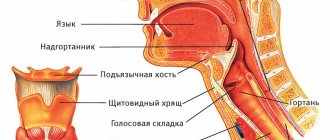
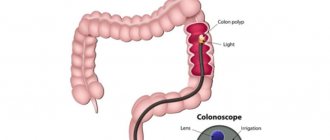
Bronchoscopy is a method of endoscopy of the respiratory organs (larynx, trachea, bronchi) to detect pathological processes in the mucous tissues of these organs. A bronchoscope is used for the procedure. The instrument consists of a flexible or rigid tube measuring 5 mm in diameter, a special lighting lamp, and a video and photo camera. Improved instruments are formed with the addition of fiber optic technologies (rigid variety), thereby achieving high efficiency of diagnostic measures.
The picture is displayed on the device monitor, and then the image is enlarged more than 10 times. It is also possible to save data for further monitoring of the progress of diseases. Thanks to the optics of the instrument, it is possible to inspect the air duct up to the second branch of the bronchi. In 98% of cases, doctors are able to establish a correct diagnosis of the disease. Bronchoscopy is intended to diagnose complicated bronchitis, secondary development of pneumonia and lung cancer. The procedure provides a material sample for biopsy.
What is bronchoscopy and why is it needed?
Lung bronchoscopy is a pulmonological method for studying the bronchial tree, showing even minimal problems that threaten the patient’s health.
This medical procedure is needed to:
- assess the internal condition of the bronchi and trachea;
- take a sample of a suspicious area of tissue for histological examination;
- remove a foreign body from the trachea.
Indications for use
Indications for the procedure:
- detection of tumors that are benign;
- diagnosis of bronchial cancer;
- identification of stagnant processes in the respiratory organs (sanitation bronchoscopy is required);
- suspicion of infection and inflammation;
- establishing the causes of bloody discharge when coughing;
- a feeling of shortness of breath, incomplete inhalation and exhalation (when heart disease and asthma are excluded);
- excessive production of mucus that has an unpleasant odor;
- pronounced symptoms of chronic cough.
Contraindications
Contraindications for the study:
- narrowing of a pathological nature, in which the endoscope is unable to penetrate the trachea and bronchi;
- the patient has asthma or diseases of the vascular or cardiac system;
- mental problems;
- respiratory failure;
- hypertension (high blood pressure);
- pregnancy.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages and disadvantages of the procedure:
| pros | Minuses |
| The method allows the operation to be performed without incisions, only thanks to several punctures | Possibility to examine only the mucous surface |
| During the examination, it is possible to obtain a cell for subsequent examination (biopsy) | Insertion of the bronchoscope is unpleasant for the patient |
| Allows for simultaneous treatment | Irritation of the mucous membrane after manipulation |
Does it hurt or not?
Bronchoscopy of the lungs does not cause pain, but the insertion of the device is accompanied by:
- numbness of the palate;
- lump in throat;
- difficulty swallowing.
Bronchoscopy can be unpleasant at the initial stage of the procedure, but then the negative sensations disappear.
What does it reveal?
This examination method reveals:
- neoplasms of various etiologies;
- bronchial deformities;
- tuberculosis;
- stenosis of the branches of the windpipe;
- decreased tone of large bronchi.
The Health-Saving Channel briefly describes what bronchoscopy shows and determines.
Contraindications
There are also a number of contraindications to this procedure, the absolute ones of which are:
- stenosis of the larynx and trachea 2 and 3 degrees;
- respiratory failure 3rd degree;
- exacerbation of bronchial asthma.
These three conditions carry a risk of bronchial injury when the endoscope is inserted.
- Aortic aneurysm - nervous overstrain of the patient and manipulation with the endoscope can provoke rupture of the aneurysm.
- Heart attack and stroke less than 6 months old;
- Bleeding disorders;
- Mental illnesses (schizophrenia, psychosis, etc.). Stress and acute lack of oxygen during the procedure can significantly worsen the patient’s condition, causing another attack of the disease.
- Individual intolerance to painkillers. A reaction to them can provoke an allergy in any degree of its manifestation, up to the most severe – anaphylactic shock and suffocation.
Among the relative contraindications - conditions in which it is desirable to postpone the procedure to a later date, are:
- acute course of infectious diseases;
- menstrual bleeding (due to decreased blood clotting during this period);
- asthmatic attack;
- 2-3 trimester of pregnancy.
