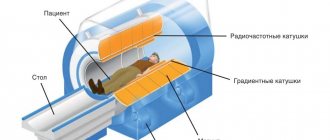
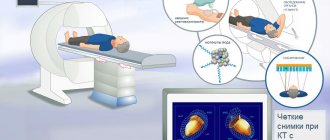
Computed tomography is a method of diagnosing internal organs that allows one to obtain layer-by-layer images to detect serious diseases.
CT is a radiation method, which is based on the different absorption of X-ray radiation by tissues. It is the similarity with radiography that makes many patients doubt whether it is harmful to have a computed tomography scan and how often can this study be done? In addition, they are concerned about the need to use a contrast agent when performing bolus-enhanced CT, which may be accompanied by the development of allergic reactions.
Natural radiation background
All people constantly receive radiation energy even without medical examinations. The Federal Law “On Radiation Safety of the Population” uses the term natural background radiation. This is the combination of human exposure to cosmic radiation and natural radionuclides in the earth’s crust.
Natural background radiation is 5-10 mSv per year. For comparison, exposure when flying on an airplane is 0.1 mSv. The background of the city of Moscow is 0.02 mSv.
The human body has adapted to such a radiation background in the process of evolution.
Advantages of CT on new tomographs
Technology does not stand still and scientists around the world are making every effort to improve various devices for studying the body and making diagnoses. Before talking about how dangerous computed tomography is, the harm from which cancels out its benefits, it is worth knowing that this applies only to old equipment. It often happens that patients want to save on expensive examinations and undergo diagnostics using old devices, thereby putting their health at risk. According to research by American scientists, about 2% of cancers are provoked precisely by examinations on harmful old-type tomographs.
Modern tomographs require minimal radiation exposure to the body and, accordingly, minimal risk of damage to health. But as a result of such an examination, doctors receive valuable information about the condition of all body structures and prescribe effective treatment.
How does radiation affect the body?
The main danger to the human body from regular exposure to ionizing radiation is an increase in the number of mutations in cells and an increased risk of developing tumors.
In a CT scan, the device takes multiple x-rays, which are then combined into one 3D image.
The risk of developing oncological pathologies depends on the frequency of CT scanning and the duration of the procedure:
- in the first 3 years after a computed tomography scan, the risk of malignant neoplasms is 30% higher;
- in the next 4-8 years - by 15-20%;
- in the period 9-14 years - by 10%.
These statistics indicate an increased risk of developing tumors. Therefore, doctors are recommended to prescribe X-ray methods only for strict medical reasons and monitor the total volume of radiation received by the patient.
CT scan using contrast media
Iodine-containing substances are used to increase the contrast of the organs being examined and to visualize tumors; therefore, CT with contrast is indicated for the study of blood vessels and internal organs.
When a bolus of contrast agent is injected into a vein, it enters the left chambers of the heart, the aorta and branches, then penetrates the tissues.
1-2 minutes after intravenous administration, a study is performed in the arterial, venous and, if necessary, delayed contrast phases.
Complications with the administration of contrast occur in 2-5% of cases and manifest as an allergic reaction of varying degrees. Contraindications to the use of contrast agents:
One of the main and absolute contraindications is an allergy to iodine!
- severe kidney disease;
- allergic reactions;
- heart failure;
- pulmonary hypertension;
- also undesirable for COPD and bronchial asthma;
- disorders of the thyroid gland;
- diabetes mellitus, multiple myeloma and pheochromocytoma.
The radiologist makes a decision on the advisability of the procedure in each specific case.
Radiation doses from tomography
The amount of ionizing radiation affecting the human body during computed tomography depends on the characteristics of the examination. The total dose for study subtypes may differ several times. This is affected by:
- body area under study. With a chest CT scan, the patient receives a radiation dose 2-3 times greater than with a head scan;
- differences in absorption coefficient, since the structures of the human body absorb ionizing radiation unevenly;
- type of tomograph used. Old devices (SCT) are exposed to hard X-rays, which lead to radiation exposure of up to 20 mSv. In new multislice computed tomographs (MSCT) this figure does not exceed 4 mSv.
