What causes eosinopenia and whether it needs to be treated
The normal level of this type of leukocytes in the blood is determined in an adult at a level of 1 to 5%. In children, the percentage of eosinophils in the blood is higher, but gradually decreases and reaches normal levels by the age of 13-15 years. Therefore, during adolescence, many regular allergies that previously tormented the child may disappear. However, what does it mean if eosinophils are low? Most often, the key factors leading to the occurrence of eosinopenia are:
- the course of an acute bacterial infection;
- the presence of acute appendicitis, peritonitis, sepsis, etc.;
- previous surgery leading to a high level of injury to various tissues;
- severe bodily injury, trauma, fractures, burns;
- poisoning, toxic shock;
- intense physical fatigue, especially if it is regular;
- severe one-time mental disorder or constant stress on the psyche;
- regular lack of sleep caused by a variety of reasons.
Thus, the reasons that tests show low eosinophils in the blood can be very diverse. Therefore, if you receive a result showing a low level of eosinophils, you should not be upset
It is important to understand what this means and find a more or less rational explanation for the detected level of this type of leukocytes
If a person is sick with an acute infectious disease or is at the stage of recovery from it, then the low percentage of eosinophils may simply be due to a sharp increase in the blood of neutrophils necessary to fight pathogenic infectious agents. The absolute number of eosinophils may remain normal, while the analysis will show their relative decrease.
In general, during infections, you should not panic about a decrease in this indicator.
In addition to the reasons listed above, taking certain medications can also lower the level of eosinophils. Therefore, if a doctor is looking for the cause of this deviation in a blood test, he must list what medications the patient has taken over the past two weeks. In addition, a reduced level of this type of leukocytes may be due to recent childbirth. What to do if a blood test shows a significantly reduced level of eosinophils?
Eosinopenia itself is not a painful condition. It should not be perceived as a dangerous diagnosis and considered as a disease for which direct therapeutic measures should be taken. A decreased percentage of eosinophils is important because it may indicate the development of a disease. Most often, this disease (for example, an acute bacterial infection) has already been identified and treated, so the doctor may not pay much attention to this item from the blood test. This shouldn't be surprising.
If before the tests the person was not sick, was not injured, did not undergo surgery or acute stressful conditions, then a decrease in the percentage level of eosinophils can become an important symptom. In this case, the doctor must comprehensively review the test results to identify other abnormalities indicating a particular disease. If there are none, and the patient feels fine, then you just need to wait. Eosinophils may well return to normal.
This situation happens, for example, after some kind of excessive physical stress. A man who was not used to actively moving ran after a departing bus or climbed the steps to the fifth floor of the clinic. This was a significant, albeit temporary, physical shock for him. After that, he passed the tests, and forgot to think about his random “adventures”. He will not remember them even when the doctor looks for the reason for the decrease in eosinophil levels.
However, most often this indicator indicates the possible presence of serious problems
It is especially important to pay attention to it for people who regularly experience stressful conditions. Such test results may indicate that mental shocks are already deeply affecting the physical state of the body. In this situation, you need to consult a doctor
In this situation, you need to consult a doctor.
What to do
Sometimes it is not possible to find out why there is a decrease in eosinophils in the blood. In addition, with a short-term decrease in the level of these bodies, separate therapy is not required.
The goal of treatment is to combat the factor of change in test results:
- When the cause is bacterial infection, the basis of therapy is most often antibacterial drugs. As a supplement, you may be prescribed medications that support the intestinal microflora - probiotics and restrictions on the consumption of fried, fatty, canned and smoked products.
- If a low level of eosinophils is caused by toxic substances, detoxification treatment and symptomatic therapy are prescribed. In case of disruption of the heart and blood vessels, arrhythmia and shock are treated, and tracheal intubation is performed against the background of acute respiratory failure. In case of a critical disorder in the functioning of vital systems, artificial blood circulation or ventilation, hemodialysis can be used.
With sustained relief of painful sensations through local action, antispasmodic and analgesic drugs, the level of eosinophilic cells in the blood is normalized.
