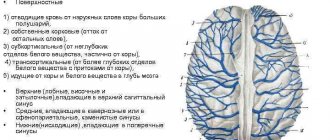
The body of any living creature must work smoothly, like a clockwork. Any disruptions will certainly affect your overall well-being. In the last century, scientists determined that the brain emits electrical signals that are produced by many neurons. They pass through bone and muscle tissue and skin.
They can be detected by special sensors attached to different parts of the head. The amplified signals are transmitted to an electroencephalograph. After deciphering the resulting electroencephalogram (EEG), neurologists often make a frightening diagnosis, which may sound like “mild diffuse changes in the bioelectrical activity of the brain.”
Recorded bioelectrical activity is an indicator of the functioning of brain cells. Neurons must be connected to each other to exchange data on the functioning of all organs. Any deviations in the BEA indicate malfunctions in the brain. If finding the lesion is problematic, then the term “diffuse changes” is used - uniform changes in the functioning of the brain.
What is an EEG?
The interaction of neurons is carried out through impulses. Diffuse transformations of the BEA of the brain indicate an incorrect connection between nerve cells or its absence. Electrodes are responsible for the difference in biological potentials between individual parts of the brain. Such devices are distributed throughout the head.
The information obtained is displayed on thin paper in the form of parallel EEG curves. Diffuse changes mean the difference between normal values and the value obtained on the encephalograph. Let's consider several factors that can distort the results of such a survey:
- General health of the subject.
- Age category.
- The examination is carried out in motion or at rest.
- Tremor.
- Use of medications.
- Last food items eaten.
- Clean hair, use styling mixtures.
EEG provides the opportunity to determine the functional characteristics of different parts of the brain. Poor vascular conductivity, neuroinfections, and damage to the body provoke diffuse transformations in the head. Electrical sensors can record the following rhythms:
Alpha rhythms appear in the crown and back of the head if a person is calm. The average frequency is 8-15 Hz, the maximum amplitude is 110 μV. Biorhythm rarely manifests itself during sleep, intellectual tension, and nervousness. When girls are menstruating, the numbers may be elevated.
The beta rhythm is the most common in adult patients. Frequency 15-35 Hz, amplitude 5 µV. In the process of physical and intellectual stress, during irritation of various sensors on the body, the signals intensify. Most often manifests itself in the frontal lobes. Deviations on the EEG indicate neuroses, depression, and the use of several substances.
Delta rhythm . In adults, it is recorded during sleep; in some patients, during wakefulness, it takes up to 15% of all generated impulses. In babies under one year old, this type of activity is considered the main one; it is noted already in the first month of life.
The frequency corresponds to 1-4 Hz, the amplitude is a maximum of 40 μV. Such data makes it possible to find out the depth of the coma, find out the use of psychotropic drugs, find tumors and places of cell death.
The theta rhythm is considered the main one in children under six years of age.
Sometimes found in older children. Its frequency is 4-8 Hz.
Decoding the encephalogram
During the session, the patient sits with a cap to which sensors are attached. They capture impulses and transmit information to paper in the form of a wave-like graph.
Moderate and severe rhythm disturbances are easily noticed by a medical specialist. He can see:
- wave asymmetry;
- disturbed distribution of alpha and beta flows;
- frequency and amplitude exceeding normal limits;
- double increase in beta waves, indicating the onset of an epileptic seizure.
During the procedure, photostimulation is performed. The normal wave rhythm should correspond to the frequency of the light flashes. It is not considered pathological if it exceeds the norm by a maximum of 2 times. But if there is a decrease in the rhythm or a significant increase, then there is definitely a pathology.
The alpha rhythm signals disturbances if:
- absent (this is an indication of interhemispheric asymmetry);
- fixed in the frontal lobe;
- interhemispheres are asymmetrical by more than 35%;
- a distortion of the wave sinusoidality is detected;
- frequency irregularity is noted (high frequency indicates head injury);
- amplitude indicator is below 25 or above 95 μV.
Violation of alpha activity in childhood signals a delay in mental development. The absence of this rhythm is a sign of the child’s dementia.
