Often, it is based on the results of ultrasound that a final diagnosis can be made. But how is an ultrasound of the kidneys performed on children, how to properly prepare for the procedure, are there any nuances in the procedure, what are the age norms, and what changes are detected in certain pathologies? All about this in our article.
The essence of the study
Ultrasound is a method of non-invasive visualization of internal organs, which is based on the use of high-frequency ultrasonic waves. They penetrate well through biological tissues and are partially repelled from them (this indicator depends on the density). Then the broken part is caught by a special sensor, the information from which is transmitted to the computer and displayed on the screen in the form of an image.
The information content of the diagnosis depends on the type of organ. Parenchymal structures (liver, spleen, kidneys) are well visualized using ultrasound. The technique allows you to detect the smallest tissue changes, neoplasms, inflammatory and degenerative changes. The technique is of particular value in children for diagnosing congenital malformations.
A significant advantage of ultrasound of the kidneys for a child is availability and price. The study can be carried out for a fee not only in Moscow and large cities, but in almost every hospital and clinic. In terms of price, it is significantly cheaper than computer or magnetic resonance therapy.
Norm
When research is being done, you can hardly understand anything by looking at the screen. For an experienced specialist this is an easy task. The doctor will comment on his every action.
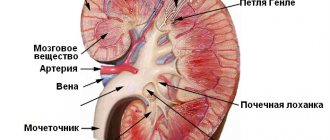
First of all, the specialist will look at the size of each kidney. He will find out the parameters of the organ, then mark the contours of the kidneys and the visibility of the fibrous capsule, and finally report on the thickness of the kidney tissue.
Parents should understand that these indicators will differ at different ages. As for newborn babies, the structure of their organs is not yet complete, they have a bumpy outline, a lobular structure, and the organs themselves are located below the required level.
I bring to your attention the norms for kidney sizes according to ultrasound in children of different ages:
Indications and possible contraindications for children
Indications for prescribing an ultrasound of the kidneys in a child are the following symptoms:
- acute urinary retention, which is accompanied by severe pain;
- change in urine color (cloudy, dark yellow, or bloody);
- aching pain in the lumbar region, which is accompanied by an increase in temperature, fever;
- suspicion of congenital anomalies of kidney development;
- the appearance of arterial hypertension in childhood;
- the presence of signs of renal failure (development of extensive edema, ascites, decrease in the amount of daily urine, increase in intoxication syndrome);
- suspicion of the presence of malignant neoplasms.
An important feature of ultrasound is the fact that it has no absolute contraindications.
Ultrasound waves are safe for the child’s body, which has been repeatedly confirmed in independent studies and observations. Also, diagnostics do not affect the progression of existing diseases and do not contribute to the emergence of new ones. The only temporary contraindication may be the need for emergency resuscitation measures.
Normal ultrasound indicators of different age categories
After completing an ultrasound of the kidneys in children, the results of the examination are immediately given to the parents. Only a doctor can competently interpret ultrasound data, but the preliminary ultrasound result can be recognized independently. The decoding consists in the correlation of the obtained indicators with age norms. Each age corresponds to a certain norm; this should not be forgotten when doing independent decoding.