When the condition stabilizes, remission occurs or the underlying pathology is cured, the indicators in laboratory blood flow tests stabilize. Do not forget that it is strictly forbidden to use medications when there are few eosinophils in the bloodstream, without medical advice.
To prevent the occurrence of conditions that can lead to the eosinophil count being lower than normal, and to strengthen the immunity of the entire body, you need to follow some rules. A person should adhere to a balanced diet, drinking regime, exercise the body moderately, walk outside more often, not get too cold, and be sure to follow a work and rest schedule.
Source: MedicalOk.ru
Reasons for the downgrade
Let us consider in detail the reasons leading to eosinopenia. However, it is first necessary to clarify how eosinophils are produced and how they perform their functions. Eosinophils are produced in the bone marrow from stem cells, like all types of white blood cells. Once formed, they enter the bloodstream for several hours, and then into organ tissue, where they function for several days. Eosinophils accumulate in the greatest numbers in organs that are in intensive contact with the external environment (skin, lungs, digestive canal).
So, eosinophils are below normal: what does this mean?
- Bone marrow suppression. This occurs when taking potent medications (large doses of antibiotics, antitumor and chemotherapy drugs), as well as in severe poisoning. In this case, the production of all leukocytes is suppressed, so the relative content of eosinophils may not change much, but absolute eosinopenia is observed.
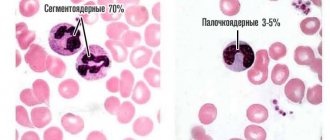
- Infectious diseases in the attack stage and acute period. With a pronounced inflammatory process of a bacterial or viral nature, the absolute indicators of the content of eosinophils in the blood may not change, but their relative content drops sharply, because in the leukocyte formula the number of neutrophils and some other types of leukocytes that fight pathogenic microorganisms increases significantly. Thus, relative eosinopenia is observed. A similar process occurs during toxic shock.
- Physical overexertion. In this situation, the mechanism of the relative decrease in eosinophils is the same as in the previous case: with excessive physical activity, the number of other forms of leukocytes increases.
- Strengthening the work of the adrenal glands. When the level of corticosteroid hormones in the blood increases, there is a response decrease in eosinophils, since corticosteroid hormones suppress their maturation and prevent their exit from the bone marrow. The same thing happens when corticosteroids enter the body from the outside, that is, during therapy with Cortisone, Prednisolone, etc.
- Other causes of low eosinophils in adults include: severe emotional stress, conditions after major surgery, certain malignant tumors, and interleukin-5 deficiency.
Thus, a situation where eosinophils are low can be a sign of a large number of pathological conditions of various etiologies and varying degrees of danger.
Therapeutic and preventive measures for eosinopenia
Often the mechanisms of development of eosinopenia remain unclear. Moreover, a short-term decrease in the concentration of these cells does not require separate treatment. Therapy should be aimed at eliminating the root cause of changes in laboratory parameters:
1. If it is a bacterial infection, antibiotics are usually the mainstay of treatment. Additionally, drugs can be used to maintain the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract - probiotics, and restrictions on the consumption of fried and fatty foods, canned food and smoked meats can be introduced.
2. In case of poisoning with toxins of various origins, detoxification therapy is usually prescribed, as well as symptomatic intensive treatment according to indications. In case of disturbances in cardiovascular activity, pharmacological therapy for arrhythmias and shock may be prescribed; in case of acute respiratory failure, tracheal intubation can be prescribed. In case of critical dysfunction of vital organs, methods such as artificial artificial circulation or ventilation, hemodialysis can be used.
3. With persistent relief of pain using local effects, antispasmodics and analgesics, laboratory tests gradually return to normal.
When the condition is stabilized, remission or recovery from the underlying disease, the picture of a clinical blood test usually normalizes. It should be remembered that under no circumstances should you use any medications without a doctor’s prescription.