Beta waves with a high amplitude indicate a concussion, while short ones indicate an inflammatory infectious disease. In children, the rhythm indicates a lag in mental development at 15 Hz and 40 μV.
Theta waves exceeding 45 μV indicate functional impairment. Moreover, an increase in all parts of the organ is a signal of a serious pathology of the central nervous system. High frequency is a sign of a tumor. In a child, an excess of theta and delta indices in the occipital tissues indicates a delay in mental development or impaired blood circulation.
EEG can express various changes in BEA:
- relatively rhythmic activity – an indication of headaches;
- diffuse BEA in combination with generalized pathological processes and paroxysms is a sign of convulsive and epileptic seizures;
- reduced BEA reactivity indicates psychoemotional disorders.
In conclusion, the doctor may write:
- minor regulatory changes, diffuse processes in the brain parenchyma;
- residual (residual) cerebral changes;
- general cerebral bioelectrical disorientation with the inclusion of median hypothalamic structures;
- relatively rhythmic BEA, dysfunction of the median and stem structures with areas of paroxysms.
Diffuse changes in biopotentials
Deviations in brain functioning can be caused by diffuse and localized damage. In the second example, it is difficult to determine the location of the violation. Such changes are classified as diffuse. During localized lesions, the area of infection is easier to identify. For example, problems with the cerebellum are indicated by deterioration in balance and characteristic nystagmus.
Diffuse mutations can be diagnosed in several ways:
- MRI or CT. Thin sections of the entire brain can be studied using this procedure. In this way, it will be possible to diagnose the consequences of atherosclerosis and dementia of blood vessels. Such deviations occur at elevated rates.
- EEG allows you to determine quantitative characteristics of the functionality of brain cells. Epilepsy can be diagnosed before the first seizures occur. When diagnosing, you need to indicate the degree of the disorder. A mild stage is recorded even in absolutely healthy patients.
EEG results always show diffuse changes in the cerebral cortex. This does not always indicate the presence of local damage. The main sign of epileptic activity is changes in delta rhythms, periodic examination of peak-wave complexes.
The danger of changing BEA
With moderate manifestations, altered bioelectrical activity does not aggravate the body’s condition. But disorganization of the system after some time necessarily develops into dangerous pathologies.
Sometimes, together with dysrhythmia, a disturbance in the functional state of the thalamus and hypothalamus is detected. This leads to the development of diencephalic syndrome, in which neurological, endocrine, and metabolic pathologies are recorded: the functioning of the thyroid gland, heart and blood vessels, digestive organs, and reproductive system is disrupted. The functioning of the regulatory system responsible for maintaining normal body temperature is disrupted. Depression, insomnia, and uncontrollable mood swings occur.
In a child, a convincing violation of impulse patency can cause serious psycho-emotional disorders, problems with motor skills, and developmental delays.
Symptoms
Problems with brain function initially do not appear as clearly as other pathologies of internal organs. People with characteristic diffuse changes experience: deterioration in performance, mental disorders, frequent depression, nervousness, problems concentrating, poor memory, speech dysfunction, deterioration in intellectual abilities, hormonal imbalances, lethargy, constant colds, nausea, migraines.
These signs are often left without proper attention, since they can easily be attributed to fatigue or stress. In the future, symptoms become more distinct and worsen.
Causes
Doctors believe that diffuse changes in bioelectrical activity affecting brain structures can provoke, firstly, injuries and surgical procedures. The severity of the damage received determines the degree of violation. Head injuries cause characteristic transformations of the BEA. Minor concussions are not reflected in future brain activity .
Secondly, inflammation that changes the cerebrospinal fluid indicates meningitis and encephalitis. The primary stages of atherosclerosis provoke moderate changes. The gradual death of cells causes problems with blood supply and patency of nerve tissue. Anemia causes insufficient oxygen supply to areas of the brain.
Toxic poisoning. Destructive processes occur in the brain, which significantly impair the performance of patients. In this case, treatment is necessary. Radiation exposure also causes diffuse changes in BEA. The changes are irreversible and require constant treatment. If this is not done, the patient will eventually lose the ability to do normal daily activities.