Approximate normal values (all values are in mm):
Newborns
| Right | 13,6 – 29,4 | 15,9 – 27,4 | 36,8 — 59 | |
| Left | 14,1 – 26,9 | 13,6 – 27,3 | 36,2 – 60,6 | |
| Girls up to 3 months. | Right | 15,9 – 29,4 | 17,6 – 29,8 | 41,9 – 61,4 |
| Left | 15,7 – 29,1 | 17,2 – 28,2 | 40,8 – 63,8 | |
| Boys up to 3 months | Right | 15,8 — 31,6 | 17,9 — 29,6 | 38,9 — 69 |
| Left | 15,8 — 30,3 | 13,5 — 30,3 | 39,9 — 71,1 | |
| From 3 months up to six months | Right | 18,1 — 31,9 | 19 — 30,4 | 45,5 — 70,1 |
| Left | 17,1 — 31,1 | 18,9 — 30,7 | 46,9 — 72,1 | |
| 3 years | Right | 20,8 — 35,4 | 20,3 — 31,7 | 54,6 — 82,4 |
| Left | 19,1 — 36,5 | 21,1 — 34,1 | 55,5 — 84,9 | |
| 6 years | Right | 26,1 — 41,1 | 23,6 — 38,6 | 66,2 — 95,6 |
| Left | 23,4 — 40,8 | 21,3 — 42,7 | 66,9 — 99,5 | |
| 10 years | Right | 24,4 — 45 | 23,8 — 39,6 | 67,6 — 103,4 |
| Left | 25,9 — 44,1 | 26,9 — 41,1 | 71,1 — 103,7 | |
| 14 years | Right | 27,9 — 48,8 | 25,4 — 43,2 | 74,3 — 113,7 |
| Left | 27,1 — 47,8 | 26,9 — 46,4 | 74,3 — 116,1 |
The absence of deviations from the norm indicates the health of your child’s kidneys. But there are diseases that cannot be detected using ultrasound diagnostics, so you should not count on absolute health with normal indicators and the persistence of alarming symptoms. The cause of the disease may not only be an obvious change in size or the development of tumors. When interpreting an ultrasound of the bladder, they look to see whether the thickness and contours of the walls are increased, and what is the volume of residual urine after the bladder is completely emptied. The existence of inflammatory processes and the presence of stones are determined.
Preparing a child for examination
Preparation for an ultrasound of the child’s kidneys depends on whether examinations of the urinary system and digestive tract will also be carried out. If you plan to exclusively diagnose the kidneys, then special preparation (except for certain situations that will be described later) is not required.
If the ureter and bladder are examined at the same time, then immediately before the procedure (10-15 minutes) the patient needs to drink table water (500-1500 ml) or feed the newborn well. Filling the bladder significantly increases the information content of its diagnosis.
Preparing a child for an ultrasound of the kidneys and examination of the abdominal organs necessarily includes a diet and avoidance of food on the day of diagnosis. The diet is indicated for children who have chronic constipation. They can reduce the information content of the study. Products containing chocolate, fresh baked goods, canned or pickled foods, fatty meats and legumes are excluded from the diet.
When preparing an ultrasound of the kidneys in an infant, the last feeding should be 2 hours before the planned diagnosis. As a last resort, the baby can be given a small amount of water to drink (a few sips).
The psychological attitude of the parents is very important, since it is easily transmitted to the child. In some cases (for example, with severe fear of ultrasound), drug sedation (sleep) may be performed. The child should also be explained that the procedure is completely safe and painless. The friendly attitude of the medical staff is also important.
Indications for use
Ultrasound examination of the kidneys is done depending on a large number of indications. For older children, the study is prescribed for pain in the lumbar region, pain during urination, migraines, after injury to the abdomen or lower back, increased temperature for an unknown reason, pronounced swelling of the extremities, changes in urine tests, a large amount of salt in the general urine test, visible impurities of blood or mucus in the urine, changes in its color.
Ultrasound of the kidneys in children 1.5 months old is performed for the purpose of prevention. The procedure is mandatory if there are deviations from the norms. Ultrasound in newborns is indicated for:
increased blood pressure; changes in urine tests; swelling of the extremities; detection of formations in the abdominal cavity; increased levels of bilirubin in the blood; deviations in the development of external organs; dysbacteriosis; severe pregnancy and childbirth in the mother; congenital pathologies or urological diseases in close relatives; if At birth, the child required resuscitation or treatment in intensive care conditions was applicable. Return to contents
How is an ultrasound of the kidneys performed for children: features of the procedure
The basic principles of ultrasound diagnostics for children do not differ from those for adults. The study is carried out in a special office in an inpatient or outpatient setting. The child lies on his side. A special gel is applied to his skin, which increases its permeability to ultrasonic waves.
When examining the kidneys, the doctor pays attention to the following criteria:
- localization of the kidneys (exclusion of nephroptosis);
- transverse and longitudinal dimensions of the kidney;
- characteristics and condition of the parenchyma (homogeneity, presence of areas of degenerative changes or neoplasms);
- condition of the renal pelvis (size, presence of dilations, absence of concretions or stones);
- state of the blood supply to the kidneys in Doppler mode (arterial patency, presence/absence of vascular development abnormalities, dysplasia).
After the diagnosis is completed, the gel is removed from the baby's skin using disposable towels. When conducting research, you should avoid pressing the sensor hard, since it is much easier to provoke the development of uncomfortable sensations in children.
The duration of the procedure is 5-15 minutes.
What does it show?
Timely ultrasound diagnostics allows you to identify the problem in the early stages of its development, begin treatment and prevent deterioration.
Congenital pathologies, inflammatory processes in the kidneys, and anomalies of organ development include:
- Pyelonephritis. An inflammatory disease that is accompanied by thickening of the wall of the renal pelvis. It is the second most common in children, after ARVI. The most common cause is E. coli.
- Formation of kidney stones. It is diagnosed more often in children 3-10 years old. The cause may be a metabolic disorder.
- Hydronephrosis. Accompanied by expansion of the renal pelvis. The disease can be determined at the stage of intrauterine development.
- Cysts. Cystic formations are classified as benign tumors. The pathology may be hereditary.
- Nephrosclerosis. A disease accompanying congenital kidney pathologies. The consequence of development is a decrease in the volume of the kidney, loss of its function.
- Double kidneys. A common congenital anomaly, which can be triggered by the mother’s bad habits during pregnancy. One of the signs is asymmetry in the size of the kidneys.
- Nephroptosis. It is characterized by the mobility of the kidneys, their displacement relative to the initial location. The reasons may be heredity, thin physique, or some previous diseases.
- Frehley's syndrome. Pathology of the renal arteries prevents the full functioning of the kidney. It can be detected in the earliest months of a child’s life.
- Tumor (nephroblastoma). Ultrasound determines the size and structure of the tumor. Timely treatment can prevent the impact on other organs.
- Third kidney. A rare defect. Requires conservative treatment and constant monitoring.
When diagnosing the kidneys of children with ultrasound, salts appear in the form of echogenic inclusions. The study makes it possible to detect the crystallization of salts, which subsequently leads to their transformation into sand and then into stones. A timely ultrasound will help to exclude the development of pathologies when treatment is prescribed by a qualified specialist.
Features of ultrasound during the newborn period
How to prepare a child for a kidney ultrasound? Ultrasound diagnostics of a newborn has its own nuances:
- Smaller sensors are used, which are more suitable for research in patients of this age category.
- The psychological attitude of parents and the attitude of staff play a key role. Naturally, the child will be afraid of the examination and explaining to him that it is painless is very difficult. Therefore, it is important for a doctor to have a special approach to newborns.
- The influence of maternal nutrition on the digestive processes during breastfeeding of the baby. Moms are often advised to exclude from their diet foods that could cause increased gas formation, which makes it difficult to diagnose the abdominal organs.
- More frequent use of drug sedation if urgent kidney diagnostics are needed (for example, in case of acute urinary retention, severe pain due to pathology of the excretory system).
- Emphasis on identifying developmental defects. At this age, 80% of the structure of kidney pathology consists of various disorders of their formation, localization and blood supply. Therefore, the doctor must first identify them and describe them as informatively as possible.
Pathology on ultrasound
Abnormalities in children can be detected using ultrasound.
Ultrasound examination can reveal various anomalies in the development of organs, congenital pathologies or inflammatory processes in the kidneys. A comprehensive examination, which also includes an ultrasound of the bladder, helps to identify the following diseases:
accessory third kidney (a formation similar to a kidney, but smaller in size); connecting effect (a formation similar to a septum, has hyperechogenicity and has a triangular shape); Bertin's column (homogeneous formation in the center of the kidney); Frehley's syndrome (congenital anomaly of blood vessels in kidneys); wandering kidney (displacement of an organ from its normal position; if the displacement is 1.8% -3% of the child’s height, we can talk about excessive mobility, if more than 3% - nephroptosis); doubling (one of the most common forms of congenital pathology, its cannot always be detected by ultrasound; asymmetry of size is one of the more obvious signs of doubling); pyelonephritis (in this disease the walls of the renal pelvis are thickened; quite easily recognized by ultrasound); nephrosclerosis (gradual death of functional cells and the formation of connective tissue in their place ); urolithiasis (formation of kidney stones; seen on ultrasound as a clear acoustic shadow); cysts (small round cavities filled with fluid; well visualized on ultrasound); glomerulonephritis (increase in organ size; a definitive diagnosis cannot be made using ultrasound); trauma (ultrasound can detect both small tears and more serious injuries); tumors (benign or malignant formations, difficult to diagnose using ultrasound , therefore, a biopsy, CT or MRI is used); hydronephrosis (enlargement of the calyces of the kidney and pelvis); “salts in the kidneys” (accumulation of salts in this organ; ultrasound is done to determine the presence of stones, their size, shape, and identify pathology).
Timely ultrasound of the kidneys in children will help identify the problem in the early stages of its development, begin treatment on time and prevent the worsening of possible consequences. For some time, the symptoms of the disease may not be noticeable. It is very important to consult a specialist at the first sign. It is most difficult to notice problems in infants, since they cannot tell what and where it hurts. In this case, everything depends on the attentiveness of the child’s mother.
After conducting an ultrasound examination and interpreting its results, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment. The child may be prescribed a special diet, medication, or surgery. A repeat ultrasound may be performed to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment used.
Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder in children is one of the main diagnostic methods that allows identifying a wide range of pathologies of the urinary system. Ultrasound of the kidneys in children in half an hour of painless and safe diagnosis will show whether a change in the structure of this organ has occurred due to various diseases and conditions.
The content of the article
This study allows you to evaluate the size, structure, anatomy of the organs of the urinary system.
Helps in diagnosing a child’s kidneys for the following diseases:
Congenital anomalies of the development of both the organs of the urinary system and the vessels feeding them. Enlargement of the renal pelvis. Stones or sand. Inflammatory diseases of the organs. Tumors. Cysts. Abscesses.
An ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder is performed in children if the following symptoms occur:
a large amount of salts (oxalates, urates) was detected in a general urine test; change in the color of urine; pain or discomfort when going to the toilet in a small way; pain in the lumbar region; blood in the urine; freezing lower back; there was an injury to the abdomen in the lower parts or a bruise in the lumbar region; swelling; increased temperature without signs of a respiratory viral disease; increased blood pressure was detected.
Ultrasound of the kidneys in newborns should be performed for a large number of indications:
An increase in the level of bilirubin above the “physiological” level in this period. Changes in urine analysis. If some formation is felt in the abdominal cavity. Edema. More than 6 visually noticeable deviations in the development of external organs without disrupting their functions (that is, for example, double fingers, double earlobe, close-set eyes, etc.). In this case, there is a possibility that there are developmental anomalies and internal organs. Parents or close relatives have diseases of the urinary system. In case of dysbacteriosis, which was discovered in the neonatal period. If treatment was necessary in a neonatal intensive care unit. In severe pregnancy and childbirth in the mother. If the baby needed to be resuscitated at birth. Decrease in the amount of daily urine. High blood pressure (“upper” - above 75-80 mm Hg, “lower” - above 65 mm Hg).
How to prepare your child for the procedure
The preparation process itself depends on age. Diagnostics of the kidneys of children must be carried out with a full bladder.
So, if you want to conduct a study on a child under 8 months old who is only breastfed or bottle-fed, then the preparation will consist of giving a small (preferably about 100 ml) amount of water or formula 20 minutes before the procedure.
If the kidneys of a child who has already been introduced to complementary feeding (from 8 months to 1.5 years) are being diagnosed, it is advisable to refrain from feeding him white bread, raw vegetables or fruits for the next 24 hours. And before the procedure, you need to give your baby water, formula, juice or compote (at least 100 ml) to drink 20 minutes before the procedure.
Children over 2 years of age should also refrain from taking carbonated drinks, legumes, large amounts of white bread or baked goods, fresh fruits and vegetables for 24 hours (if they suffer from increased body weight or flatulence, then for 3 days). An hour before the ultrasound, the child needs to urinate and then drink water, tea or compote in an amount of about 10 ml/kg. You can also proceed from the following calculation:
at the age of 3-7 years - drink about 200 ml of still water; from 8 to 11 years - 1.5 glasses of water; over 11 years - about 400 ml of still water 40-60 minutes before the test.
You should also not drink too much water, since in this case the bladder and ureters may become overstretched, which will distort the result of the study.
How is the procedure performed?
Carrying out a “children’s” ultrasound of the kidneys is no different from examining the urinary system in adults (see the article on how to do an ultrasound of the kidneys). The child needs to lie down on the couch, freeing the stomach to the pubis and lower back from clothing. Next, a small amount of a transparent special gel is applied to the abdominal area, and the examination begins.
An ultrasound of children's kidneys involves moving an ultrasound probe over different areas of the abdomen and lower back, while older children are asked to inhale and hold their breath for a few seconds. If a pathology of the bladder is suspected, the child may be asked to empty it, after which the doctor will conduct a repeat examination.
How to understand the research results
Interpretation of kidney ultrasound in children should be carried out by a pediatric urologist or nephrologist. The sonologist who performed the procedure only writes down his conclusions based on a comparison of the normative indicators for a given age with the existing sizes.
Ultrasound standards for children depend on gender, age, as well as the child’s body weight and height . They are determined by an ultrasound doctor based on specially compiled tables.
Norms for children in the first two months of life
In boys 1-2 months of age, the left kidney on average has the following parameters in millimeters:
thickness: 13.6 - 30.2 width: 15.9 - 31 length: 40 - 71
The right kidney at this age is considered normal, having the following indicators:
thickness: 18 – 29.5 width: 15.9 – 31.5 length: 39 – 68.9 mm.
In this case, for girls, these parameters for the left kidney will be as follows (in millimeters):
thickness: 17.3 - 28.1 width: 15.8 - 29 length: 40.9 - 63.7,
on the right - as follows:
thickness: 17.7 – 29.7 width: 16 – 29.6 length: 42 – 61.3.
There will also be a correlation of sizes depending on the height and weight of the child.
Normal kidney ultrasound in newborns
thickness: 16 – 27.3 width: 13.7 – 29.3 length: 36.9 – 58.9 thickness: 13.7 – 27.4 width: 14.2 – 26.8 length: 36.3 – 60.7 mm
Norms at 3-6 months
thickness: 19 – 30.6 width: 17.2 – 31 length: 47 – 72 mm thickness: 19.1 – 30.3 width: 18.2 – 31.8 length: 45.6 – 70 mm.
Norms from 1 to 3 years
thickness: 20.4 – 31.6 width: 20.9 – 35.3 length: 54.7 – 82.3 mm thickness: 21.2 – 34 width: 19.2 – 36.4 length: 55.6 – 84.8 mm.
Norms from 5-7 years
Right kidney:
thickness: 23.7 – 38.5 width: 26.2 – 41 length: 66.3 – 95.5 mm thickness: 21.4 – 42.6 width: 23.5 – 40.7 length: 67 – 99.4 mm.
How to do an ultrasound of the kidneys, you can watch the video
Norms from 7 to 10 years
thickness: 23.9 – 39.5 width: 24.5 – 44.9 length: 67.7 – 103.3 mm.
Left kidney:
thickness: 27 - 41 width: 26 - 44 length: 71.2 - 103.6 mm.
Norms from 10 to 14 years
Right kidney:
thickness: 25.5 – 43.1 width: 28 – 48.7 length: 74.4 – 113.6 mm thickness: 27 – 46.3 width: 27.2 – 47.7 length: 74.4 – 116 mm.
Interpretation of results: norm and pathology
The buds should be localized in a typical location (example in the photo). Normally, they are fully developed, the pelvis is not dilated, and the parenchyma of the organs is uniform. There should be no neoplasms, calcifications, connective tissue growths or cysts among the kidney tissue.