To prevent conditions that can cause eosinophilia, as well as to strengthen the immune system in general, you should adhere to the basic rules of a healthy lifestyle: eat rationally, maintain a drinking regime, give the body moderate physical activity, spend enough time in the fresh air, avoid hypothermia, and be sure to observing the work and rest schedule.
Diagnosis of the pathological condition
An imbalance in the composition of blood elements can be identified through a blood test. The procedure is carried out in the morning. You are not allowed to eat or drink before the event. The last meal is 8-10 hours before.
To ensure an accurate diagnosis, the patient is recommended to follow a number of necessary rules:
- 1-2 days in advance you need to eliminate tea, coffee and alcohol;
- plain water without gas is allowed;
- fried, fatty foods should be excluded;
- Seasonings and smoked meats are also not recommended to be taken 2-3 days before blood sampling;
- when taking medications, you need to warn your doctor and laboratory assistant - this will be indicated in the diagnostic sheet;
- physical activity is prohibited;
- It is necessary to exclude moral overexertion and stress;
- You should not smoke before the blood collection procedure.
The completed recommendations will allow you to conduct a high-quality examination with a minimum of error. A correct diagnosis will speed up the healing process.
Doctors take into account an important point in the decrease in granulocytes - the period of ovulation. At this time, there is a high level of progesterone, which contributes to a natural decrease in eosinophils. A blood draw at this point will indicate the presence of eosinopenia. The same effect will occur under stress and overwork. This requires repeating the procedure.
How to stop eosinopenia
A decrease in the level of eosinophils in the blood means the presence of a disease. There are many reasons for their occurrence, but the mechanism of development is still not clear.
There is no specific treatment for low levels of eosinophils, and the fight is aimed at treating the disease that provoked this deviation.
Correct diagnosis and treatment of the disease that caused the decrease in eosinophils will lead to the elimination of eosinopenia and the patient’s recovery.
Also, do not forget that a decrease in eosinophils can occur during pregnancy, so before starting treatment you should conduct a test or undergo an examination by a gynecologist.
What does it mean when eosinophils are low in a child?
Reduced eosinophils in the blood of a child indicate diseases of the immune system or endocrine pathologies. In addition, a decrease in the rate is observed in premature infants.
The absence of a clear clinical picture of the disease in a child indicates the need for careful examination and observation by doctors. Since some diseases can manifest themselves for a long time without pronounced symptoms. Their early detection is only possible with constant monitoring.
The indicator is below normal values after surgery or the acute stage of appendicitis. However, upon recovery, test results, including the level of eosinophils, should return to normal limits. The absence of positive dynamics indicates the need for additional examination.
Among the non-pathological reasons, it is worth highlighting - violation of the child’s daily routine or nutrition and emotional stress. It should be emphasized that we are not talking about isolated cases of a child refusing to eat or sleep, but about chronic lack of sleep or malnutrition.
In addition, children are characterized by all the causes of decreased eosinophils found in adults.
Reasons for deviations in eosinophil concentration from normal
Causes of eosinophilia at different ages:
- allergic manifestations;
- reaction to taking medications;
- malignant neoplasms;
- inflammation in internal organs;
- acute infectious diseases;
- parasitic infection;
- blood diseases;
- lung disease.
If an increased cell content is detected, a blood test for biochemistry, a stool test for worm eggs, and an ultrasound examination of the gastrointestinal tract are additionally prescribed. The woman is additionally examined by a gynecologist and endocrinologist. Without fail, regardless of age and gender, a nasal swab is taken to check for the presence of eosinophils, spirometry and an allergy test are performed.
A decrease in eosinophils is associated with severe purulent infections and recovery in the postoperative period. The number of cells decreases in the first day after myocardial infarction, with severe metal poisoning and with chronic stress.
Among women
Reasons for abnormal eosinophils in women:
- menstrual irregularities;
- autoimmune diseases;
- complicated pregnancy;
- liver pathology, including cirrhosis;
- open form of tuberculosis;
- magnesium deficiency in the body;
- ascariasis or other parasites;
- blood diseases, anemic syndrome or leukemia.