Related problems in the lower areas of the brain: hypothalamus or pituitary gland. Pathological processes of different frequencies provoke the destruction of the pituitary systems . A slowdown in bioelectrical maturity is more often observed during childhood, and the passage of neurons becomes more difficult in adult patients. Negative consequences cannot be avoided if the disease is left untreated.
Treatment
Diffuse polymorphic disorganization can only be cured in specialized medical institutions. A correct diagnosis allows you to prescribe the appropriate treatment, which will get rid of the pathology and its consequences, and restore the normal functioning of cells.
You should not delay treatment - any delay will complicate it and provoke complications.
The restoration of natural connections largely depends on the degree of damage. The smaller it is, the better the result of the treatment. The usual way of life will become possible only after a few months.
The treatment plan is developed taking into account the causes of changes in BEA. It is easy to normalize brain activity only at the initial stage of atherosclerosis. The most severe cases are considered to be radiation and intoxication.
A set of medications is prescribed. Its action should be aimed at eliminating the root cause (treatment of the underlying disease), psychopathological and neurological syndromes, normalizing metabolic processes and cerebral circulation. To restore normal blood circulation, various groups of drugs are used:
- pentoxifylline to improve blood microcirculation;
- calcium ion antagonists for effects at the cerebral level;
- nootropics;
- metabolic drugs;
- antioxidants;
- vasoactive agents, etc.
Treatment of disorganization of bioelectrical activity may include physiotherapeutic methods: magnetic and electrotherapy, balneotherapy.
Hyperbaric oxygenation and ozone therapy
Vascular diseases - the culprits of oxygen starvation - are treated using hyperbaric oxygenation: through a mask, oxygen is supplied to the respiratory organs at a pressure of 1.25-1.5 atm. At the same time, the tissues are saturated with oxygen and the symptoms of brain dysfunction are alleviated. But the method has a number of contraindications:
- hypertension;
- confluent bilateral pneumonia;
- poor patency of the auditory tubes;
- pneumothorax;
- acute respiratory diseases;
- high sensitivity to oxygen.
Ozone therapy shows good results, but its implementation requires expensive equipment and trained personnel, which not every medical institution can afford.
In severe cases with concomitant diseases, the help of a neurosurgeon is required. Self-medication is life-threatening!
Diagnostics
Diffuse changes in the bioelectrical activity of the brain are determined in several ways. For better diagnosis, a specialist analyzes the results of such examinations:
- A visual examination of the patient is carried out, chronic diseases, genetic predispositions, and other symptoms are identified.
- The EEG procedure makes it possible to determine the cause of deviations. For this purpose, a set of electrode sensors is placed on the patient’s head.
- MRI is performed to detect bielectric activity. When it is fixed, there is a reason for the deviation, which is displayed on the tomography.
- Angiography is performed if the patient has atherosclerosis.
Object and methods of examination
The study was conducted at the Department of Vascular Pathology of the Brain of the State Institution Institute of Gerontology named after D.F. Chebotarev of the National Academy of Medical Sciences of Ukraine" within the framework of the project "Multicenter population study of risk factors, clinical features and prognostic significance of the initial manifestations of cerebrovascular diseases with the aim of developing a system for the prevention of cerebrovascular accidents for primary health care institutions" (2011–2016).
We examined 217 people aged 40–59 years (average age 51.44±5.9 years) living in the Shevchenkovsky district of Kyiv. Based on the results of a comprehensive examination of these patients, 140 people with the initial stage of DE were identified, who were divided into three groups depending on the etiological factor in the development of DE.
The group of patients with initial manifestations of GDE included 41 people who, according to the anamnesis and clinical and instrumental examination, had an increase in blood pressure (BP) to a level of 140–150 mm Hg. Art. over the past 3–5 years, while duplex ultrasound scanning (USD) of brachiocephalic vessels did not reveal signs of cerebral atherosclerosis.
The group of people with the initial stages of ASDE included 47 people without a persistent increase in blood pressure in the anamnesis, in whom, according to ultrasonography of the main vessels of the head and neck, signs of the development of cerebral atherosclerosis were revealed (thickening of the intima-media complex, the presence of single atherosclerotic plaques).