These factors are individual. In this regard, the total radiation dose from computed tomography must be determined for each patient.
Preparing for a CT scan
Depending on what part of your body is being scanned, you may be asked to:
- Remove some or all clothing
- Remove metal objects such as belt, jewelry, dentures, and glasses that may interfere with image acquisition
- Avoid eating or drinking for several hours before your scan
Contrast material
Some CT scans require the injection of a special dye called contrast material to highlight the areas of your body that are being examined. The contrast material blocks x-rays and appears white on images, which can help highlight blood vessels, intestines, or other structures.
Contrasting material can be provided to you:
- Through the mouth . If your esophagus or stomach is being scanned, you may need to swallow a liquid that contains contrast material. This drink may taste unpleasant.
- By injection . Contrast agents can be injected through a vein in the arm to help highlight the gallbladder, urinary tract, liver, or blood vessels in images. You may feel warmth during the injection or a metallic taste in your mouth.
- Enema . Contrast material is placed into the rectum to help visualize the bowel. This procedure may cause a feeling of bloating.
Preparing your child for a scan
If it is necessary to have a CT scan at an early age, the doctor may recommend a sedative to calm the child or parent. Increased motor activity during scanning makes the image blurry.
How much radiation does the body receive?
The Russian Ministry of Health issues special guidelines for CT examinations, which regulate the permissible radiation exposure of the patient during examination. It depends on the area of the body being examined and should not exceed:
- with computed tomography of the abdominal organs - 14 mSv;
- when examining the chest or lungs - 11 mSv;
- when diagnosing the hip joint area - 9.5 mSv;
- for any CT procedures of the spinal column - 5.5 mSv;
- when examining legs and arms - 2 mSv;
- with CT of the head - 2 mZV.
The ionizing radiation that is retained in the body depends on the area of the body. The total radiation dose during examination of the abdominal or chest cavity increases.
Is CT scanning harmful or not?
The danger of chronic radiation exposure after a medical examination can be traced over a long period of time. If the dose does not exceed the permissible annual level established by the Ministry of Health (1 mSv), there is no local damage to organs. Numerous scientific studies of the effects of radiation have shown the likelihood of long-term consequences of CT in the form of genomic changes. Ionizing rays damage DNA, which theoretically causes mutations.
It is impossible to establish a direct relationship between the level of radiation and the nature of cellular damage. Scientists have been unable to link gene damage to the likelihood of developing cancer and tumors. Only the theoretical dependence remains.
Attention! The harm of computed tomography does not appear immediately, but after years. Clinical consequences are unpredictable. Most people do not experience any health changes. In immunodeficiency states, the death of blood cells during intense X-ray irradiation can provoke infectious diseases (pneumonia, bronchitis, cystitis).
CT and other examination methods
In medicine, various methods are used based on studying the body using X-rays. The most commonly used are radiography and computed tomography. Their radiation doses are different.
During radiography, the patient's body receives up to 0.5 mSv. The procedure is not performed for severe pathologies, since the doctor receives only 2-3 projections of the lesion with changes. This is not enough to make a diagnosis.
During a computed tomography scan, the device takes up to 100 sequential images, which are collected into a single three-dimensional image using special programs. The total radiation dose increases and reaches 20 mSv. With PET-CT, the radiation dose increases as radioactive drugs are introduced into the body.
What harm can a CT scan cause to a person?
Three different allergic reactions can occur with the use of contrast. The coloring agent is not absorbed into the surrounding tissue, but the components of the product are harmful. The contrast is poorly tolerated by people who suffer from kidney, liver, and heart diseases. If there is insufficiency in the functioning of these organs, various side effects from the drug may be observed.
The harm from CT is reduced to disruption of the sense of smell and taste. After administration of contrast, you may experience:
- fever;
- dizziness;
- redness of the skin;
- vomiting or nausea.
In isolated situations, Quincke's edema, difficulty breathing, and involuntary spasms of the larynx and pharynx develop. A reaction to harmful contrast may include shortness of breath and loss of consciousness. Side effects from the administered harmful drug are especially common among allergy sufferers. The development of a reaction to the administered harmful drug for them is the harm of computed tomography of organs to health.