What are the symptoms in women with eosinophilia:
- with helminthic infestation, the lymph nodes enlarge, general intoxication of the body occurs, and headache is present;
- with allergies, a rash appears, the face and eyelids swell, less often itching and spots appear;
- with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, a rash appears on the skin, pain in the liver area, diarrhea and nausea are disturbing.
Treatment will depend on the cause.
A regular increase in eosinophils at certain times of the year does not pose a health hazard, but is a sign of seasonal allergies or poisoning of the body.
In pregnant women
A normal eosinophil count during pregnancy will be between 0 and 5%. When this indicator increases, we are talking about an allergic reaction or helminthic infestation. Cell levels also increase after eating certain foods, including citrus fruits. Before donating blood for testing, a pregnant woman must undergo standard preparation.
There are no external manifestations of minor deviations from the norm. In rare cases, a pregnant woman may experience peeling, redness of the skin and mild itching.
In men
The normal concentration of eosinophils at different ages does not depend on gender. For men, the norm is the same, ranging from 0.5 to 5%. In old age (after 70 years), the normal indicators change upward to 1-5.5%. The reason for the increase in cells are similar factors. The decrease may be associated with severe injuries, exhaustion of the body due to grueling physical activity. The indicator decreases with regular lack of sleep and stress.
Note! In severe diseases of infectious origin, eosinophils can completely disappear from the blood
What are eosinophils and what functions do they perform in the human body?
Eosinophilic blood cells are a subtype of leukocytes, namely granulocytes. Leukocytes in general perform the function of protecting the body from internal and external foreign pathogenic agents. In the blood, eosinophils, like all other leukocyte bodies, do not have their own color. They got their name precisely because, unlike other leukocytes, they are stained only with the help of eosin, a special acidic dye.
Another important difference between this type of leukocyte is that they are microphages, that is, they are capable of destroying only microscopic foreign bodies and cells. However, this is not the main function of eosinophils. Their most important task is to combat parasitic infestations. When an inflammatory process appears in the body, eosinophils penetrate into its focus and contribute to the activation of cellular receptors responsible for natural antiparasitic defense.
This protection consists in the fact that the cells closest to the parasitic microorganism self-destruct and enclose the pathogenic agent in a kind of cocoon that prevents harmful cells from developing. After the creation of such a barrier in the body, other immunological mechanisms are activated, which already act aimed at the identified danger. Thus, eosinophils seem to form the body’s response to internal and external stimuli. This reaction can be too active, leading to allergies. Or, on the contrary, it may become dull in response to various factors. If eosinophils are below normal, then this situation is called eosinopenia. What factors cause it?
Deviations in tests during pregnancy: what is the impact?
A decrease in granulocytes during the period after conception is a normal condition, since immunity should be reduced. This is explained by the fact that after the fertilized egg migrates to the uterus, leukocytes identify it as a foreign body and try to destroy it. To prevent fetal rejection, the immune system must be weakened. That is why the content of the amount of EO during pregnancy is reduced.
Due to childbirth, the percentage drops even further. The fact is that any physical overload, muscle spasms and pain are accompanied by eosinopenia. And labor pains just meet all the listed characteristics.
Deviations in test results during pregnancy are not assessed without other indicators. If significant disturbances are observed in other types of leukocyte cells, then it is worth establishing an accurate diagnosis and solving the problem. A drop in the level of immunocompetent cells can become a threat of infection by infectious agents. If this happens, severe pathogenic inflammation will disrupt the development of the fetus and can cause premature birth or early miscarriage.
Normal, deviations from the norm
The norm of eosinophils in the blood of adults is 0.02 – 0.44 *109/l. The relative number of eosinophils in the leukocyte blood count is normally 0.5% - 5%.
The condition when eosinophils are increased by more than 5% is called eosinophilia. If eosinophils in the blood of an adult are elevated, reaching values greater than 6–8%, this indicates the possibility of infection, rheumatological disorders, and autoimmune processes.