However, in cases of resuscitation (emergency), bronchoscopy is performed regardless of the presence of contraindications.
Types of research
Types of bronchoscopy differ depending on the type of device used, as well as the purpose of the procedure.
Depending on the device
Depending on the bronchoscope, there are:
Fiberglass bronchoscopy (FBS) is a study using a flexible endoscope and is used when there are no direct indications for using another type of instrument. The thin tubes of the device make it easy to move into the lower parts of the bronchi.
Bronchoscopy of the lungs using a rigid device has another name - rigid. It is used to examine large bronchi and is widely used for resuscitation purposes.
Depending on the purpose of the event
Depending on the purpose of bronchoscopy, there are:
- diagnostic;
- medicinal;
- virtual.
Diagnostic bronchoscopy
The purpose of the procedure is to examine the respiratory organs to identify certain lesions that can confirm the doctor’s preliminary diagnosis.
Diagnostic bronchoscopy is:
- Fluorescent. It involves administering a special acid to the patient, after which the light system of the device can determine the red zone (indicating the presence of a tumor).
- Autofluorescent. Also used to detect various tumors. A special light system causes a green glow of the bronchus (its submucosal layer).
Therapeutic bronchoscopy
The need for therapeutic bronchoscopy may arise when:
- rinsing of the airways to remove blood clots or sputum is required;
- the patient suffers from a severe form of pneumonia, in which it is recommended to administer an antibiotic to a specific bronchus;
- you have to stop bleeding in the lungs;
- it is necessary to get rid of pus if the accumulation is located near the bronchus.
Virtual bronchoscopy
Features of virtual bronchoscopy:
- represents an alternative study - CT scan of the bronchi;
- X-ray sections and a special program allow you to see the smallest details and pathologies;
- This method does not involve external intervention.
Indications
Bronchoscopy of the lungs is prescribed and performed by a pulmonologist, who, taking into account the age and expected diagnosis of the patient, decides on the depth of the examination and the need for repeated procedures. The same doctor deciphers the results and, if necessary, prescribes treatment.
Indications for bronchoscopy in adults:
- long-term, recurrent inflammatory processes in the lungs and bronchi.
- foreign object in the respiratory tract.
- darkened areas in the lungs on an x-ray.
- suspicion of a malignant tumor.
- bronchial asthma (identifying its cause).
- purulent abscesses in the lungs and bronchi.
- hemoptysis or bleeding from the respiratory tract.
- persistent shortness of breath for an unknown reason.
- abnormal narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi, making breathing difficult.
- monitoring the results of treatment.
Preparation for the procedure
Preparation for bronchoscopy includes:
- preliminary analyses;
- consultation with a doctor;
- diet and taking sedatives.
What research needs to be done?
Before the procedure you need to do:
- radiography;
- electrocardiography;
- take blood tests: general and biochemical, coagulation tests;
- determine the level of gases in the blood.
Consultation with a doctor
With the results obtained, you should consult your physician. He will tell you whether additional examinations are required from specialized specialists, and will also answer all questions about the procedure. If no contraindications are found, the specialist will refer the patient to undergo pulmonary bronchoscopy.
Proper diet and sedatives
The following rules will help the patient prevent negative consequences:
- You should eat eight hours before the procedure. It is important not to eat heavy foods or those that cause bloating. You also need to limit yourself in fluid intake.
- So that the patient can fully rest, the specialist will prescribe sedatives and sleeping pills.
What should you do immediately before bronchoscopy?
Immediately before the procedure you need to:
- calm down and set yourself in a positive mood;
- empty your bladder;
- take a towel for examination - after completion of the examination, a short cough with blood discharge is likely to occur;
- refrain from smoking;
- in the morning, before visiting the clinic, cleanse the intestines (using an enema or replacing with glycerin suppositories).
Possible complications
The risk of negative consequences, although minimal, is possible. Therefore, you should immediately consult a doctor if you notice the following symptoms:
- hemoptysis for a long time;
- pain in the chest;
- audible wheezing;
- feeling of suffocation;
- nausea and vomiting;
- rise in body temperature.
These symptoms may be signs of pneumothorax, bronchial injury, bronchospasm, pneumonia, allergies, bleeding, etc.
