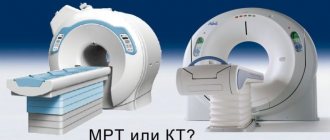
Perfusion computed tomography (perfusion computed tomography - PCT) allows you to evaluate the nature and speed of blood flow in pathologically altered tissue and compare blood flow parameters with the norm.
CT perfusion is used in patients with ischemic stroke and brain tumors. Perfusion complements CT angiography by allowing the assessment of blood flow in the smallest vessels - capillaries.
The method was introduced into practice in the early 90s of the 20th century with the advent of multi-slice scanners, but its theoretical foundations were described much earlier - back in the 70s of the same century.
Basics of the method
The perfusion study is based on the assessment of changes in the density characteristics of pathological tissue compared to normal tissue. After contrast is administered, the area of interest is monitored and a graph of the density of the lesion versus time is plotted. Several fundamental parameters are measured in this type of study.
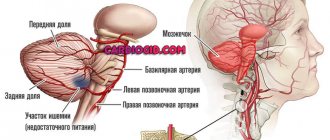
Total cerebral blood volume (ml/100 g of brain matter), CBV (cerebral blood volume). This parameter allows you to estimate the entire volume of blood (venous, arterial, capillary) in a certain area of tissue. The higher the value, the more vascularized the tissue.
High vascularization is characteristic of active tumors.
Cerebral blood flow velocity, CBF: the amount of blood passing through a volume of tissue per unit time. Measured in ml per 100 g of brain matter (any area of interest) per minute. In some tumors this figure may be higher than in unaltered brain tissue. In areas of necrosis and cysts - much lower than normal. Norm: 50-80 ml/100 g per minute.
- The average time for blood to pass through the vessels in a certain area of the brain (area of interest), MTT, mean transit time, in seconds. In the zone of necrosis, the average time increases, in tumors it decreases.
- Time elapsed before the maximum (peak) contrast concentration occurs in the area of interest, TTP (time to peak). In tumors, the peak of contrast accumulation occurs, on average, faster than in healthy tissue, in contrast to cysts and acute infarction.
What is perfusion
After intravenous administration, a bolus of contrast agent (gadolinium) is distributed through the blood arteries and capillaries. The connection changes the MRI signal, which makes it possible to assess intracerebral hemodynamics.
It is necessary to understand how gadolinium infusion during contrast scanning differs from perfusion - assessing different characteristics and accumulation phases.
With classical magnetic resonance imaging with contrast, the arterial and venous phases of the distribution of the substance are assessed, and a perfusion study helps to quantitatively measure intracerebral blood supply.
To perform tissue perfusion, a contrast compound is administered as a bolus - an injection of a small dose of gadolinium chelate, sufficient to study brain microcirculation.
Progress of the procedure
After placing the person on the diagnostic table, a catheter is installed through which 40 ml of contrast is administered at a dosage of 4 ml every second.
Scanning is carried out at the same time - tomograms are made at intervals of 1 second.
The picture is normal and pathological
Normal parameter values in the gray matter of the brain: 60, 4, 4; in white matter: 25, 2, 5 (CBF, CBV, MTT, respectively). There are several areas in the infarction zone. This:
- zone of reduced vascularization in the periphery - oligemia;
- zone of potentially viable tissue - penumbra;
- infarct core (non-viable tissue).
If assistance is provided on time, blood supply in the penumbra and oligemia zones is restored, and the volume of the infarction decreases. Otherwise, the necrosis zone expands, which leads to adverse consequences.
- The oligemic zone is characterized by a significant decrease in central perfusion pressure (CPP), and CBF, CBV and MTT values are moderately increased.
- In the penumbra, there is a greater decrease in perfusion pressure and CBF, but an increase in CBV and MTT.
- In the core of the infarction, the values of CPP and CBF decrease even more, and the values of CBV and MTT increase.
- In tumors, CBV and CBF may be increased and MTT decreased.
Disadvantages and advantages
The method has a number of significant disadvantages:
- the examination time is higher than with traditional CT, and reaches 10 minutes, while the patient must lie still to avoid artifacts;
- The radiation exposure is slightly higher than with traditional CT: it can reach 4-5 mSv.
Advantages: the ability to visualize a stroke in the most acute phase with an absolutely normal picture on traditional CT. As a result:
- treatment is prescribed faster;
- the infarction area decreases;
- the patient recovers better;
- the severity of neurological disorders decreases.
CT allows you to comprehensively evaluate other tissues in the scanning area and identify concomitant pathologies: skull fractures, tumors, etc.