Standard indicators for pediatric kidney ultrasound are presented in the following table:
| Age | Length, mm | Width, mm | Thickness, mm |
| Up to 1 month | 39-57 | 15-28 | 14-27 |
| 1-6 months | 43-72 | 17-30 | 17-30 |
| 6-12 months | 47-77 | 20-32 | 20-30 |
| 1-3 years | 56-88 | 21-36 | 21-35 |
| 4-7 years | 65-97 | 24-42 | 23-39 |
| 8-12 years | 72-105 | 27-45 | 27-45 |
| 13-16 years old | 75-125 | 31-51 | 30-49 |
The most characteristic pathologies are the following:
- nephroptosis – abnormally low location of the kidney;
- aplasia or hypoplasia – absence or underdevelopment of an organ;
- pyelonephritis – thickening of the wall of the renal pelvis, its slight expansion;
- tumors - the appearance of areas with hypoechogenicity and uneven parenchyma;
- cysts are areas with cavities that are filled with fluid;
- abnormal development of blood vessels (many options are possible);
- pyeloectasia is a congenital defect that is accompanied by pronounced dilation of the renal pelvis;
- metabolic disorders - deposition of calcifications in the parenchyma of the organ.
Normal values
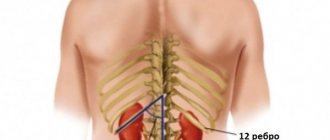
In normal condition, a child should have two kidneys located on both sides of the spinal column at the level of the XI-XII rib - I-III lumbar vertebrae, depending on age. In newborns and infants, they are located lower, since the spine is shorter than in older children.
In newborns, the kidney continues to rise from the small pelvis and by the age of 2 its upper pole reaches the level of the first lumbar vertebra. The right one is normally located slightly lower than the left one, since it is located under the liver.
The left kidney is usually larger than the right. The permissible difference between them is within 1 cm. In newborn full-term children, the length of the kidney is on average 4.5 cm. By 1 year it reaches 6.2 cm. Then the kidney grows evenly and normally adds about 3 mm every year. Normal kidney sizes are determined using special tables in accordance with the age or height of the child.
The contour depends on the age of the child. In newborns and infants, it is clear, but may be uneven (lumpy), which is associated with the lobulation of the kidney due to its incomplete structure. In younger and older children it becomes even.
When scanning longitudinally, the kidney has an oval shape. There may be a local bulge in the area of the lateral contour—the so-called “humpbacked kidney” or in the area of the medial contour—the so-called “pseudotumor” (with normal echostructure of the kidney). On a cross section, the shape of the bud is round.
Normally, a child should have a clear differentiation of the renal parenchyma into the cortical and medulla layers. The echogenicity of the kidney parenchyma in children after 6 months is slightly lower or comparable to the parenchyma of a healthy liver - these are indicators of healthy kidneys.
Usually the pelvis is not visualized. If they are visible and located intrarenally, then their thickness should not exceed 3 mm in children under 5 years of age, 5 mm in children under 10 years of age, and up to 7 mm in adolescents. If the pelvis is located extrarenal, then its thickness should not exceed 6 mm in children under 5 years of age, 10 mm in a child from 5 to 10 years of age, and 14 mm in older children.
The diameter of the cups, if visible, should not be greater than the thickness of the pelvis at the appropriate age.
Ultrasound of the child's abdomen and kidneys
It is important to know that ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity and kidneys is often performed separately. But in some cases, joint diagnostics are prescribed. This is necessary if the child suffers from the following clinical symptoms:
- Pain in the side, abdomen and lumbar region;
- A feeling of bitterness in the mouth and frequent nausea;
- Digestive disorders.
During the procedure, the doctor may also ask you to hold your breath. The best time for diagnosis is in the morning on an empty stomach.
Get a free doctor's consultation
Is there any harm from ultrasound?
Parents often have questions regarding the safety of ultrasound diagnostics for children. Doctors consider the procedure absolutely harmless and acceptable even for children in their first days of life. Sound waves are not ionizing radiation and therefore do not carry radiation load.
Today, there is no known safer and more informative method for diagnosing diseases of the urinary organs than ultrasound. It is permissible to carry it out in the first days of a newborn’s life, if there is such a need. Thanks to the study, a specialist can easily and painlessly assess the condition of organs and their function.