A separate group included 52 patients with concomitant pathology: atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic vessels (according to ultrasonography) and a history of high blood pressure (HBP).
The control group (CG) consisted of 51 people without signs of cerebral atherosclerosis and high blood pressure.
The EEG study was carried out on a 16-channel electroencephalograph "Neurofax EEG-1100K" (Nihon Kohden, Japan) with standardized parameters (Sensitivity 7 uV/mm, Time constant 0.03 s, High Cut Filter 15 Hz). The sensors were installed according to the standard Base Monopolar lead reconstruction scheme with refractory ipsilateral ear electrodes (A1+A2). Signals were recorded in 16 leads (F1, F2, F3, F4, F7, F8, T3, T4, T5, T6, C3, C4, P3, P4, O1, O2). Let us recall that when encoding the names of EEG electrodes, alphabetic symbols indicate the main areas of the brain: F - frontal, C - central, T - temporal, O - occipital, digital symbols indicate hemispheres: odd numbers are on the left, even numbers are on the right.
To assess atherosclerotic changes in the brachiocephalic arteries, ultrasound scanning was performed using a Philips EnVisor device (Philips, the Netherlands) using a linear sensor with a frequency of 7.5 MHz.
As a result of the analysis of the data obtained in the studied groups, it was established that most of the indicators do not correspond to the normal distribution law according to the Kolmogorov-Smirnov criterion. Based on this, when describing them, the median (Me) and interquartile range Q1–Q3 (25; 75%) were indicated. For intergroup comparison of independent samples, the nonparametric Mann-Whitney U test was used. Differences were considered significant at p<0.05. For statistical processing of the obtained data, application packages “Microsoft® Excel 2010” and “Statistica 6.0” were used.
Normalization of the condition
If diffuse changes in the BEA of the brain were detected in time, competent treatment was carried out, and indicators of brain activity will have to be brought back to normal. Patients often wait too long to see a specialist, ignore symptoms, and let their illness progress. No doctor can guarantee recovery . The result of treatment will depend on the degree of damage to brain tissue. Recovery will take months or even years.
Treatment for BEA transformations involves drug therapy or surgical procedures. It all depends on the disease. For problems with blood vessels, you need a balanced diet and homeopathic remedies. Statins reduce the amount of cholesterol produced. Only a qualified specialist can prescribe them to patients in rare cases.
Fibrates help reduce lipid production and prevent the subsequent development of atherosclerosis. Medicines have a negative effect on the liver and gallbladder. The amount of cholesterol can be reduced due to the action of nicotinic acid.
What is brain BEA
Diffuse changes in biopotentials are disorders that are detected during an electroencephalographic study of the brain, which usually means there is a reason for diagnosis. Electroencephalography is used to determine:
- Degree of maturity of neuronal structures.
- Dynamics of cortical-subcortical relationships.
- Functional state of brain structures.
Diagnostic significance often belongs to the modulation of the alpha rhythm. The results of the study are based on the severity of slow oscillations, which include the theta and delta ranges. The electroencephalogram shows the nature of BEA after the application of functional loads - tests with opening and closing the eyes, hyperventilation, rhythmic photostimulation.
Using an EEG, a diagnosis of epilepsy is made, regardless of the patient’s degree of susceptibility to epileptic seizures. The appearance of epileptiform activity is indicated by a special delta rhythm. A predisposition to the development of epilepsy is suspected if the threshold (level) of convulsive readiness decreases.
Changes in normal indicators of bioelectrical activity of a diffuse nature, identified during brain examinations in children, usually indicate pathologies that lead to disorders:
- Difficulties in learning at school.
- Social maladjustment.
- Conduct disorder.
Slowing of BEA during an EEG examination is often observed in many malfunctions of the central nervous system. These include mild cognitive impairment, ischemic stroke, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and personality disorder. These diseases are characterized by patterns (schemes) - a special character of biorhythmics, which makes it possible to diagnose the pathology and differentiate it from diseases with similar symptoms.