Carrying out the procedure
Before the CT and MRI perfusion procedure, it is necessary to remove all jewelry and metal objects. Clothing should not restrict movement, since the procedure lasts about half an hour. If you have a pacemaker or implants, you should inform your doctor about this before prescribing the procedure.
It is important to learn about NSH of the brain in newborns: what can be detected using neurosonography.
Note: what is a brain echogram and for what diseases is the procedure indicated?
What parents need to know about EEG of the brain in children: features of the study, indications.
Indications and contraindications
CT perfusion is indicated for patients with stroke symptoms but no changes on conventional CT. Another indication is brain space-occupying lesions to assess their vascularization.
The method is contraindicated:
- with motor excitement (anesthesia required);
- with insufficiency of renal function (high levels of endogenous creatinine and urea).
Caution: CT perfusion is a complex and expensive imaging modality. It is used limitedly and only for strict indications.
Perfusion assessment
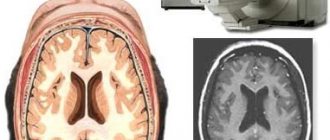
Magnetic resonance or computed tomography with perfusion assessment is a method of studying the brain to determine the capacity of blood vessels and the intensity of blood flow.
The central nervous system is generously supplied with a network of blood vessels for adequate nutrition and respiration of cells. Impaired cerebral perfusion can lead to the following symptoms:
- Weakness, fainting.
- Darkening of the eyes, noise in the ears.
- Autonomic dysfunction.
What does throbbing pain in the head indicate: causes of pathology.
Everything about angiography of cerebral vessels: how the procedure is performed, preparation for the examination.
This can occur due to atherosclerotic processes, vasculitis, and problems with the cardiovascular system. Reduced perfusion increases the risk of developing parkinsonism, vascular dementia, ischemic stroke, and cell death from oxygen starvation.
In case of tumor diseases, their blood supply is examined using a tomograph. The level of perfusion affects the further growth of the tumor. Malignant tumors differ from benign tumors in the speed of blood flow and type of vascularization.
Method of performing the procedure
The study is performed on spiral CT scanners with a number of slices from 16. 40-80 ml of contrast containing iodine is used, for example, Ultravist, Omnipaque, or Iopamiro. The injection rate is 3-5 ml/sec. The contrast is introduced automatically by an injector.
The width of the scanning area is small and usually amounts to several centimeters (5-15). The study takes 5-10 minutes. The received data is converted into color maps separately for each of the above parameters.
Please note: PCT is most often used in patients in emergency conditions.
Everything you wanted to know about MRI brain perfusion!
MRI cerebral perfusion is a non-invasive technique for semi-quantitative analysis of cerebral circulation using magnetic resonance imaging, which is performed at the time of bolus intravenous administration of gadolinium-based contrast. MRI perfusion visualizes blood circulation: its inflow, vascular permeability and outflow. MR perfusion evaluates blood flow by calculating the density of capillaries in brain tissue. In this way, various pathological conditions of brain structures are differentiated.
The goals of MRI brain perfusion are:
– analysis of the effectiveness of the courses of radiation and chemotherapy;
– detection of progression of brain cancer pathology after surgical or other treatment;
– assessment of the severity of blood flow disturbances after ischemic stroke;
– analysis of cerebral blood flow before surgery on the vessels of the neck.
MRI brain perfusion is contraindicated in the presence of implanted electronic devices, metal structures incompatible with MRI, fragments and other foreign objects in the patient’s body, uncontrolled motor activity, and claustrophobia.
No special preparation is required for the study. Before the examination, metal jewelry and accessories, hearing aids, and removable dental structures are removed. The patient undresses to his underwear and puts on a robe. The X-ray technician provides earplugs to prevent noise from the MRI machine.
How is MR brain perfusion performed:
1. The patient lies down on the tomography table, and an intravenous catheter connected to an automatic injection device is placed in the elbow area.
2. Classic MRI without contrast is performed.
3. Next, the patient is injected intravenously with a contrast agent based on gadolinium at a rate of 5 ml/sec, and at the same time a tomography is performed - a new image is taken every second.
4. Using special software, the resulting images are processed and color perfusion maps are constructed.
5. The results are assessed and described by a radiologist.
To analyze MR perfusion of the brain, standardized indicators are used: the volume of cerebral blood flow decreases with ischemia, the volumetric blood flow velocity decreases with vascular obstruction, and the average circulation time increases with vascular occlusion.
An alternative diagnostic method is CT brain perfusion. Differences in CT perfusion: the scanning area includes not the entire brain, but individual parts; the study is accompanied by radiation exposure; Allergic reactions to iodine-based contrast agents may occur.
