosis. The study can demonstrate a difference in the upper levels of blood pressure in the shoulders, such a symptom reflects blockage of the vessels of the vertebral artery.
Reading and deciphering the results is the task of a neurologist or vascular surgeon. A normal vessel has a uniform surface, sufficient lumen width and wall thickness to ensure uninterrupted blood flow. The doctor, describing the diagnostic results, indicates the characteristics of the deformities, their location, quality indicators, and the type of vascular damage.
To determine the degree of deviation, research data are compared with normal values. Based on the results obtained, diseases of the arteries, heart, and brain are diagnosed. Duplex scanning of the BCA is an intermediate procedure; the final diagnosis requires additional measures and tests.
How affordable is it?
Such diagnostics require the use of expensive specialized equipment and specially trained medical personnel, so the prices for the study are not very liberal .
In large cities of the Russian Federation, the average cost of a duplex is from 2,000 to 5,000 rubles. In areas more distant from the capital, you can do the procedure for 800-1500 rubles. Abroad, you can undergo color duplex scanning of the main arteries of the head and vessels of the neck for $500-600 and more.
Let's summarize. Ultrasound scanning of the BCA is a special type of ultrasound diagnostics of vessels that provide nutrition to the brain, other organs of the head, neck, and upper limbs .
This is an accessible, safe, detailed and informative study, which in ten minutes can show the condition of the blood vessels and identify the cause of some unpleasant symptoms. An annual examination will allow you to predict the development of a cerebral stroke by 90%.
Advantages
Duplex diagnostics combines two main types: ultrasound and Dopplerography.
The technique has an advantage over each of them, it is expressed in the following:
- identification of vascular pathologies at the very beginning of their development;
- exploration of channels from the inside;
- the ability to visualize problem areas even in hard-to-reach places;
- three-dimensional echographic images;
- high level of information content;
- safety;
- painlessness.
There is no need to specially prepare for the procedure, and no highly qualified specialist is required to decipher the data.
The technique is safe and has no contraindications.
Detection of congenital vascular anomalies
Another task of ultrasound examination of the brachiocephalic vessels is to detect congenital features (anomalies), which can be detected in childhood, or may not manifest themselves for a long time. However, later, when other diseases occur, such congenital features can aggravate the course of the disease.
One of the common anomalies is a significantly smaller (<2.5 mm) diameter of one of the vertebral arteries (vertebral artery hypoplasia) than it should be. Symptoms associated with this feature can occur only in adulthood due to a decrease in the elasticity of blood vessels and the development of atherosclerosis.
In this case, there is a decrease in blood flow to certain parts of the brain. The body can compensate for the lack of blood supply for some time, but in emergency situations the defense mechanisms may fail.
With this anomaly, sudden movements or simply tilting the head can cause:
- dizziness,
- feeling of disorientation
- distortion of the perception of body position in space,
- staggering or even falling.
Hypoplasia of the vertebral artery increases the risk of developing cerebral stroke due to impaired blood supply to the brain and damage to the walls of blood vessels in the event of atherosclerosis.