Normally, a slowdown in BEA is observed in adults during sleep. The condition manifests itself in a specific EEG pattern. If moderately pronounced deviations in BEA of a diffuse nature occur during wakefulness, they indicate functional and morphological changes that have occurred in the brain.
In cerebrovascular disorders associated with vascular pathologies and slowing of cerebral blood flow, pronounced changes in diffuse bioelectrical activity indicators occur with serious damage to brain tissue, when, in addition to the focus of ischemic stroke, all parts of the brain are involved in the pathological process. Increased power of the delta rhythm is a nonspecific marker of dysfunction of cortical structures, ADHD, epilepsy, bipolar disorder.
If, according to the conclusion of electroencephalography (EEG), moderate diffuse changes are irritative in nature, there is a high probability of meningovascular neoplasms - meningioma, meningeal sarcoma. Such biopotentials indicate irritation of the structures of the cerebral cortex. Typically, the patient experiences disorganization of cortical rhythms against the background of an uneven amplitude of alpha oscillations and a 2-3-fold increase in the amplitude of beta oscillations.
Irritation of cortical structures occurs as a result of intense exposure to afferent impulses that come from angioreceptive zones and the meninges, which have rich innervation. As tumors grow, the amplitude of rapid rhythms usually decreases, and delta waves with low amplitude appear in the general rhythm. Wave activity appears equally in both hemispheres.
Irritative cerebral disturbances of biopotentials are characteristic of vascular neoplasms localized in the anterobasal, sagittal and adjacent parts of the brain. An EEG study allows one to suspect serious diseases in the early stages, including cerebral infarction, stroke, intracerebral tumors, and mental disorders.
What are the complications?
Diffuse changes in the brain are accompanied by swelling, tissue death and inflammatory processes. Patients are often diagnosed with: swelling and slowing of metabolic processes, poor health, problems with brain activity, motor skills, children are clearly lagging behind in development, and epilepsy appears.
Negative transformations of the BEA also indicate neoplasms, so if signs are detected, you should contact a neurologist. Diffuse brain changes are not a disorder that can be eliminated through self-medication. Errors in choosing medications or dosage can lead to the death of such patients.
Signs of irritation
How the irritation process will manifest itself depends on the area of the brain in which the changes develop, their prevalence and stage of development.
Depending on the location, the lesion may be accompanied by:
- development of convulsive attacks;
- seizures affecting large muscle groups;
- uncontrolled swallowing movements;
- attacks of epilepsy;
- auditory hallucinations;
- olfactory hallucinations;
- short-term loss of consciousness;
- enlargement of the nose and tongue;
- development of pathologies of the genital organs;
- obesity.
If any of these signs occur, you should visit a specialist and undergo an examination.
Prevention
To get rid of diffuse changes in BEA, you need to minimize or get rid of the habit of drinking alcohol, coffee, and smoking. It is not recommended to expose the body to overheating or hypothermia and other negative influences; you should try to work less at height.
A milk diet shows positive results , frequent exposure to fresh air, light exercise, adherence to a rest and work schedule help improve health. You must not work near open sources of fire, near equipment moving on vehicles, interact with toxic products, or regularly be under nervous tension.
If an EEG reveals foci of increased BEA, it means that the patient may soon experience epileptic seizures.
Results and its discussion
One of the subtle characteristics of the functional state of the brain in patients with initial manifestations of GDE and ASDE is the mosaic of bioelectrical activity of the brain (Kropotov Yu.D., 2010). A comparative analysis of the power of the main EEG rhythms in the studied groups showed that changes in the bioelectrical activity of the brain in patients with various pathogenetic variants of DE are predominantly expressed in the power range of slow rhythms (Tables 1, 2).
Thus, in patients with initial manifestations of GDE, compared to the control group, the power in the delta rhythm range in the left frontal and right temporal regions of the brain was significantly higher. Power in the theta rhythm range is higher in patients with the initial stage of GDE in both frontal and right central regions of the brain (see Tables 1, 2, and also Fig. 1). Table 1. Power indicators in the delta rhythm range in patients with the initial stage of DE and in the CG, μV
In table 1 and 2: *significant differences compared to the CG, p<0.05; **significant differences between the GDE and ASDE groups, p<0.05; ***significant differences between the ASDE and SDE groups, p<0.05; ****significant differences between the GDE and SDE groups, p<0.05.
Table 2. Power indicators in the theta rhythm range in patients with the initial stage of DE and in the CG, μV
Rice. 1. The direction of significant differences between power indicators in the range of slow rhythms in individuals with the initial stage of GDE compared with the control group
In patients with the initial stage of ASDE, compared with the control group, there was a tendency towards a decrease in power in the range of slow rhythms in the central regions of the brain, which did not reach the level of statistical significance.
In patients with initial GDE, compared with patients with ASDE, higher power in the theta rhythm range was detected in both frontal areas, as well as in the right hemisphere - in the temporal, central and occipital regions. Note that with GDE, the power in the delta rhythm range in the frontal region of the left hemisphere, as well as in the temporal and occipital regions of the right hemisphere, is significantly higher than with ASDE. At the same time, in patients with GDE, the frequency of the alpha rhythm (9.77) in the right frontal region is significantly lower compared to individuals with ASDE (10.16) Hz (see Tables 1, 2, and also Fig. 2) .
Rice. 2. The direction of significant differences between power indicators in the range of slow rhythms, alpha rhythm frequency in patients with the initial stage of GDE compared to patients with the initial stage of ASDE
A comparative analysis of the bioelectrical activity of the brain in patients with the initial stage of GDE and ASDE demonstrated similarities with the direction of changes in the power of slow rhythms in patients with GDE compared to the CG, and also revealed some features. Thus, it was additionally established that in patients with GDE, compared with ASDE, there is higher power in the delta and theta rhythm range in the right occipital region, higher power in the theta rhythm range in the temporal region, and a lower alpha rhythm frequency in the right frontal region. region (see Table 1, 2, Fig. 1, 2).
In patients with SDE, compared with the control group, there is significantly higher power in the delta rhythm range in both occipital and right temporal regions, and in the theta rhythm in the right central region (see Tables 1, 2).
The results of a comparative analysis of the power structure of the main EEG rhythms indicate that in patients with SDE, compared with ASDE, there is significantly higher power in the range of the delta rhythm in the left frontal and right occipital regions, and the theta rhythm in the right central and temporal regions (see Table. 1, 2, and also Fig. 3).
Rice. 3. The direction of significant differences between power indicators in the range of slow rhythms in patients with ASDE compared with SDEris. 4. The direction of significant differences between power indicators in the range of slow rhythms and alpha frequency in patients with GDE compared with SDE
So, at the initial stage of SDE, compared to ASDE, the power in the range of slow rhythms increases in certain areas of the brain. Also noteworthy is the presence of hemispheric features of increased power of slow rhythms in patients with SDE compared to ASDE: higher power of slow rhythms was noted predominantly in the right hemisphere (in the occipital and temporal region) (see Tables 1, 2, Fig. 3, 4 ).
For patients with the initial stage of all considered pathogenetic variants of DE, no significant differences in the level of power in the range of alpha and beta rhythms were revealed (see Tables 3–4).
Table 3. Power indicators in the alpha rhythm range in patients with the initial stage of DE and in the control group, µV
Table 4. Power indicators in the beta rhythm range in patients with the initial stage of DE and in the CG, µV
Thus, an increase in power in the range of slow rhythms and the absence of significant differences in its indicators in the range of alpha and beta rhythms in patients with the initial stage of DE of various origins indicate that the pathology in question is to a certain extent characterized by dysfunction of predominantly subcortical brain structures generating slow spectrum of bioelectrical activity of the brain (Coffey EC, Cummings JL, 2000).
The mechanism that determines the dysfunction of the subcortical structures of the brain is due to the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the cerebral blood flow: these structures are in an unfavorable position, on the border of the vascular basins (Zakharov V.V., Gromova D.O., 2015). According to magnetic resonance imaging, magnetic resonance spectroscopy, and single-photon emission computed tomography, functional and metabolic changes are noted in the subcortical structures already at the initial stage of DE (Geyer JD, Gomez CR, 2009).