CT perfusion - contraindications
The study is contraindicated if the patient has an allergic reaction to the contrast element. The next contraindication is pregnancy, but if there is an urgent need for an examination, when a person’s life is at stake, perfusion must be done. Additionally, cisternography of the brain is performed if a stroke or intracerebral infarction is suspected.
For the safety of the unborn baby, a lead apron will need to be placed on the pregnant woman's stomach before the scan. The radiation dose will be negligible.
Evaluation of perfusion data
In the mathematical program for calculating perfusion data, the following hemodynamic parameters are assessed:
- cerebral blood flow (CBF)
- cerebral blood flow volume (CBV)
- average blood transit time (MTT)
- time to start (TTS) and time to peak (TTP)
In this case, the main perfusion parameters are related by the following ratio: CBV=CBFxMTT. For each of these main parameters, a corresponding perfusion map is constructed, from which the dynamics of the process can subsequently be visually assessed. In addition to these indicators, the degree of stenosis at the mouth of the internal carotid artery is also taken into account. If there is a risk of stroke, there will be a decrease in CBF, normal or slightly increased CVD, and, consequently, an increased MTT. If a stroke has already developed and necrosis of brain tissue has occurred, then decreased CBF and CBV will be observed, and MTT will be normal or slightly increased. Ischemic damage is reversible at rates of 10-25 ml/100 g tissue/min, irreversible at <10 ml/100 g tissue/min.
Indications for use
Computed tomography of this kind is most often used in situations where it is necessary to diagnose any lesions of the brain, for example, the pituitary gland. This examination method will help specialists most accurately identify the causes of damage, as well as their nature. With the help of perfusion computed tomography, it is even possible to quite accurately predict the further state of the brain and its blood supply.
Here are the main indications for which doctors often prescribe a referral for this type of CT:
- The need to study the condition after the head has suffered any trauma. This method is excellent for treating intracranial hematomas, as well as bruises or even bleeding.
- The method will also be of great help if it is necessary to examine the cerebral hemispheres due to suspicion of the development of oncology.
- The method will help if specialists suspect the development of an aneurysm; the condition of the vessels will be studied as accurately as possible.
- If patients complain of severe headaches or even fainting, or regular dizziness, then perfusion is excellent for identifying the problem.
- If for some reason a person requires surgical intervention in the future, then computed tomography perfusion will help obtain the information necessary for this.
- There is a suspicion of the development of an ischemic stroke. This technique has proven itself in the early detection of such a serious illness, and it can be accurately distinguished from other pathological processes.
- Detection of the current blood flow speed. When fighting various diseases, specialists may need to find out the speed of blood flow, and, as mentioned earlier, the essence of this procedure is based precisely on this.
- The need to determine the degree of narrowing of the arteries located in the brain.
- Search for a tumor, as well as assessing its size and other things.
Note! The presence of many of these indications, or, conversely, their absence, does not yet indicate an unambiguous decision by a specialist, because it is always made on the basis of a whole complex of information. The examination is taken into account, as well as consultation and test results. Many patients also have the results of various diagnostic procedures performed previously; these should also be taken into account in order to correctly select the type of study.
Retrograde perfusion to protect the heart - what is it?
Retrograde perfusion is not one of the ways to study the brain. The technique is used during surgical interventions in areas of the heart. Initially, it performed a protective function during operations of the cranial cerebral region, the conus arteriosus of the left ventricle, and the aortic arch. The use of the method by surgeons is uncommon. The method was previously used in conjunction with the treatment of blockage of the bloodstream by air particles, and later began to be used as a protective mechanism for targeted cooling of the body for artificial blood supply.
The perfusion technique is used by cardiac surgical medical institutions for the treatment of myocardial hypoxia when installing aortic valve prostheses, surgical correction of combined cardiac defects and correction of cardiac structural defects in infants.
Regional type perfusion is used, which is carried out by using a special device that records the flow of drugs through a catheter into the main vessel of the heart muscle’s own veins, arteries supplying blood to the myocardium. Performed under conditions of artificially created normal and low body temperature. Correction of defects in the structure of the heart is carried out through regional artificial blood supply to the heart while stopping the blood flow of other organs by squeezing the descending aorta. Coronary-carotid perfusion is performed by placing a catheter in the carotid arteries, superior and inferior vena cava, and the largest unpaired arterial vessel (aorta).
Carrying out the process at normal temperatures often leads to the accumulation of under-oxidized particles in the lower region of the body. The return of free radicals nullifies all previously obtained results. Perfusion during hypothermia smoothes the attitude of internal organs to oxygen starvation.