When eosinophils in an adult are increased by more than 15–20% in a blood test, this condition is called hypereosinophilia, which is accompanied by a massive accumulation (infiltration) of eosinophilic leukocytes in the site of inflammation. The tissues of the target organ in which inflammation has occurred are, as it were, saturated with eosinophils.
The reason why eosinophils in adults are elevated in hypereosinophilia or hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) is a change in the ratio of lymphocytes in the blood. The content of B lymphocytes decreases, and the number of T lymphocytes increases in these conditions, which stimulates the production of eosinophil cells in the bone marrow.
HES includes diseases characterized by elevated levels of eosinophils - eosinophilic inflammation of the lungs, heart (endocarditis), neurological disorders, leukemia.
Eosinopenia is a condition when the number of eosinophilic granulocytes is less than 0.5%, or in absolute terms less than 0.02*109/l. For more information about the normal values of eosinophils in the blood in adults and children, read the article “Eosinophil Norms.”
Summary of Reduced Eosinophils
To summarize, it should be emphasized that:
- low eosinophils in the blood indicate bacterial infection, intoxication with adrenal hormones, or pathologies of the lungs and kidneys;
- severe stress and psycho-emotional disorders lead to a decrease in the number of eosinophils in the blood;
- detection of eosinopenia in the analysis of a nasal smear indicates a non-allergic cause of a prolonged runny nose;
- to establish eosinopenia, repeated analysis is required twice with an interval of 2 weeks;
- It is important to consider the rules for preparing for the collection of biomaterial: avoid hormonal and antiallergic medications.
Read further: What do elevated eosinophils mean in adults and children?
Source: medseen.ru
Eosinophils are the causes of increase in adults
White blood cells, leukocytes, have their own type - eosinophils. The quantitative content of these blood cells in the body can inform about the state of health and its specific parameters.
An increase in the number of eosinophils may be evidence of the presence of various autoimmune disorders, allergic diseases and reactions, and leukemia.
Less often, the quantitative content of eosinophils is below normal. And this circumstance also indicates the presence of pathological processes - such as immunodeficiency or infectious inflammation, etc. Let's consider the reasons for this phenomenon.
Reasons for the decrease in eosinophils in the blood
A deviation from normal eosinophil levels in one direction or another is considered a pathology. An increased content of these white blood cells is called eosinophilia, and a decreased content is called eosinopenia. The state of eosinopenia means that a person has a reduced resistance of his body to the influence of various factors of the external and internal environment.
This change is detected during the analysis of the content of white blood cells and eosinophils in the blood:
- A change in blood tests towards a decrease in the number of eosinophils is observed mainly in certain infectious diseases. Some acute inflammatory processes are characterized by the complete disappearance of eosinophils, and their occurrence in the future may indicate the beginning of the patient’s recovery;
- Physical overexertion and various stressful situations can lead to a decrease in the number of eosinophil cells in the blood - the body’s resistance at such moments is noticeably reduced, which results in a decrease in the level of eosinophils in the blood;
- The cause of the same phenomenon can be severe intoxication of the body, exacerbation of existing infectious diseases;
- In the postoperative period, reduced eosinophil counts indicate a serious condition of the patient;
- During pregnancy, the number of eosinophilic cells is also often below normal, which is also explained by the weakening of the pregnant woman’s immunity, as well as the restructuring occurring in her body. But this can only be said if there are other normal blood indicators. Directly during labor, a sharp decrease in the number of eosinophils in the blood can be observed;
- The same sharp decrease in the level of eosinophils occurs when receiving severe burns.
- Another reason for a decrease in the level of eosinophils is various conditions associated with irritation of the adrenal cortex during treatment with corticosteroid drugs - cortisone, prednisone, etc.
Complications with elevated eosinophils
The action of factors that stimulate the formation of eosinophils can cause an exaggerated response, a kind of “inflammatory” blood reaction - hypereosinophilia.
The number of eosinophils in hypereosinophilia can be increased hundreds of times compared to normal. In this state, leukocytes are increased to 50*109/l, while 60–90% of the total number of white blood cells may be eosinophils.
When proteolytic enzymes are released from granules, not only pathogenic microorganisms are damaged, but also their own cells. First of all, the cells of the inner lining of blood vessels (endothelium) of the entire circulatory system are affected.
Lesions in severe eosinophilia
The action of enzymes that enter the blood from granulocytes provokes inflammation, which is why tissue cells in the affected area die. With a massive accumulation of granulocytes, the damage is so significant that it disrupts the functioning of the target organ.
This means that if eosinophils in the blood are elevated for a long time, and their levels are much higher than normal, then vital organs such as the heart suffer. Signs of endocardial and myocardial damage are found very often in conditions associated with prolonged elevated levels of eosinophilic leukocytes in the blood.
This condition, when eosinophils are elevated in a blood test, in children indicates helminthic infestation and allergies; in adults, this means that inflammation develops in the joints, skin, and respiratory system.
With the accumulation of an increased number of granulocytes in the lung tissue, eosinophilic pneumonia develops. This condition has a high risk of pulmonary edema.
For children, typical causes of elevated test scores are atopic dermatitis and bronchial asthma. An increased content of granulocytes in the tissues and blood of both adults and children has a damaging effect on the central nervous system.
Based on the level of increase in eosinophilic granulocytes in the blood, it is not always possible to correctly assess the degree of tissue damage. In tissues, the number of eosinophilic granulocytes may be significantly higher than what a blood test shows.
To diagnose the real cause of the increase in eosinophils in the blood, additional examinations are always required, such as a biochemical blood test, liver tests, a test for troponin levels, and serological tests to detect parasitic infection.
The norm of eosinophils in the blood
The number of eosinophils is determined during a detailed general blood test with leukocyte count and ESR.
Normal eosinophil count for adult men and women
The calculation can be carried out in absolute (EO#) and relative (EO%) values. The absolute content is determined if the relative number of leukocytes as a whole deviates from normal.
However, if in healthy men the level of eosinophils is stable in the specified reference range, then in women of reproductive age characteristic “waves” are observed. This fluctuation occurs due to menstrual cycles, and it is its indicators that are used in the test to assess the functioning of the ovaries and determine the onset of ovulation.
The norm of eosinophils (EO%) in the blood of pregnant women is about 1.5%.
The norm of eosinophils for a child of different ages
What is characteristic is that the number of eosinophils changes throughout the day, and directly depends on the cyclic fluctuations in the functioning of the adrenal glands: in the morning the values are below the daily average, and at night they are increased, but are within the reference limits.
Preparing for a blood test
To obtain the most reliable test result, you should adhere to some rules for donating blood:
- Blood should be donated in the morning on an empty stomach.
- A few days before the test, you should stop eating sweets and alcoholic beverages.
- Women should not take tests during their menstrual cycle, as ovulation can affect or distort the test result. For this purpose, a special test has been developed that will help identify the peak of egg maturation. The level of eosinophils is inversely proportional to the level of progesterone in a woman's blood. And with an increase in estrogen, the level of eosinophils in the blood increases.
It should also be noted that the highest level of eosinophils is observed at night, when the indicator can exceed the norm by 30%, and the lowest level is observed in the morning and evening, when the indicator drops by almost 20% of the norm.
The features of a blood test for eosinophils are described in the video:
Normal concentration of eosinophils in the blood
In medical practice, two values of the total number are distinguished. The total volume characterizes the total number of eosinophilic cells. Relative level coefficients express the quantitative composition of eosinophils in relation to leukocytes.
Normal indicators in the female and male body are almost the same, but often fluctuate with age categories. Absolute indicators are not as important for diagnosis as the leukocyte formula.
In an adult, eosinophils are normal if their number does not exceed 5% of the total number of leukocytes. In a small child under 13 years of age, the norm of eosinophils is from 0.5% to 7%, in adults from 0.5 to 5%.