To avoid allergies, people are given an antihistamine medication. This measure allows you to avoid harmful side reactions from the body. Is a CT scan harmful if there is no allergic reaction? To get a detailed answer, you need to know about the degree of radiation exposure at the time of the procedure.
CT scan and frequency of examinations
There is no clear answer about the duration of the intervals between tomography. It depends on the reason for which a CT scan is performed.
If the method was used to identify an acute disease, then the frequency of its use should not exceed 1-2 times a year. Radiation examination of the whole body is not performed.
For chronic tuberculosis, oncology, CT is performed 3-4 times a year with an interval of three months. This leads to a serious increase in radiation dose! The salvation for people with such a frequency of examination is the development of a new principle of radiography - tomosynthesis. The method has a radiation dose of up to 0.07 mSv, where the dose is reduced relative to a new MSCT by 57 times, in the case of an old CT machine - by 285 times!
How is a CT scan performed?
You can have a CT scan at a hospital or a facility that specializes in CT scans. The CT scan procedure is painless and takes only a few minutes on new machines. The entire process usually takes about 30 minutes.
During the procedure
CT scanners are shaped like a large donut standing on its side. You lie on a narrow motorized table that moves around the scanning area. Cushions, straps and restraints can be used to help you stay in place. During the head scan, a special stand may be placed on the table to hold your head still.
Each rotation of the detectors and X-ray tube produces multiple images of your body. You may hear tapping, buzzing, and buzzing sounds.
A technologist in a separate room can see and hear you. You will be able to communicate with the technologist via intercom. The technologist may ask you to hold your breath for a certain amount of time to avoid blurry images.
If you received contrast material, you may receive special instructions after the procedure. In some cases, you may be asked to wait a while before leaving to ensure you are well. After the scan, you will likely be asked to drink plenty of fluids to help your kidneys clear the contrast agents from your body.
Radiation protection and removal from the body
Methods for removing radiation from the body are described on the Internet, from the use of intestinal sorbents to the regular consumption of dry red wine. However, this is false information.
for protection (before use, be sure to consult with your doctor):
- emergency action (drug B-190);
- short-acting (RS-1);
- prolonged action (diethylstilbestrol).
X-ray
When conducting an X-ray examination, a beam of X-Ray rays . As they pass through the tissues of the body, they lose their intensity depending on the density of the objects encountered. Soft tissues and hollow organs are reflected on the film in the form of shaded areas, bones and other dense elements have a lighter color . The procedure lasts a few seconds.
X-ray examination is used for the following purposes:
- Clarification of the shape and size of the chest and abdominal organs.
- Determination of narrowing of the lumen in the bile ducts.
- Presence of stones in the gall bladder and kidneys.
- Detection of pathological changes in tissue, for example caused by neoplasms or infectious disease.
- Detection of traumatic bone injuries.
- In the presence and progression of degenerative-dystrophic changes in spinal tissue.
Since during an X-ray examination, soft tissues are visible less clearly than bones, in order to obtain more pronounced contours of the muscular organs in the image, the patient is prescribed a special dye , for example, barium sulfate . The disadvantage of radiography is the display of internal organs in one plane. Therefore, for a three-dimensional picture of the condition of the affected organ, it is necessary to take at least 2 x-rays from different angles.
Is it possible to do X-ray and MRI on the same day?
It should not be assumed that magnetic and x-ray radiation somehow influence each other, so it is not unusual for a patient to be prescribed two examinations a day. If the question is asked whether it is possible to do x-rays and tomography on the same day, then sometimes this is a medical necessity. For severe injuries, two or three examinations may be prescribed in one day, and the sooner the results are received, the more effective the treatment will be.
You shouldn’t “get carried away” with X-rays and tomography at your own discretion: the less, the better. Therefore, you should not study medical reference books and prescribe examinations for yourself on your own. It is preferable to have a short consultation with a doctor who can assess all the possible risks of a particular examination. If the use of MRI and X-rays is necessary, the doctor will outline a step-by-step examination plan, reducing the risks of all sorts of subsequent pathological processes.