Bronchoscopy is considered relatively safe, the most modern and most informative diagnostic procedure. Timely and high-quality implementation of the procedure, competent interpretation of the study results allow us to establish the correct diagnosis with 100% accuracy and prescribe adequate treatment. Or refute assumptions about the presence of a disease, thereby avoiding a medical error and saving the patient’s health, and sometimes even life.
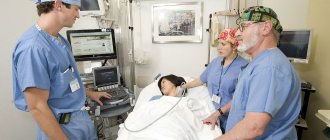
How is bronchoscopy done?
If the manipulation takes place without the use of general anesthesia, the procedure involves the following algorithm of actions:
- The patient undresses to the waist and lies down on the couch, or remains in a sitting position on a chair; the rules of behavior during the procedure and how it goes are explained to him.
- An injection with a special drug is injected into the shoulder area, which has a suppressive effect on salivation.
- A sedative is administered.
- Drugs are sprayed into the mouth area to dilate the bronchi.
- Local anesthesia is given to the root of the tongue and the device itself (its outer part) is treated with the same solution.
- The bronchoscope tube is passed through the mouth or nose while the patient takes a deep breath and begins to look at the respiratory organs.
- An endoscopy is performed strictly according to the scheme, first examining the glottis and larynx. When there is a need for a biopsy, material is collected for research.
After completing the bronchoscopy, the patient is given a protocol of the completed examination with photographs.
General or local anesthesia?
Most bronchoscopy cases require only local anesthesia.
The need to use general anesthesia may be due to the peculiarities of the patient’s mental state or his age. This type of anesthesiology is used to examine children and patients in stress and shock.
How long does the procedure take?
Bronchoscopy of the lungs takes no more than half an hour. The duration depends on the purpose of its implementation, but as practice shows, this is a fairly quick study.
Progress of endoscopy
The study is carried out in a hospital in a special room. The body position in children is horizontal, since the study is carried out under general anesthesia. Adults (if there is no anesthesia) can sit, but if general anesthetics are administered, the procedure requires a horizontal position of the person. A few minutes before the start of the procedure without anesthesia, the adult patient is given local anesthesia with a special inhaler canister containing an anesthetic, which reduces the likelihood of pain. After the procedure, children and adults may be prescribed a course of antibacterial drugs to prevent the development of a lung infection if they have risk factors for its occurrence.
Each patient after bronchoscopy is under the supervision of specialists for one hour. If general anesthesia was used, the observation time increases to 24 hours.
Decoding the results
The results of the study may be as follows:
| Disease | Endoscopic picture |
| Polyp on vocal cords | A neoplasm that prevents the ligaments from closing completely. Has different lengths. |
| Tuberculosis | Sputum of cloudy and viscous consistency on the walls of the bronchi. The mucous membrane is thickened and inflamed. |
| Foreign body present | Visualized at the level of the junction of the pharynx and esophagus. These can be pieces of food, small toys (for children). |
| Malignant formation | Narrowing of the lumen, proliferation of the bronchus on the mucous membrane, some blood clots. The tumor has an irregular shape |
| Bronchitis (chronic) | In the lumen there is a small amount of mucus with a thick consistency. |
What is the price?
The average cost by region looks like this:
| Region | Price | Firm |
| Moscow | from 4500 rub. | "Miracle Doctor" |
| Saratov | from 1420 rub. | "SarNIITO" |
| Saint Petersburg | from 2400 rub. | "Consultative and Diagnostic Center of the Military Medical Academy" |
| Ufa | from 860 rub. | "BSMU" |
| Novosibirsk | from 1050 rub. | "Diagnostic Center of the Research Institute of Tuberculosis" |
Photo gallery
The principle of bronchoscopy
Bronchoscope
Closer view
Close-up
Foreign body removal during bronchoscopy
In the photo - conventional bronchoscopy (left) and fluorescent (right)
Video
The video describes in detail the cases in which bronchoscopy is performed. Video published by Deltaclitic.
Do you have any questions? Specialists and readers of the HROMOSOMA website will help you ask a question
Was this article helpful?
Thank you for your opinion!
The article was useful. Please share the information with your friends.
Yes
No
X
Please write what is wrong and leave recommendations on the article
Cancel reply
Rate the benefit of the article: Rate the author ( 1 vote(s), average: 5.00 out of 5)
Discuss the article: