Ultrasound diagnostics is the basis for examining a patient with gynecological complaints.
This is the simplest and at the same time informative diagnostic method, which allows you to quickly detect inflammatory, degenerative and oncological processes in the uterus and its appendages. In addition, it can be safely performed during pregnancy, since ultrasound does not harm the development of the fetus. This article will look at what uterine fibroids look like on ultrasound, what are the reasons for its development, and what types of this tumor are usually identified.
Indications for ultrasound
Myoma is a benign tumor that begins to develop in the muscle tissue of the uterus. One single muscle cell begins to divide, forming tumor cells, from which a myomatous node develops.
The main symptoms of fibroids can be considered long-term periods, characterized by profuseness, the appearance of pain in the lower abdomen, a pulling nature, urination problems and infertility. Any of these conditions may be an indication for ultrasound examination and other diagnostic methods.
Also, indications for ultrasound may include characteristic manifestations of myomatous formation, namely:
- pain in the lower abdomen not associated with the menstrual cycle;
- the appearance of acyclic discharge containing blood;
- change in the duration of the menstrual cycle;
- growth of the abdomen due to an increase in the size of myomatous nodes.
The indication for diagnosis using ultrasound is an increase in the symptoms of previously detected fibroids. The circumstance when the symptoms began to intensify and appeared in a new quality serves as a compelling reason for an unscheduled ultrasound examination. Often these new manifestations are evidence of a change in the growth rate of the node, their necrosis, torsion, which, in turn, requires urgent surgical care.
How to prepare for research
To know how to prepare for an ultrasound with fibroids (or suspicion of it), you need to know in advance exactly how the study will be carried out.
- Ultrasound through the anterior wall of the abdomen (transabdominal method) will be more effective if the patient’s bladder is full, so it is recommended to drink half a liter of plain clean water half an hour to an hour before the scheduled examination.
- If the ultrasound probe is inserted directly into the vagina (transvaginal method), the patient will need to empty her bladder before the procedure.
Doctors also recommend, on the eve of the procedure, to avoid foods that cause increased gas formation in the gastrointestinal tract, which include:
- Vegetables containing coarse fiber.
- Legumes.
- Yeast bread and sweet baked goods.
- Alcohol.
- Fermented milk products and milk.
A large amount of intestinal gases makes it difficult to examine the uterus on ultrasound and may interfere with diagnosis. To avoid such incidents, it is recommended to empty the intestines on the morning of the procedure (on your own or with the help of medications), and 10-12 hours before the study, take any of the drugs that reduce gas formation - Smecta, Espumisan, activated carbon.
Drugs that reduce gas formation - “Smectu”, “Espumizan”, activated carbon.
Examination technique
The diagnostic procedure and further examination of fibroids are carried out in the usual way, almost indistinguishable from studies of other organs. Not the least place in the obtained ultrasound results is given to the regularity of the procedure, since in this case it is important to trace the dynamics of changes occurring in the tumor. During the examination, two methods can be used in the form of transvaginal and transabdominal ultrasound.
As is known, myomatous nodes always increase in size over time, which cannot but affect the nature of the clinical picture of the disease and the treatment tactics. For this reason, it is especially important to monitor changes in the condition of the tumor in order to make timely adjustments to treatment. If you constantly monitor changes in the condition of organs located in the abdominal cavity using ultrasound, it becomes possible to identify the development of pathologies in the early stages. In addition, carrying out such diagnostics makes it possible to identify many of the pathological disorders associated with fibroids that are gynecological in nature.
About the disease
Uterine fibroids are a disease that is benign in origin, and the tumor develops against the background of hormonal dependence and originates in the smooth muscle tissue that forms the walls of the organ.
Photos of the uterus with different types of fibroids
Possessing all the pronounced signs of oncological manifestations, the tumor, however, does not pose a mortal danger to the woman and is treatable. At the same time, it can regress and remain in a latent state for a long time.
The anomaly is diagnosed quite often - every third patient with gynecological problems is characterized, to one degree or another, by certain forms of the disease.
Transvaginal ultrasound
Transvaginal ultrasound is performed using a sensor inserted into the vaginal cavity. A condom with applied gel is first placed on the sensor. During a hysterographic examination, a solution is injected into the uterus to facilitate diagnosis.
Using the tactics used, it is possible to accurately determine the size of the uterus, the condition of its cervix, the location of tumor formation, as well as its structure and existing features. The examination will be especially informative in the case of submucosal fibroids.
A special feature of the study is that it does not require filling the bladder.
Classification of fibroids: size matters
The diameter of fibroids in centimeters and the size of the uterus in weeks are the leading criteria for classifying pathology. The characteristics of this tumor depending on its size are presented in the overview table:
| Myoma and its characteristics | Tumor size in centimeters | Enlargement of the uterus in weeks of pregnancy | Leading symptoms | Treatment approaches |
| Clinically insignificant | Up to 2 cm | Up to 4-5 weeks | Asymptomatic | Dynamic observation |
| Small sizes | 2-2.5 cm | Up to 5-6 weeks | Menstrual irregularities, moderate nagging pain in the lower abdomen | Hormone therapy |
| Medium size | 3-6 cm | 6-12 weeks | Menstrual irregularities, nagging pain in the lower abdomen, acyclic bleeding | Conservative myomectomy, uterine artery embolization |
| Large sizes | More than 6 cm | More than 12 weeks | All symptoms of medium-sized fibroids plus compression of the pelvic organs | Myomectomy or removal of the tumor along with the uterus (hysterectomy) |
Classification of uterine fibroids by size allows you to understand what to expect from such a tumor and what complications it may be accompanied by. For example, if a doctor tells a patient that she has fibroids for 7-8 weeks, then we are talking about a medium-sized tumor - up to 4-5 cm. Is this too much? Yes, such education will no longer go unnoticed. Most likely, the patient came to the appointment with complaints of heavy and prolonged menstruation - the most common symptom with medium-sized tumors. The best option would be to remove the tumor, possibly with preliminary preparation with hormonal drugs.
Photo of a medium-sized leiomyoma.
A completely different picture emerges when a woman with uterine bleeding is urgently admitted to a gynecological hospital. If after examination a fibroid is detected, most likely it is a large tumor. The uterus can be enlarged up to 12-14 weeks or more, extend beyond the pelvis, leading to an enlarged abdomen. In the treatment of such a tumor it is impossible to do without surgery, and it would be good if we could limit ourselves to removing only the nodes. A giant fibroid with clear clinical symptoms may be an indication for hysterectomy.
The photo shows an operation to remove large uterine fibroids.
To assess the correspondence of the diameter of fibroids and the size of the uterus to certain stages of pregnancy, you should use another table:
| Fibroids size in weeks of pregnancy | Size of the uterus at the corresponding week of pregnancy in centimeters from the womb | The location of the uterus in the corresponding week of pregnancy in relation to the navel and womb |
| Up to 12 weeks | Not determined | Doesn't go beyond the womb |
| 16 weeks | 16 cm | 4 transverse fingers above the pubis or midway between the pubic bone and the umbilical ring |
| 20 weeks | 20 cm | 2 cross fingers below the navel |
| 24 weeks | 24 cm | At navel level |
| 28 weeks | 28 cm | 4 transverse fingers above the navel |
| 32 weeks | 32 cm | Midway between the umbilical ring and the xiphoid process of the sternum |
| 36 weeks | 36 cm | At the level of the xiphoid process of the sternum and the edge of the costal arch |
Schematic representation of the height of the uterine fundus depending on the weeks of pregnancy.
It is almost impossible to draw a parallel between the size of fibroids and the size of the uterus. The volume of the uterus increases due to all the nodes located in the muscular and subserous layer. In this case, the diameter of one formation may be insignificant. On the contrary, with a single fibromyoma of large size, the uterus can extend beyond the pelvis, reaching the navel or ribs. In practice, such giant tumors are rare, since when they reach a size of 3-4 cm, the formation causes considerable discomfort and becomes a reason for a visit to the doctor.
Transabdominal ultrasound
Transabdominal ultrasound is intended to visually examine the uterus and surrounding tissue through the abdominal wall. During the procedure, the patient lies on her back, and a special product in the form of a gel is applied to the study area, which improves the conductivity of ultrasound and facilitates better movement of the sensor throughout the body.
With the help of this study, it is possible to examine the body of the uterus, the location of the myomatous formation and its size, and do this in great detail.
Transabdominal ultrasound can detect tumors up to a centimeter in size; to obtain more accurate results, the bladder must be full.
Classification of myomatous neoplasms
Most often (in 95% of cases) fibroids are localized in the body of the uterus, and only in 5% - in the cervix. They can be single or multiple (multiple fibroids are much more common in clinical practice).
Classification of fibroids according to the location of the direction of growth in the uterus
1. Myomatous neoplasms with typical localization:
Subserous (subperitoneal) fibroid is a tumor on a stalk or broad base, located in the peritoneum on the surface of the uterine body and growing towards the abdominal cavity. In this case, myomatous nodes located on the stalk are able to attach to nearby structures (intestine, omentum or mesentery), developing a secondary blood supply. If the tumor loses its primary blood supply, a parasitic leiomyoma is diagnosed, and in the case where the myomatous nodes are located between the broad ligaments, we are talking about intraligamentary myoma.
Submucous (submucosal) fibroids are a neoplasm localized under the endometrial mucosa, the growth of nodes of which is directed towards the uterine cavity. It may also have a stem or a wide base. Pedicled fibroids can sometimes “fall out” of the cervical canal, becoming twisted and infected.
Interstitial (intermuscular) fibroids are a tumor whose nodes are located in the thickness of the uterine wall.
2. Myomatous neoplasms with atypical localization:
Interligamentous (subserous myoma located behind the peritoneum).
Classification of fibroids by localization in relation to the uterine axis
- Corporal fibroids are the most common tumor (90.2%), which is localized in the body of the uterus.
- Isthmic or isthmic fibroids are neoplasms that cause pain in the bladder area.
- Cervical (cervical) fibroids are a tumor that grows in the vagina and provokes the development of various infectious complications.
WHO classification
1. Leiomyoma
A). Ordinary leiomyoma is a mature hormone-dependent tumor, which is a node of dense consistency, clearly demarcated from healthy tissue. This neoplasm, consisting only of smooth muscle cells of the myometrium, is surrounded by a hyalinized connective tissue layer resembling a capsule. Tumor growth occurs towards the soft tissues, without compromising the integrity of the endothelium.
b). Cellular leiomyoma is a tumor of soft consistency with clear boundaries, usually located inside the uterine wall. This tumor can actively grow during pregnancy. Histological sections examined under a microscope reveal cells with enlarged, slightly elongated nuclei and low mitotic activity.
V). Bizarre leiomyoma is a neoplasm consisting of not only round muscle cells. It also includes multinucleated giant cells of a polygonal shape, which is why this tumor is sometimes confused with leiomyosarcoma. However, confirmation of its benign nature is the small number (or complete absence of mitoses), as well as the absence of infiltrative growth.
G). Epithelial leiomyoma, or leiomyoblastoma, is a tumor that is quite rare in clinical practice. It consists of smooth muscle tissue and elements of the vascular walls.
d). Metastatic leiomyoma is also a very rare type of tumor. Histological examination confirms the benign nature of this neoplasm, but at the same time, it is capable of metastasizing into vascular clefts and growing into the lumen of the vessel. When tumor cells break off, they can travel through the bloodstream into the stomach or lungs, where a new myomatous node begins to develop.
e). Proliferating or growing leiomyoma is a neoplasm characterized by slow growth and the presence of proliferation zones located in the thickness or along the periphery of the tumor. At first, the cellular elements contained in them are presented in the form of couplings, and then they gradually transform into smooth muscle cords that grow and merge with nearby tissues.
and). Myoma with symptoms of presarcoma (malignizing leiomyoma) is a neoplasm in which atypical cells and cell nuclei are detected.
2. Fibromyoma. Depending on the age of the fibroid, its microstructure changes. Over time, the neoplasm turns into a clearly defined node, acquiring the character of a fibromyoma (a tumor consisting of connective tissue and muscle elements).
Note: as fibroids age, the connective tissue becomes coarser and hyalinized, and its quantity increases.
3. Rhabdomyoma is a benign neoplasm consisting of striated muscle tissue.
4. Angiomyoma is a formation presented in the form of a myomatous node with a developed network of blood vessels.
Preparing for the examination
The nature of preparation for the upcoming study depends on the method used, which is explained by the following circumstances:
- Ultrasonic waves are very difficult to overcome in the air, but in a dense water environment they propagate unhindered. Therefore, the image obtained in the second case will be more accurate and clear. In this regard, differences appear in the preparation of the procedure carried out in different ways.
- During a vaginal examination, the bladder should be empty, for which you need to visit the toilet just before the ultrasound.
- In the case of an external examination through the abdominal wall, on the contrary, the bladder cavity should be as full as possible until the end of the procedure. Why, an hour before it, you need to drink at least a liter of water and refrain from going to the toilet.
In other cases, preparation for the study does not differ in any particulars; you need to behave naturally and without tension.
Size of uterine fibroids in weeks and centimeters
Uterine fibroids
At an early stage, fibroids last 4 weeks. It has no symptoms and does not bother the woman. The main thing is to identify this disease before 7 weeks. It will bring much fewer problems than in later stages of detection.
When it increases to 5 cm and a period of about 10 weeks of obstetric pregnancy, the first symptoms begin to appear.
- Menstruation with pain that does not respond to painkillers.
- Upon reaching 12 weeks, the cervix enlarges, causing bloating.
- If the diagnosis is pedunculated fibroid, then there will be a sharp pain in the abdomen.
- With large fibroids, its enlargement leads to compression of neighboring organs, which interferes with normal urination and defecation. Pain begins in the lower back and near the rectum.
Fibroids, the size of which is more than 12 weeks, entail the formation of adhesions in the tissues of the body and nearby organs.
When a patient complains, an ultrasound examination is performed and appropriate tests are taken. Ultrasound is the most accurate detection of this disease, as well as the timing of its onset. Thanks to the examination, it is possible to accurately determine whether a tumor is benign or not. The possibility of a benign tumor becoming malignant depends on the timing of its detection. Every woman needs to make it a rule that she undergoes ultrasound regularly.
After examination and further diagnosis, the doctor makes a decision on the operability of the tumor. For this, the following indicators are available:
- Uterine fibroids measure 6 cm and last for more than 12 weeks. This tumor size is life-threatening for the patient. Myoma nodes that are more than 12 weeks old must be urgently removed.
- Consistently intense pain. This feature is typical for medium and large fibroids. The myomatous node leads to compression of nearby organs and also puts pressure on the rectum. Defecation is impaired, which can lead to intestinal inflammation and intoxication of the body.
- Bleeding began. Basically, it is caused by fibroids for a period of 15 weeks or more.
- Pregnancy planning. If a woman cannot become pregnant or bear a child, medium-sized fibroids are often the cause. Hormonal levels change during pregnancy, which leads to tumor growth and poses a threat to the baby.
If uterine fibroids are more than 12 weeks old and are located on the back wall of the uterus, this can cause premature birth. Oxygen starvation of the fetus may occur.
There is a risk of benign fibroids developing into malignant ones. This opportunity arises with the rapid growth of fibroids.
Small or medium fibroids can be treated without surgery, provided there are no complications. If the tumor is benign and even a few millimeters in size, you still should not relax and start treating it, because it may be located in a harmful area.
On what day of the cycle?
Ultrasound of the uterus should be performed on certain days directly related to the individual menstrual cycle. The most accurate and objective results of the examination can be obtained only if this requirement is strictly followed.
First of all, the maturation period of the follicle is taken into account, as well as the thickness of the endometrial layer.
Since follicle maturation occurs only once a month, all the changes that occur are associated with this process.
When examining myomatous formations, it is important to perform ultrasound not during menstruation, but in the first phase of the menstrual cycle, since it is during this period that the thickness of the endometrium becomes so insignificant that it makes it possible to identify the slightest pathological compaction in the uterine cavity. During the rest of the cycle, the endometrium looks like folded tissue lining the inside of the uterus, so it becomes almost impossible to see anything in it at this time.
The optimal time for performing an ultrasound is considered to be the period from 5 to 7 days of the cycle, it is at this time that the thickness of the muscle layer is minimal. It is more difficult to calculate this period if the menstrual cycle is unstable. For this category of patients, in order to more fully examine the fibroids, they will have to be examined several times.
What to do if uterine fibroids are detected
Modern medicine has several methods for treating pathology. Traditional methods of treating yamyoma are:
Conservative treatment - gives results in the earliest stages and small sizes of nodes (up to 3 cm). Indicated for women up to 30 years old. The active ingredient is ulipristal acetate, which blocks progesterone receptors. The course of treatment is quite long - it includes up to 4 cycles with breaks of up to 2 months.
Surgical treatment involves physical removal of the fibroids, and in severe cases, the entire uterus. The advantage of the method is that there is a guarantee of getting rid of fibroids; relapse is unlikely (no more than 14%), and if the uterus is removed, it is excluded. But the disadvantages are also obvious: stress from anesthesia, traumatic effects, negative consequences of the operation, including the loss of the woman’s ability to bear children. In any case, after myomectomy you will have to abstain from childbearing for at least six months (preferably a year).
Previously, among the disadvantages, cosmetic damage was noted - a noticeable scar in the intimate area. But now open operations (through an incision) are performed quite rarely. The standard is considered to be surgical intervention using laparoscopy - the fibroid is removed through a puncture, leaving only a barely noticeable mark on the patient’s body.
The UAE method (uterine artery embolization) is the most progressive and gentle way to solve the problem. It is based on the use of a special composition containing microscopic balls (emboli). The composition is injected into the uterine arteries with a catheter through a puncture on the thigh - no invasive invasion of the tissue is required, no scars are left.
The UAE method is safe for a woman’s reproductive health, therefore it is especially indicated for women and girls planning a pregnancy.
In addition, the volume of blood loss during menstruation and its pain are reduced, and other positive effects are observed.
To prevent sad developments, women need to undergo regular gynecological examinations, and if alarming symptoms are detected, an ultrasound scan of the uterus. Remember that only if the disease is detected in a timely manner is its effective treatment possible.
Bibliography:
- Bobrov B.Yu. Obstetrics and gynecology / Bobrov B.Yu., Alieva, A.A.-No. 5, 2004.-68 p.
- Sidorova I.S. Uterine fibroids (modern aspects of etiology, pathogenesis, classification and prevention). In the book: Uterine fibroids. Ed. I.S. Sidorova. M: MIA 2003; 5-66.
- Kustarov V.N. Uterine fibroids / Kustarov V.N., Linde V.A., Aganezova N.V. - SPb.: Special. Lit -2001- 360 p.
What fibroids look like: description
After an ultrasound examination of the uterus and fibroids, the patient is given a description and a photo attached to it, where you can see in detail what the fibroids look like. From the resulting image it is easy to determine the nature of the myomatous formation:
- Interstitial fibroids do not change the shape of the uterus itself; its nodes are often formed in the myometrial layer. They have different sizes from 15 mm to 35 and above and are often well defined.
- Submucous fibroids lead to a noticeable enlargement of the uterus; its nodes are distinguished by clearly defined boundaries, homogeneous structure and have a rounded shape.
- Subserous fibroids, images of which show their rounded shape, can cause significant changes in the outline of the uterus; a large nodule can lead to a change in the position of the uterus relative to other organs.
If the fibroid consists of multiple nodes, which is detected more often in practice, then the surface of the uterus looks bumpy in the pictures.
How is the size of a benign tumor determined?
Assessing the size of fibroids is carried out in several stages:
Gynecological examination
The primary diagnosis is made during bimanual examination. The patient is positioned in a gynecological chair, and the doctor, having inserted two fingers of one hand into the vagina, assesses the condition of the uterus and appendages with the other hand.
The doctor pays attention to the size of the reproductive organ and determines it in weeks, as during pregnancy, and evaluates the surface of the uterus (smooth or bumpy). At this stage the diagnosis has not yet been made
The doctor cannot see whether the uterus is enlarged due to fibroids or another pathology. For further diagnosis, the patient is sent for an ultrasound examination.
Large subserous nodes located in the fundus of the uterus can be palpated through the anterior abdominal wall.
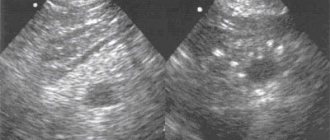
Ultrasonography
Ultrasound is the main method for diagnosing uterine fibroids. On ultrasound examination, a benign tumor appears as a hypoechoic formation. The heterogeneous structure of the node may indicate the inclusion of calcifications. During ultrasound, three parameters are assessed:
- Size of formation in millimeters. For each node, the diameter (for example, 35 mm) and location in relation to the walls of the uterus are determined;
- Size of the uterus (length and width);
- The presence of changes in the structure of the tumor: degeneration, formation of calcifications, cystic cavities.
Ultrasound is the “gold standard” for detecting fibroids and assessing their condition.
The blood flow around the fibroid is necessarily assessed, and the thickness of the endometrium (M-echo) is determined to identify concomitant pathology.
Histological examination
Accurate data about the fibroid can only be obtained after its excision. The removed node is sent to the laboratory, where its diameter is measured and weighed
It is not so important how much the tumor weighs - this parameter is not important for further tactics and is only of scientific interest
Histological examination evaluates the structure of the fibroid and the cells of which it consists - to exclude oncological processes.
How often is ultrasound performed for fibroids?
With fibroids, there is a need to monitor its condition, and you have to undergo the procedure with an ultrasound examination much more often than usual, at least twice a year, and in some special cases every three months. This is important for determining the nature of the fibroid and tracking its behavior.
With the help of this study, it is possible not only to understand whether myoma is growing or its size remains at the same level, but also to evaluate the effectiveness of the therapy. Ultrasound examination allows you to decide whether to continue treatment with certain drugs or replace them with more effective ones.
Hysteroscopy view
It is prescribed when standard methods of diagnosing and determining the clinical picture of the development of pathology are clearly not enough.
This study is characterized by the highest accuracy in diagnosing the disease, and also suggests the possibility of radical elimination of pathology through manipulation.
Hysteroscopy is prescribed when, according to the doctor’s preliminary predictions, the size of the nodular formation is no more than 5 cm in diameter.
During the procedure, the doctor receives detailed information about the condition of the fallopian tubes, the density of the pathology, its size, as well as how uniform the soft mucous tissues are. In addition, the doctor clearly sees the nature of the tumor and accurately diagnoses it as fibroids or cancerous oncology.
Ultrasound during pregnancy with fibroids
Although fibroids, like any kind of neoplasm, have a negative effect on the reproductive capabilities of the body, however, there are often cases in which a woman successfully conceives with the development of further pregnancy.
Monitoring the fibroid at this moment using ultrasound allows us to trace the following conditions:
- The proximity of the location of the placenta attachment to the formed tumor is determined. The smaller this distance, the greater the likelihood of miscarriage due to impaired blood supply to the fetal membrane.
- It is possible to control the activity of fibroids and its growth. Due to changes in hormonal levels caused by pregnancy, the growth of the node may accelerate, which will negatively affect the development of the child.
- The location of the tumor allows you to decide on the method of delivery; most often in this case, a cesarean section is used.
If you manage to get pregnant with fibroids and the pregnancy progresses without complications, then an ultrasound scan is performed as usual, once every trimester. If pregnancy-threatening conditions develop during pregnancy with bleeding, pain and other negative symptoms, examinations can be carried out every two weeks.
Types of fibroid treatment
Unfortunately, very often, due to the fact that a woman did not pay attention to the alarming symptoms in time, the size of the tumor becomes so large that it has to be removed through surgery. This can be either curettage of the organ or complete removal of the uterus. The course of surgery largely depends on the age and position of the woman. If a girl has not given birth, they will try to save her uterus. Removal of the uterus during surgery will be performed if the ultrasound photo shows that the fibroid node is no longer separable from the organ itself, or when the tumor has grown through the entire cavity and layers of the uterus. If the ultrasound photo and the results of other tests of the organ indicate that the tumor is beginning to transform into a malignant one, part of the appendages may also be removed during surgery. The curettage method is unsafe from the point of view of possible punctures of the uterus and possible infection.
If the size of the tumor and its quality in the ultrasound photo do not pose a threat to the life and health of the woman, then the doctor can use conservative treatment regimens. His method consists, first of all, of hormonal therapy with Duphaston and Ustrozhestan. Embolization of the uterine arteries is also used, which involves blocking the blood flow in the tumor node. The procedure is carried out using a catheter, which is inserted into the uterine artery and, reaching the fibroids, blocks the flow of blood to it. This method is one of the most effective and at the same time harmless, which prevents organ loss.
Another way to remove fibroids from the body is FUS ablation, which is a method of evaporating the tumor using an ultrasound beam. This method is also quite effective and even less traumatic compared to embolization.
Possibility of diagnostic errors
Despite the extreme accuracy of diagnosis during ultrasound, a certain probability of errors in determining the disease still remains. Sometimes a myomatous node can be mistaken for a formation of a different nature, and this depends little on the professionalism of the specialist. In such situations, the following diagnostic errors are most often found:
- Uniform increase in the size of the uterus. This feature can easily be confused with fibroids, since uterine enlargement may be a consequence of frequent childbirth or evidence of abnormal development.
- Intramural type fibroid nodes can be confused with dilated veins running in the endometrium.
- A neoplasm in the ovary can be mistaken for a subserous node. Transvaginal ultrasound does not allow such a mistake.
- Polyps can easily be mistaken for submucous nodes. To clarify, an additional examination and medical history is carried out.
Even taking into account possible errors in determining the nature of the pathology, ultrasound nevertheless remains one of the main diagnostic studies. It is accessible, available in almost every medical institution and specialists’ offices, and is also quite informative, and therefore is used for many diseases.
Visualization on echograms (gallery)
Pictures in order:
fibroid intramural node
Uterine fibroids with necrosis
fibroid subzerous nodule
fibroid submucosal formation
myomatous node
Endometrial polyp on ultrasound
Dilatation of myometrial veins up to 4 mm
Submucosal myomatous node
Subserous myomatous node
Uterine fibroids on ultrasound: signs and visualization - subtleties of diagnosis on ForeverHealth.ru
Source
Share the link and your friends will know that you care about health. Thank youツ